本文主要是介绍浅谈 Guava 中的 ImmutableMap.of 方法的坑,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
作者:明明如月学长, CSDN 博客专家,大厂高级 Java 工程师,《性能优化方法论》作者、《解锁大厂思维:剖析《阿里巴巴Java开发手册》》、《再学经典:《EffectiveJava》独家解析》专栏作者。
热门文章推荐:
- (1)《为什么很多人工作 3 年 却只有 1 年经验?》
- (2)《从失望到精通:AI 大模型的掌握与运用技巧》
- (3)《AI 时代,程序员的出路在何方?》
- (4)《如何写出高质量的文章:从战略到战术》
- (5)《我的技术学习方法论》
- (6)《我的性能方法论》
- (7)《AI 时代的学习方式: 和文档对话》
一、背景
Guava 的 ImmutableMap类提供了 of方法,可以很方便地构造不可变 Map。
ImmutableMap<Object, Object> build = ImmutableMap.of("a",1,"b",2);
然而,实际工作开发中很多人会从开始认为非常方便,后面到发现很多大家都会遇到相似的“问题”。
比如 ImmutableMap类的 of 存在很多重载的方法,但是最多只有五个键值对。
有无参的方法:
/*** Returns the empty map. This map behaves and performs comparably to {@link* Collections#emptyMap}, and is preferable mainly for consistency and maintainability of your* code.** <p><b>Performance note:</b> the instance returned is a singleton.*/@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")public static <K, V> ImmutableMap<K, V> of() {return (ImmutableMap<K, V>) RegularImmutableMap.EMPTY;}
有支持一个键值对的方法:
/*** Returns an immutable map containing a single entry. This map behaves and performs comparably to* {@link Collections#singletonMap} but will not accept a null key or value. It is preferable* mainly for consistency and maintainability of your code.*/public static <K, V> ImmutableMap<K, V> of(K k1, V v1) {return ImmutableBiMap.of(k1, v1);}到支持五个键值对的方法:
/*** Returns an immutable map containing the given entries, in order.** @throws IllegalArgumentException if duplicate keys are provided*/public static <K, V> ImmutableMap<K, V> of(K k1, V v1, K k2, V v2, K k3, V v3, K k4, V v4, K k5, V v5) {return RegularImmutableMap.fromEntries(entryOf(k1, v1), entryOf(k2, v2), entryOf(k3, v3), entryOf(k4, v4), entryOf(k5, v5));}很多人会遇到的坑:
- 超过五个键值对怎么办?
- key 和 value “居然”都不能为 null?
- 同一个 key 重复 put 报错
二、场景还原
2.1 超过 5 个键值对问题
虽然 of 方法很好用,但是经常会遇到超过 5 个键值对的情况,就非常不方便。
解法1:升级版本
在 guava 31.0 版本以后,已经拓展到了 10 个键值对!
/*** Returns an immutable map containing the given entries, in order.** @throws IllegalArgumentException if duplicate keys are provided* @since 31.0*/public static <K, V> ImmutableMap<K, V> of(K k1,V v1,K k2,V v2,K k3,V v3,K k4,V v4,K k5,V v5,K k6,V v6,K k7,V v7,K k8,V v8,K k9,V v9,K k10,V v10) {return RegularImmutableMap.fromEntries(entryOf(k1, v1),entryOf(k2, v2),entryOf(k3, v3),entryOf(k4, v4),entryOf(k5, v5),entryOf(k6, v6),entryOf(k7, v7),entryOf(k8, v8),entryOf(k9, v9),entryOf(k10, v10));}
解法2:使用 builder 方法
com.google.common.collect.ImmutableMap#builder 方法可以通过构造器的方式不断 put 键值对,最后 build即可,也非常方便。
ImmutableMap<Object, Object> build = ImmutableMap.builder().put("a", 1).put("b", 2).put("c", 3).put("d",4).put("e",5).put("f",6).build();
也可以参考 2.2 中的解法。
2.2 键值都不允许为 null
复现
很多人看到名字就知道不可“修改” 但不太清楚它的键值都不允许为 null。
key 为空的情况:
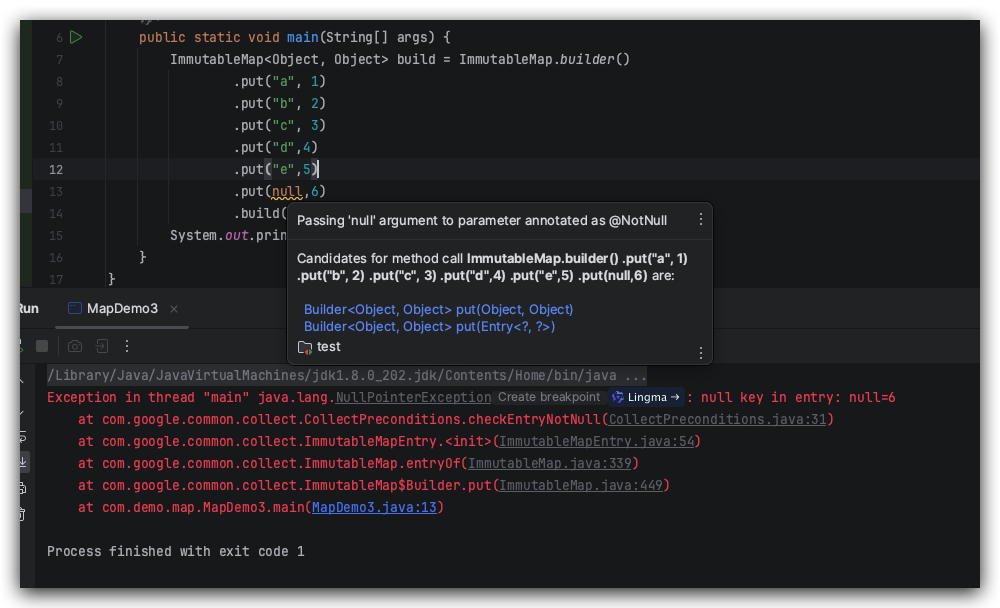
value 为空的情况:
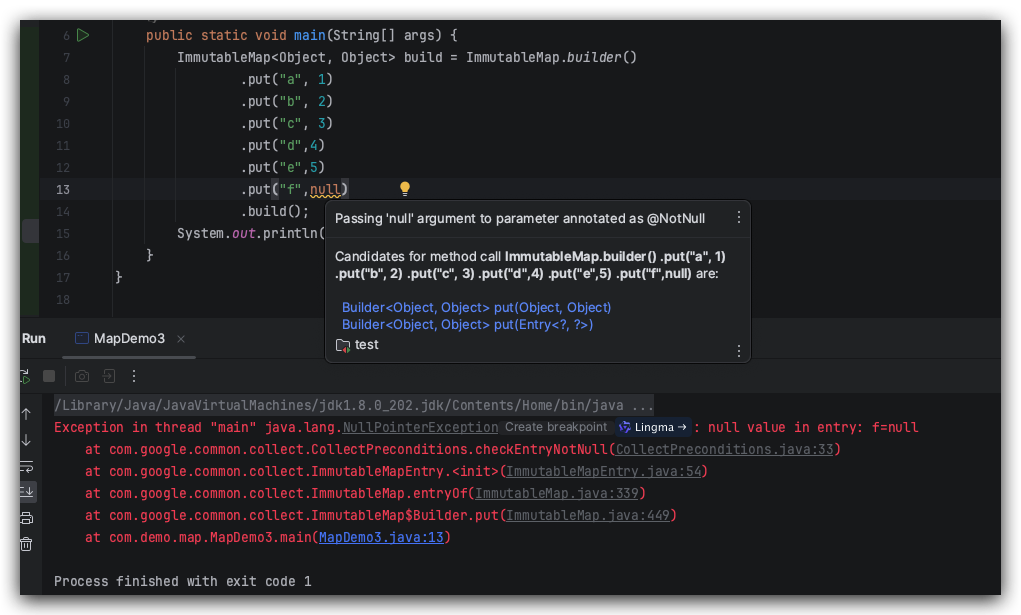
真正开发时不会那么简单,有时候需要调用某个接口获取返回值然后再构造一个不可编辑的 Map 返回给下游使用。很可能在测试的时候都没有出现 null 值,发布上线,发现 key 或者 value 为 null,就会造成线上问题 或者 bug。
源码
对于 of的多参数重载:
/*** Returns an immutable map containing the given entries, in order.** @throws IllegalArgumentException if duplicate keys are provided*/public static <K, V> ImmutableMap<K, V> of(K k1, V v1, K k2, V v2, K k3, V v3) {return RegularImmutableMap.fromEntries(entryOf(k1, v1), entryOf(k2, v2), entryOf(k3, v3));} /*** Verifies that {@code key} and {@code value} are non-null, and returns a new immutable entry* with those values.** <p>A call to {@link Entry#setValue} on the returned entry will always throw {@link* UnsupportedOperationException}.*/static <K, V> Entry<K, V> entryOf(K key, V value) {return new ImmutableMapEntry<>(key, value);} ImmutableMapEntry(K key, V value) {super(key, value);checkEntryNotNull(key, value);}
static void checkEntryNotNull(Object key, Object value) {if (key == null) {throw new NullPointerException("null key in entry: null=" + value);} else if (value == null) {throw new NullPointerException("null value in entry: " + key + "=null");}}
当然,如果你比较心细的话会发现 IDE 中会有警告,也可以很大程度上避免这个问题。
解法
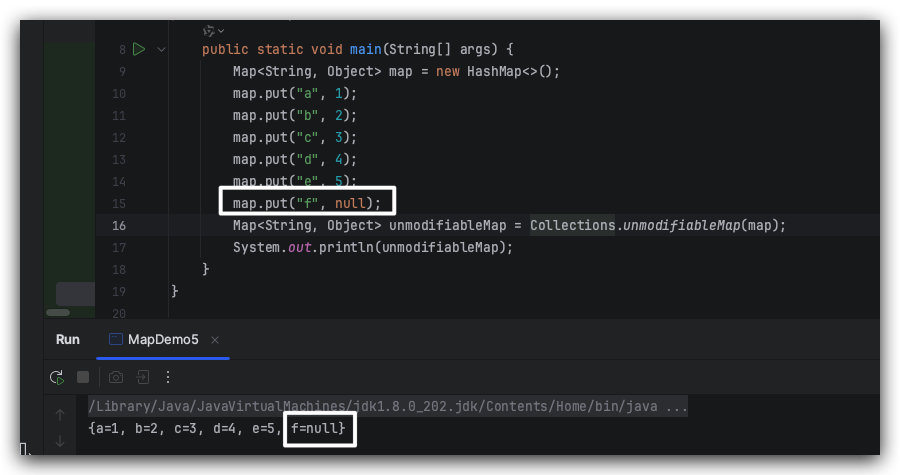
不如换个“殊途同归”的办法,先用 HashMap 去实现同一个 key 的值覆盖的功能,然后通过 Collections.unmodifiableMap来实现不可编辑功能。
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();map.put("a", 1);map.put("b", 2);map.put("c", 3);map.put("d", 4);map.put("e", 5);map.put("f", null);Map<String, Object> unmodifiableMap = Collections.unmodifiableMap(map);System.out.println(unmodifiableMap);
2.3 key 重复报错
复现
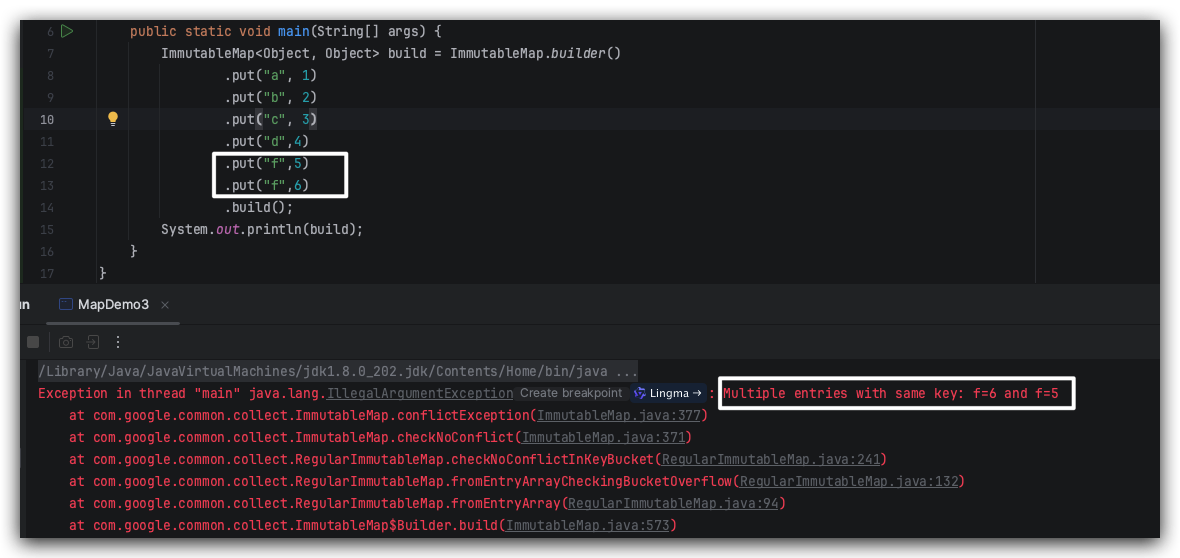
如果一不小心 key 重复,也会报 java.lang.IllegalArgumentException异常。
ImmutableMap<Object, Object> build = ImmutableMap.builder().put("a", 1).put("b", 2).put("c", 3).put("d",4).put("f",5).put("f",6).build();System.out.println(build);
源码
/*** Returns an immutable map containing the given entries, in order.** @throws IllegalArgumentException if duplicate keys are provided*/public static <K, V> ImmutableMap<K, V> of(K k1, V v1, K k2, V v2) {return RegularImmutableMap.fromEntries(entryOf(k1, v1), entryOf(k2, v2));}最底层会对 entry 进行校验:
/*** Checks if the given key already appears in the hash chain starting at {@code keyBucketHead}. If* it does not, then null is returned. If it does, then if {@code throwIfDuplicateKeys} is true an* {@code IllegalArgumentException} is thrown, and otherwise the existing {@link Entry} is* returned.** @throws IllegalArgumentException if another entry in the bucket has the same key and {@code* throwIfDuplicateKeys} is true* @throws BucketOverflowException if this bucket has too many entries, which may indicate a hash* flooding attack*/@CanIgnoreReturnValuestatic <K, V> @Nullable ImmutableMapEntry<K, V> checkNoConflictInKeyBucket(Object key,Object newValue,@CheckForNull ImmutableMapEntry<K, V> keyBucketHead,boolean throwIfDuplicateKeys)throws BucketOverflowException {int bucketSize = 0;for (; keyBucketHead != null; keyBucketHead = keyBucketHead.getNextInKeyBucket()) {if (keyBucketHead.getKey().equals(key)) {if (throwIfDuplicateKeys) {checkNoConflict(/* safe= */ false, "key", keyBucketHead, key + "=" + newValue);} else {return keyBucketHead;}}if (++bucketSize > MAX_HASH_BUCKET_LENGTH) {throw new BucketOverflowException();}}return null;}
最终报错:
static IllegalArgumentException conflictException(String conflictDescription, Object entry1, Object entry2) {return new IllegalArgumentException("Multiple entries with same " + conflictDescription + ": " + entry1 + " and " + entry2);}
解法
ImmutableMap的 builder除了提供 buid 之外, 在 31.0 版本之后还通过了 buildKeepingLast和 buildOrThrow。
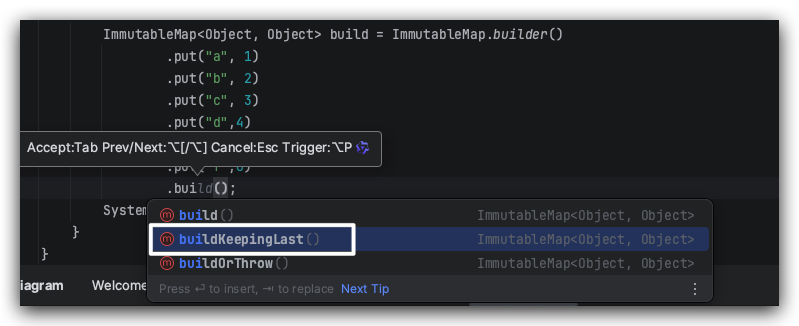
可以通过 buildKeepingLast设置当 key 重复时取后面的值。
/*** Returns a newly-created immutable map. The iteration order of the returned map is the order* in which entries were inserted into the builder, unless {@link #orderEntriesByValue} was* called, in which case entries are sorted by value.** <p>Prefer the equivalent method {@link #buildOrThrow()} to make it explicit that the method* will throw an exception if there are duplicate keys. The {@code build()} method will soon be* deprecated.** @throws IllegalArgumentException if duplicate keys were added*/public ImmutableMap<K, V> build() {return buildOrThrow();}/*** Returns a newly-created immutable map, or throws an exception if any key was added more than* once. The iteration order of the returned map is the order in which entries were inserted* into the builder, unless {@link #orderEntriesByValue} was called, in which case entries are* sorted by value.** @throws IllegalArgumentException if duplicate keys were added* @since 31.0*/public ImmutableMap<K, V> buildOrThrow() {return build(true);}/*** Returns a newly-created immutable map, using the last value for any key that was added more* than once. The iteration order of the returned map is the order in which entries were* inserted into the builder, unless {@link #orderEntriesByValue} was called, in which case* entries are sorted by value. If a key was added more than once, it appears in iteration order* based on the first time it was added, again unless {@link #orderEntriesByValue} was called.** <p>In the current implementation, all values associated with a given key are stored in the* {@code Builder} object, even though only one of them will be used in the built map. If there* can be many repeated keys, it may be more space-efficient to use a {@link* java.util.LinkedHashMap LinkedHashMap} and {@link ImmutableMap#copyOf(Map)} rather than* {@code ImmutableMap.Builder}.** @since 31.1*/public ImmutableMap<K, V> buildKeepingLast() {return build(false);}低版本的话可以考虑先用 HashMap 构造数据,然后使用 com.google.common.collect.ImmutableMap#copyOf(java.util.Map<? extends K,? extends V>) 转换即可。
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();map.put("a", 1);map.put("b", 2);map.put("c", 3);map.put("d", 4);map.put("f", 5);map.put("f", 6);ImmutableMap<Object, Object> build = ImmutableMap.copyOf(map);System.out.println(build);
三、为什么?
3.1 为什么默认是 5 个键值对?
其实 31.0 版本,已经支持 10 个键值对了。
此处,斗胆猜测,of方法仅是为了提供更简单的构造 ImmutableMap的方法,而“通常” 5 个就足够了。
然而,实践中很多人发现 5 个并不够,因此高版本中支持 10个键值对。
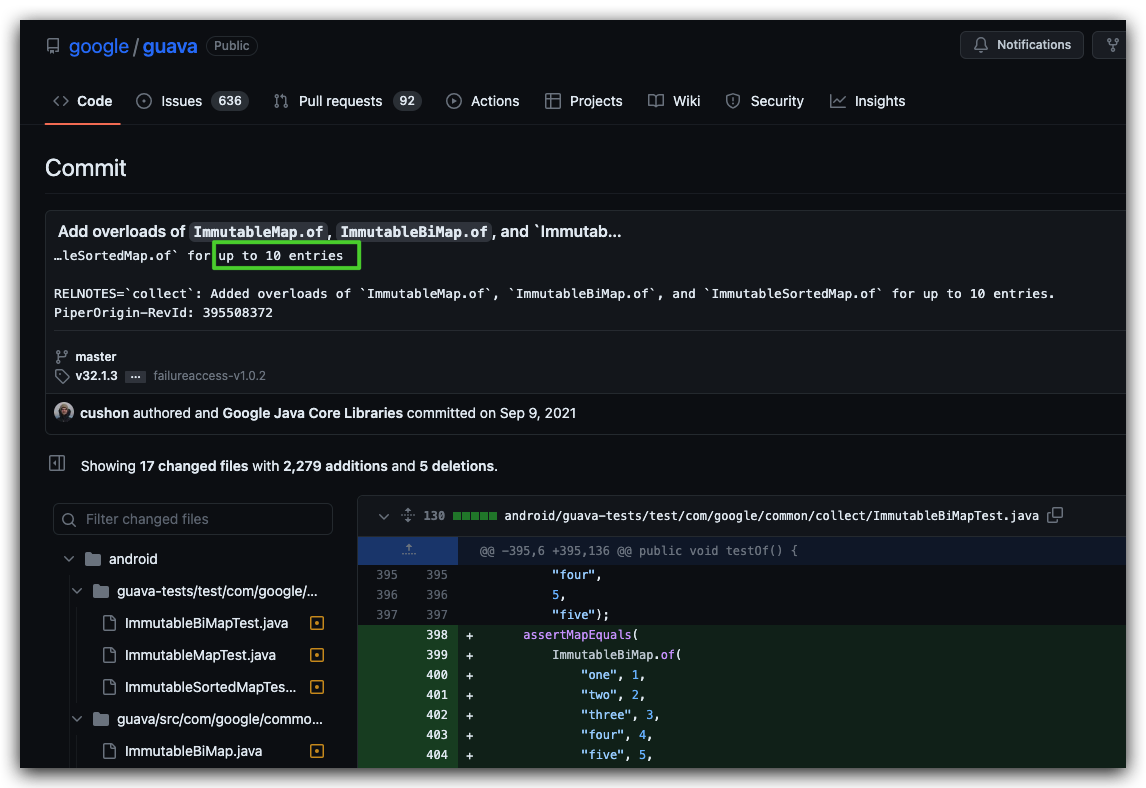
Guava 也有相关 Issues 的讨论 ImmutableMap::of should accept more entries #2071:
https://github.com/google/guava/issues/2071
3.2 为什么不允许键值为 null ?
Github 上也有相关讨论:
Question: Why RegularImmutableMap.fromEntryArray enforces “not null” policy on values? #5844
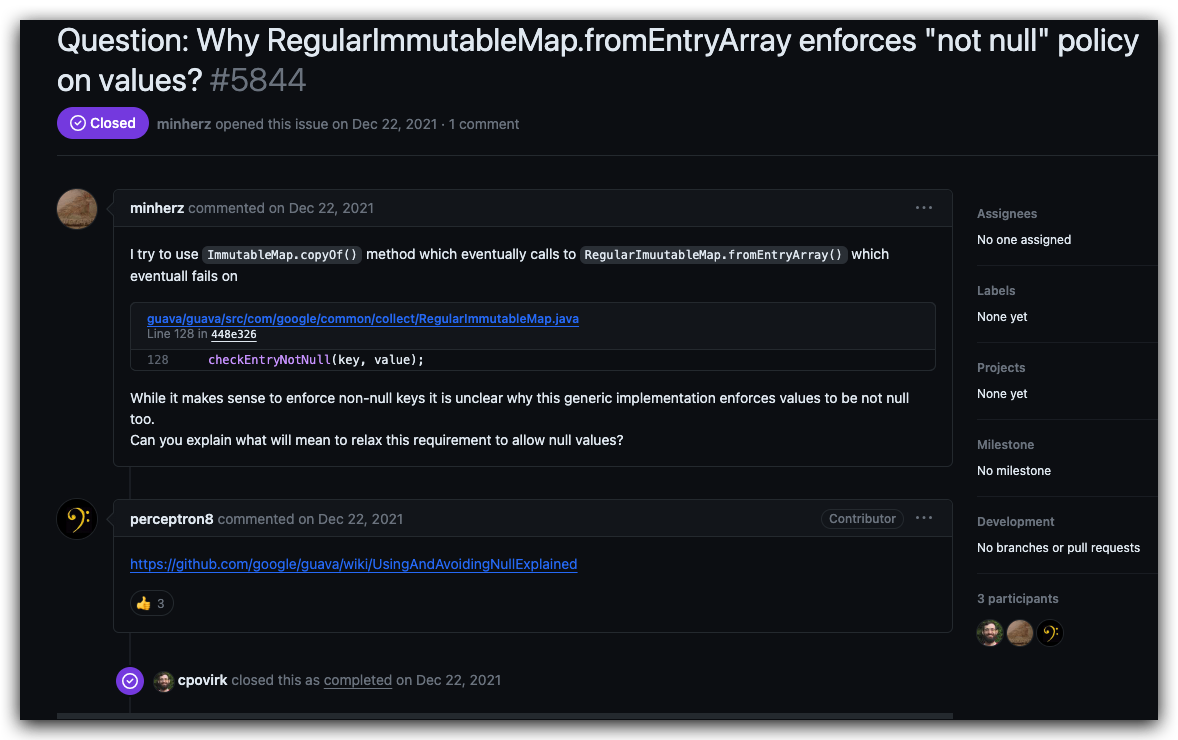
wiki 上有相关解释:
https://github.com/google/guava/wiki/UsingAndAvoidingNullExplained
使用 ChatGPT 对上述 wiki 进行关键信息提取:
在谷歌的 Guava 库的设计哲学中,不允许在 ImmutableMap(或其他类似的集合)中使用 null 值有几个关键原因:
防止错误:Guava 团队发现在 Google 的代码库中,大约 95% 的集合不应包含任何 null 值。允许 null 值会增加出错的风险,比如可能导致空指针异常。让这些集合在遇到 null 时快速失败(fail-fast)而不是默默接受 null,对开发者来说更有帮助。
消除歧义:null 值的含义通常不明确。例如,在使用 Map.get(key) 时,如果返回 null,可能是因为映射中该键对应的值为 null,或者该键在映射中不存在。这种歧义会导致理解和使用上的困难。
提倡更清晰的实践:在 Set 或 Map 中使用 null 值通常不是一个好的做法。更清晰的方法是在查找操作中显式处理 null,例如,如果你想在 Map 中使用 null 作为值,最好将那个条目留空,并保持一个单独的非空键集合。这样做可以避免混淆那些映射中键存在但值为 null,和那些映射中根本没有该键的情况。
选择适当的替代方案:如果你确实需要使用 null 值,并且遇到了不友好处理 null 的集合实现时,Guava 建议使用不同的实现。例如,如果 ImmutableList 不满足需求,可以使用 Collections.unmodifiableList(Lists.newArrayList()) 作为替代。
总体而言,Guava 库通过避免在其集合中使用 null,旨在提供更清晰、更健壮、且更易于维护的代码实践。
3.3 为什么重复 key 会报错?
我认为,主要是为了符合“不可变”的语义,既然是不可变,那么相同的 key 不应该重复放入到 map 中。其次,也可以避免意外的数据覆盖或丢失。
四、总结
虽然这个问题并不难,但很多人并不知道会有那么多“坑”,很多人都需要重复思考如何解决这些限制。
因此,本文总结在这里,希望对大家有帮助。

这篇关于浅谈 Guava 中的 ImmutableMap.of 方法的坑的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




