本文主要是介绍SplayTree高分测试用例,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
测试用例结果展示
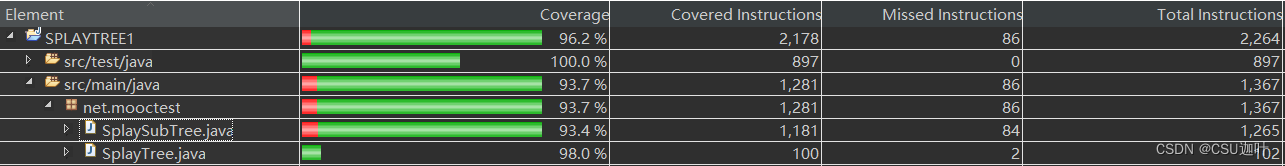
覆盖率
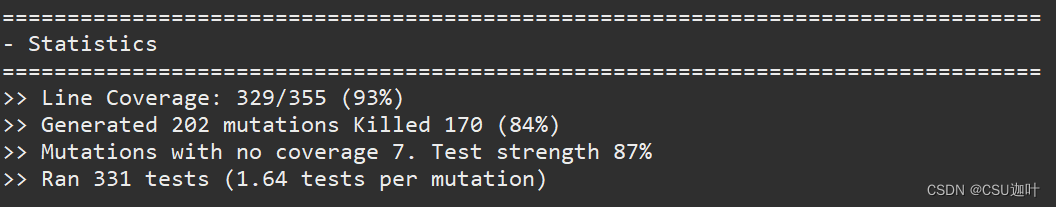
变异得分
测试注意点
- 从SplayTree测起,然后再测SubSplayTree,因为前者调用后者。
- SplaySubTree的remove方法大部分内容需要通过反射才能测到。
- value和index在SplayTree当中都不是唯一的。一个index可能对应多个value。
不足之处
- 没考虑到异常怎么接住。
- 对SplayTree这个数据结构的理解还很浅显。
测试文件MyTest.java
package net.mooctest;import static org.junit.Assert.*;import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.Arrays;import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;public class MyTest {private Integer valArr[];private Integer remArr[];private Integer conArr[];private SplayTree<Integer> splayTree;private int howmanynumbers;private int removeCnt;private int containsCnt;@Beforepublic void initializeValArr() {this.howmanynumbers = 100;this.removeCnt = 0;this.containsCnt = 0;valArr = new Integer[howmanynumbers]; remArr = new Integer[howmanynumbers/7+1]; conArr = new Integer[howmanynumbers/9+1];for(int i=0;i<this.howmanynumbers;i++) {int val = (int)(Math.random()*100);
// System.out.println(val);valArr[i] = val;if(i%7==0) {remArr[this.removeCnt++] = val;}if(i%9==0) {conArr[this.containsCnt++] = val;}}}@Testpublic void testMain() {SplayTree.main(null);}// 测试remove和contains@Testpublic void test001() {splayTree = new SplayTree<Integer>();for(int i=0;i<this.howmanynumbers;i++) {splayTree.add(valArr[i]);assertNull(splayTree.root.join(splayTree.root));}assertNotNull(splayTree.root.add(null));assertEquals(howmanynumbers, splayTree.size());for(int i=0;i<this.removeCnt;i++) {int valToRemove = remArr[i];assertTrue(splayTree.contains(valToRemove));splayTree.remove(valToRemove);}assertEquals(howmanynumbers-removeCnt, splayTree.size());for(int i=0;i<this.containsCnt;i++) {int valToVarify = conArr[i];assertTrue(splayTree.contains(valToVarify));}}// 测试remove和contains@Testpublic void test002() {splayTree = new SplayTree<Integer>();for(int i=0;i<this.howmanynumbers;i++) {splayTree.add(valArr[i]);assertNull(splayTree.root.split(splayTree.root.getData()));}assertEquals(howmanynumbers, splayTree.size());for(int i=0;i<this.removeCnt;i++) {int valToRemove = remArr[i];assertTrue(splayTree.contains(valToRemove));splayTree.remove(valToRemove);}assertEquals(howmanynumbers-removeCnt, splayTree.size());for(int i=0;i<this.containsCnt;i++) {int valToVarify = conArr[i];assertTrue(splayTree.contains(valToVarify));}}// 测试get和indexOf// 不能再用随机生成的数据,因为随机数据很可能重复@Testpublic void test003() {splayTree = new SplayTree<Integer>();for(int i=0;i<this.howmanynumbers;i++) {splayTree.add(i*17);}assertEquals(howmanynumbers, splayTree.size());long idxArr[] = new long[howmanynumbers];for(int i=0;i<splayTree.size();i++) {idxArr[i] = splayTree.indexOf(i*17);}for(int i=0;i<splayTree.size();i++) {assertEquals(i*17, (int)splayTree.get(idxArr[i]));}assertNull(splayTree.get(-1));assertNull(splayTree.get(splayTree.size()+1));}//测试toString()@Testpublic void test004() {int primeArr[] = {2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47, 53, 59, 61, 67, 71 };splayTree = new SplayTree<Integer>();for(int i=0;i<primeArr.length;i++) {splayTree.add(primeArr[i]);}// System.out.println(splayTree.toString());
// String expectedStr = " data=2 left= null right null sz=1 cnt=1\n";
// assertEquals(expectedStr, splayTree.toString());String expectedStr = " data=71 left=67 right null sz=20 cnt=1\n" + " data=67 left=61 right null sz=19 cnt=1\n" + " data=61 left=59 right null sz=18 cnt=1\n" + " data=59 left=53 right null sz=17 cnt=1\n" + " data=53 left=47 right null sz=16 cnt=1\n" + " data=47 left=43 right null sz=15 cnt=1\n" + " data=43 left=41 right null sz=14 cnt=1\n" + " data=41 left=37 right null sz=13 cnt=1\n" + " data=37 left=31 right null sz=12 cnt=1\n" + " data=31 left=29 right null sz=11 cnt=1\n" + " data=29 left=23 right null sz=10 cnt=1\n" + " data=23 left=19 right null sz=9 cnt=1\n" + " data=19 left=17 right null sz=8 cnt=1\n" + " data=17 left=13 right null sz=7 cnt=1\n" + " data=13 left=11 right null sz=6 cnt=1\n" + " data=11 left=7 right null sz=5 cnt=1\n" + " data=7 left=5 right null sz=4 cnt=1\n" + " data=5 left=3 right null sz=3 cnt=1\n" + " data=3 left=2 right null sz=2 cnt=1\n" + " data=2 left= null right null sz=1 cnt=1\n";assertEquals(expectedStr, splayTree.toString());}//测试SplaySubTree--find@Test(timeout=4000)public void test005() {SplaySubTree<Integer> splaySubTree = new SplaySubTree<Integer>(null);assertNull(splaySubTree.find(1));int primeArr[] = {2, 41, 5, 7, 67, 23, 11, 17, 19};for(int i=0;i<primeArr.length;i++) {splaySubTree = splaySubTree.add(primeArr[i]);}
// System.out.println(splaySubTree.toString());assertNull(splaySubTree.find(20));}//测试SplaySubTree--remove@Test(timeout=4000)public void test006() throws NoSuchFieldException, SecurityException, IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException {SplaySubTree<Integer> splaySubTree = new SplaySubTree<Integer>(0);int primeArr[] = {2, 41, 5, 7, 23, 11, 67, 17, 19};System.out.println(primeArr.length);for(int i=0;i<primeArr.length;i++) {splaySubTree = splaySubTree.add(primeArr[i]);}assertNotNull(splaySubTree.remove(20));assertEquals(primeArr.length+1,splaySubTree.remove(null).size());// 获取 SplaySubTree<Integer> 的 Class 对象 Class<?> splaySubTreeClass = splaySubTree.getClass(); // 获取私有属性 count 的 Field 对象 Field countField = splaySubTreeClass.getDeclaredField("count"); // 设置私有属性 count 的可访问性 countField.setAccessible(true); splaySubTree = splaySubTree.remove(7);// 访问私有属性 count 的值 int countValue = (int) countField.get(splaySubTree);
// System.out.println("countValue: " + countValue);assertEquals(0, countValue);
// System.out.println(splaySubTree.toString());splaySubTree = splaySubTree.remove(7);countValue = (int) countField.get(splaySubTree);
// System.out.println("countValue: " + countValue); assertEquals(-1, countValue);}//测试SplaySubTree--remove@Test(timeout=4000)public void test007() {SplaySubTree<Integer> splaySubTree = new SplaySubTree<Integer>(1);splaySubTree.remove(1);}//测试SplaySubTree--remove@Test(timeout=4000)public void test008() throws NoSuchFieldException, SecurityException, IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException, NullPointerException {SplaySubTree<Integer> splaySubTree = new SplaySubTree<Integer>(1);// 获取 SplaySubTree<Integer> 的 Class 对象 Class<?> splaySubTreeClass = splaySubTree.getClass(); // 获取私有属性 count 的 Field 对象 Field leftField = splaySubTreeClass.getDeclaredField("left"); // 设置私有属性 count 的可访问性 leftField.setAccessible(true); SplaySubTree<Integer> splaySubTree2 = new SplaySubTree<Integer>(2);leftField.set(splaySubTree,splaySubTree2);splaySubTree.remove(1);}//测试SplaySubTree--remove@Test(timeout=4000)public void test009() throws NoSuchFieldException, SecurityException, IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException, NullPointerException {SplaySubTree<Integer> splaySubTree = new SplaySubTree<Integer>(1);// 获取 SplaySubTree<Integer> 的 Class 对象 Class<?> splaySubTreeClass = splaySubTree.getClass(); // 获取私有属性 count 的 Field 对象 Field rightField = splaySubTreeClass.getDeclaredField("right"); // 设置私有属性 count 的可访问性 rightField.setAccessible(true); SplaySubTree<Integer> splaySubTree2 = new SplaySubTree<Integer>(2);rightField.set(splaySubTree,splaySubTree2);splaySubTree.remove(1);}//测试SplaySubTree--remove@Test(timeout=4000)public void test0010() throws NoSuchFieldException, SecurityException, IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException, NullPointerException {SplaySubTree<Integer> splaySubTree = new SplaySubTree<Integer>(1);// 获取 SplaySubTree<Integer> 的 Class 对象 Class<?> splaySubTreeClass = splaySubTree.getClass(); // 获取私有属性 count 的 Field 对象 Field leftField = splaySubTreeClass.getDeclaredField("left");Field parentField = splaySubTreeClass.getDeclaredField("parent"); // 设置私有属性 count 的可访问性 leftField.setAccessible(true); parentField.setAccessible(true); SplaySubTree<Integer> splaySubTree2 = new SplaySubTree<Integer>(2);leftField.set(splaySubTree,splaySubTree2);SplaySubTree<Integer> splaySubTree3 = new SplaySubTree<Integer>(3);parentField.set(splaySubTree,splaySubTree3);splaySubTree.remove(1);}//测试SplaySubTree--remove@Test(timeout=4000)public void test0011() throws NoSuchFieldException, SecurityException, IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException, NullPointerException {SplaySubTree<Integer> splaySubTree = new SplaySubTree<Integer>(1);// 获取 SplaySubTree<Integer> 的 Class 对象 Class<?> splaySubTreeClass = splaySubTree.getClass(); // 获取私有属性 count 的 Field 对象 Field rightField = splaySubTreeClass.getDeclaredField("right"); Field parentField = splaySubTreeClass.getDeclaredField("parent"); // 设置私有属性 count 的可访问性 rightField.setAccessible(true); parentField.setAccessible(true); SplaySubTree<Integer> splaySubTree2 = new SplaySubTree<Integer>(2);rightField.set(splaySubTree,splaySubTree2);SplaySubTree<Integer> splaySubTree3 = new SplaySubTree<Integer>(3);parentField.set(splaySubTree,splaySubTree3);splaySubTree.remove(1);}//测试SplaySubTree--remove@Test(timeout=4000)public void test0012() throws NoSuchFieldException, SecurityException, IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException, NullPointerException {SplaySubTree<Integer> splaySubTree = new SplaySubTree<Integer>(1);// 获取 SplaySubTree<Integer> 的 Class 对象 Class<?> splaySubTreeClass = splaySubTree.getClass(); // 获取私有属性 count 的 Field 对象 Field rightField = splaySubTreeClass.getDeclaredField("right"); Field leftField = splaySubTreeClass.getDeclaredField("left"); // 设置私有属性 count 的可访问性 rightField.setAccessible(true); leftField.setAccessible(true); SplaySubTree<Integer> splaySubTree2 = new SplaySubTree<Integer>(2);rightField.set(splaySubTree,splaySubTree2);SplaySubTree<Integer> splaySubTree3 = new SplaySubTree<Integer>(3);leftField.set(splaySubTree,splaySubTree3);String expectedStr = " data=1 left=3 right=2 sz=1 cnt=1\n" + " data=3 left= null right null sz=1 cnt=1\n" + " data=2 left= null right null sz=1 cnt=1\n";assertEquals(expectedStr, splaySubTree.toString());}}
被测文件(1/2)SplayTree.java
package net.mooctest;import java.util.Arrays;public class SplayTree <T extends Comparable<T>> {SplaySubTree<T> root;public SplayTree(){root = new SplaySubTree<T>(null);}/*** @param index - of the node to search for.* @return - null if index<=0 or index>=size otherwise SubTree at index. */public T get(long index) {SplaySubTree<T> cT = root.get(index);if(cT==null)return null;cT.splay();root = cT;return cT.getData();}/*** @return - the number of nodes in the tree.*/public long size() { return root.size();}/*** @param node - to search for.* @return - the index of node. All nodes are ordered according to the compareTo(T) method.* */public long indexOf(T node) {long index = root.indexOf(node);get(index);return index;}/*** @param node - is added to the tree.* If node is null tree is unchanged.*/public void add(T node) {root = root.add(node);}/*** @param node - is removed from the tree.* If node is null tree is unchanged.*/public void remove(T node) {root = root.remove(node);}/*** @param node* @return*/public boolean contains(T node) {SplaySubTree<T> temp = root.find(node);if(temp!=null){temp.splay();root = temp;}return temp != null;}@Overridepublic String toString(){return root.toString();}public static void main(String[] args) {SplayTree<Integer> test = new SplayTree<Integer>();int howmanynumbers = 10000;for (int i = 0; i < howmanynumbers; i++) {int val = (int)(Math.random()*100);test.add(val);}System.out.println(test);}
}
被测文件(2/2)SubSplayTree.java
package net.mooctest;public class SplaySubTree<T extends Comparable<T>> {private T data;private SplaySubTree<T> left, right, parent;private long size; // number of nodes in treeprivate int count;/*** @param node* - If node==null then size will be 0 otherwise node will be in the* tree and size will be 1*/public SplaySubTree(T node) {data = node;if (node != null) {size = count = 1;}}public String toString() {String lft = "";String rght = "";String myData = " data=" + data;if (left != null) {myData += " left=" + left.data;lft = left.toString();} else {myData += " left= null";}if (right != null) {myData += " right=" + right.data;rght = right.toString();} else {myData += " right null";}myData += " sz="+size + " cnt="+count;return myData + "\n" + lft + rght;}public T getData() {return data;}/*** @param index* - of the node to search for.* @return - null if index<=0 or index>=size otherwise SubTree at index.*/public SplaySubTree<T> get(long index) {if (index > size || index < 0)return null;long cS = 1;SplaySubTree<T> cT = this;if (cT.left != null)cS += cT.left.size;while (cS != index) {if (cS > index) {cS--;cT = cT.left;if (cT != null && cT.right != null)cS -= cT.right.size;} else {cS++;cT = cT.right;if (cT != null && cT.left != null)cS += cT.left.size;}}return cT;}/*** @return - the number of nodes in the tree.*/public long size() {return size;}/*** @param node* - to search for.* @return - the index of node. All nodes are ordered according to the* compareTo(T) method.* */public long indexOf(T node) {if (node == null)return -1;long cI = 1;SplaySubTree<T> cT = this;if (cT.left != null)cI += cT.left.size;while (!cT.data.equals(node)) {if (cT.data.compareTo(node) > 0) {cI--;cT = cT.left;if (cT != null && cT.right != null)cI -= cT.right.size;} else {cI++;cT = cT.right;if (cT != null && cT.left != null)cI += cT.left.size;}if (cT == null)return -1;}return cI;}/*** @param node* - is added to the tree. If node is null tree is unchanged.* @return - New root of the tree.*/public SplaySubTree<T> add(T node) {if (node == null)return this;if (this.data == null)return new SplaySubTree<T>(node);SplaySubTree<T> current = this;SplaySubTree<T> child = null;if (this.data.compareTo(node) < 0)child = this.right;else if(this.data.compareTo(node)>0)child = this.left;while (child != null && current.data.compareTo(node)!=0) {current = child;if (current.data.compareTo(node) < 0)child = current.right;else if(current.data.compareTo(node)>0)child = current.left;}SplaySubTree<T> newNode = new SplaySubTree<T>(node);if (current.data.compareTo(node) < 0) {current.right = newNode;} else if(current.data.compareTo(node)>0){current.left = newNode;}else {current.size++;current.count++;newNode = current;current = newNode.parent;}newNode.parent = current;if (newNode.splay())return newNode;return this;}/*** @param node* - is removed from the tree. If node is null tree is unchanged.* @return - New root of the tree.*/public SplaySubTree<T> remove(T node) {if (node == null)return this;SplaySubTree<T> x = find(node);if (x == null)return this;if(x.data.equals(node)) {x.count--;x.size--;if(size>0) {x.splay();return x;}}// To delete a node x:// if x has no children remove it.if (x.left == null && x.right == null) {if (x.parent != null) {if (x.parent.left == x) {parent.left = null;} elseparent.right = null;} elsereturn new SplaySubTree(null);}// if x has one child remove x, and put the child in place of xif (x.left == null) {if (x.parent != null) {if (x.parent.left == x) {parent.left = x.right;x.right.parent = parent;x = x.right;} else {parent.right = x.right;x.right.parent = parent;x = x.right;}} else {x.right.parent = null;return x.right;}} else if (x.right == null) {if (x.parent != null) {if (x.parent.left == x) {parent.left = x.left;x.left.parent = parent;x = x.left;} else {parent.right = x.left;x.left.parent = parent;x = x.left;}} else {x.left.parent = null;return x.left;}} else {// if x has two children, swap its value with that of// the rightmost node of its left sub treeSplaySubTree<T> rmc = x.left;while (rmc.right != null)rmc = rmc.right;x.data = rmc.data;// Then remove that node instead.rmc.left.parent = rmc.parent;if (rmc.parent == x) {x.left = rmc.left;} else {rmc.parent.right = rmc.left;}x = rmc;}// After deletion, splay the parent of the removed node to the top of// the tree.x.splay();return x;}/*** @param other* @return*/public SplaySubTree<T> join(SplaySubTree<T> other) {return null;}/*** @param node* @return*/public SplaySubTree<T> split(T node) {return null;}/*** @param node* @return*/public SplaySubTree<T> find(T node) {SplaySubTree<T> current = this;if (this.data == null)return null;while (current != null) {if (node.equals(current.data))return current;if (node.compareTo(current.data) < 0)current = current.left;elsecurrent = current.right;}return current;}/*** Assuming this node is an interior or leaf node of a larger tree this method* moves this node up to the root balancing the tree in the process*/public boolean splay() {while (this.parent != null) {SplaySubTree<T> p = this.parent;SplaySubTree<T> g = p.parent;if (g == null && this == p.left) {zig();} else if (g == null && this == p.right) {zag();} else if (p.left == this && g.left == p) {zigzig();} else if (p.right == this && g.right == p) {zagzag();} else if (p.right == this && g.left == p) {zigzag();} else {zagzig();}}return true;}/*** This is a helper method used in the splay() operation*/private void zig() {SplaySubTree<T> b = this.right;SplaySubTree<T> p = this.parent;this.right = p;p.parent = this;p.left = b;if (b != null)b.parent = p;this.parent = null;p.size = p.count;if (p.right != null)p.size += p.right.size;if (b != null)p.size += b.size;this.size = p.size + this.count;if (this.left != null)this.size += this.left.size;}/*** This is a helper method used in the splay() operation*/private void zag() {SplaySubTree<T> b = this.left;SplaySubTree<T> p = this.parent;this.left = p;p.parent = this;p.right = b;if (b != null)b.parent = p;this.parent = null;p.size = p.count;if (b != null)p.size += b.size;if (p.left != null)p.size += p.left.size;this.size = p.size + this.count;if (this.right != null)this.size += this.right.size;}/*** This is a helper method used by zigzig, zagzag, zigzag, zagzig This "fixes"* the great grandparent*/private void fixGG(SplaySubTree<T> g) {SplaySubTree<T> gg = g.parent;if (gg != null) {if (g == gg.left)gg.left = this;if (g == gg.right)gg.right = this;}this.parent = gg;// might need to update size}/*** This is a helper method used in the splay() operation*/private void zigzig() {SplaySubTree<T> g = parent.parent;SplaySubTree<T> b = this.right;SplaySubTree<T> p = this.parent;SplaySubTree<T> c = p.right;fixGG(g);if (b != null)b.parent = p;p.left = b;if (c != null)c.parent = g;g.left = c;g.parent = p;p.right = g;p.parent = this;this.right = p;g.size = g.count;if (c != null)g.size += c.size;if (g.right != null)g.size += g.right.size;p.size = p.count;if (g != null)p.size += g.size;if (b != null)p.size += b.size;this.size = p.size + this.count;if (this.left != null)this.size += this.left.size;}/*** This is a helper method used in the splay() operation*/private void zagzag() {SplaySubTree<T> g = parent.parent;SplaySubTree<T> b = this.left;SplaySubTree<T> p = this.parent;SplaySubTree<T> c = p.left;fixGG(g);if (b != null)b.parent = p;// above line throws java.lang.NullPointerExceptionp.right = b;if (c != null)c.parent = g;g.right = c;g.parent = p;p.left = g;p.parent = this;this.left = p;g.size = g.count;if (g.left != null)g.size += g.left.size;if (c != null)g.size += c.size;p.size = g.size + p.count;if (b != null)p.size += b.size;this.size = p.size + this.count;if (this.right != null)this.size += this.right.size;}/*** This is a helper method used in the splay() operation*/private void zigzag() {SplaySubTree<T> g = parent.parent;SplaySubTree<T> b = this.left;SplaySubTree<T> p = this.parent;SplaySubTree<T> c = this.right;fixGG(g);if (b != null)b.parent = p;p.right = b;if (c != null)c.parent = g;g.left = c;p.parent = this;this.left = p;g.parent = this;this.right = g;g.size = g.count;if (g.right != null)g.size += g.right.size;if (c != null)g.size += c.size;p.size = p.count;if (p.left != null)p.size += p.left.size;if (b != null)p.size += b.size;this.size = g.size + p.size + this.count;}/*** This is a helper method used in the splay() operation*/private void zagzig() {SplaySubTree<T> g = parent.parent;SplaySubTree<T> b = this.right;SplaySubTree<T> p = this.parent;SplaySubTree<T> c = this.left;fixGG(g);if (b != null)b.parent = p;p.left = b;if (c != null)c.parent = g;g.right = c;p.parent = this;this.right = p;g.parent = this;this.left = g;g.size = g.count;if (g.left != null)g.size += g.left.size;if (c != null)g.size += c.size;p.size = p.count;if (p.right != null)p.size += p.right.size;if (b != null)p.size += b.size;this.size = g.size + p.size + this.count;}}
这篇关于SplayTree高分测试用例的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!







