本文主要是介绍JAVA 实现人机猜拳,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
任务
1.完成人机猜拳互动游戏的开发
主要功能
1.选取对战角色
2.猜拳
3.记录分数
方法思路:
- 创建用户类User来实现用户出拳
- 创建电脑类Computer来实现电脑出拳
- 创建游戏类Game来实现猜拳游戏,其中方法Judge实现判断本局输赢StartGame方法实现菜单打印以及循环游戏并判断最终结果。
具体实现如下
1.实现User类:
import java.util.Scanner;public class User {public int showFist(int i) {//打印用户出拳switch (i) {case 1:System.out.println("你出拳:剪刀");break;case 2:System.out.println("你出拳:石头 ");break;case 3:System.out.println("你出拳:布");break;default:System.out.println("输入错误,请重新输入:");break;}return i;}
}
2.实现Computer类:
import java.util.Random;public class Computer {int showHand = 0;//记录所出拳String heroName;//储存对战英雄名称public void showFist() {//电脑随机出拳并打印电脑出拳Random sc = new Random();showHand = sc.nextInt(3) + 1;switch (showHand) {case 1:System.out.println(heroName + "出拳:" + "剪刀");break;case 2:System.out.println(heroName + "出拳:" + "石头");break;case 3:System.out.println(heroName + "出拳:" + "布");break;}}public String getHeroName(int i) {switch (i) {case 1:heroName = "刘备";break;case 2:heroName = "孙权";break;case 3:heroName = "曹操";break;}return heroName;}}3.实现Game类:
import java.util.Scanner;public class Game {int score = 0;//平局统计int score1 = 0;//电脑胜利数int score2 = 0;//玩家胜利数Computer computer =new Computer();User user=new User();public int judge(int i)//判断此局胜负,并记录分数{Game game=new Game();if (i == computer.showHand) {System.out.println("和局,嘿嘿,等着瞧吧!");System.out.println();score++;} else if (i == 1 && computer.showHand == 2) {System.out.println("你输了,真笨!");System.out.println();score1++;} else if (i == 1 && computer.showHand == 3) {System.out.println("恭喜,你赢了!");System.out.println();score2++;} else if (i == 2 && computer.showHand == 1) {System.out.println("此局:恭喜,你赢了");score2++;} else if (i == 2 && computer.showHand == 3) {System.out.println("此局:很遗憾,你输了");score1++;} else if (i == 3 && computer.showHand== 1) {System.out.println("此局:很遗憾,你输了");score1++;} else if (i == 3 && computer.showHand == 2) {System.out.println("此局:恭喜,你赢了");score2++;}return i;}public void startGame() {Game game=new Game();System.out.println("********************");//打印菜单System.out.println("******猜拳,开始******");System.out.println("********************");System.out.println("出拳规则:1,剪刀 2,石头 3,布");System.out.println("请选择你想和谁对战(1:刘备 2:孙权 3:曹操):");Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);int a = sc.nextInt();computer.getHeroName(a);//获取用户所寻找对象System.out.println("请输入你的名字:");String name = sc.next();//录入用户信息switch (a) {case 1:System.out.println("你选择了刘备对战");break;case 2:System.out.println("你选择了刘邦对战");break;case 3:System.out.println("你选择了曹操对战");break;}System.out.println(name + "vs" + computer.heroName + "对战");int court = 1;//储存对战局数System.out.print("要开始吗?(y/n):");Scanner sr = new Scanner(System.in);String choose = sr.next();while (true) {//死循环来重复进行游戏直到用户退出游戏if (choose.equals("n")) {System.out.println("结束");return;} else if (choose.equals("y")) {System.out.print("请出拳:1.剪刀 2.石头 3.布(输入相应数字):");int c = sr.nextInt();//获取用户出拳user.showFist(c);//打印用户出拳computer.showFist();//打印电脑出拳judge(c);//判断本局结果并打印System.out.println("是否开始下一轮(y/n):");System.out.println("------------------------------------------");String m = sr.next();//获取用户是否想要进行下一轮比赛if (m.equals("y")) {court++;//累加一次比赛局数} else if (m.equals("n")) {System.out.println("------------------------------------------");//打印比赛最后比分System.out.println(computer.heroName + "VS" + name);System.out.println("对战次数:" +court + " " + "平局" + score + "次");System.out.println("姓名" + " " + "得分");System.out.println(name + " " + score2);System.out.println(computer.heroName + " " +score1);if (score1 < score2)//打印比赛最后结果{System.out.println("恭喜恭喜,你赢得了比赛!");break;} else if (score1 ==score2) {System.out.println("打成平手,下次和你一较高下!");break;} else {System.out.println("呵呵,笨笨,下次加油啊!");break;}}}}}}
具体运行如下
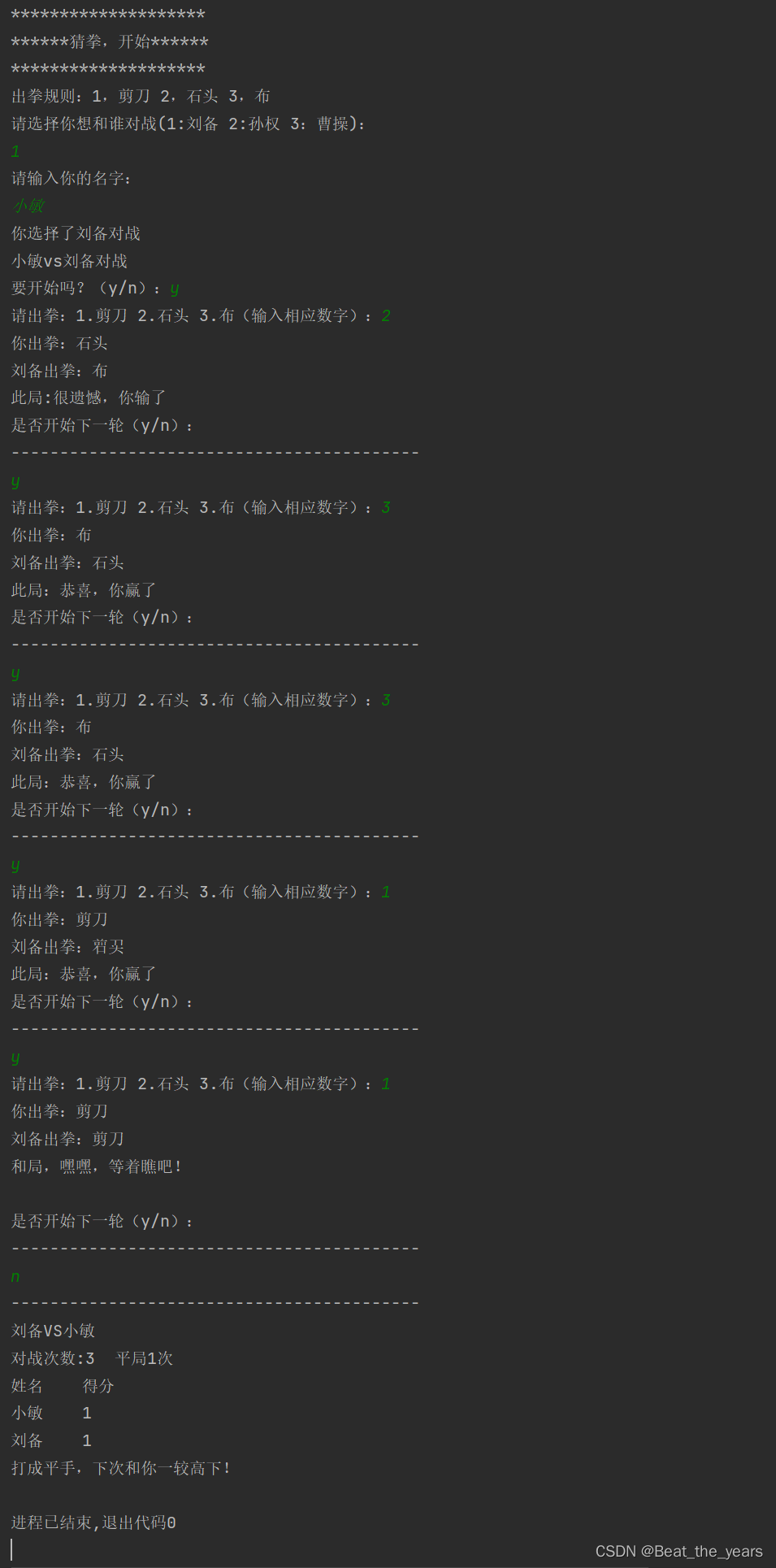
至此,人机猜拳已经完成,有什么问题欢迎来询问!
这篇关于JAVA 实现人机猜拳的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




