本文主要是介绍Orchestrator介绍三 命令行工具,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
orchestrator 支持两种方式通过命令行操作
通过命令orchestrator
需要在服务器上安装 orchestrator,但是可以不作为服务启动。
需要配置orchestrator的文件,以便能够连接后端数据库
通过命令orchestrator-client
需要在服务器上安装orchestrator-client 脚本
不需要配置文件,但是需要指定ORCHESTRATOR_API 环境变量
orchestrator命令
./orchestrator -c help 查看帮助
./orchestrator -c help
Available commands (-c):
Smart relocation:relocate Relocate a replica beneath another instancerelocate-below Synonym to 'relocate', will be deprecatedrelocate-replicas Relocates all or part of the replicas of a given instance under another instancetake-siblings Turn all siblings of a replica into its sub-replicas.regroup-replicas Given an instance, pick one of its replicas and make it local master of its siblings
Classic file:pos relocation:move-up Move a replica one level up the topologymove-up-replicas Moves replicas of the given instance one level up the topologymove-below Moves a replica beneath its sibling. Both replicas must be actively replicating from same master.move-equivalent Moves a replica beneath another server, based on previously recorded "equivalence coordinates"repoint Make the given instance replicate from another instance without changing the binglog coordinates. Use with carerepoint-replicas Repoint all replicas of given instance to replicate back from the instance. Use with caretake-master Turn an instance into a master of its own master; essentially switch the two.make-co-master Create a master-master replication. Given instance is a replica which replicates directly from a master.get-candidate-replica Information command suggesting the most up-to-date replica of a given instance that is good for promotion
Binlog server relocation:regroup-replicas-bls Regroup Binlog Server replicas of a given instance
GTID relocation:move-gtid Move a replica beneath another instance.move-replicas-gtid Moves all replicas of a given instance under another (destination) instance using GTIDregroup-replicas-gtid Given an instance, pick one of its replica and make it local master of its siblings, using GTID.
Pseudo-GTID relocation:match Matches a replica beneath another (destination) instance using Pseudo-GTIDmatch-up Transport the replica one level up the hierarchy, making it child of its grandparent, using Pseudo-GTIDrematch Reconnect a replica onto its master, via PSeudo-GTID.match-replicas Matches all replicas of a given instance under another (destination) instance using Pseudo-GTIDmatch-up-replicas Matches replicas of the given instance one level up the topology, making them siblings of given instance, using Pseudo-GTIDregroup-replicas-pgtid Given an instance, pick one of its replica and make it local master of its siblings, using Pseudo-GTID.
Replication, general:enable-gtid If possible, turn on GTID replicationdisable-gtid Turn off GTID replication, back to file:pos replicationwhich-gtid-errant Get errant GTID set (empty results if no errant GTID)gtid-errant-reset-master Reset master on instance, remove GTID errant transactionsskip-query Skip a single statement on a replica; either when running with GTID or withoutstop-replica Issue a STOP SLAVE on an instancestart-replica Issue a START SLAVE on an instancerestart-replica STOP and START SLAVE on an instancereset-replica Issues a RESET SLAVE command; use with caredetach-replica-master-host Stops replication and modifies Master_Host into an impossible, yet reversible, value.reattach-replica-master-host Undo a detach-replica-master-host operationmaster-pos-wait Wait until replica reaches given replication coordinates (--binlog=file:pos)enable-semi-sync-master Enable semi-sync replication (master-side)disable-semi-sync-master Disable semi-sync replication (master-side)enable-semi-sync-replica Enable semi-sync replication (replica-side)disable-semi-sync-replica Disable semi-sync replication (replica-side)restart-replica-statements Get a list of statements to execute to stop then restore replica to same execution state. Provide --statement for injected statement
Replication information:can-replicate-from Can an instance (-i) replicate from another (-d) according to replication rules? Prints 'true|false'is-replicating Is an instance (-i) actively replicating right nowis-replication-stopped Is an instance (-i) a replica with both replication threads stopped
Instance:set-read-only Turn an instance read-only, via SET GLOBAL read_only := 1set-writeable Turn an instance writeable, via SET GLOBAL read_only := 0
Binary logs:flush-binary-logs Flush binary logs on an instancepurge-binary-logs Purge binary logs of an instancelast-pseudo-gtid Find latest Pseudo-GTID entry in instance's binary logslocate-gtid-errant List binary logs containing errant GTIDslast-executed-relay-entry Find coordinates of last executed relay log entrycorrelate-relaylog-pos Given an instance (-i) and relaylog coordinates (--binlog=file:pos), find the correlated coordinates in another instance's relay logs (-d)find-binlog-entry Get binlog file:pos of entry given by --pattern (exact full match, not a regular expression) in a given instancecorrelate-binlog-pos Given an instance (-i) and binlog coordinates (--binlog=file:pos), find the correlated coordinates in another instance (-d)
Pools:submit-pool-instances Submit a pool name with a list of instances in that poolcluster-pool-instances List all pools and their associated instanceswhich-heuristic-cluster-pool-instances List instances of a given cluster which are in either any pool or in a specific pool
Information:find Find instances whose hostname matches given regex patternsearch Search instances by name, version, version comment, portclusters List all clusters known to orchestratorclusters-alias List all clusters known to orchestratorall-clusters-masters List of writeable masters, one per clustertopology Show an ascii-graph of a replication topology, given a member of that topologytopology-tabulated Show an ascii-graph of a replication topology, given a member of that topologytopology-tags Show an ascii-graph of a replication topology and instance tags, given a member of that topologyall-instances The complete list of known instanceswhich-instance Output the fully-qualified hostname:port representation of the given instance, or error if unknownwhich-cluster Output the name of the cluster an instance belongs to, or error if unknown to orchestratorwhich-cluster-alias Output the alias of the cluster an instance belongs to, or error if unknown to orchestratorwhich-cluster-domain Output the domain name of the cluster an instance belongs to, or error if unknown to orchestratorwhich-heuristic-domain-instance Returns the instance associated as the cluster's writer with a cluster's domain name.which-cluster-master Output the name of the master in a given clusterwhich-cluster-instances Output the list of instances participating in same cluster as given instancewhich-cluster-osc-replicas Output a list of replicas in a cluster, that could serve as a pt-online-schema-change operation control replicaswhich-cluster-gh-ost-replicas Output a list of replicas in a cluster, that could serve as a gh-ost working serverwhich-master Output the fully-qualified hostname:port representation of a given instance's masterwhich-downtimed-instances List instances currently downtimed, potentially filtered by clusterwhich-replicas Output the fully-qualified hostname:port list of replicas of a given instancewhich-lost-in-recovery List instances marked as downtimed for being lost in a recovery processinstance-status Output short status on a given instanceget-cluster-heuristic-lag For a given cluster (indicated by an instance or alias), output a heuristic "representative" lag of that cluster
Key-value:submit-masters-to-kv-stores Submit master of a specific cluster, or all masters of all clusters to key-value stores
tags:tags List tags for a given instancetag-value Get tag value for a specific instancetagged List instances tagged by tag-string. Format: "tagname" or "tagname=tagvalue" or comma separated "tag0,tag1=val1,tag2" for intersection of all.tag Add a tag to a given instance. Tag in "tagname" or "tagname=tagvalue" formatuntag Remove a tag from an instanceuntag-all Remove a tag from all matching instances
Instance management:discover Lookup an instance, investigate itforget Forget about an instance's existencebegin-maintenance Request a maintenance lock on an instanceend-maintenance Remove maintenance lock from an instancein-maintenance Check whether instance is under maintenancebegin-downtime Mark an instance as downtimedend-downtime Indicate an instance is no longer downtimed
Recovery:recover Do auto-recovery given a dead instancerecover-lite Do auto-recovery given a dead instance. Orchestrator chooses the best course of actionwithout executing external processesforce-master-failover Forcibly discard master and initiate a failover, even if orchestrator doesn't see a problem. This command lets orchestrator choose the replacement masterforce-master-takeover Forcibly discard master and promote another (direct child) instance instead, even if everything is running wellgraceful-master-takeover Gracefully promote a new master. Either indicate identity of new master via '-d designated.instance.com' or setup replication tree to have a single direct replica to the master.graceful-master-takeover-auto Gracefully promote a new master. orchestrator will attempt to pick the promoted replica automaticallyreplication-analysis Request an analysis of potential crash incidents in all known topologiesack-all-recoveries Acknowledge all recoveries; this unblocks pending future recoveriesack-cluster-recoveries Acknowledge recoveries for a given cluster; this unblocks pending future recoveriesack-instance-recoveries Acknowledge recoveries for a given instance; this unblocks pending future recoveries
Instance, meta:register-candidate Indicate that a specific instance is a preferred candidate for master promotionregister-hostname-unresolve Assigns the given instance a virtual (aka "unresolved") namederegister-hostname-unresolve Explicitly deregister/dosassociate a hostname with an "unresolved" nameset-heuristic-domain-instance Associate domain name of given cluster with what seems to be the writer master for that cluster
Meta:snapshot-topologies Take a snapshot of existing topologies.continuous Enter continuous mode, and actively poll for instances, diagnose problems, do maintenanceactive-nodes List currently active orchestrator nodesaccess-token Get a HTTP access tokenresolve Resolve given hostnamereset-hostname-resolve-cache Clear the hostname resolve cachedump-config Print out configuration in JSON formatshow-resolve-hosts Show the content of the hostname_resolve table. Generally used for debuggingshow-unresolve-hosts Show the content of the hostname_unresolve table. Generally used for debugging
Meta, internal:redeploy-internal-db Force internal schema migration to current backend structure
Internal:internal-suggest-promoted-replacement Internal only, used to test promotion logic in CI
Agent:custom-command Execute a custom command on the agent as defined in the agent conf
:disable-global-recoveries Disallow orchestrator from performing recoveries globallyenable-global-recoveries Allow orchestrator to perform recoveries globallycheck-global-recoveries Show the global recovery configurationbulk-instances Return a list of sorted instance names known to orchestratorbulk-promotion-rules Return a list of promotion rules known to orchestrator
Run 'orchestrator help <command>' for detailed help on given command, e.g. 'orchestrator help relocate'Usage for most commands:orchestrator -c <command> [-i <instance.fqdn>[,<instance.fqdn>]* ] [-d <destination.fqdn>] [--verbose|--debug]./orchestrator -c find help 查看子命令的帮助
./orchestrator -c find help
find:Find instances whose hostname matches given regex pattern. Example:orchestrator -c find -pattern "backup.*us-east"需要指定配置文件
需要添加参数 --ignore-raft-setup,如果不加该参数报错
2023-09-13 15:50:56 FATAL Orchestrator configured to run raft ("RaftEnabled": true). All access must go through the web API of the active raft node. You may use the orchestrator-client script which has a similar interface to the command line invocation. You may override this with --ignore-raft-setup查看信息
打印所有匹配到的实例
./orchestrator -config orchestrator-sample.conf.json --ignore-raft-setup -c find -pattern "ehr-db-mysql-test-s0*"打印根据名字 ,端口,版本匹配到的实例
./orchestrator -config orchestrator-sample.conf.json --ignore-raft-setup -c search -pattern "5.7.28"./orchestrator -config orchestrator-sample.conf.json --ignore-raft-setup -c search -pattern "5306"打印所有被oc管控的集群
./orchestrator -config orchestrator-sample.conf.json --ignore-raft-setup -c clusters打印所有被orc管控的集群的别名
./orchestrator -config orchestrator-sample.conf.json --ignore-raft-setup -c clusters-alias所有集群的所有可写的主库
./orchestrator -config orchestrator-sample.conf.json --ignore-raft-setup -c all-clusters-masters根据集群中某个实例的名称打印集群拓扑
./orchestrator -config orchestrator-sample.conf.json --ignore-raft-setup -c topology -i ehr-db-mysql-test-s03.zjy:5306./orchestrator -config orchestrator-sample.conf.json --ignore-raft-setup -c topology-tabulated -i ehr-db-mysql-test-s03.zjy:5306./orchestrator -config orchestrator-sample.conf.json --ignore-raft-setup -c topology-tags -i ehr-db-mysql-test-s03.zjy:5306这两种只是格式不同
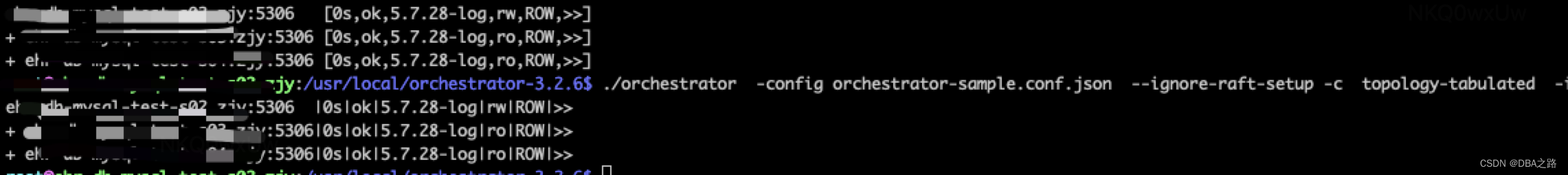
打印所有的实例
./orchestrator -config orchestrator-sample.conf.json --ignore-raft-setup -c all-instances
根据实例返回实例所在的集群别名
./orchestrator -config orchestrator-sample.conf.json --ignore-raft-setup -c which-cluster -i
根据实例返回实例所在的集群别名
./orchestrator -config orchestrator-sample.conf.json --ignore-raft-setup -c which-cluster-alias -i ehr-db-mysql-test-s03.zjy:5306
根据实例返回实例所在的集群域名
./orchestrator -config orchestrator-sample.conf.json --ignore-raft-setup -c which-cluster-domain -i ehr-db-mysql-test-s03.zjy:5306
根据实例返回实例所在的集群主库
./orchestrator -config orchestrator-sample.conf.json --ignore-raft-setup -c which-cluster-master -i ehr-db-mysql-test-s03.zjy:5306
根据实例返回实例所在的集群中所有实例
./orchestrator -config orchestrator-sample.conf.json --ignore-raft-setup -c which-cluster-instances -i ehr-db-mysql-test-s03.zjy:5306
返回实例状态
./orchestrator -config orchestrator-sample.conf.json --ignore-raft-setup -c instance-status -i ehr-db-mysql-test-s03.zjy:5306
输出集群中的副本列表,可以作为 pt-online-schema-change 操作控制副本
./orchestrator -config orchestrator-sample.conf.json --ignore-raft-setup -c which-cluster-osc-replicas -i ehr-db-mysql-test-s03.zjy:5306
输出集群中的副本列表,可以作为 gh-ost 工作服务器
./orchestrator -config orchestrator-sample.conf.json --ignore-raft-setup -c which-cluster-gh-ost-replicas -i ehr-db-mysql-test-s03.zjy:5306
Orchestrator-client是一个包装 API 调用的脚本,使用起来更方便。
它可以自动确定orchestrator的Leader角色,并在这种情况下将所有请求转发给Leader。
有了orchestrator-client,您:
- 不需要到处安装
orchestrator的二进制文件;仅在运行该服务的主机上安装即可 - 不需要到处部署配置
orchestrator;仅在服务主机上即可。 - 不需要访问后端数据库
- 需要访问 HTTP api
- 需要设置
ORCHESTRATOR_API环境变量。- 要么为代理提供单个端点,例如
export ORCHESTRATOR_API=https://orchestrator.myservice.com:3000/api
- 或者提供所有
orchestrator端点,并orchestrator-client自动选择领导者(不需要代理),例如
export ORCHESTRATOR_API="https://orchestrator.host1:3000/api https://orchestrator.host2:3000/api https://orchestrator.host3:3000/api"
- 您可以在 中设置环境
/etc/profile.d/orchestrator-client.sh。如果该文件存在,它将被内联orchestrator-client。
使用示例
显示当前已知的集群(复制拓扑):
<span style="background-color:var(--color-canvas-subtle)"><span style="color:#1f2328"><span style="color:var(--fgColor-default, var(--color-fg-default))"><span style="background-color:var(--bgColor-muted, var(--color-canvas-subtle))"><code>orchestrator-client -c clusters
</code></span></span></span></span>发现、忘记一个例子:
<span style="background-color:var(--color-canvas-subtle)"><span style="color:#1f2328"><span style="color:var(--fgColor-default, var(--color-fg-default))"><span style="background-color:var(--bgColor-muted, var(--color-canvas-subtle))"><code>orchestrator-client -c discover -i 127.0.0.1:22987
orchestrator-client -c forget -i 127.0.0.1:22987
</code></span></span></span></span>打印拓扑实例的 ASCII 树。通过以下方式传递集群名称-i(参见clusters上面的命令):
<span style="background-color:var(--color-canvas-subtle)"><span style="color:#1f2328"><span style="color:var(--fgColor-default, var(--color-fg-default))"><span style="background-color:var(--bgColor-muted, var(--color-canvas-subtle))"><code>orchestrator-client -c topology -i 127.0.0.1:22987
</code></span></span></span></span>示例输出:
<span style="background-color:var(--color-canvas-subtle)"><span style="color:var(--fgColor-default, var(--color-fg-default))"><span style="background-color:var(--bgColor-muted, var(--color-canvas-subtle))"><code>127.0.0.1:22987 + 127.0.0.1:22989+ 127.0.0.1:22988 + 127.0.0.1:22990 </code></span></span></span>
在拓扑中移动副本:
<span style="background-color:var(--color-canvas-subtle)"><span style="color:#1f2328"><span style="color:var(--fgColor-default, var(--color-fg-default))"><span style="background-color:var(--bgColor-muted, var(--color-canvas-subtle))"><code>orchestrator-client -c relocate -i 127.0.0.1:22988 -d 127.0.0.1:22987
</code></span></span></span></span>结果拓扑:
<span style="background-color:var(--color-canvas-subtle)"><span style="color:var(--fgColor-default, var(--color-fg-default))"><span style="background-color:var(--bgColor-muted, var(--color-canvas-subtle))"><code>127.0.0.1:22987 + 127.0.0.1:22989 + 127.0.0.1:22988 + 127.0.0.1:22990 </code></span></span></span>
ETC。
幕后花絮
命令行界面为 API 调用提供了一个很好的包装器,然后其输出从 JSON 格式转换为文本格式。
例如,命令:
orchestrator-client -c discover -i 127.0.0.1:22987
翻译为(为了方便起见,此处进行了简化):
curl "$ORCHESTRATOR_API/discover/127.0.0.1/22987" | jq '.Details | .Key'
元命令
orchestrator-client -c help:列出所有可用的命令orchestrator-client -c which-api:API 端点orchestrator-client将用于调用命令的输出。当通过 提供多个端点时,这非常有用$ORCHESTRATOR_API。orchestrator-client -c api -path clusters:调用通用 HTTP API 调用(在本例中clusters)并返回原始 JSON 响应。
这篇关于Orchestrator介绍三 命令行工具的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!







