本文主要是介绍阅读笔记:Learning to Remember Rare Events,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
Learning to Remember Rare Events
Contribution
-
NMT难以记住在train set上的rare word,导致很多包括one-shot在内的场景表现不好,本文提出一个memory module可以用在NMT和CV中多种领域和模型上,作为主题模型的附加模块,提高表现
Our module remembers training examples shown many thousands of steps in the past and it can successfully generalize from them
-
Memory module细节
-
Memory module由key-value对组成,Keys are activations of a chosen layer of a neural
network, and values are the ground-truth targets for the given example -
由于memory can be traced back to training examples,所以提供了模型做决策的可解释性
-
Memory module组成
a matrix K K K of memory keys, a vector V V V of memory values, and an addi-
tional vector A A A that tracks the age of items stored in memory假设memory values are single integers representing a class or token ID
query 向量的维度与一个key vector一致,normalized之后通过计算dot product最大值来求出top-K个nearest neighbor,并且返回相应的 V [ n 1 : k ] V[n_{1:k}] V[n1:k]
-
Memory loss
在训练阶段,memory收到一个query q q q时也相应知道ground truth value v v v.
let p be the smallest index such that $V [n_p ] $= v and b the smallest index such that $V [n_b ] $ ≠ \ne = v.

-
Memory Update
-
Memory Module 用于Seq2Seq
encoder不改变,decoder部分在每个time step使用通过attention mechanism得到的context vector作为query来对Memory Module进行检索==(注意,在Search Engine Guided Neural Machine Translation文章里讲过contect vector可以被认为是最好表示要预测词 y ‘ y‘ y‘的向量)==,最终将embedded memory output和decoder最后一个LSTM使用线性层叠加后即可进行预测下一个token。
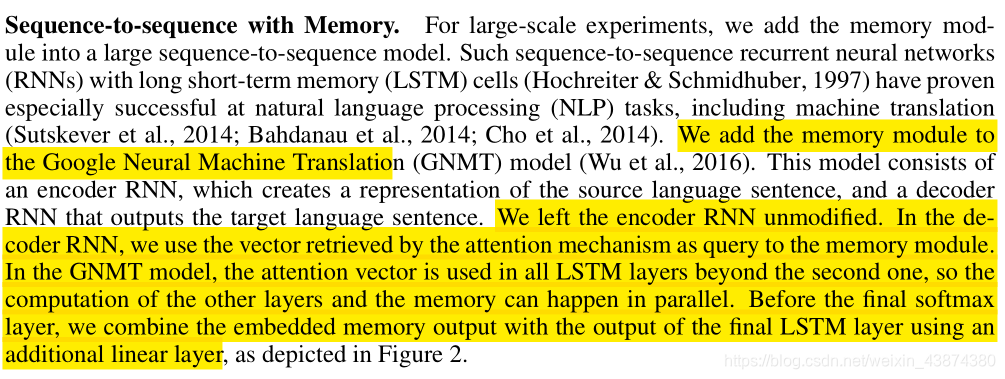
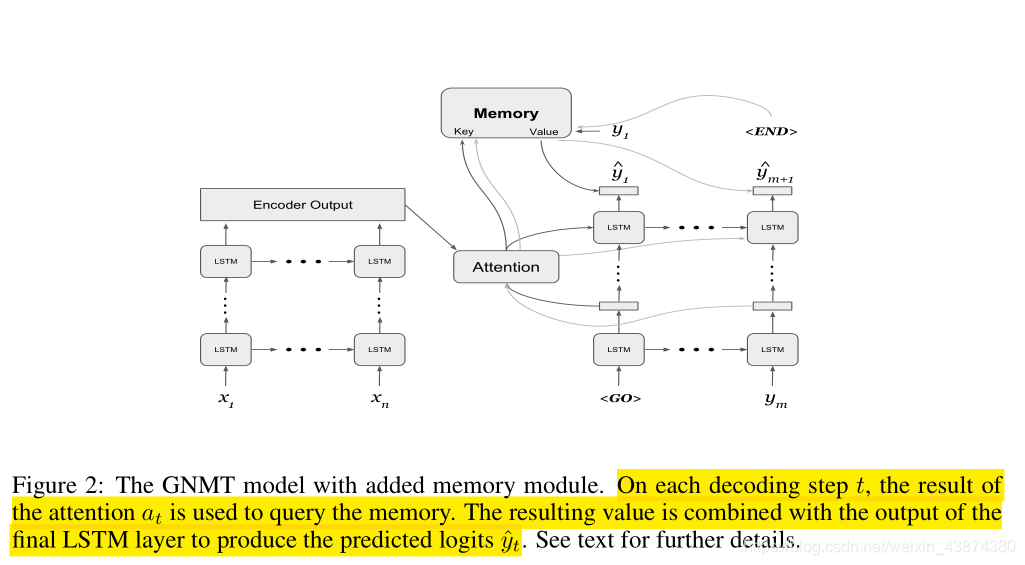
图中,灰色线条属于最后一个time step的计算流程,黑色线条为第一个time step的计算。以第一个时间步为例,attention机制通过使用来自decoder 第一个的hidden state与encoder output进行query得到context vector,进而送入Memory进行检索,检索得到的value与最后一个LSTM的输出拼接起来经过一个linear layer最终预测得到 y 1 ^ \hat{y_1} y1^。
-
这篇关于阅读笔记:Learning to Remember Rare Events的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!