本文主要是介绍埃尔米特插值(hermite 插值) C++,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
埃尔米特插值 原理

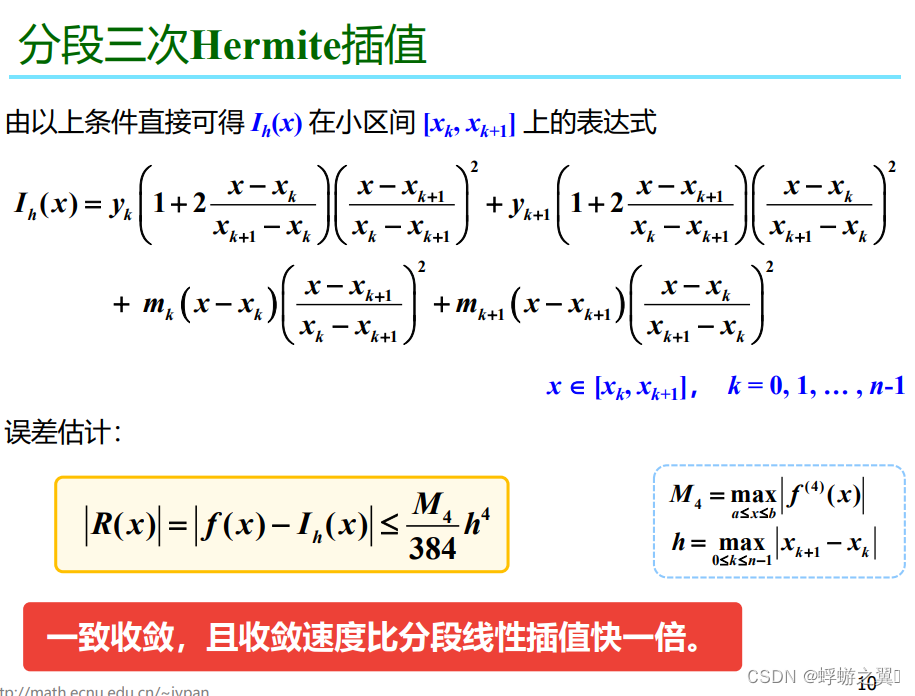
#pragma once
#include <vector>
#include <functional>
/*埃尔米特插值*/
struct InterpolationPoint {double x; // 插值点的横坐标double y; // 插值点的纵坐标double derivative; // 插值点的导数值// 默认构造函数InterpolationPoint() : x(0.0), y(0.0), derivative(0.0) {}// 带参数的构造函数InterpolationPoint(double x_val, double y_val, double derivative_val) : x(x_val), y(y_val), derivative(derivative_val) {}// 拷贝构造函数InterpolationPoint(const InterpolationPoint& other) : x(other.x), y(other.y), derivative(other.derivative) {}// 移动构造函数InterpolationPoint(InterpolationPoint&& other) noexcept : x(other.x), y(other.y), derivative(other.derivative) {other.x = 0.0;other.y = 0.0;other.derivative = 0.0;}// Copy assignment operatorInterpolationPoint& operator=(const InterpolationPoint& other) {if (this != &other) {x = other.x;y = other.y;derivative = other.derivative;}return *this;}// 设置插值点的值void set(double x_val, double y_val, double derivative_val) {x = x_val;y = y_val;derivative = derivative_val;}// 获取插值点的横坐标double get_x() const {return x;}// 获取插值点的纵坐标double get_y() const {return y;}// 获取插值点的导数值double get_derivative() const {return derivative;}
};class HermiteInterpolator {
public:HermiteInterpolator(const std::vector<InterpolationPoint>& points);HermiteInterpolator(int width, std::vector<int> &adjPoints);void setPoints(const std::vector<InterpolationPoint>& points);double interpolate(double x) ;private:// 返回连接两点的线段函数std::function<double(double)> getLineFunction( InterpolationPoint& p1, InterpolationPoint& p2);private:std::vector<InterpolationPoint> points_;
};
#include "pch.h"
#include "HermiteInterpolator.h"
#include <fstream>
HermiteInterpolator::HermiteInterpolator(const std::vector<InterpolationPoint>& points) : points_(points)
{
}
HermiteInterpolator::HermiteInterpolator(int width, std::vector<int>& adjPoints)
{float step = width / adjPoints.size();for (int i = 0; i < adjPoints.size(); i++){InterpolationPoint point(step*i, adjPoints[i] , 0);points_.push_back(point);}
}
void HermiteInterpolator::setPoints(const std::vector<InterpolationPoint>& points)
{points_ = points;
}// 返回连接两点的线段函数
std::function<double(double)> HermiteInterpolator::getLineFunction( InterpolationPoint& p1, InterpolationPoint& p2) {// 计算线段的斜率和截距double slope = (p2.y - p1.y) / (p2.x - p1.x);double intercept = p1.y - slope * p1.x;// 返回线段的lambda表达式return [slope, intercept](double x) {return slope * x + intercept;};
}
// 计算三次分段Hermite插值函数的值
double HermiteInterpolator::interpolate(double x) {int y = 0;int n = points_.size();if (n < 3){// 获取线段函数std::function<double(double)> lineFunction = getLineFunction(points_[0], points_[1]);y= lineFunction(x);}else{for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {if (x >= points_[i].x && x <= points_[i + 1].x) {double h = points_[i + 1].x - points_[i].x;double t = (x - points_[i].x) / h;// (x-x_k)/(x_{k+1} - x_k)double tk = (x - points_[i + 1].x) / (-h); // (x - x_{ k + 1 }) / (x_k - x_{ k + 1 }) double y0 = (1 + 2 * t) * tk * tk;double y1 = (1 + 2 * tk) * t * t;double y2 = (x - points_[i].x) * tk * tk;double y3 = (x - points_[i + 1].x) * t * t;y= points_[i].y * y0 + points_[i + 1].y * y1 + points_[i].derivative * y2 + points_[i + 1].derivative * y3;}}}//ofstream f;//f.open("D:\\work\\documentation\\HermiteInterpolator.txt", ios::app);//f <<x<<"," << y << endl;//f.close();return y; // 如果找不到对应的插值段,返回默认值
}
为了可视化效果可以把结果写到HermiteInterpolator.txt
画图python代码:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt# 打开文本文件进行读取
with open('D:\\work\\documentation\\HermiteInterpolator.txt') as f:data = f.readlines()# 定义两个列表分别存储横坐标和纵坐标的数据
x = []
y = [] # 遍历每一行
for i, line in enumerate(data):# 去除换行符if line:user_pwd_list = line.strip().split(',')# 横坐标是行号x.append(float(user_pwd_list[0]))# 纵坐标是数值数据y.append(float(user_pwd_list[1]))# 创建散点图
plt.scatter(x, y)# 添加标题和轴标签
plt.title('Scatter Plot')
plt.xlabel('Line')
plt.ylabel('Value')# 显示并保存图像
#plt.savefig('plot.png')
plt.show()
这篇关于埃尔米特插值(hermite 插值) C++的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





