本文主要是介绍Arduino学习(B站up张居正),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
Arduino全套零基础入门视频教程(适合0基础,含arduino项目保姆级教程)_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
Arduino全套零基础入门视频进阶教程(适合0基础,含arduino项目保姆级教程)_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
花式点灯1(Switch选择语句的学习)
#include <Arduino.h>// put function declarations here:void setup() {// put your setup code here, to run once:Serial.begin(115200);int value = 1;int a = 666;int b = 888;switch (value){case 1:Serial.println(a);break;case 2:Serial.println(b);break;default:Serial.println("无满足条件");break;}}void loop() {// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:}// put function definitions here:
花式点灯2(循环语句的学习)
for循环
#include <Arduino.h>// put function declarations here:void setup() {// put your setup code here, to run once:Serial.begin(115200);// for循环的应用int i ;for ( i = 0; i <= 10; i++){Serial.println(i);}}void loop() {// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:}// put function definitions here:
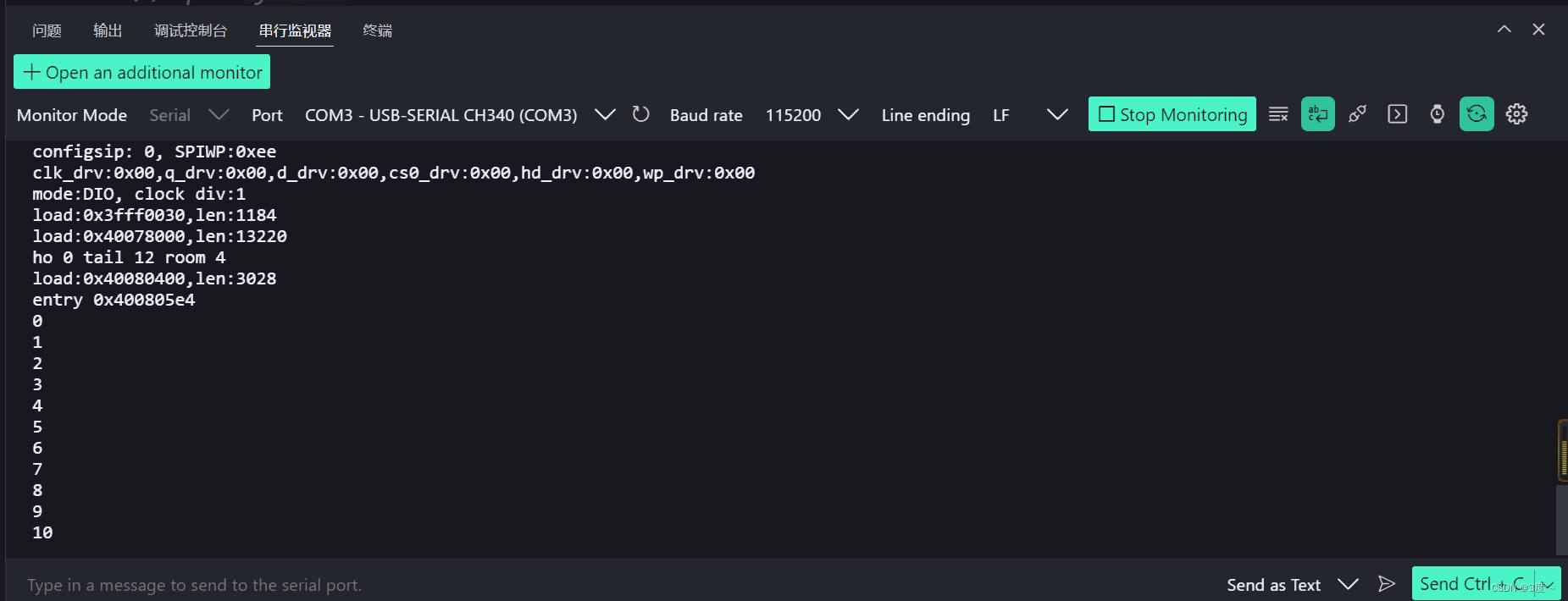
while循环
#include <Arduino.h>// put function declarations here:void setup() {// put your setup code here, to run once:Serial.begin(115200);int a = 0;while (a <= 10){// 循环体Serial.println(a);// 循环变量变化式a++;}}void loop() {// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:}// put function definitions here:
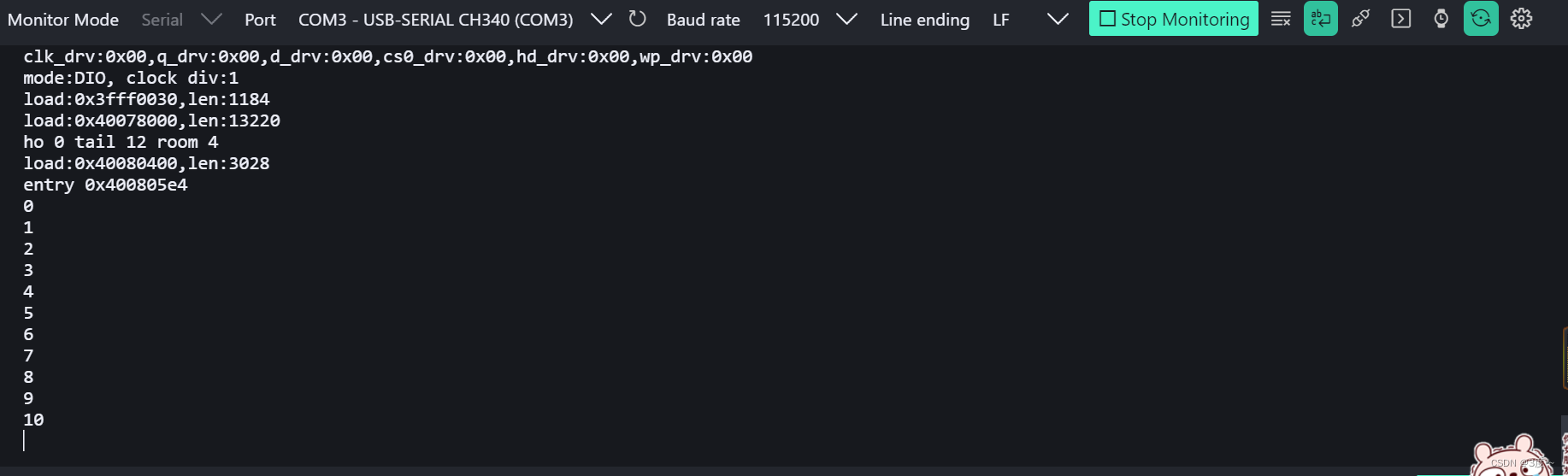
do while 使用
#include <Arduino.h>// put function declarations here:void setup() {// put your setup code here, to run once:Serial.begin(115200);int a = 0;do{// 循环体Serial.println(a);// 循环变量表达式a++;}while (a == 10);}void loop() {// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:}// put function definitions here:
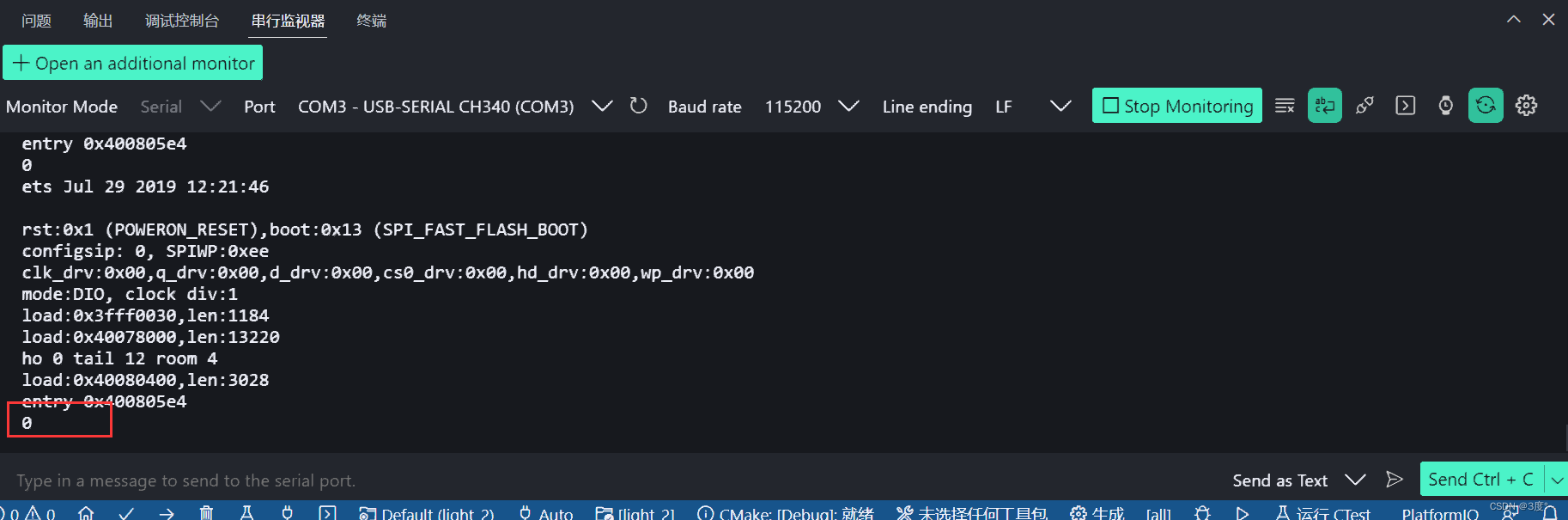
循环控制语句
#include <Arduino.h>// put function declarations here:void setup() {// put your setup code here, to run once:Serial.begin(115200);for (int a = 0; a<=10; a++){Serial.println(a);if (a == 5){break;}}}void loop() {// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:}// put function definitions here:
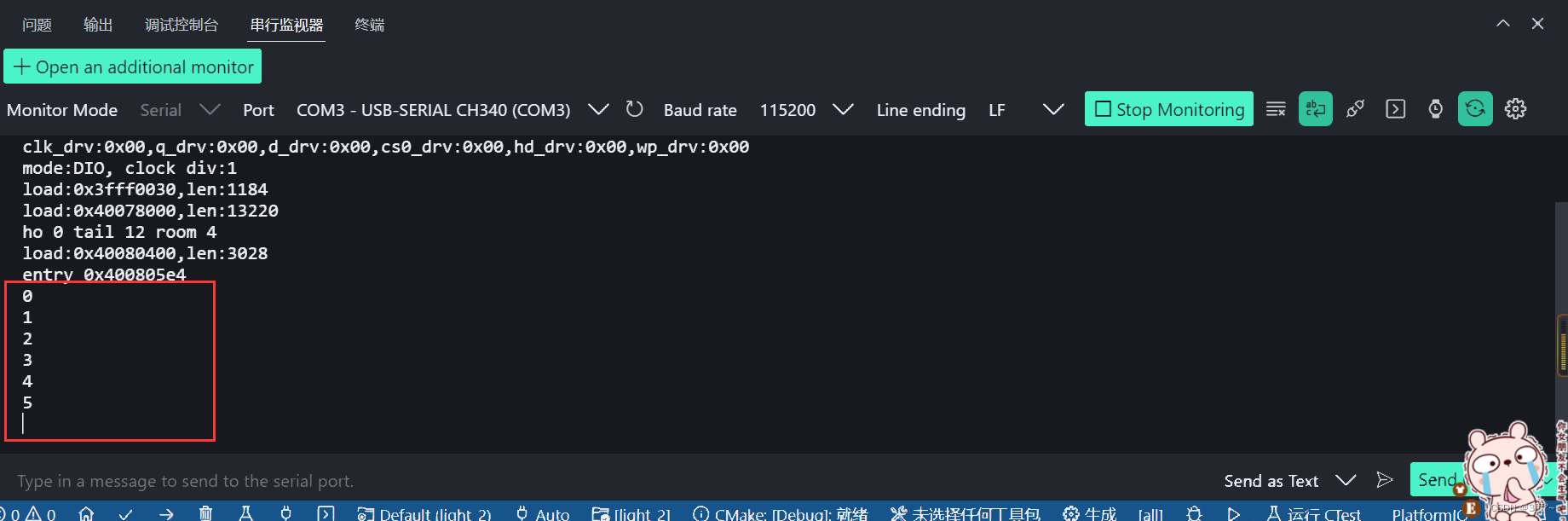
无限循环
#include <Arduino.h>// put function declarations here:void setup() {// put your setup code here, to run once:Serial.begin(115200);for (; ; ){Serial.println("123");}}void loop() {// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:}// put function definitions here:

花式点灯3 (闪灯)
for循环闪灯
#include <Arduino.h>// put function declarations here:void setup() {// put your setup code here, to run once:// 引脚模式设置(OUTPUT/INPUT)pinMode(2, OUTPUT);}void loop() {// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:for (int i = 0; i <= 10; i++){// 数字输出:高1,低0digitalWrite(2, HIGH); // 小鱼的开发板,HIGH电平灯熄灭delay(1000);digitalWrite(2, LOW);delay(1000);}delay(100000); // 循环闪烁完成以后,灯处于LOW电平}// put function definitions here:
while循环闪灯
#include <Arduino.h>// put function declarations here:void setup() {// put your setup code here, to run once:// 引脚模式设置(OUTPUT/INPUT)pinMode(2, OUTPUT);}void loop() {// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:int a = 0;while (a <= 10) {// 数字输出:高1,低0digitalWrite(2, HIGH); // 小鱼的开发板,HIGH电平灯熄灭delay(100);digitalWrite(2, LOW);delay(100);a++;}delay(100000); // 循环闪烁完成以后,灯处于LOW电平}// put function definitions here:
do while循环闪灯
#include <Arduino.h>// put function declarations here:void setup() {// put your setup code here, to run once:// 引脚模式设置(OUTPUT/INPUT)pinMode(2, OUTPUT);}void loop() {// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:int a = 0;do{digitalWrite(2, HIGH); // 小鱼的开发板,HIGH电平灯熄灭delay(100);digitalWrite(2, LOW);delay(100);a++;} while (a <= 10);delay(100000); // 循环闪烁完成以后,灯处于LOW电平}// put function definitions here:
花式点灯4
模拟输入:analogRead(pin)
模拟输出:analogWrite(pin, value)


花式点灯5(流水灯)
#include <Arduino.h>// put function declarations here:
int delayTime = 1000;void setup()
{// put your setup code here, to run once:Serial.begin(115200);for (int pin = 2; pin <= 6; pin++){pinMode(pin, OUTPUT);}
}void loop()
{// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:for (int pin = 2; pin <= 6; pin++){digitalWrite(pin, HIGH);delay(delayTime);digitalWrite(pin, LOW);delay(delayTime);}
}// put function definitions here:
花式点灯6(呼吸灯)
#include <Arduino.h>// put function declarations here:void setup()
{// put your setup code here, to run once:pinMode(3, OUTPUT);
}void loop()
{// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:while (1){for (int value = 0; value <= 255; value++){analogWrite(3, value);delay(5);}for (int value = 255; value >= 0; value--){analogWrite(3, value);delay(5);}};
}// put function definitions here:

进阶控制灯光1


进阶控制灯光 2
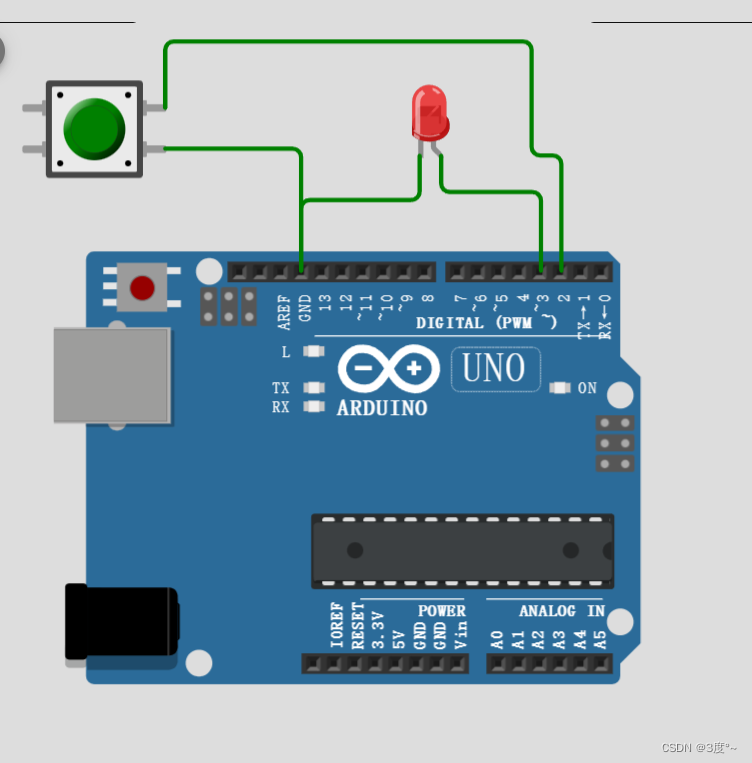
点击亮灯,松手熄灯
#include <Arduino.h>// put function declarations here:
// 点击亮灯,松手熄灯
// 一个引脚用来点亮led
// 另一个引脚检测按键int led = 16;
int botton = 15;void setup()
{// put your setup code here, to run once:pinMode(led, OUTPUT);pinMode(botton, INPUT_PULLUP); //使用输入上拉模式,不然灯会一直闪烁
}void loop()
{// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:while (1){if (digitalRead(botton) == LOW) // 接地,相当于低电平{digitalWrite(led, HIGH);}else{digitalWrite(led, LOW);}}
}// put function definitions here:
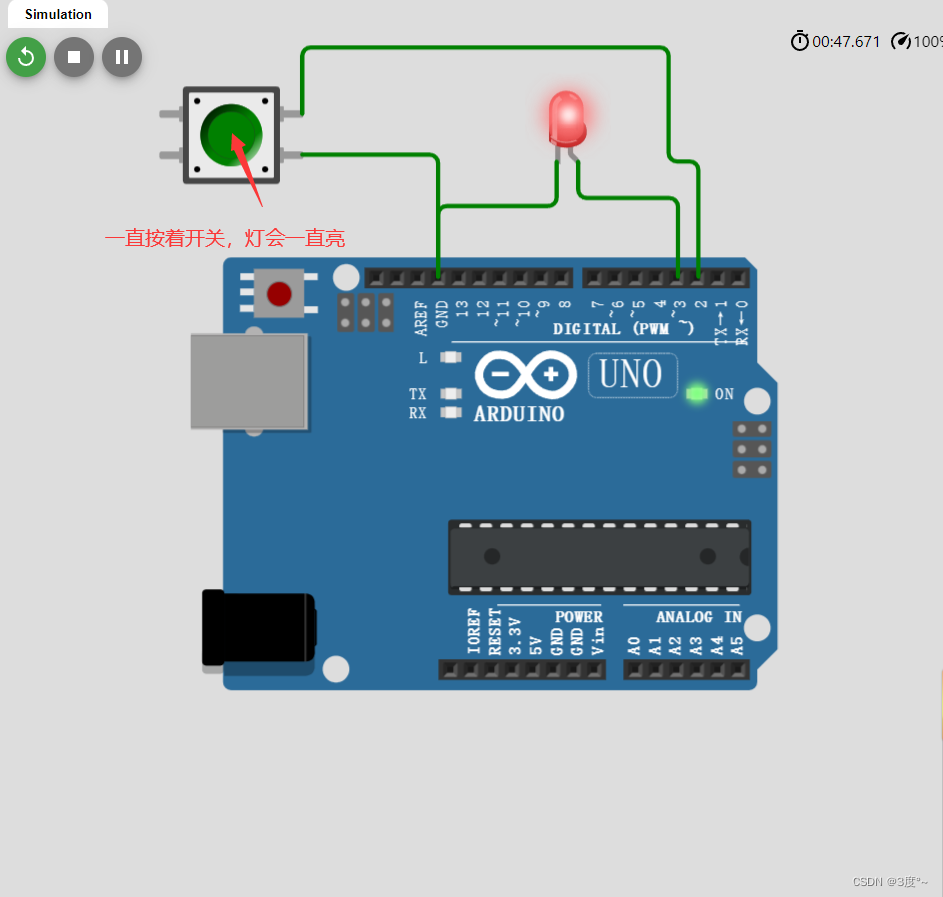
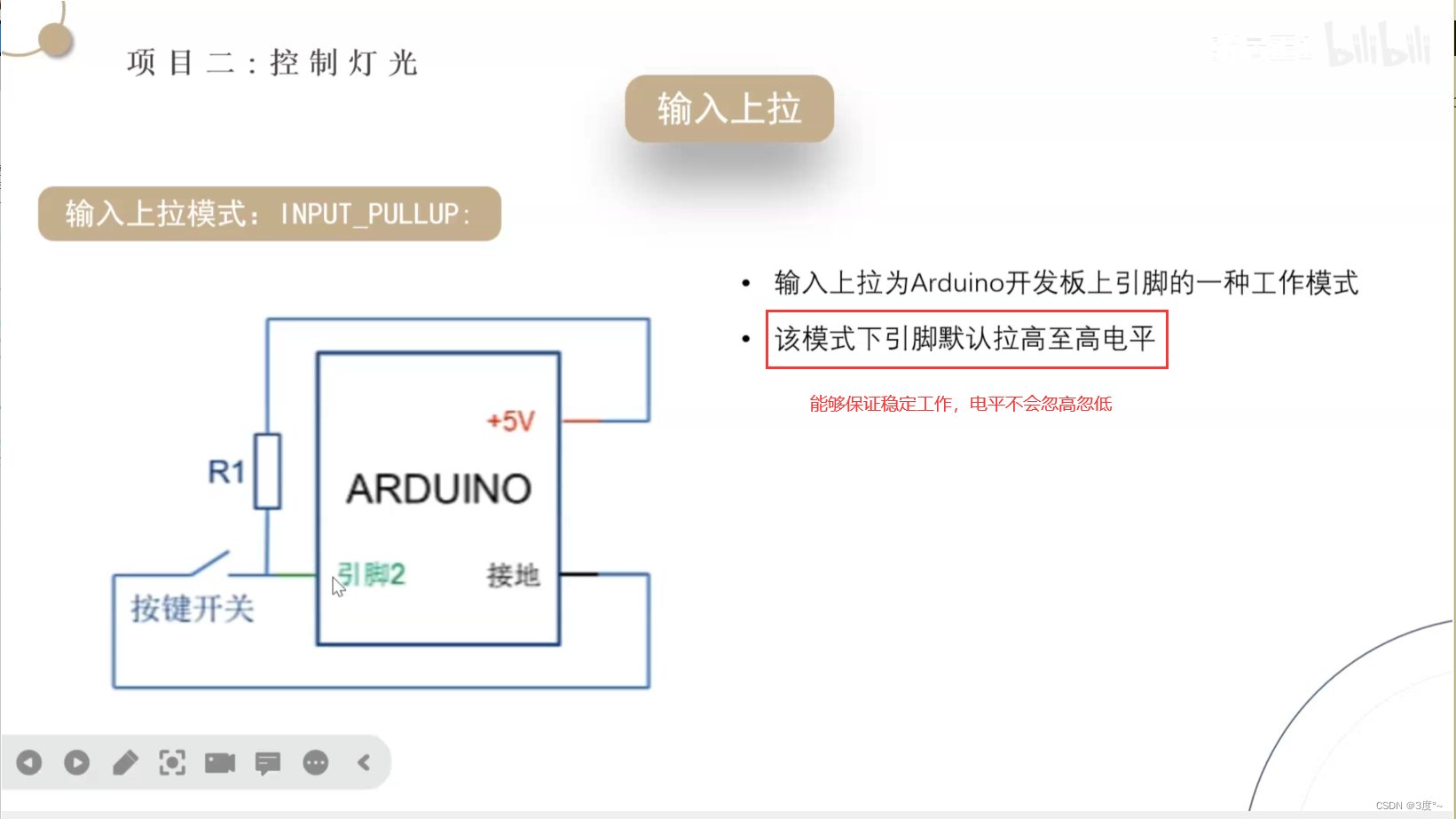
输入状态,会导致电平忽高忽低
进阶控制灯光3
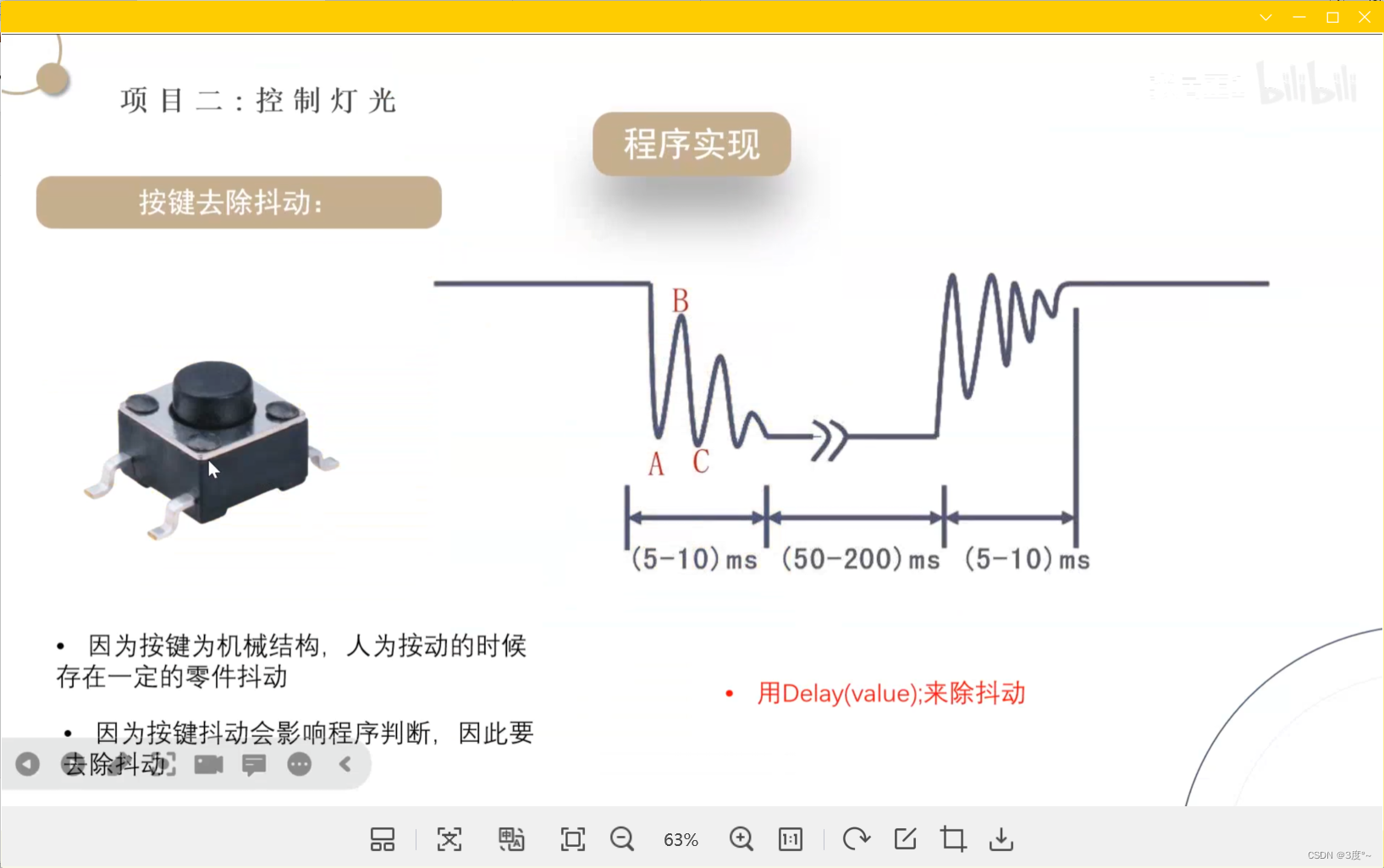
点击持续亮灯,再点击熄灯

#include <Arduino.h>// put function declarations here:
// 点击持续亮灯,再点击熄灯
// 一个引脚用来点亮led
// 另一个引脚检测按键int led = 16;
int botton = 15;void setup()
{// put your setup code here, to run once:pinMode(led, OUTPUT);pinMode(botton, INPUT_PULLUP); // 使用输入上拉模式,不然灯会一直闪烁
}void loop()
{// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:while (1){if (digitalRead(botton) == LOW) // 判断是否被按下了,接地,相当于低电平{delay(100); // 去抖动,防止误触if (digitalRead(botton) == LOW){digitalWrite(led, !digitalRead(led)); // !HIGH = LOW}}}
}// put function definitions here:
进阶控制灯光4
点击变换三挡亮度

#include <Arduino.h>// put function declarations here:
// 点击变换三挡亮度
// 一个引脚用来点亮led
// 另一个引脚检测按键int led = 16; // 要求能用模拟量输出
int botton = 15;
int value = 0;void setup()
{// put your setup code here, to run once:pinMode(led, OUTPUT);pinMode(botton, INPUT_PULLUP); // 使用输入上拉模式,不然灯会一直闪烁
}void loop()
{// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:while (1){if (digitalRead(botton) == LOW) // 判断是否被按下了,接地,相当于低电平{delay(100); // 去抖动,防止误触if (digitalRead(botton) == LOW){analogWrite(led, value); // 零档,熄灭档位(255/3 = 80)value = value + 80; // 档位变高}}if (value > 255){value = 0;}}
}// put function definitions here:
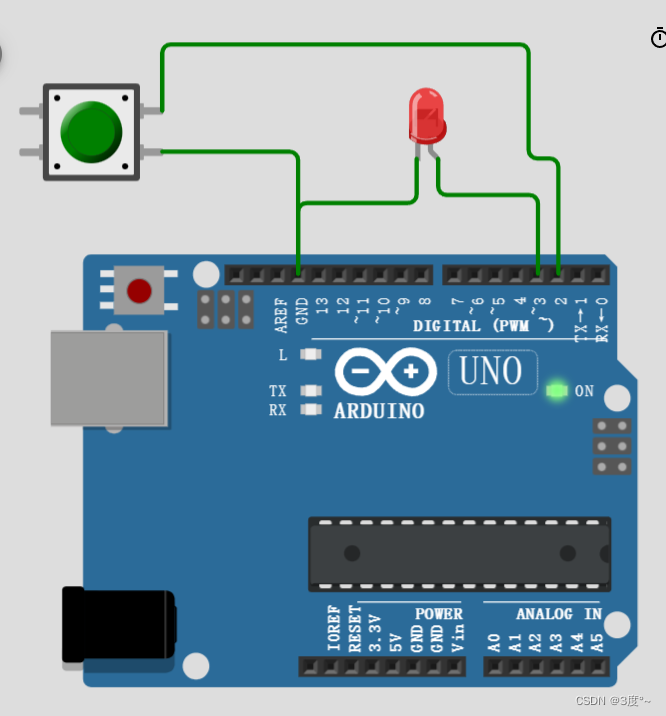
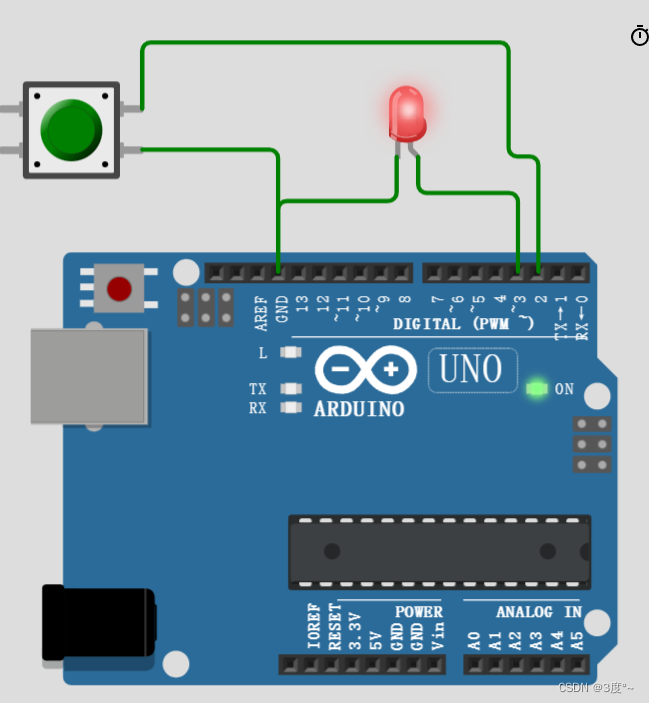
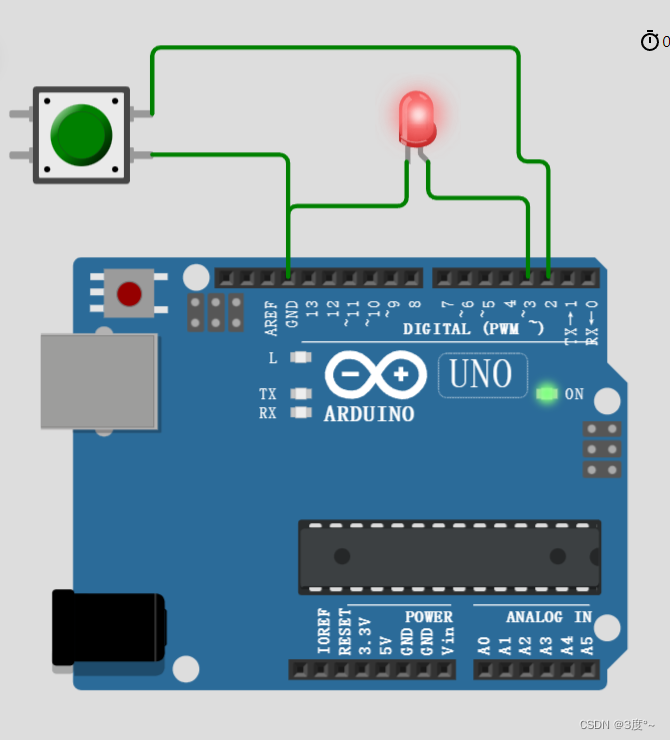
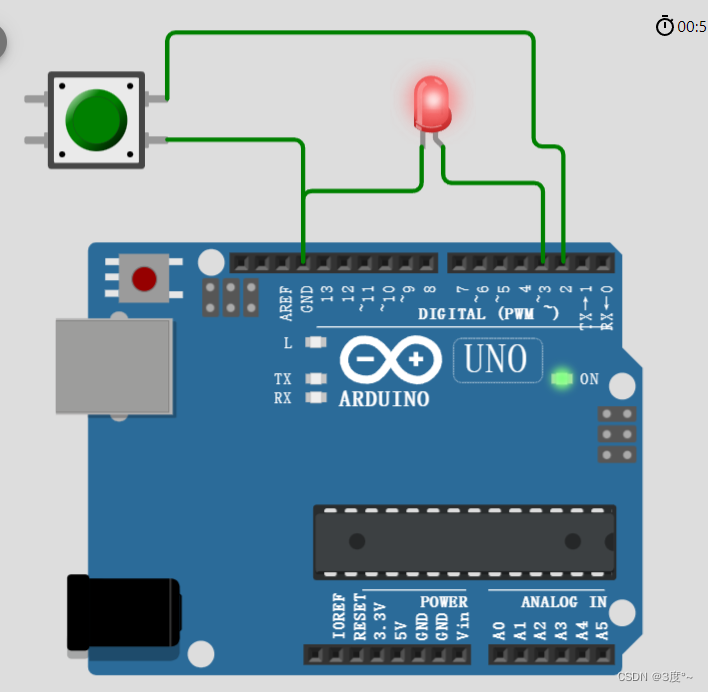
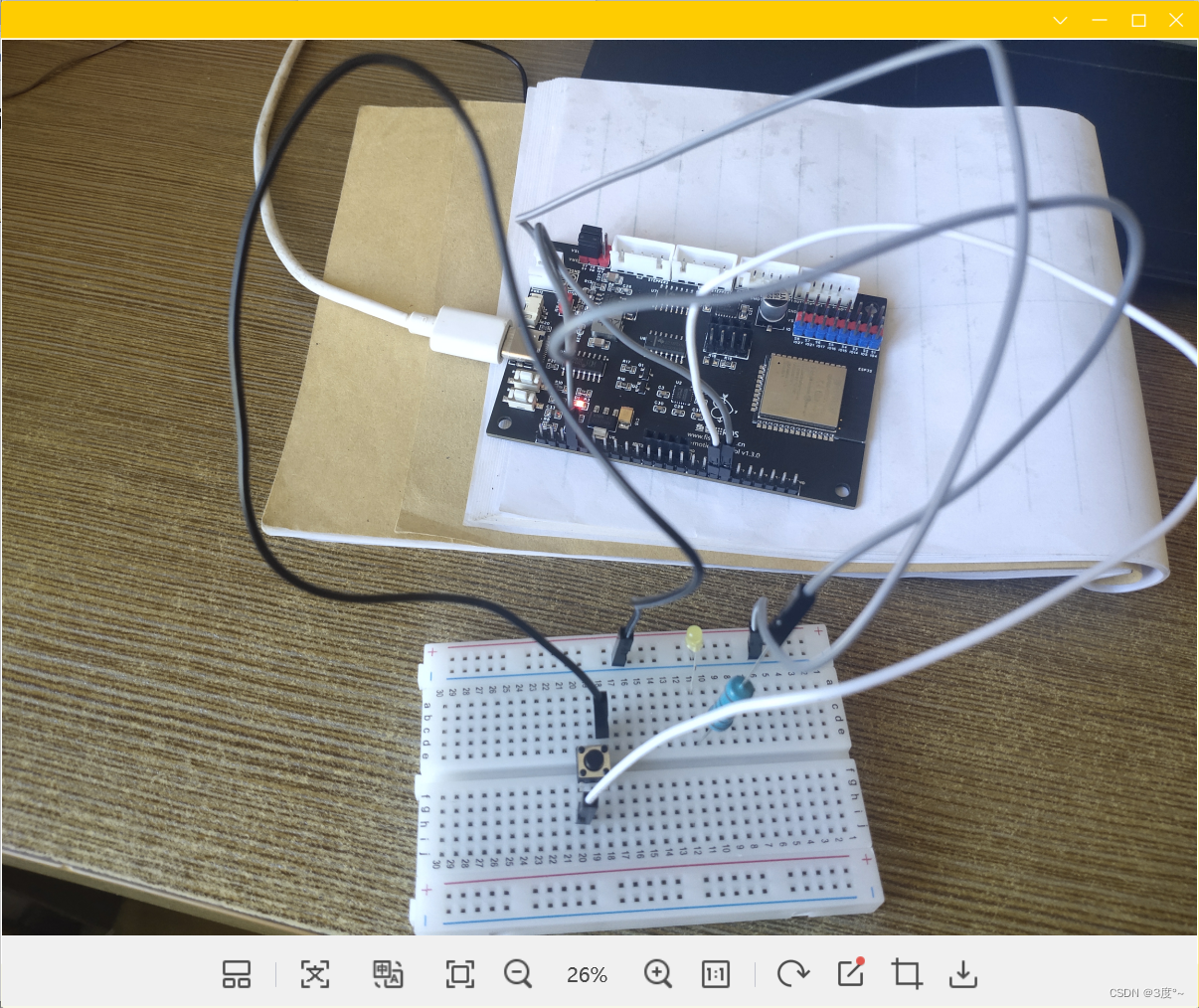
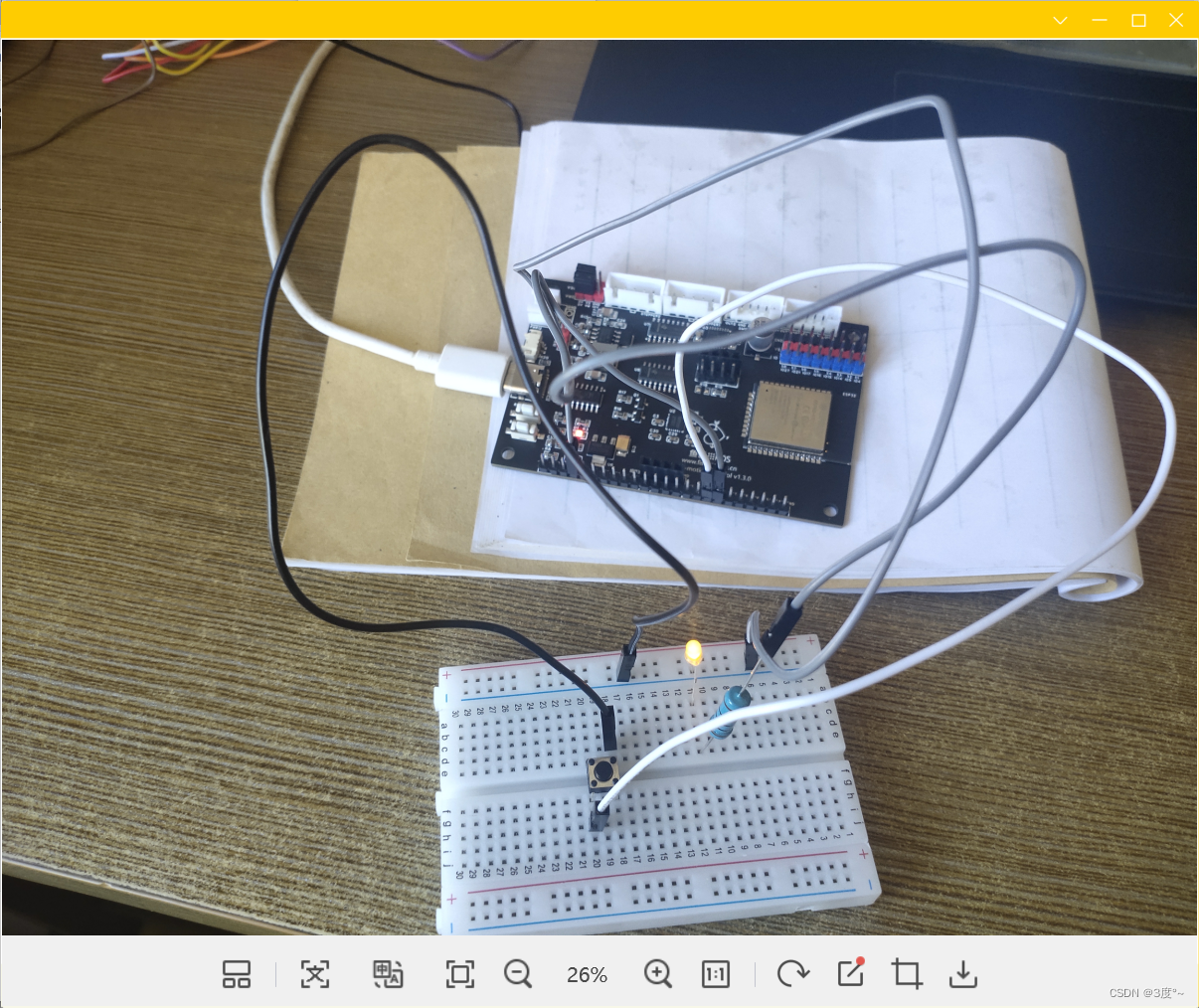
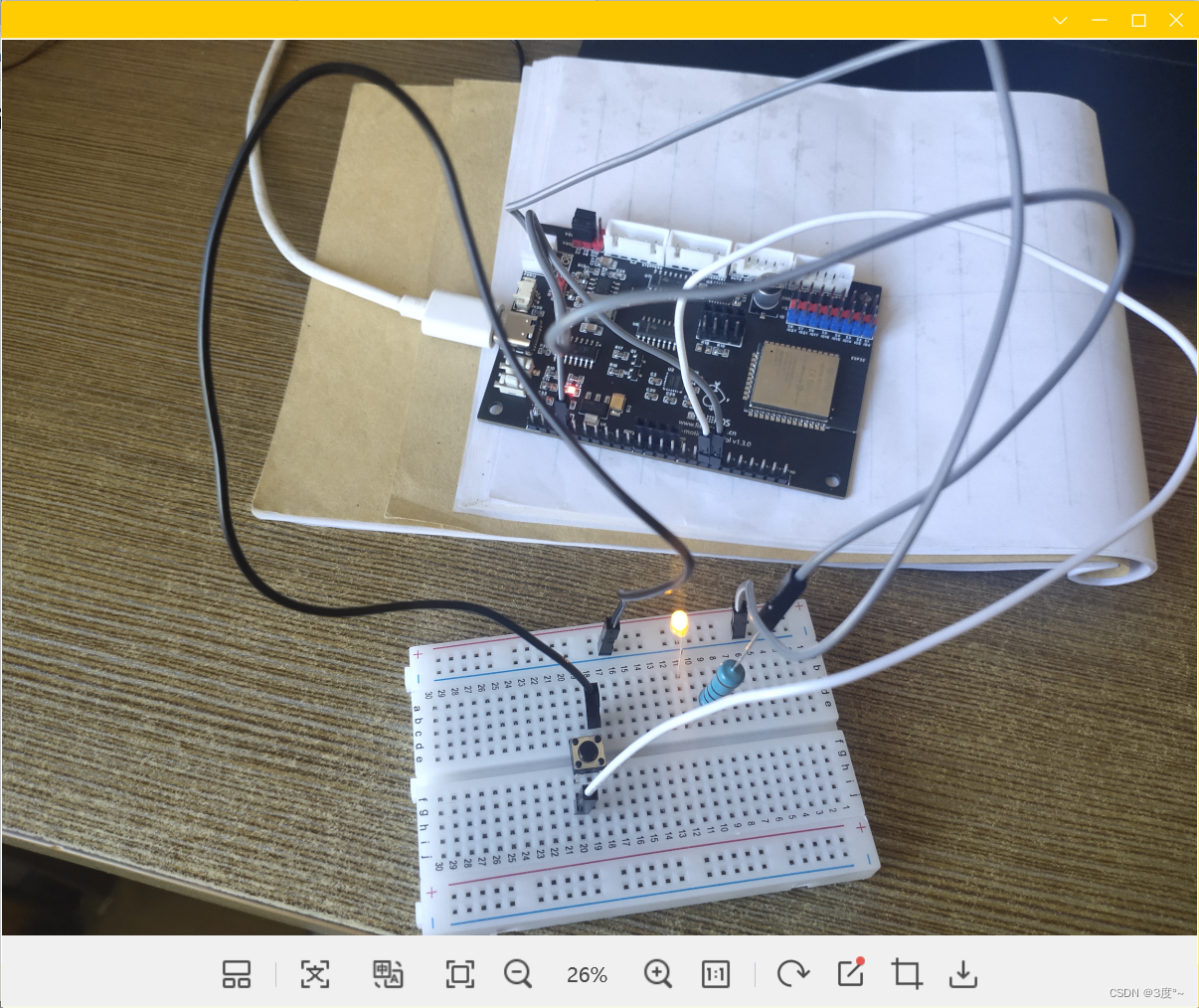
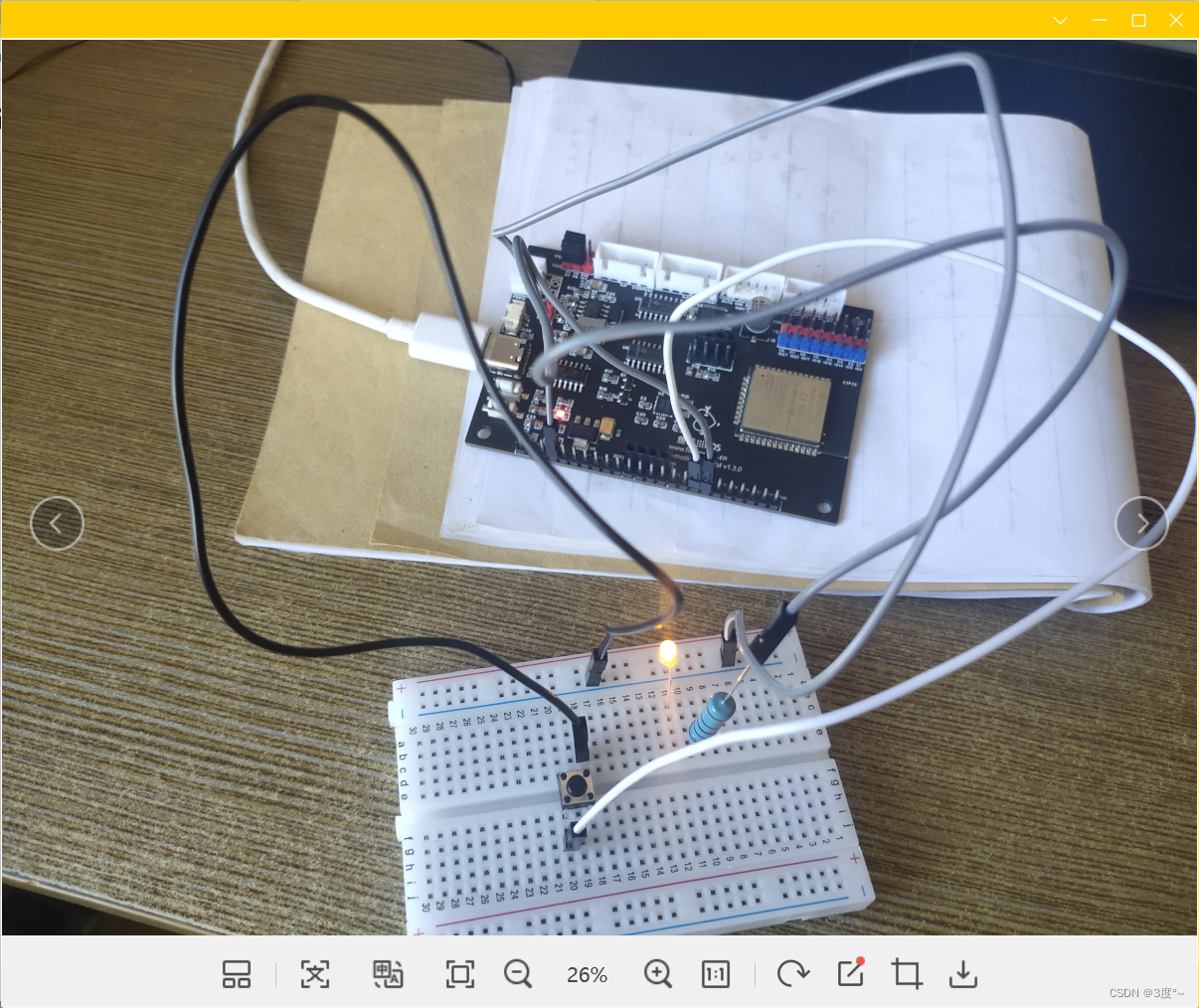
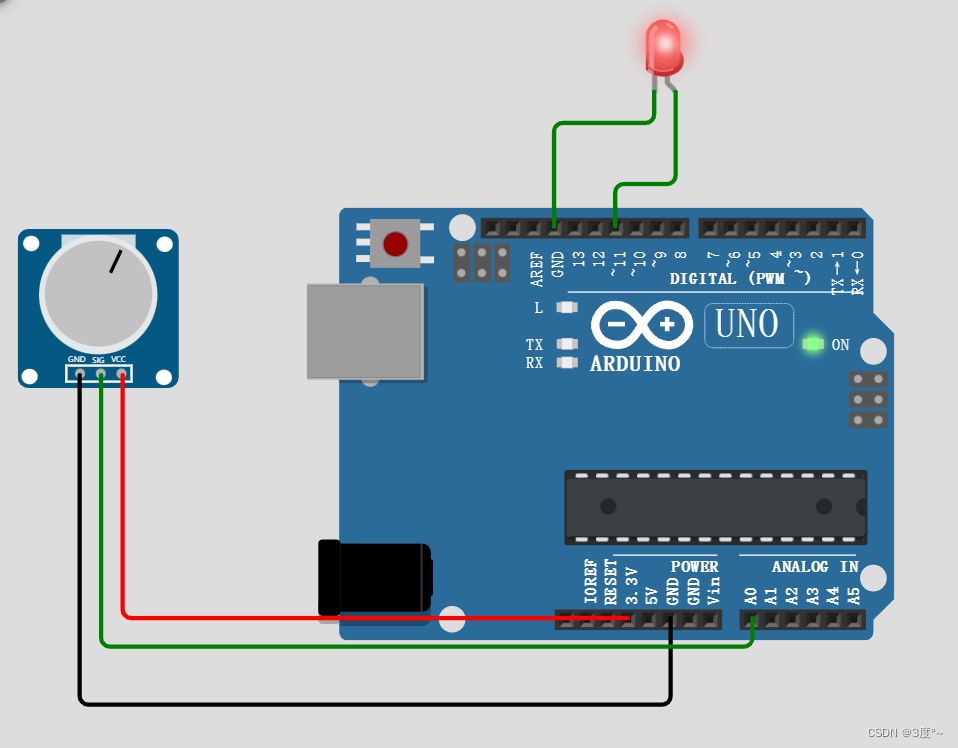
进阶控制灯光6(电位器)
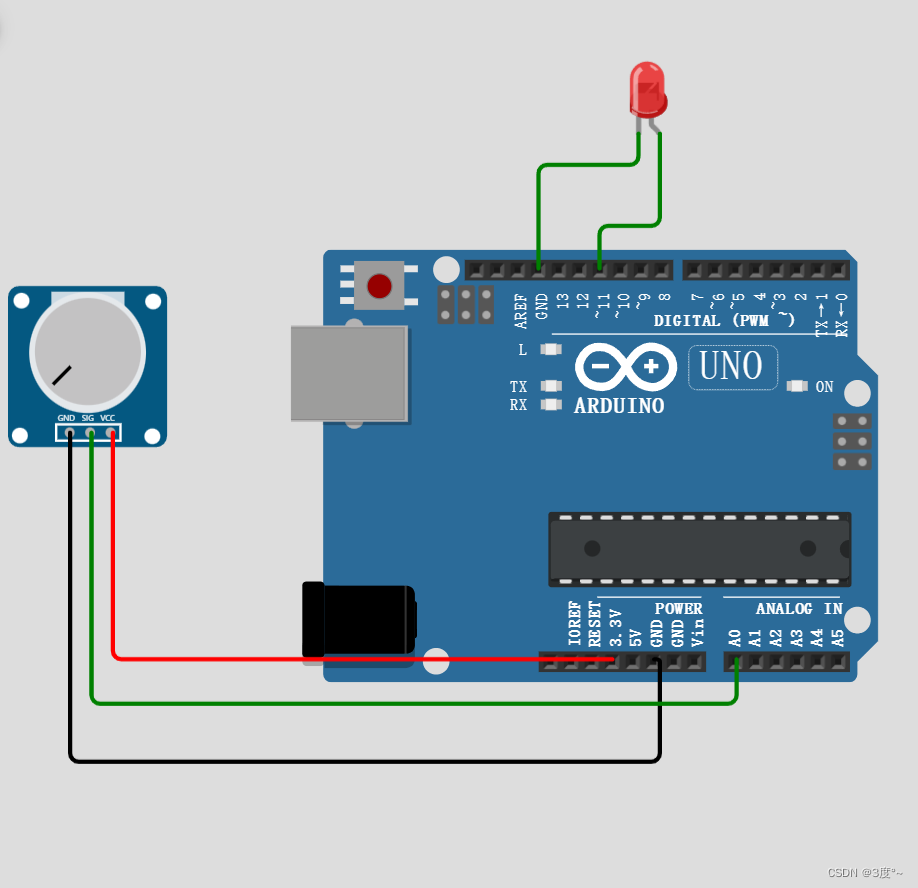

#include <Arduino.h>// put function declarations here:int led = 11; // 要求能用模拟量输出
int key = A0;
int value;
int ledValue; void setup()
{// put your setup code here, to run once:pinMode(led, OUTPUT);pinMode(key, INPUT);
}void loop()
{// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:while (1){value = analogRead(key); // 返回0-1023ledValue = map(value, 0, 1023, 0, 255);analogWrite(led, ledValue); // 返回0-255}
}// put function definitions here:
串口通讯1
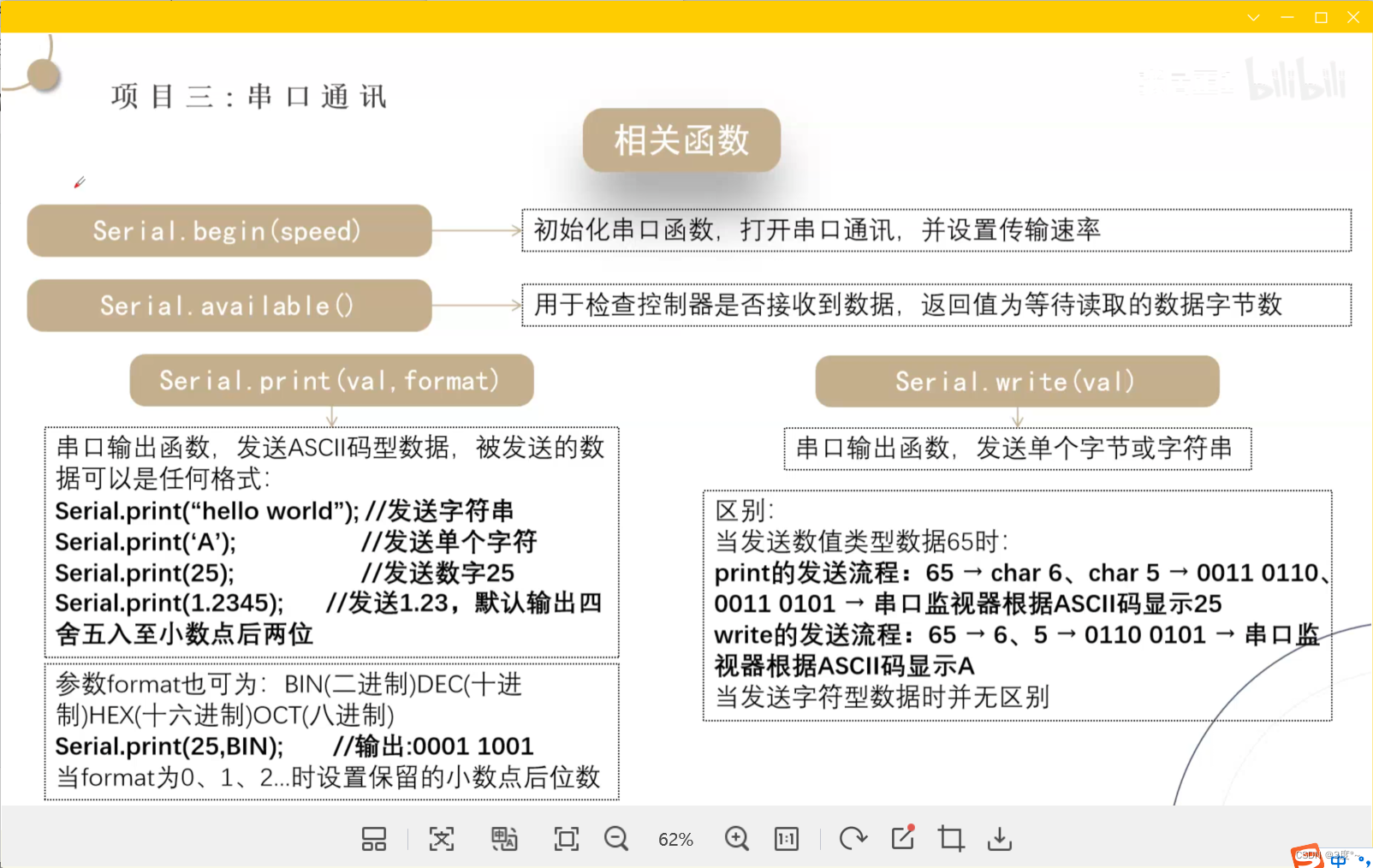
串口通讯2
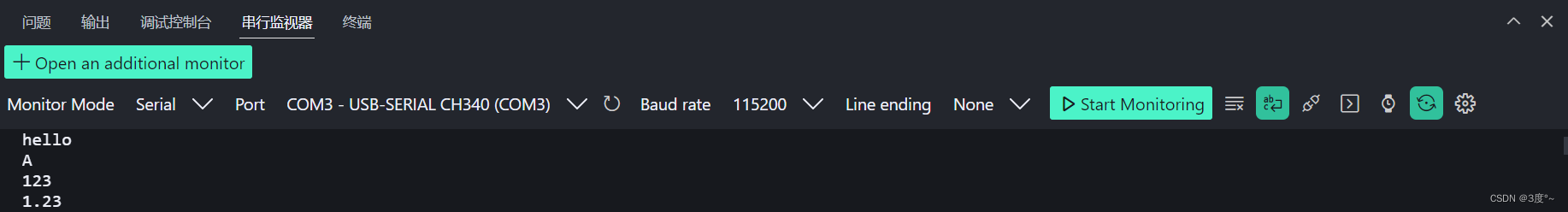
#include <Arduino.h>// put function declarations here:void setup() {// put your setup code here, to run once:Serial.begin(115200);Serial.println("hello");Serial.println("A");Serial.println(123);Serial.println(1.23456789);
}void loop() {// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:}// put function definitions here:
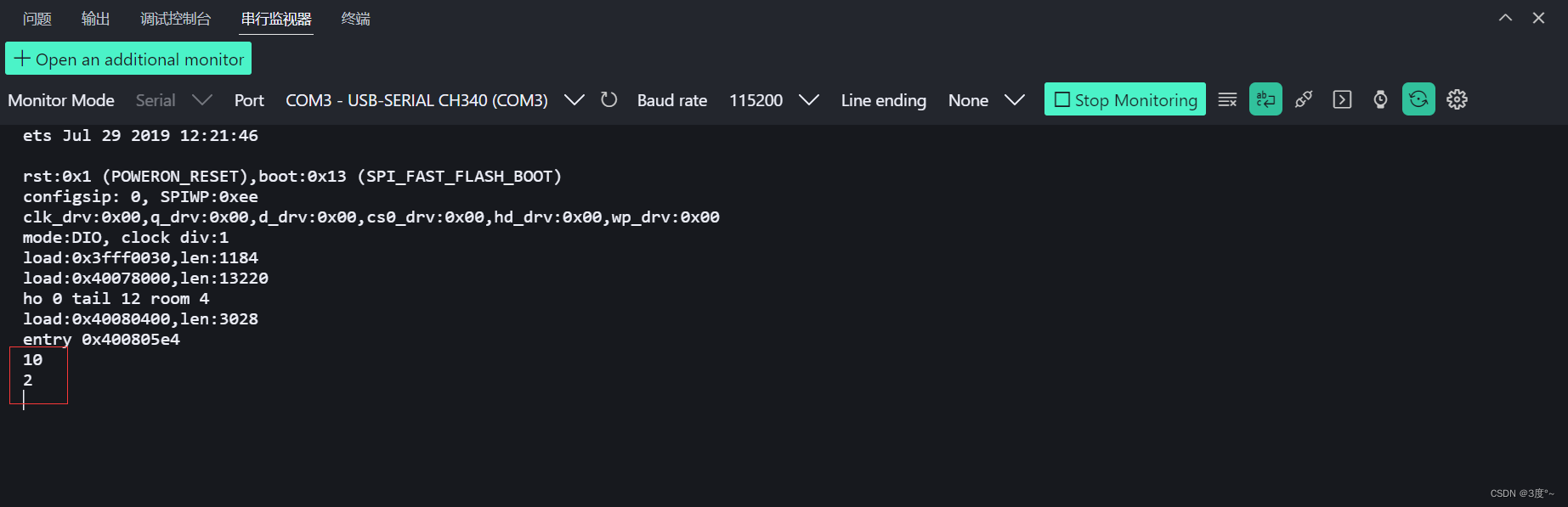
#include <Arduino.h>// put function declarations here:void setup() {// put your setup code here, to run once:Serial.begin(115200);Serial.println(2, BIN); //二进制Serial.println(2, DEC); //十进制}void loop() {// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:}// put function definitions here:
串行通讯3
ASCII码一览表,ASCII码对照表 (biancheng.net)

串行通讯4
#include <Arduino.h>// put function declarations here:void setup() {// put your setup code here, to run once:Serial.begin(115200);// Serial.println(2, BIN); //二进制// Serial.println(2, DEC); //十进制// Serial.write("A\n");// Serial.write(65 );// Serial.write(0x41);}void loop() {// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:if (Serial.available()) // >0 可以不写{Serial.println(Serial.read()); // Serial.read()返回ASCII码Serial.write(Serial.read()); // 要用Serial.write解析}}// put function definitions here:
#include <Arduino.h>// put function declarations here:void setup()
{// put your setup code here, to run once:Serial.begin(115200);// Serial.println(2, BIN); //二进制// Serial.println(2, DEC); //十进制// Serial.write("A\n");// Serial.write(65 );// Serial.write(0x41);
}void loop()
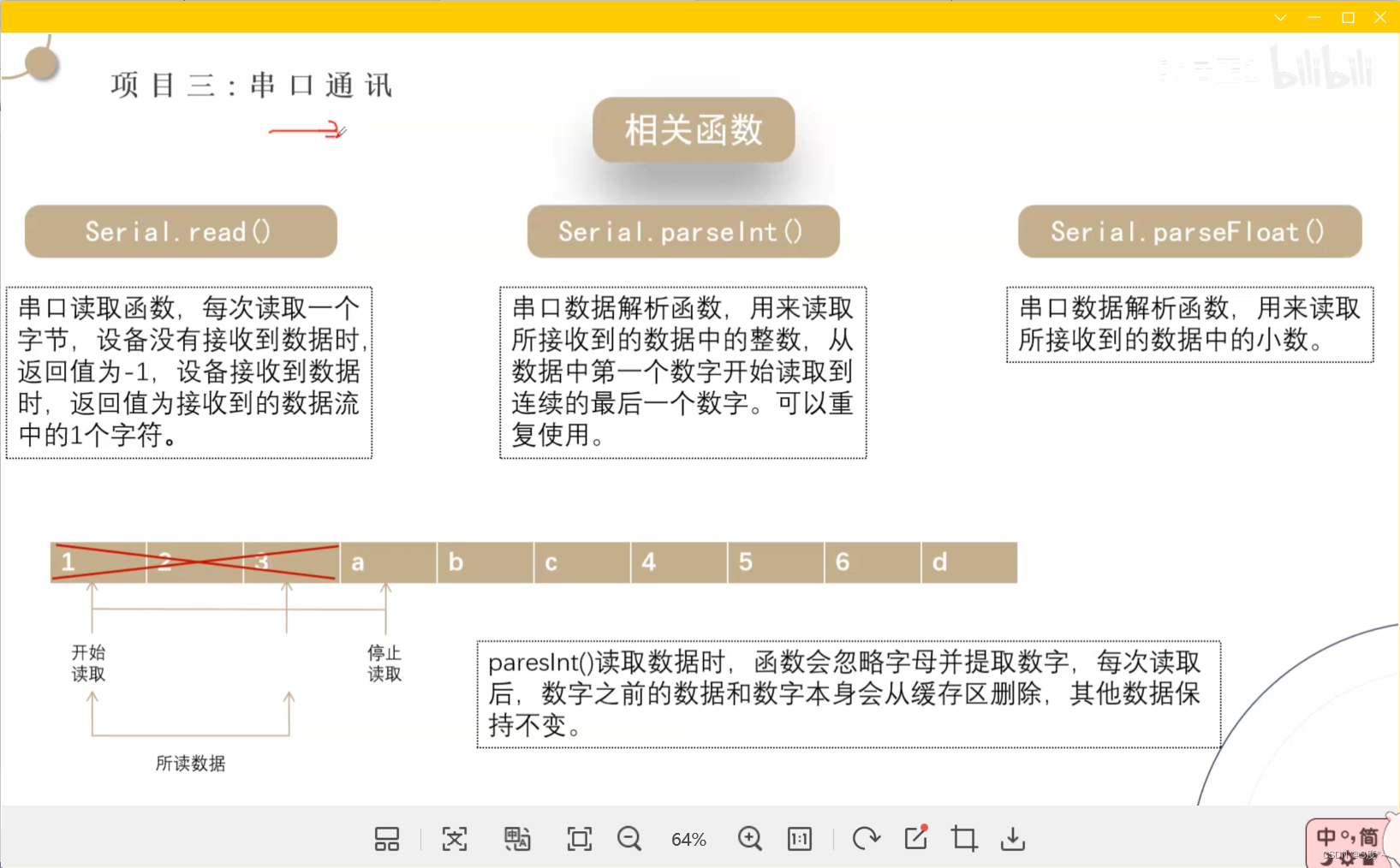
{// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:// if (Serial.available()) // >0 可以不写// {// Serial.println(Serial.read()); // Serial.read()返回ASCII码// Serial.write(Serial.read()); // 要用Serial.write解析// }if (Serial.available()){Serial.println(Serial.parseInt());Serial.println(Serial.parseFloat());}}// put function definitions here:

串行通讯5
1、建立开发板与电脑的串口通讯连接,并向电脑输出自己的姓名、年龄、身高
#include <Arduino.h>// put function declarations here:
// 1、建立开发板与电脑的串口通讯连接,并向电脑输出自己的姓名、年龄、身高
// 2、实现通过串口监视器给开发板发信息,开发板再把接收到的数据发回给电脑
// 3、实现加法计算器,如:电脑发送:“1+2”,开发版回答:”1+2=3“
// 4、实现电脑与开发板进行三句以上简单的对话。如:电脑发送:“a”,开发版回答:“Arduino”void setup()
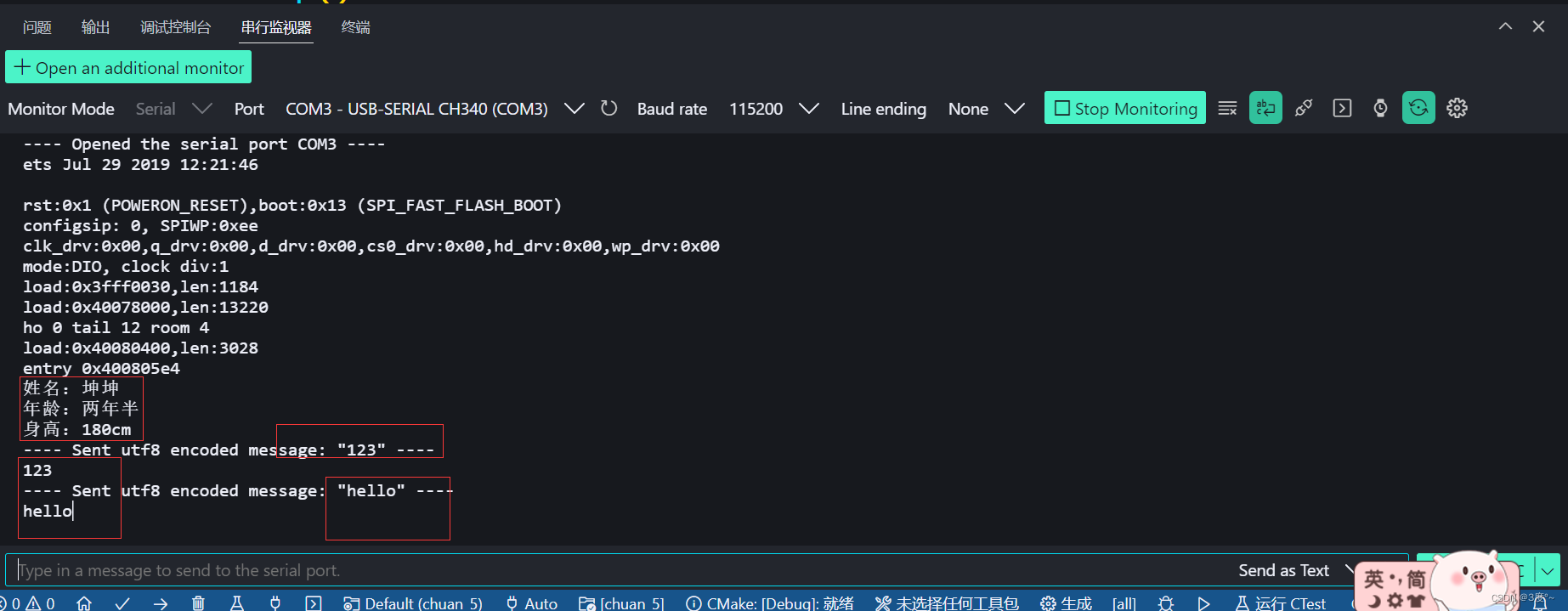
{// put your setup code here, to run once:// 题目一Serial.begin(115200);Serial.println("姓名:坤坤");Serial.println("年龄:两年半");Serial.println("身高:180cm");
}void loop()
{// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:// 题目二if (Serial.available()){Serial.write(Serial.read());}}// put function definitions here:
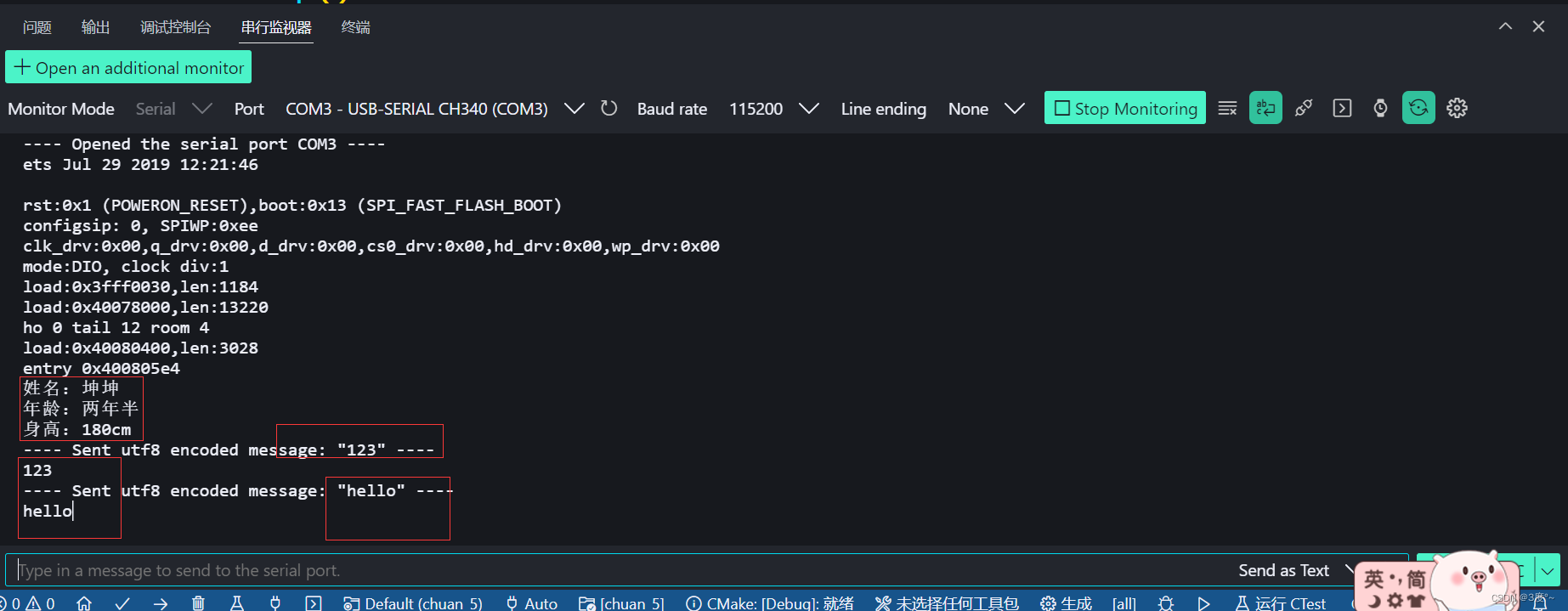
2、实现通过串口监视器给开发板发信息,开发板再把接收到的数据发回给电脑
#include <Arduino.h>// put function declarations here:
// 1、建立开发板与电脑的串口通讯连接,并向电脑输出自己的姓名、年龄、身高
// 2、实现通过串口监视器给开发板发信息,开发板再把接收到的数据发回给电脑
// 3、实现加法计算器,如:电脑发送:“1+2”,开发版回答:”1+2=3“
// 4、实现电脑与开发板进行三句以上简单的对话。如:电脑发送:“a”,开发版回答:“Arduino”void setup()
{// put your setup code here, to run once:// 题目一Serial.begin(115200);Serial.println("姓名:坤坤");Serial.println("年龄:两年半");Serial.println("身高:180cm");
}void loop()
{// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:// 题目二if (Serial.available()){Serial.write(Serial.read());}}// put function definitions here:
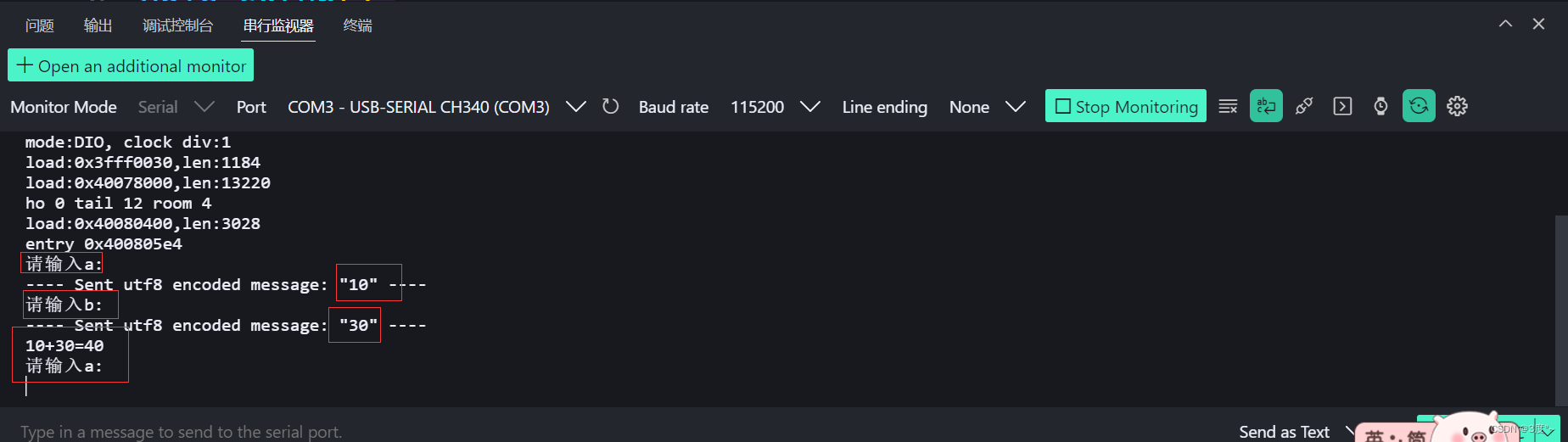
3、实现加法计算器,如:电脑发送:“1+2”,开发版回答:”1+2=3“
#include <Arduino.h>// put function declarations here:
int a = 0;
int b = 0;
int c = 0;void setup()
{// put your setup code here, to run once:Serial.begin(115200);
}void loop()
{// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:Serial.println("请输入a:");while (!a) // a不等于零{if (Serial.available()){a = Serial.parseInt();}}Serial.println("请输入b:");while (!b){if (Serial.available()){b = Serial.parseInt();}}c = a + b;Serial.print(a);Serial.print("+");Serial.print(b);Serial.print("=");Serial.println(c);a = 0;b = 0;
}
4、实现电脑与开发板进行三句以上简单的对话。如:电脑发送:“a”,开发版回答:“Arduino”
#include <Arduino.h>// put function declarations here:
int a = 0;
int b = 0;
int c = 0;void setup()
{// put your setup code here, to run once:Serial.begin(115200);
}void loop()
{// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:Serial.println("请选择(1,2,3):");while (!a){if (Serial.available()){a = Serial.parseInt();}}if (a == 1){Serial.println("你选择了1");}else if (a == 2){Serial.println("你选择了2");}else if (a == 3){Serial.println("你选择了3");}else{Serial.println("没有这个选项");}a = 0;
}

中断机制1

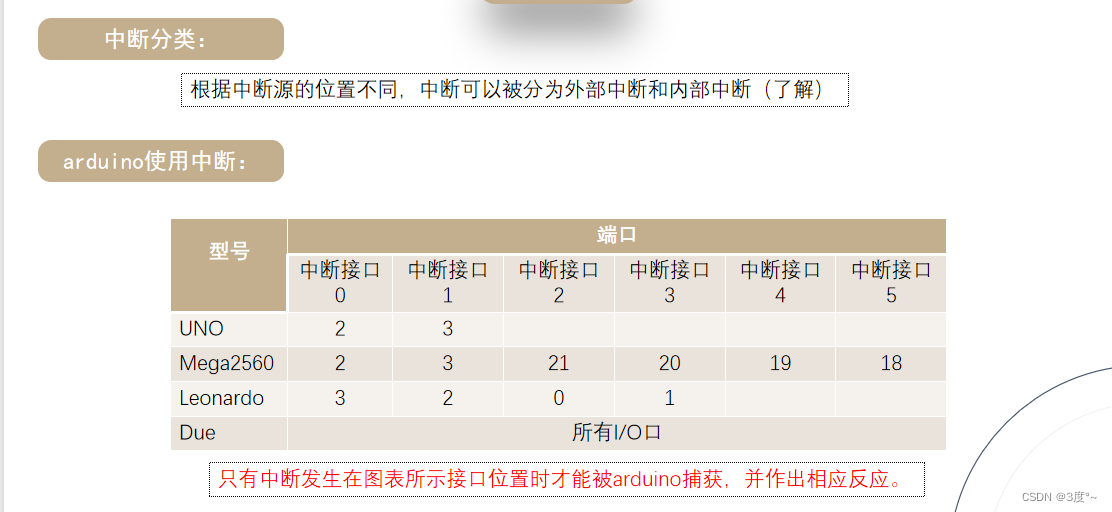
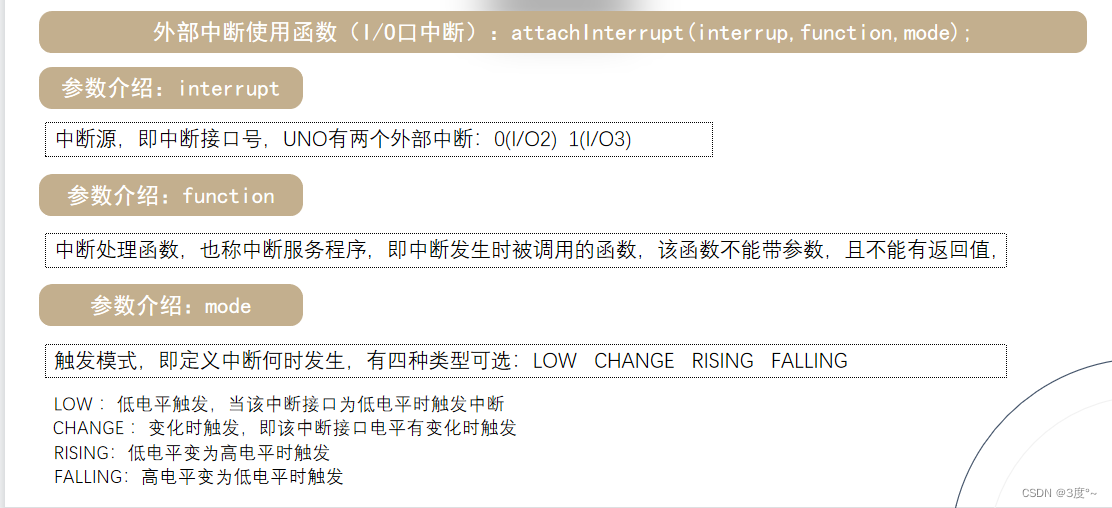
#include <Arduino.h>// put function declarations here:
int led = 2;
int button = 0;void set()
{Serial.println("按键被按下了");
}void setup()
{// put your setup code here, to run once:Serial.begin(115200);pinMode(led, OUTPUT);digitalWrite(button, HIGH);attachInterrupt(0, set, FALLING);
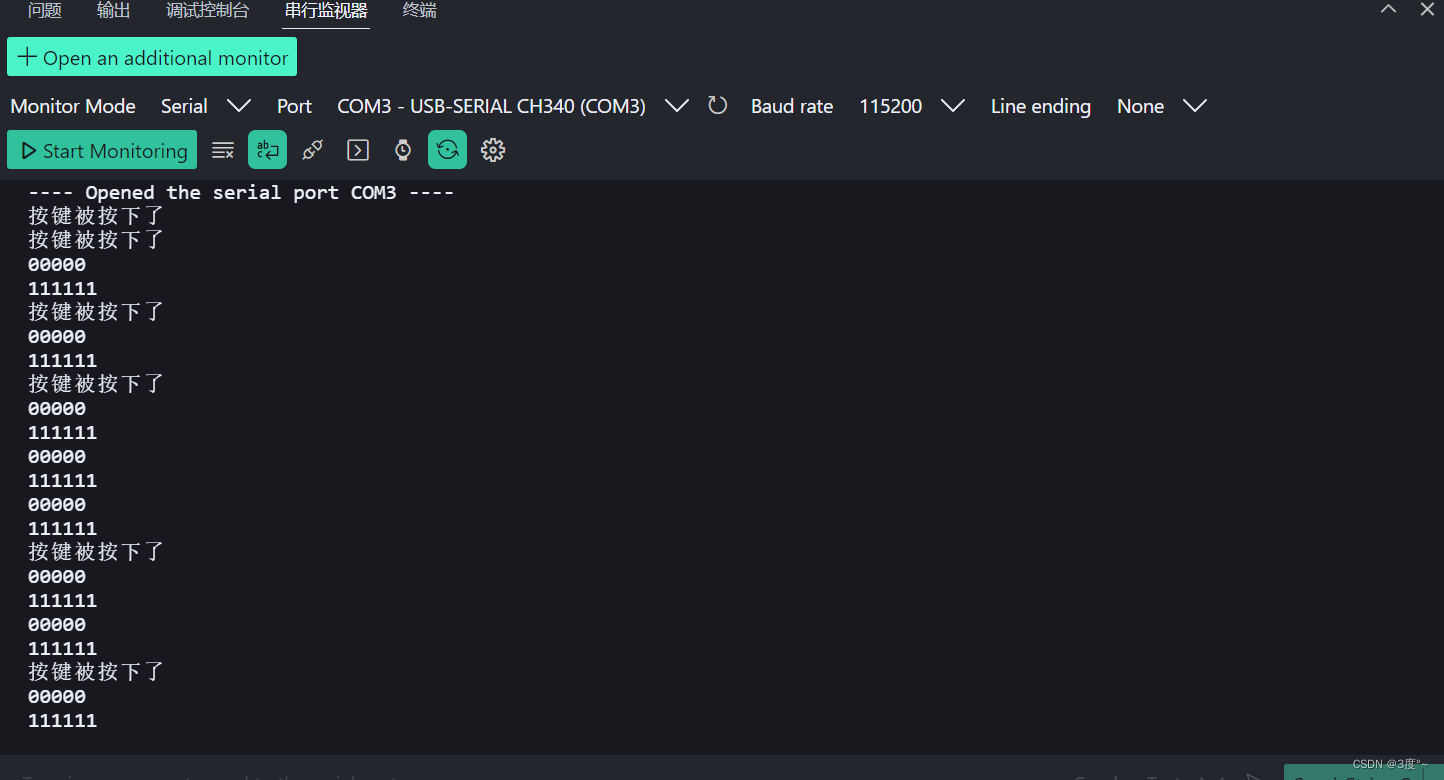
}void loop()
{// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:digitalWrite(led, HIGH);Serial.println("111111");delay(1000);digitalWrite(led, LOW);Serial.println("00000");delay(1000);
}// put function definitions here:
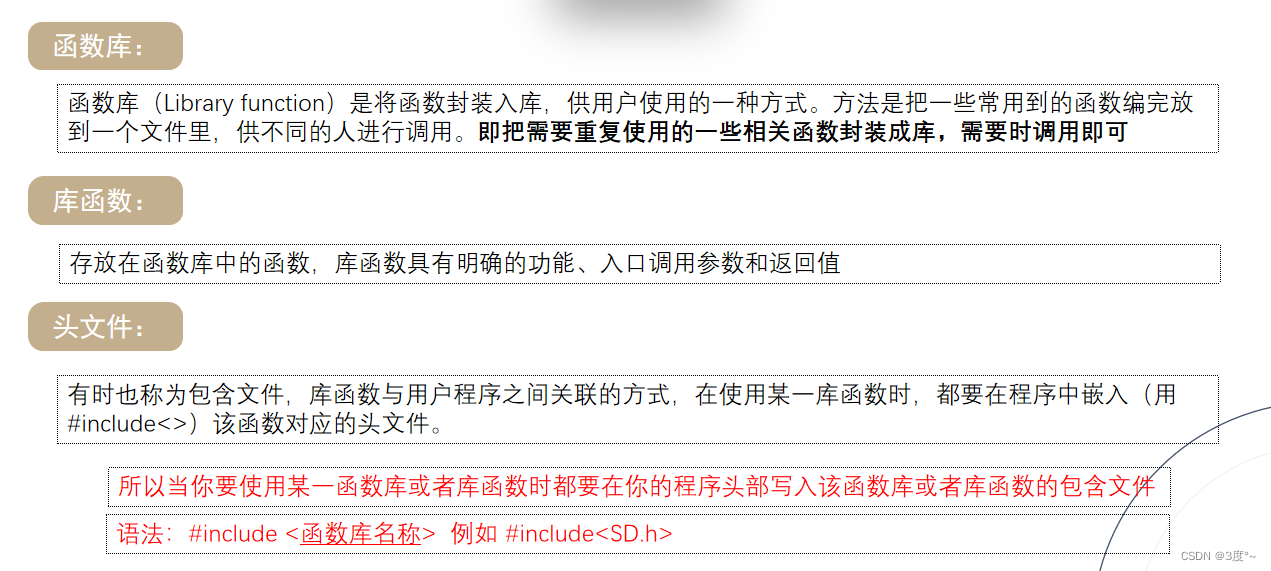
库的使用
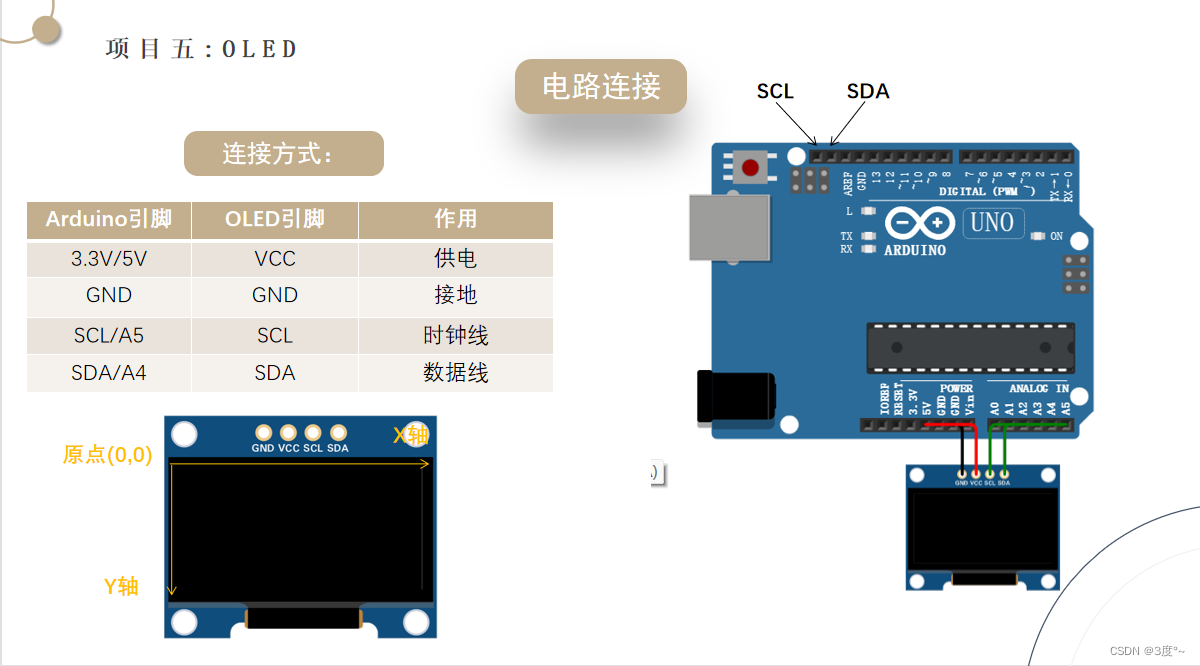
OLED1

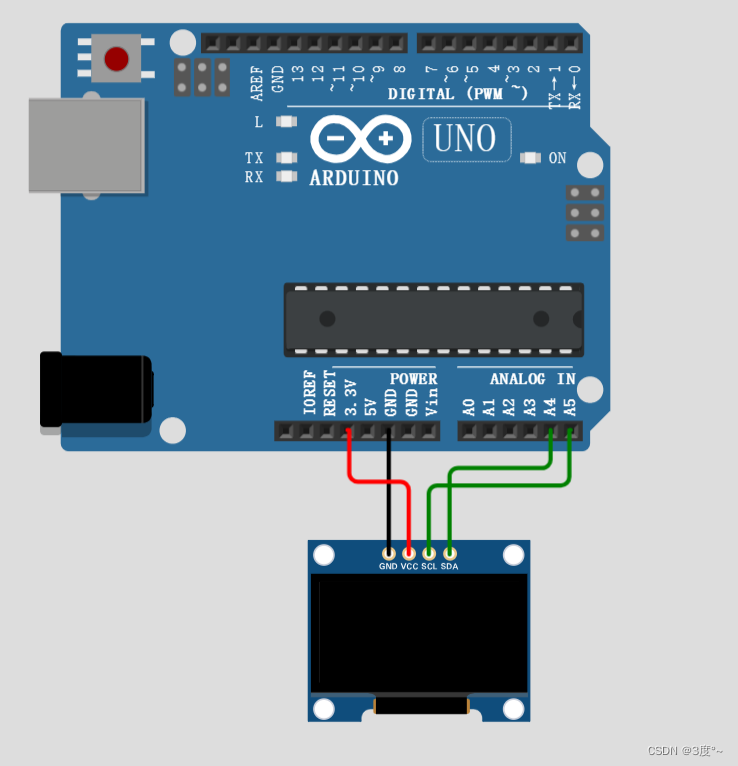

OLED2
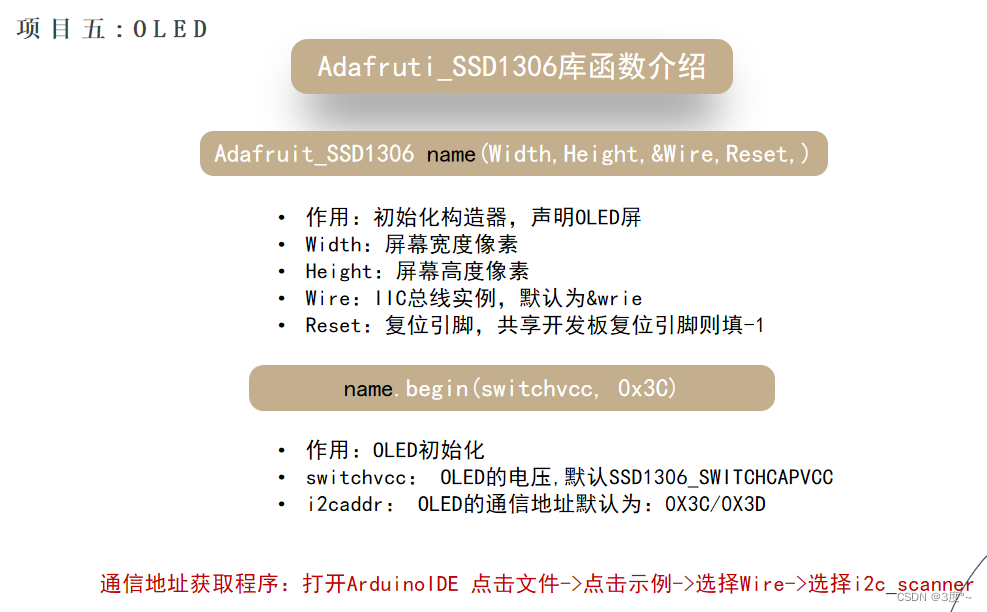

OLED3

OLED4
#include <Arduino.h>
#include <Adafruit_SSD1306.h>
#include <Wire.h>// put function declarations here:
Adafruit_SSD1306 oled(128, 64, &Wire, -1);void setup() {// put your setup code here, to run once:oled.begin(SSD1306_SWITCHCAPVCC, 0x3c);
}void loop() {// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:oled.clearDisplay(); // 清除缓存oled.setTextSize(2); //字体大小oled.setTextColor(1); //字体颜色oled.setCursor(0, 0); //光标位置oled.print("hello"); //输出,输出到缓存里边oled.display(); //显示到屏幕delay(2000);
}// put function definitions here:

OLED5(生成汉字)

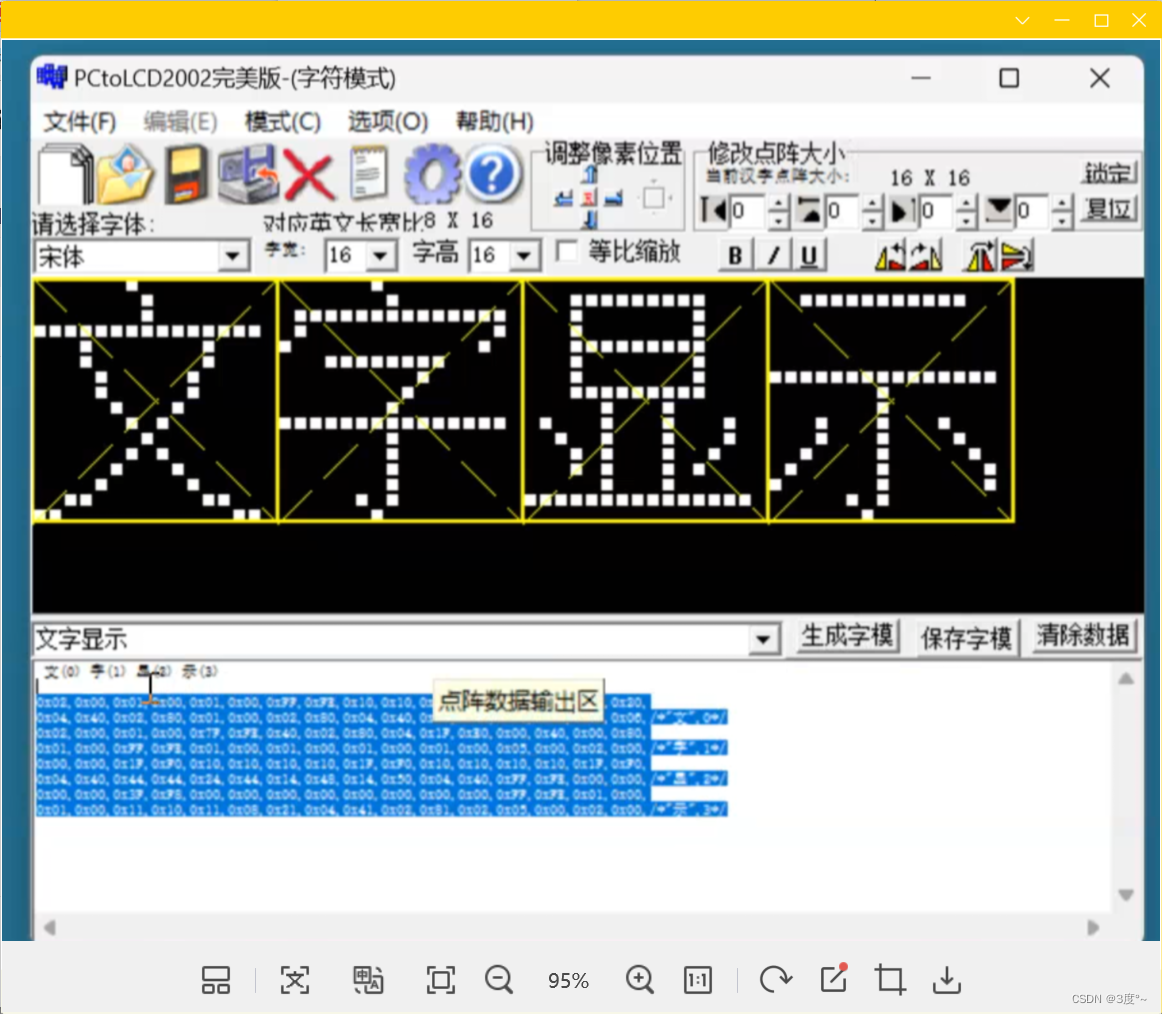
#include <Arduino.h>
#include <Adafruit_SSD1306.h>
#include <Wire.h>
// put function declarations here:
Adafruit_SSD1306 oled(128, 64, &Wire, -1);static const unsigned char PROGMEM wen[]={0x02, 0x00, 0x01, 0x00, 0x01, 0x00, 0xFF, 0xFE, 0x10, 0x10, 0x10, 0x10, 0x08, 0x20, 0x08, 0x20,0x04, 0x40, 0x20, 0x80, 0x01, 0x00, 0x02, 0x80, 0x04, 0x40, 0x80, 0x20, 0x30, 0x18, 0xC0, 0x06,
}; // 文 void setup() {// put your setup code here, to run once:oled.begin(SSD1306_SWITCHCAPVCC, 0x3c);
}void loop() {// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:oled.clearDisplay();oled.drawBitmap(0, 0, wen, 16, 16, 1); //显示中文汉字,需要几个复制几个oled.display();delay(2000);
}
OLED6(图像显示)
OLED7
找简单的图片,注意调整尺寸,保存成bmp格式
oled.drawBitmap(0, 0, wen, *, *, 1)
图片的话,**位置的尺寸必须和图片一样
OLED8(制作动画)

UU在线工具 - 便捷实用的工具集合站 (uutool.cn)
OLED9
Adafruit_SSD1306.h
drawFastHLine:画一条水平的线
drawFastHLine:画一条竖直的线
startscrollright(0x00, 0x0f)--全屏滚动:向右滚动
startscrollleft(0x00, 0x0f):向左滚动
startscrolldiagright--全屏滚动:对角线向右滚动
startscrolldiagleft:对角线向左滚动
stopscroll():停止滚动
Adafruit_GFX.h(57行开始)
LCD1602(1)
(转载)Arduino学习笔记:基于LiquidCrystal库运行LCD1602_#include <liquidcrystal.h>_zx_ecust的博客-CSDN博客
(转载)My_arduino(4)-------LiquidCrystal_I2C库文件_fatal error: liquidcrystal_i2c.h:_瞲_大河弯弯的博客-CSDN博客
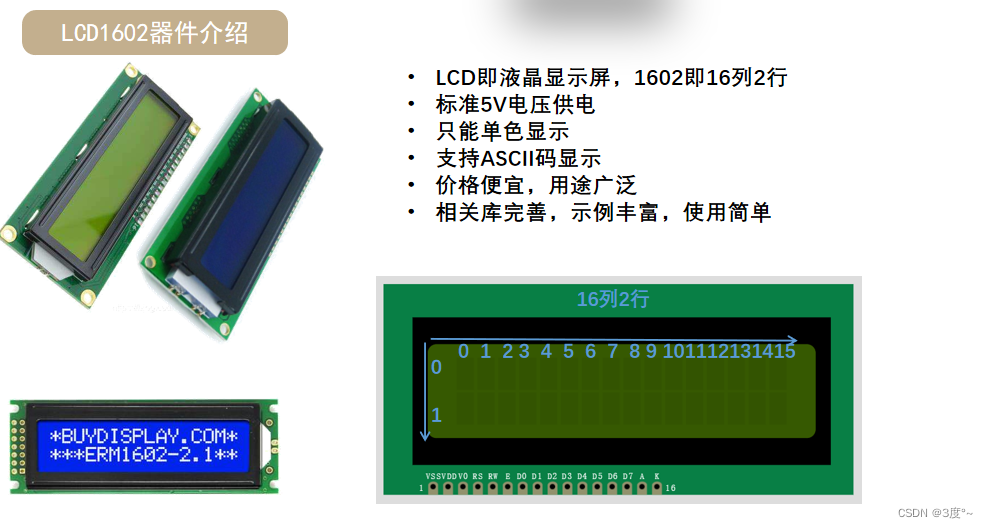
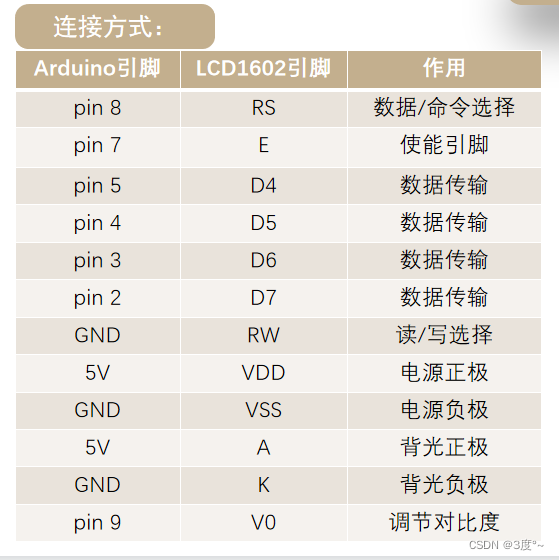

LCD1602(2)
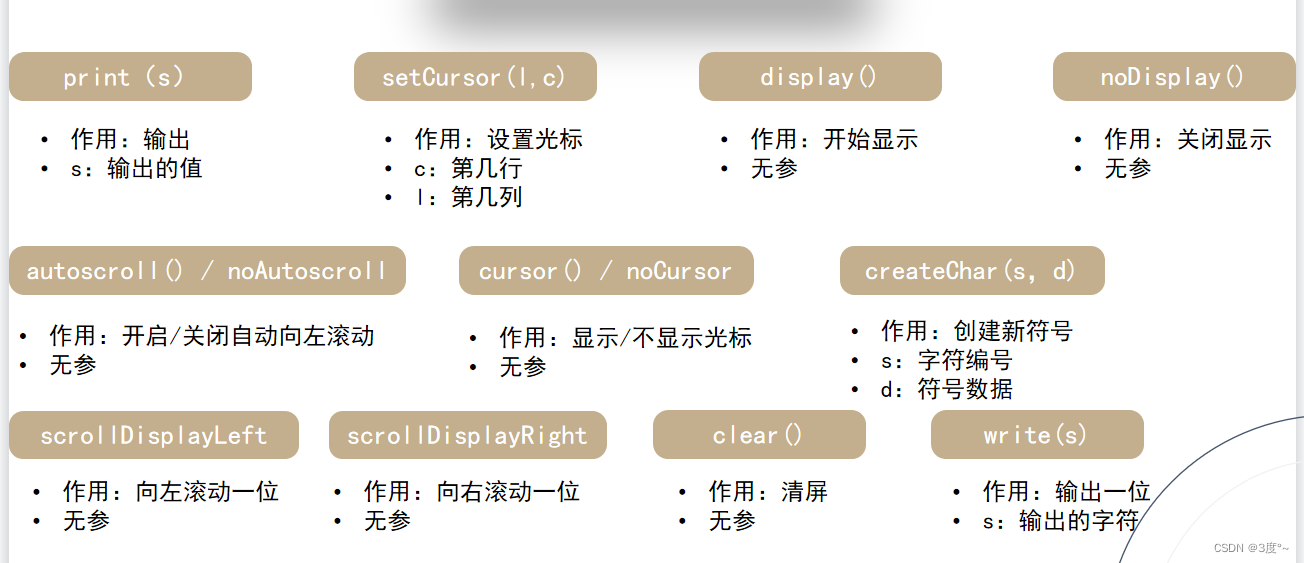
LCD1602(3)
LCD1602(4)
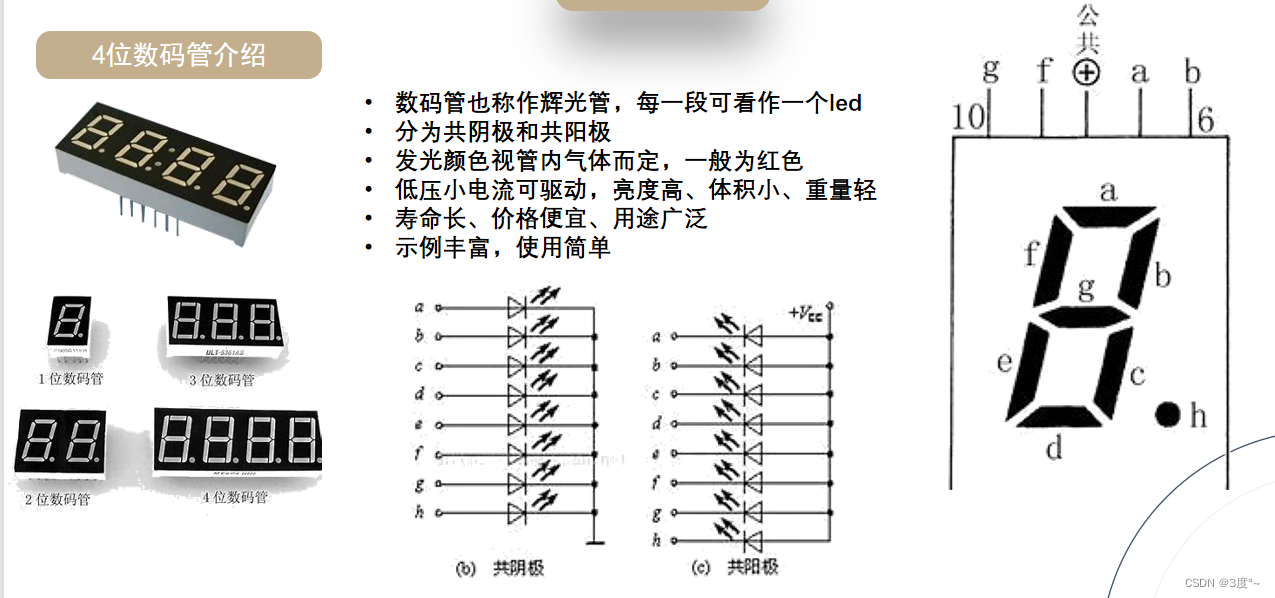
4位数码管(1)
转载:Arduino使用TM1637四位数码管_tm1637.set_蔚蓝慕的博客-CSDN博客
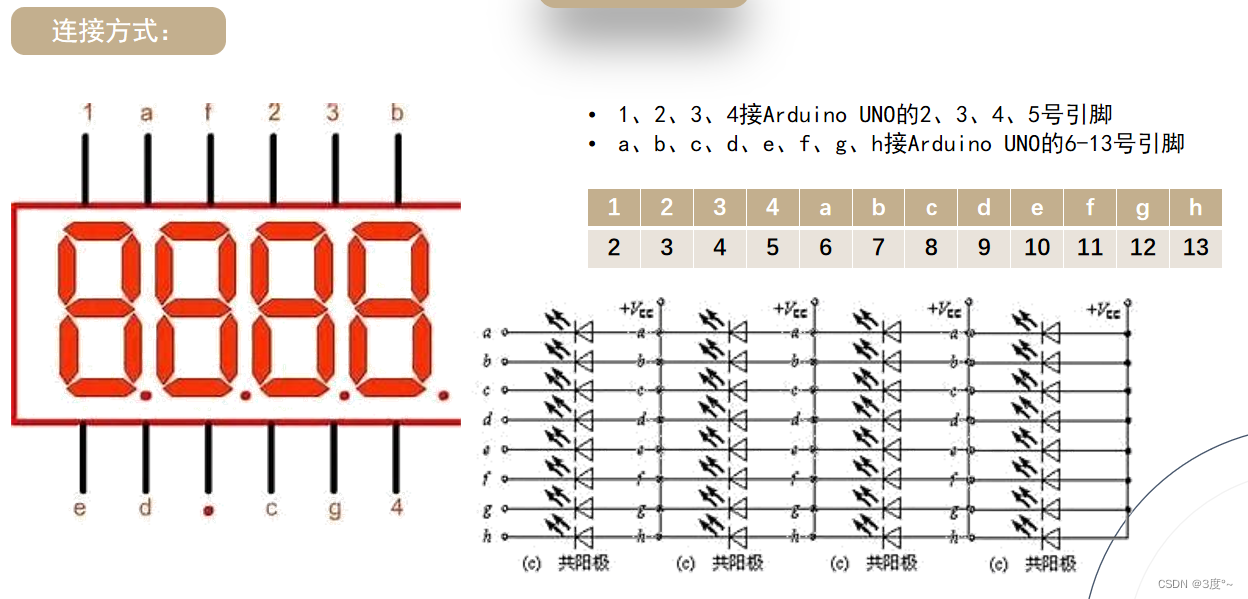

#include <Arduino.h>
void setup()
{for (int i = 2; i <= 13; i++){pinMode(i, OUTPUT);delay(10);}digitalWrite(2, HIGH); // 驱动第一位数码管digitalWrite(3, LOW); // 驱动第二位数码管digitalWrite(4, LOW); // 驱动第三位数码管digitalWrite(5, LOW); // 驱动第四位数码管digitalWrite(6, LOW); // 第a段digitalWrite(7, LOW); // 第b段digitalWrite(8, LOW); // 第c段digitalWrite(9, HIGH); // 第d段digitalWrite(10, HIGH); // 第e段digitalWrite(11, HIGH); // 第f段digitalWrite(12, HIGH); // 第g段digitalWrite(13, HIGH); // 第h段
}
void loop()
{//
}

4位数码管(2)
#include <Arduino.h>void setup()
{for (int i = 2; i <= 13; i++){pinMode(i, OUTPUT);delay(10);}
}
void loop()
{// 第一个显示1com1();num_1();delay(3);clear();// 第二个显示2com2();num_2();delay(3);clear();// 第三个显示1com3();num_1();delay(3);clear();// 第四个显示2com4();num_2();clear();
}void com1()
{digitalWrite(2, HIGH); // 驱动第一位数码管digitalWrite(3, LOW); // 驱动第二位数码管digitalWrite(4, LOW); // 驱动第三位数码管digitalWrite(5, LOW); // 驱动第四位数码管
}
void com2()
{digitalWrite(2, LOW); // 驱动第一位数码管digitalWrite(3, HIGH); // 驱动第二位数码管digitalWrite(4, LOW); // 驱动第三位数码管digitalWrite(5, LOW); // 驱动第四位数码管
}
void com3()
{digitalWrite(2, LOW); // 驱动第一位数码管digitalWrite(3, LOW); // 驱动第二位数码管digitalWrite(4, HIGH); // 驱动第三位数码管digitalWrite(5, LOW); // 驱动第四位数码管
}
void com4()
{digitalWrite(2, LOW); // 驱动第一位数码管digitalWrite(3, LOW); // 驱动第二位数码管digitalWrite(4, LOW); // 驱动第三位数码管digitalWrite(5, HIGH); // 驱动第四位数码管
}void num_0()
{digitalWrite(6, LOW); // 第a段digitalWrite(7, LOW); // 第b段digitalWrite(8, LOW); // 第c段digitalWrite(9, LOW); // 第d段digitalWrite(10, LOW); // 第e段digitalWrite(11, LOW); // 第f段digitalWrite(12, HIGH); // 第g段digitalWrite(13, HIGH); // 第h段
}
void num_1()
{digitalWrite(6, HIGH); // 第a段digitalWrite(7, LOW); // 第b段digitalWrite(8, LOW); // 第c段digitalWrite(9, HIGH); // 第d段digitalWrite(10, HIGH); // 第e段digitalWrite(11, HIGH); // 第f段digitalWrite(12, HIGH); // 第g段digitalWrite(13, HIGH); // 第h段
}
void num_2()
{digitalWrite(6, LOW); // 第a段digitalWrite(7, LOW); // 第b段digitalWrite(8, HIGH); // 第c段digitalWrite(9, LOW); // 第d段digitalWrite(10, LOW); // 第e段digitalWrite(11, HIGH); // 第f段digitalWrite(12, LOW); // 第g段digitalWrite(13, HIGH); // 第h段
}
void clear()
{digitalWrite(6, HIGH); // 第a段digitalWrite(7, HIGH); // 第b段digitalWrite(8, HIGH); // 第c段digitalWrite(9, HIGH); // 第d段digitalWrite(10, HIGH); // 第e段digitalWrite(11, HIGH); // 第f段digitalWrite(12, HIGH); // 第g段digitalWrite(13, HIGH); // 第h段
}
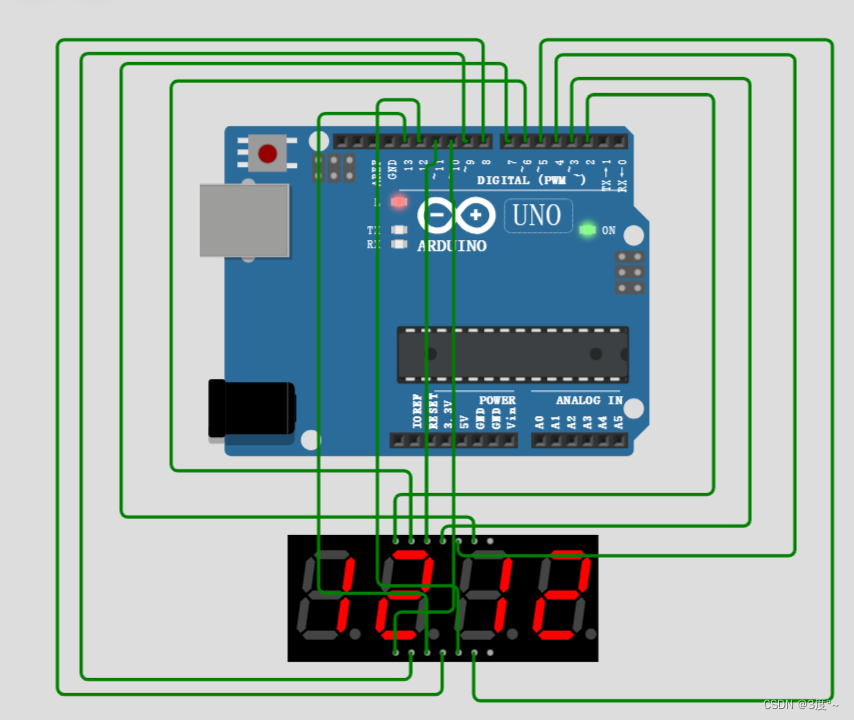
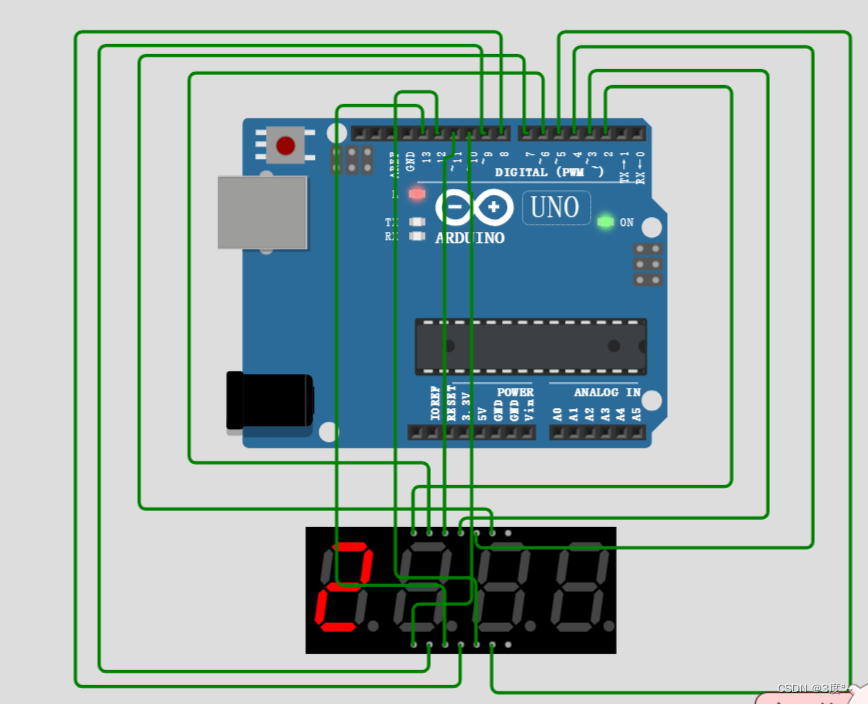
4位数码管(3)
第一位数字动态显示
#include <Arduino.h>int a = 0;
void setup()
{for (int i = 2; i <= 13; i++){pinMode(i, OUTPUT);delay(10);}
}
void loop()
{// 第一个显示,动态显示1,2if (a > 2){a = 0;}clear();com1(); // 位选if (a == 0){num_0(); // 段选}else if (a == 1){num_1(); // 段选}else if (a == 2){num_2(); // 段选}a++;delay(1000);
}void com1()
{digitalWrite(2, HIGH); // 驱动第一位数码管digitalWrite(3, LOW); // 驱动第二位数码管digitalWrite(4, LOW); // 驱动第三位数码管digitalWrite(5, LOW); // 驱动第四位数码管
}
void com2()
{digitalWrite(2, LOW); // 驱动第一位数码管digitalWrite(3, HIGH); // 驱动第二位数码管digitalWrite(4, LOW); // 驱动第三位数码管digitalWrite(5, LOW); // 驱动第四位数码管
}
void com3()
{digitalWrite(2, LOW); // 驱动第一位数码管digitalWrite(3, LOW); // 驱动第二位数码管digitalWrite(4, HIGH); // 驱动第三位数码管digitalWrite(5, LOW); // 驱动第四位数码管
}
void com4()
{digitalWrite(2, LOW); // 驱动第一位数码管digitalWrite(3, LOW); // 驱动第二位数码管digitalWrite(4, LOW); // 驱动第三位数码管digitalWrite(5, HIGH); // 驱动第四位数码管
}void num_0()
{digitalWrite(6, LOW); // 第a段digitalWrite(7, LOW); // 第b段digitalWrite(8, LOW); // 第c段digitalWrite(9, LOW); // 第d段digitalWrite(10, LOW); // 第e段digitalWrite(11, LOW); // 第f段digitalWrite(12, HIGH); // 第g段digitalWrite(13, HIGH); // 第h段
}
void num_1()
{digitalWrite(6, HIGH); // 第a段digitalWrite(7, LOW); // 第b段digitalWrite(8, LOW); // 第c段digitalWrite(9, HIGH); // 第d段digitalWrite(10, HIGH); // 第e段digitalWrite(11, HIGH); // 第f段digitalWrite(12, HIGH); // 第g段digitalWrite(13, HIGH); // 第h段
}
void num_2()
{digitalWrite(6, LOW); // 第a段digitalWrite(7, LOW); // 第b段digitalWrite(8, HIGH); // 第c段digitalWrite(9, LOW); // 第d段digitalWrite(10, LOW); // 第e段digitalWrite(11, HIGH); // 第f段digitalWrite(12, LOW); // 第g段digitalWrite(13, HIGH); // 第h段
}
void clear()
{digitalWrite(6, HIGH); // 第a段digitalWrite(7, HIGH); // 第b段digitalWrite(8, HIGH); // 第c段digitalWrite(9, HIGH); // 第d段digitalWrite(10, HIGH); // 第e段digitalWrite(11, HIGH); // 第f段digitalWrite(12, HIGH); // 第g段digitalWrite(13, HIGH); // 第h段
}
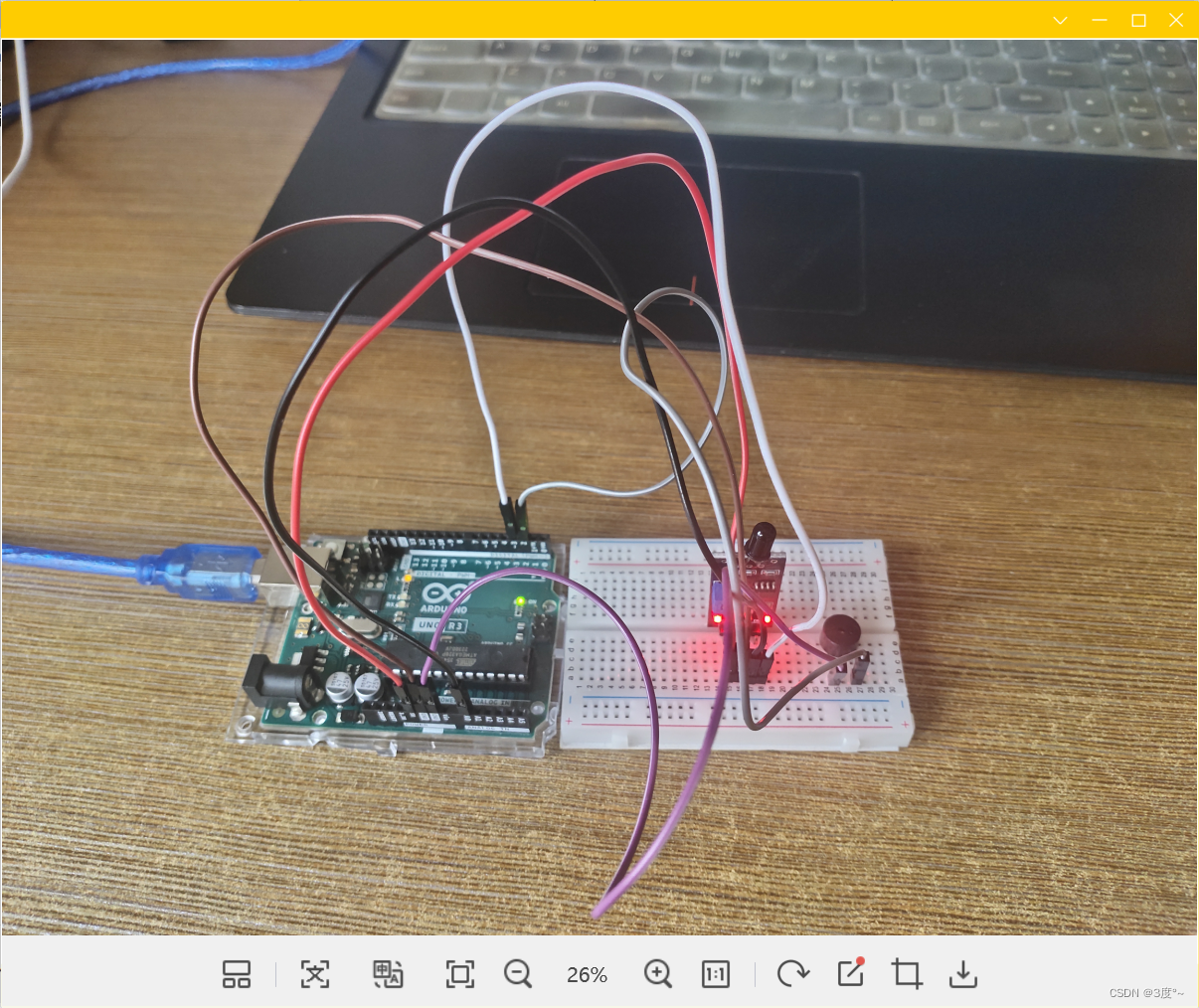
火焰检测

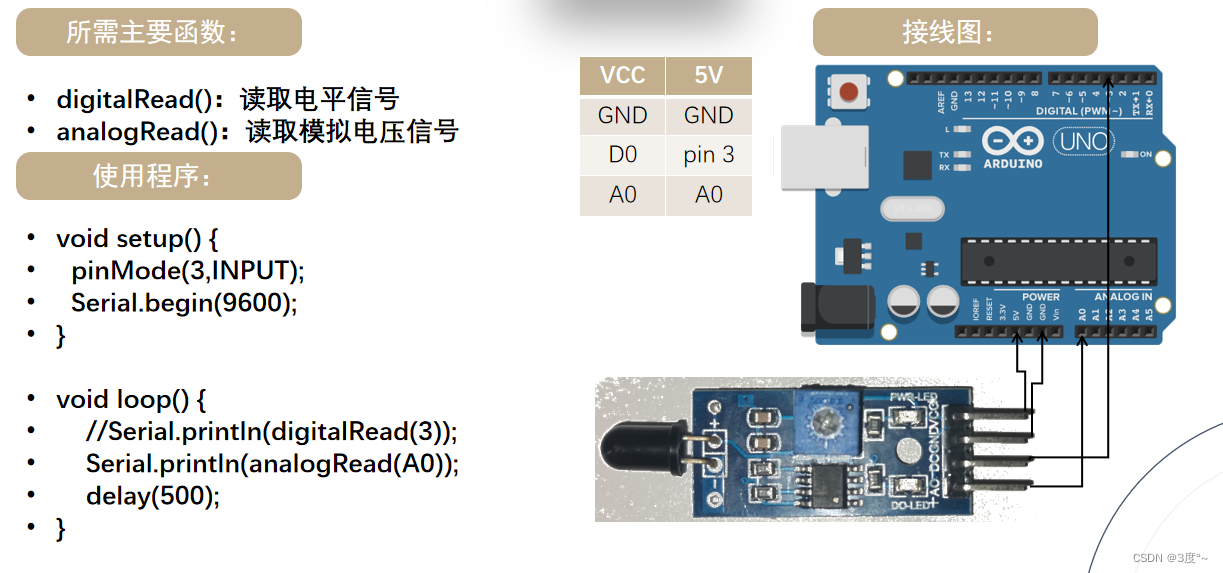
#include <Arduino.h>// put function declarations here:
#define D3 3 // 火焰传感器数字信号口
// #define A0 // 模拟信号输入口
#define D2 2 // 蜂鸣器数字信号口void setup() {// put your setup code here, to run once:Serial.begin(115200);pinMode(D3, INPUT);pinMode(D2, OUTPUT);
}void loop() {Serial.print("数字信号:");Serial.println(digitalRead(D3));Serial.print("模拟信号:");Serial.println(analogRead(A0));Serial.println("-------------------------------");delay(1000);if (analogRead(A0) < 400) {digitalWrite(D2, HIGH);delay(100);digitalWrite(D2, LOW);delay(100);} else {digitalWrite(D2, LOW);}
}// put function definitions here:#include <Arduino.h>// put function declarations here:
#define D3 3 // 火焰传感器数字信号口
// #define A0 // 模拟信号输入口
#define D2 2 // 蜂鸣器数字信号口void setup() {// put your setup code here, to run once:Serial.begin(115200);pinMode(D3, INPUT);pinMode(D2, OUTPUT);
}void loop() {// Serial.print("数字信号:");// Serial.println(digitalRead(D3));// Serial.print("模拟信号:");// Serial.println(analogRead(A0));// Serial.println("-------------------------------");// delay(1000);// if (analogRead(D3) < 400)// {// digitalWrite(D2, HIGH);// }// else// {// digitalWrite(D2, LOW);// }Serial.println(analogRead(A0));delay(2000);
}// put function definitions here: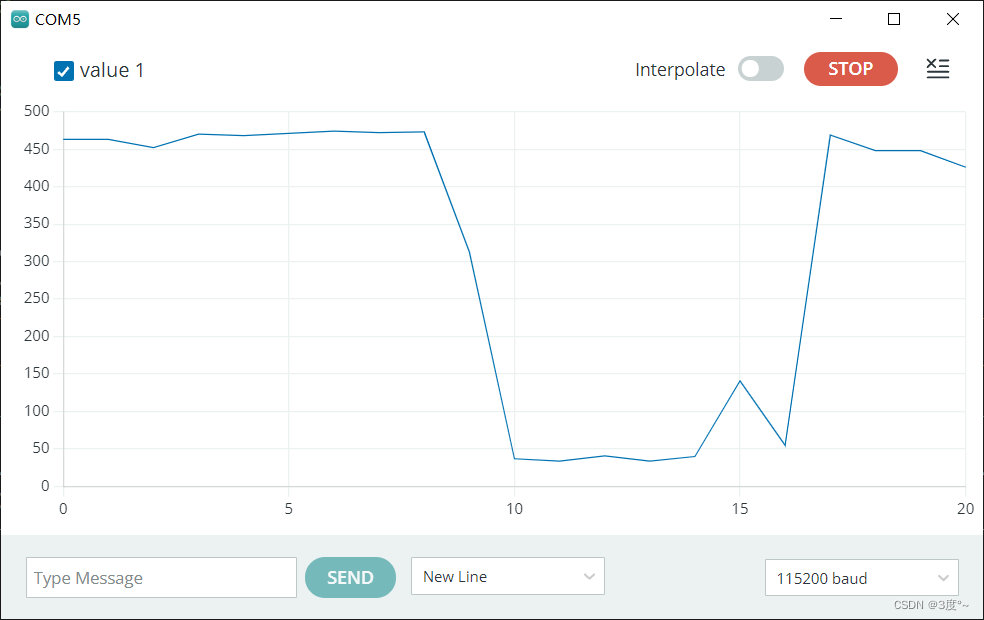
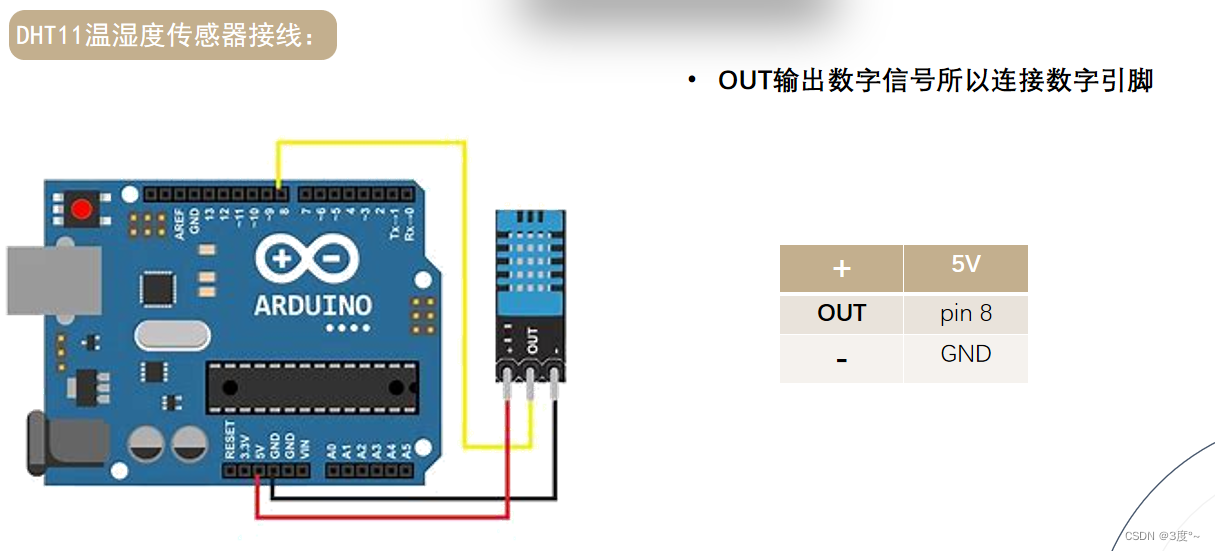
温度检测传感器
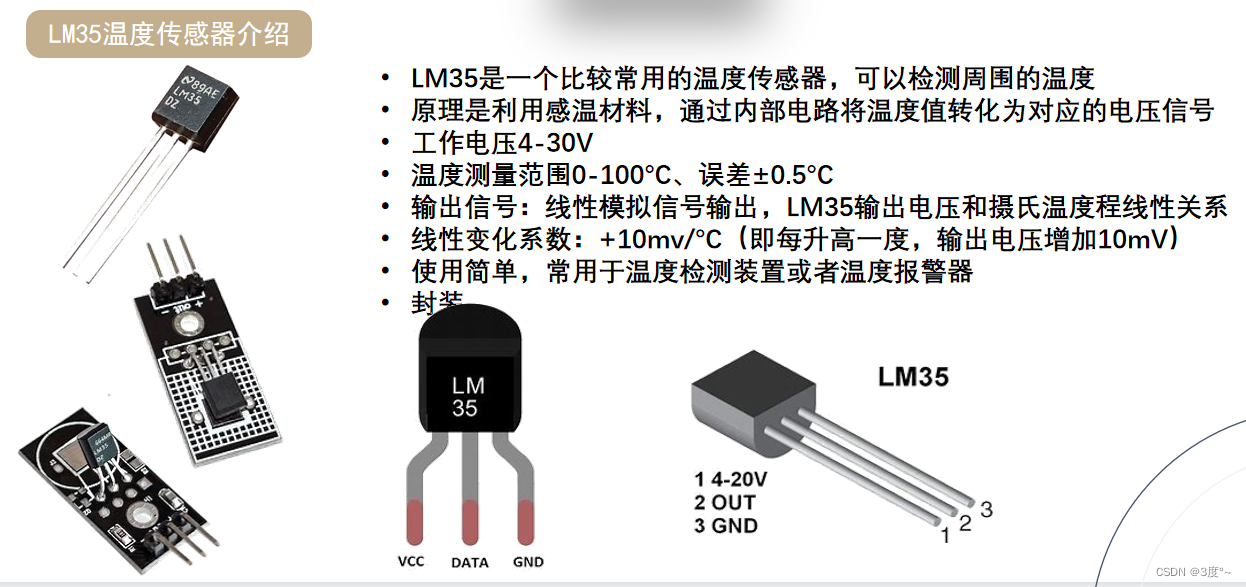
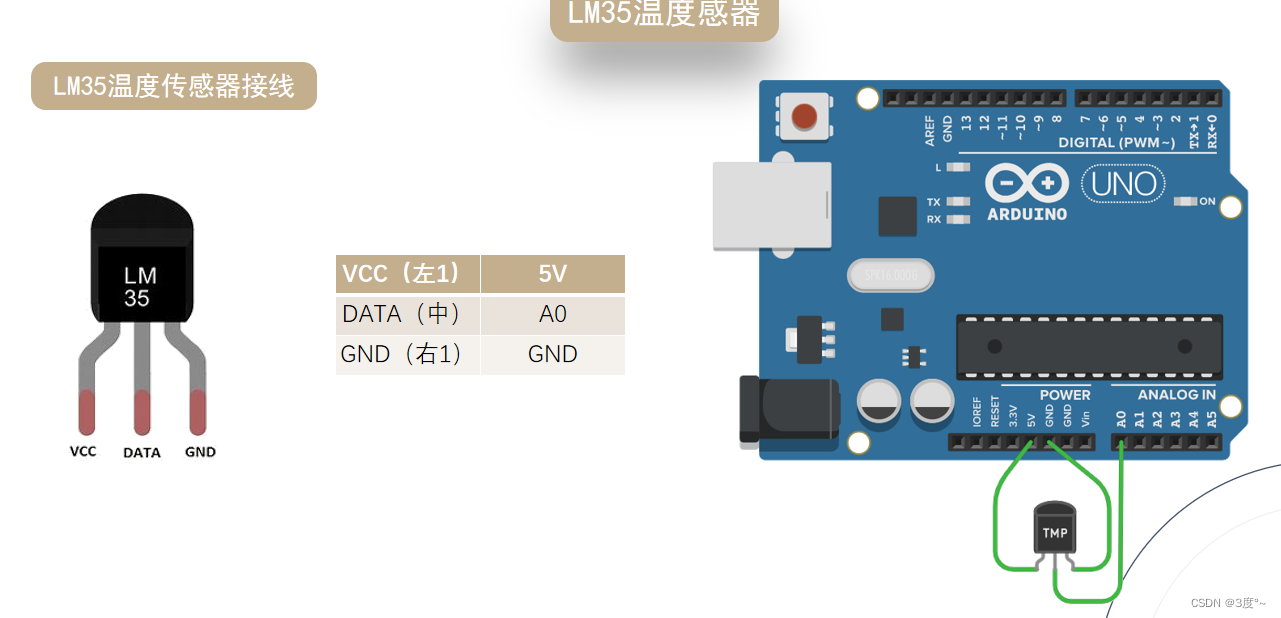


温湿度传感器



#include <Arduino.h>
#include <DHT.h>
#include <Adafruit_Sensor.h>
#define D3 3 // 温湿度信号输入
// put function declarations here:
DHT dht(D3, DHT11);
float temp = 0; // 存储温度值
float humi = 0; // 存储湿度值
float heatindex = 0; //存储酷热指数
void setup() {// put your setup code here, to run once:pinMode(D3, INPUT);Serial.begin(115200);dht.begin();
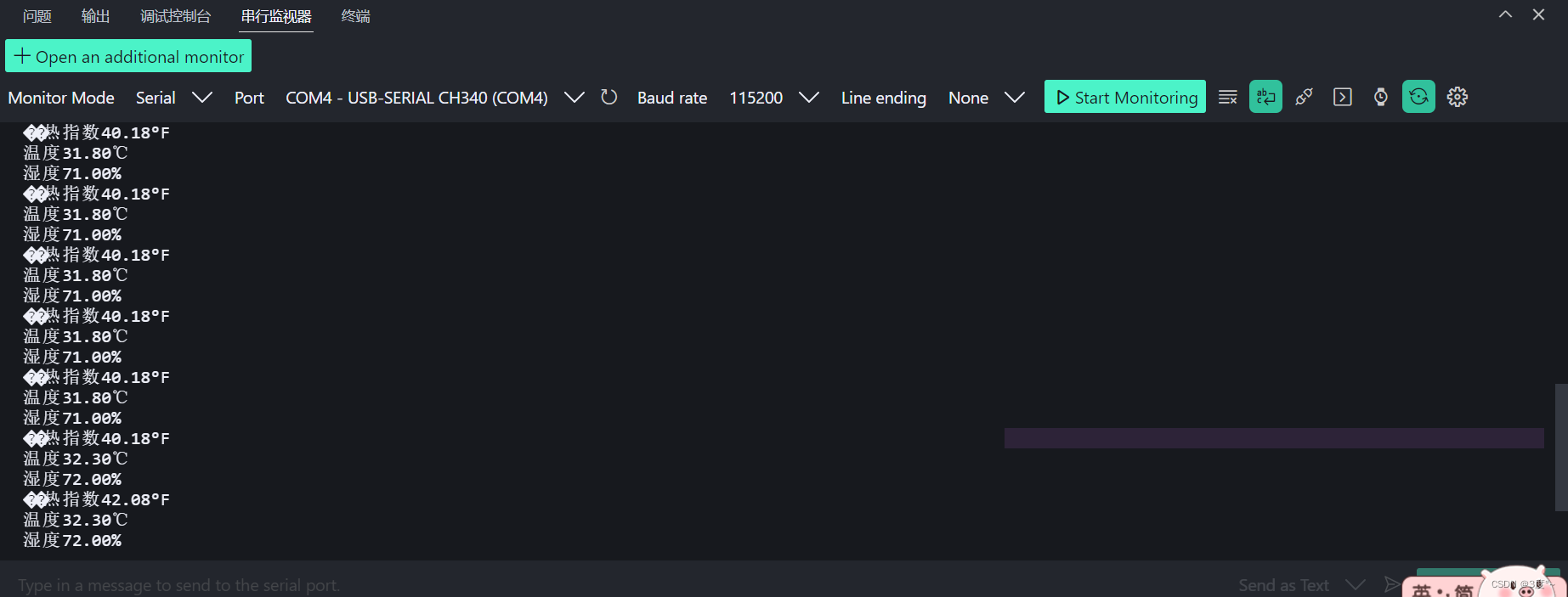
}void loop() {// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:temp = dht.readTemperature(); humi = dht.readHumidity();heatindex = dht.computeHeatIndex(temp, humi, false); // false--摄氏度, true--华氏度Serial.print("温度");Serial.print(temp);Serial.println("℃");Serial.print("湿度");Serial.print(humi);Serial.println("%");Serial.print("酷热指数");Serial.print(heatindex);Serial.println("°F");Serial.println("------------------------");delay(2000);
}
可燃气体检测传感器

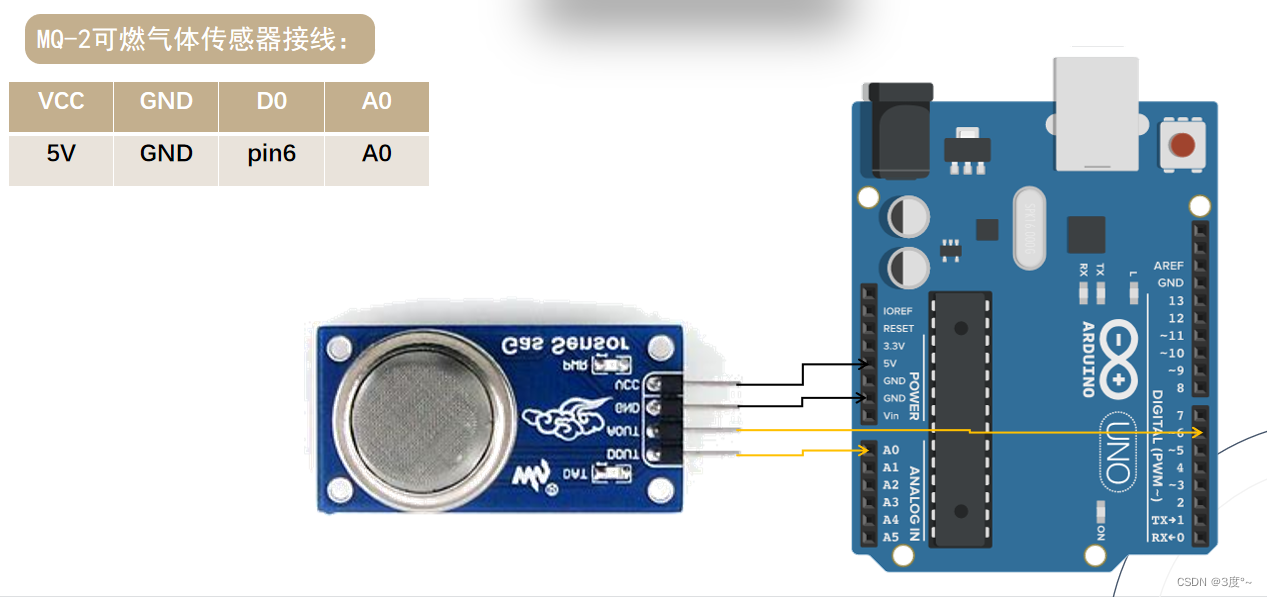
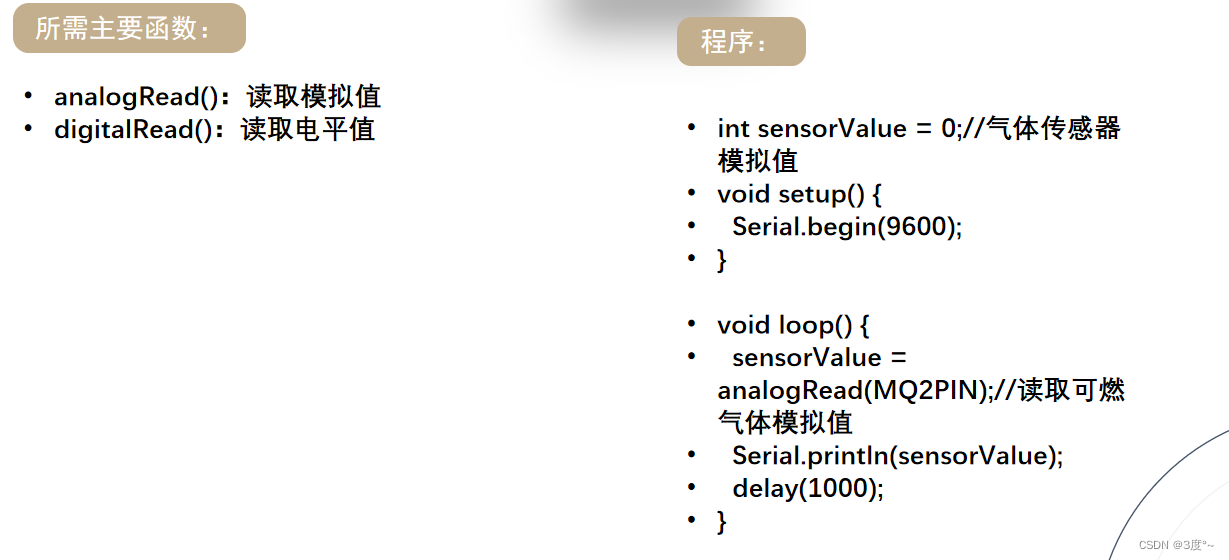
#include <Arduino.h>// put function declarations here:
#define D3 3 //可燃气体传感器数字输入
#define D2 2 //蜂鸣器数字输入int sensorValue = 0; // 可燃气体传感器void setup() {// put your setup code here, to run once:Serial.begin(115200);pinMode(D3, INPUT);pinMode(D2, OUTPUT);
}void loop() {// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:Serial.println(digitalRead(D3));Serial.println("-------------------");Serial.println(analogRead(A0));Serial.println("-------------------");delay(1000);if (analogRead(A0) > 300) {digitalWrite(D2, HIGH);delay(100);digitalWrite(D2, LOW);delay(100);} else {digitalWrite(D2, LOW);}
}
雨滴传感器

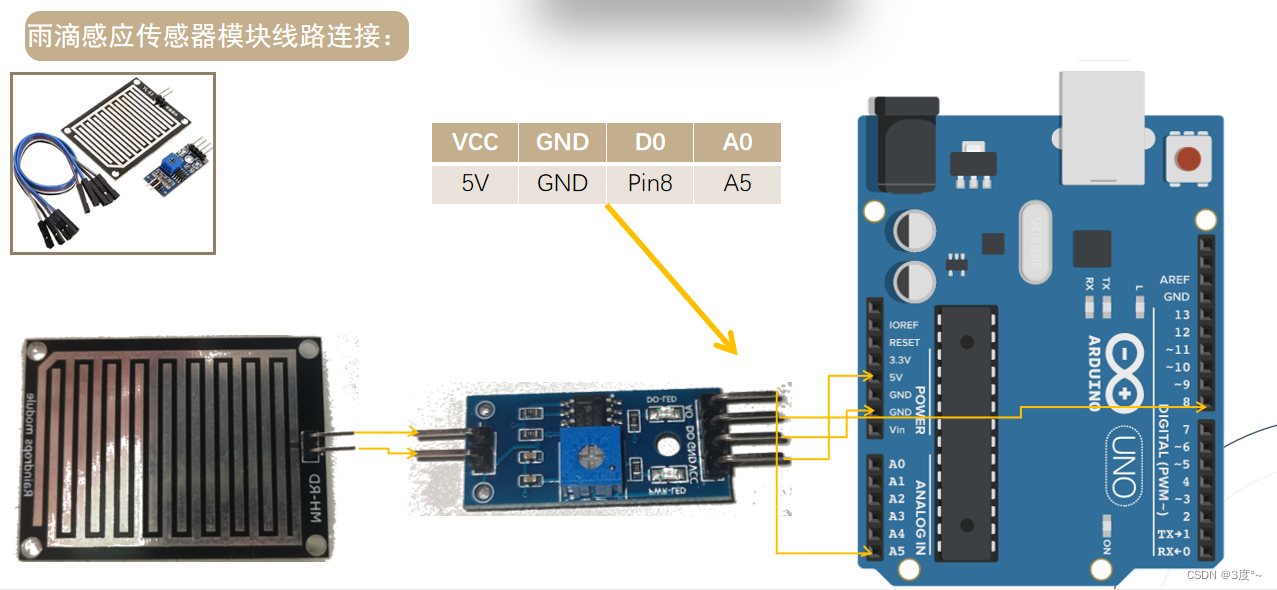

#include <Arduino.h>
#define D3 3 // 雨滴模拟器数字输入口
#define D2 2 //蜂鸣器数字输入int rain_val_2 = 0;
void setup()
{pinMode(D3, INPUT);pinMode(D2, OUTPUT);Serial.begin(115200);
}void loop()
{// rain_val_1 = digitalRead(4); // 获取数字量rain_val_2 = analogRead(A0); // 获取模拟量Serial.println(rain_val_2);delay(1000);if (analogRead(A0) < 1000) {digitalWrite(D2, HIGH);delay(100);digitalWrite(D2, LOW);delay(100);} else {digitalWrite(D2, LOW);}
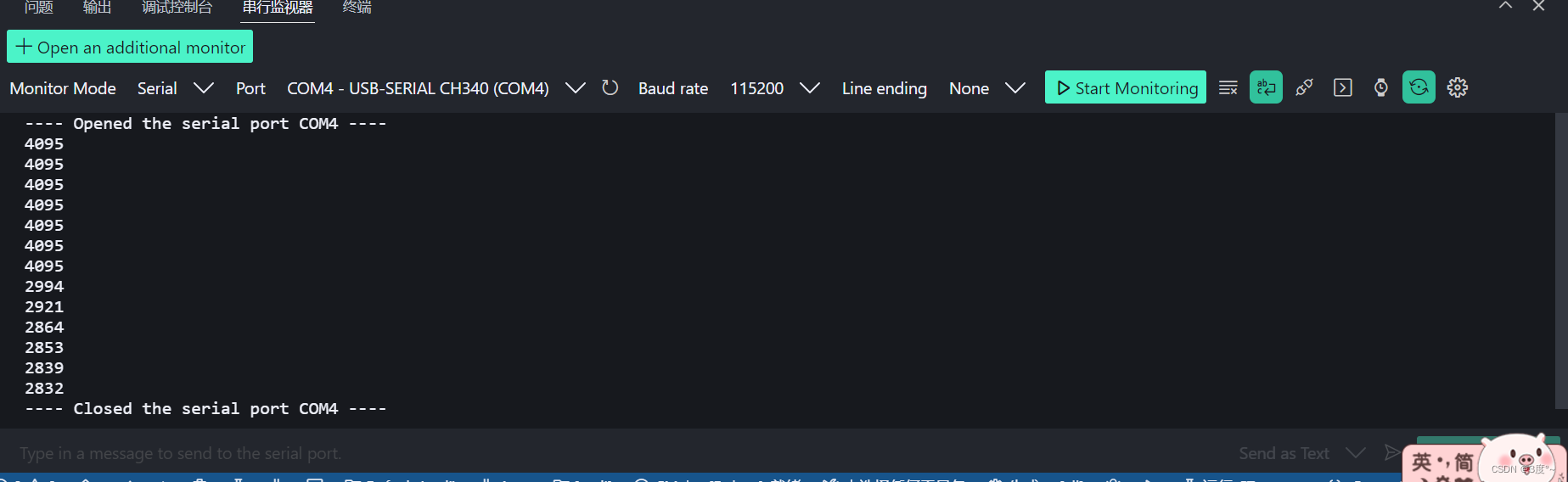
}
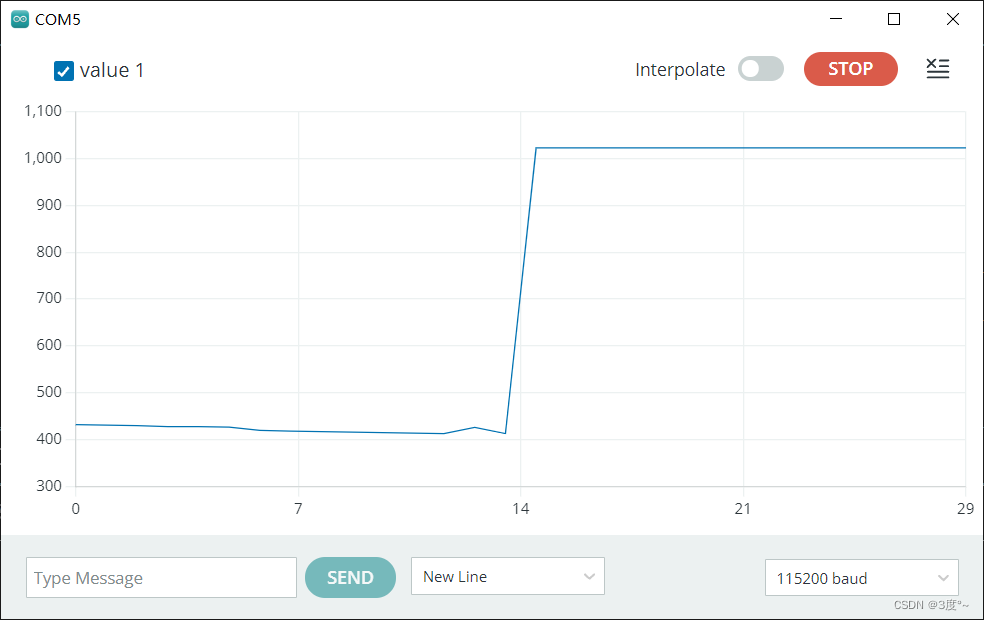
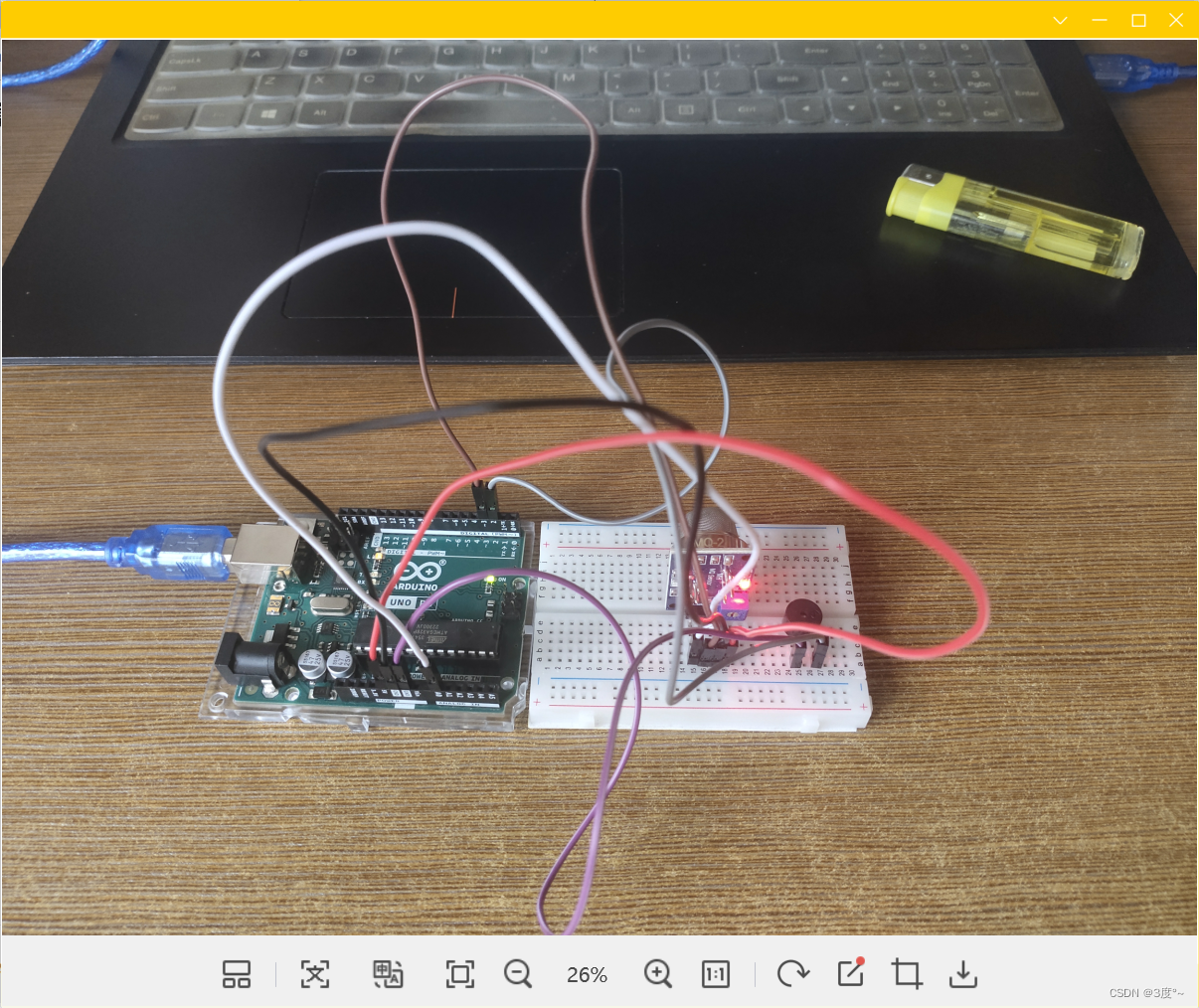
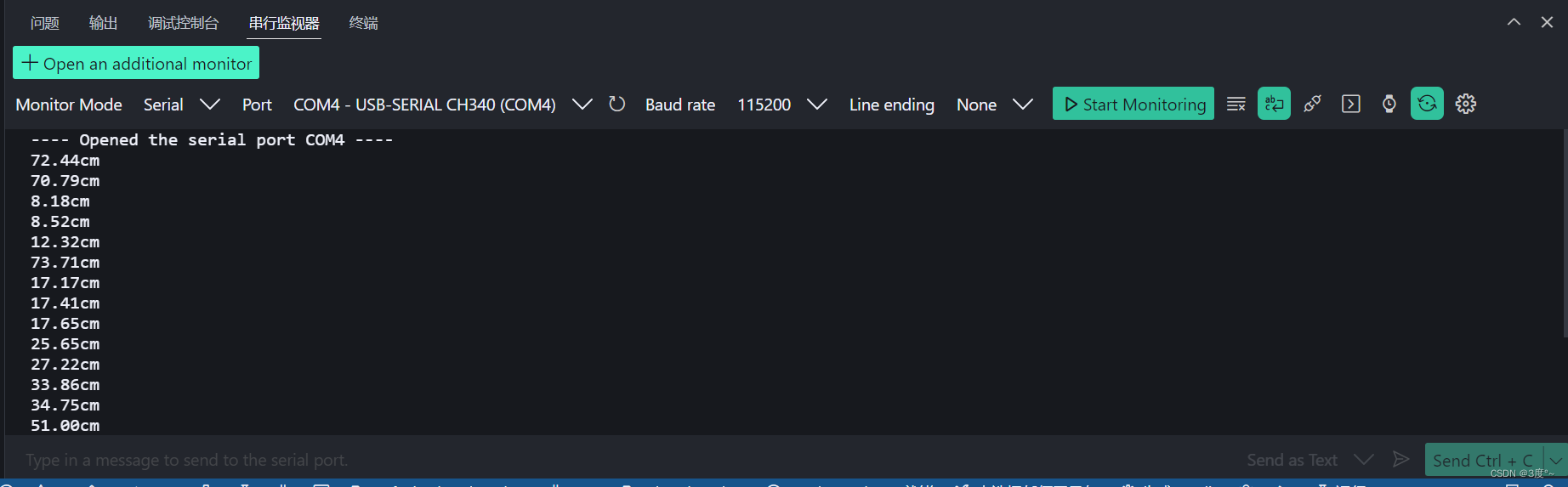
超声波传感器
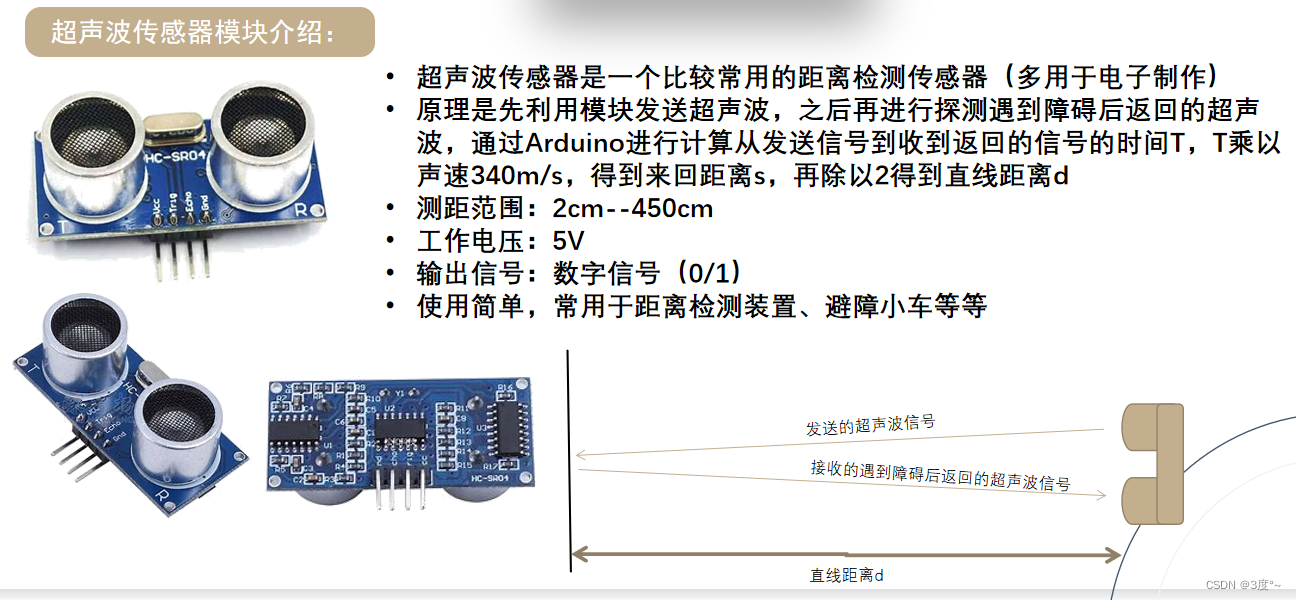
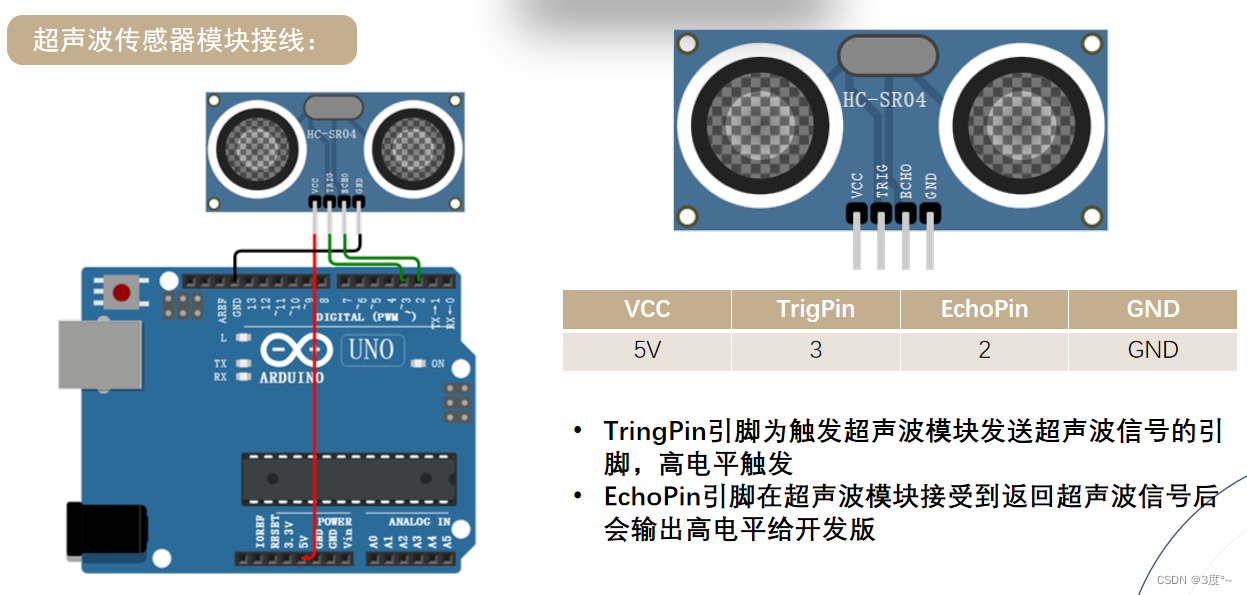


#include <Arduino.h>#define trigpin 4
#define echopin 3
#define D2 2 // 蜂鸣器数字输入口
float distance_cm; // 存储距离值,单位cm
void setup()
{Serial.begin(115200);pinMode(trigpin, OUTPUT);pinMode(echopin, INPUT);pinMode(D2, OUTPUT);
}
void loop()
{digitalWrite(trigpin, LOW); // 设置初始状态delayMicroseconds(2); // 发送前准备digitalWrite(trigpin, HIGH); // 发送超声波信号delayMicroseconds(10); // 发送持续时间digitalWrite(trigpin, LOW); // 结束发送超声波信号// 开始读取并换算为cmdistance_cm = float(pulseIn(echopin, HIGH) * 17) / 1000;Serial.print(distance_cm);Serial.println("cm");Serial.println("---------------------");// Serial.println(100 + distance_cm * 10);delay(1000);if (distance_cm < 45) {digitalWrite(D2, HIGH);delay(100 + distance_cm * 10);digitalWrite(D2, LOW);delay(100 + distance_cm * 10);} else {digitalWrite(D2, LOW);}
}
蜂鸣器

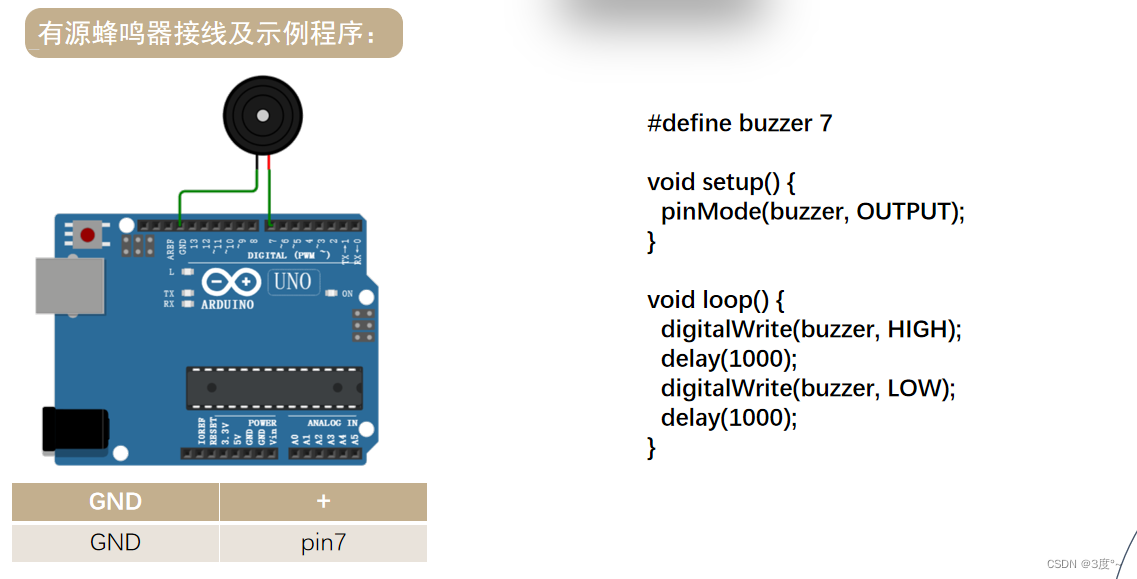
#include <Arduino.h>// put function declarations here:
#define buzzer 4
void setup() {// put your setup code here, to run once:pinMode(buzzer, OUTPUT);
}void loop() {// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:digitalWrite(buzzer, HIGH); //发声delay(1000);digitalWrite(buzzer, LOW); //不发声delay(1000);
}L298N电机驱动
转载:
L298N电机驱动模块的接线使用与代码实现_l298npwm调速接线_Clichong的博客-CSDN博客

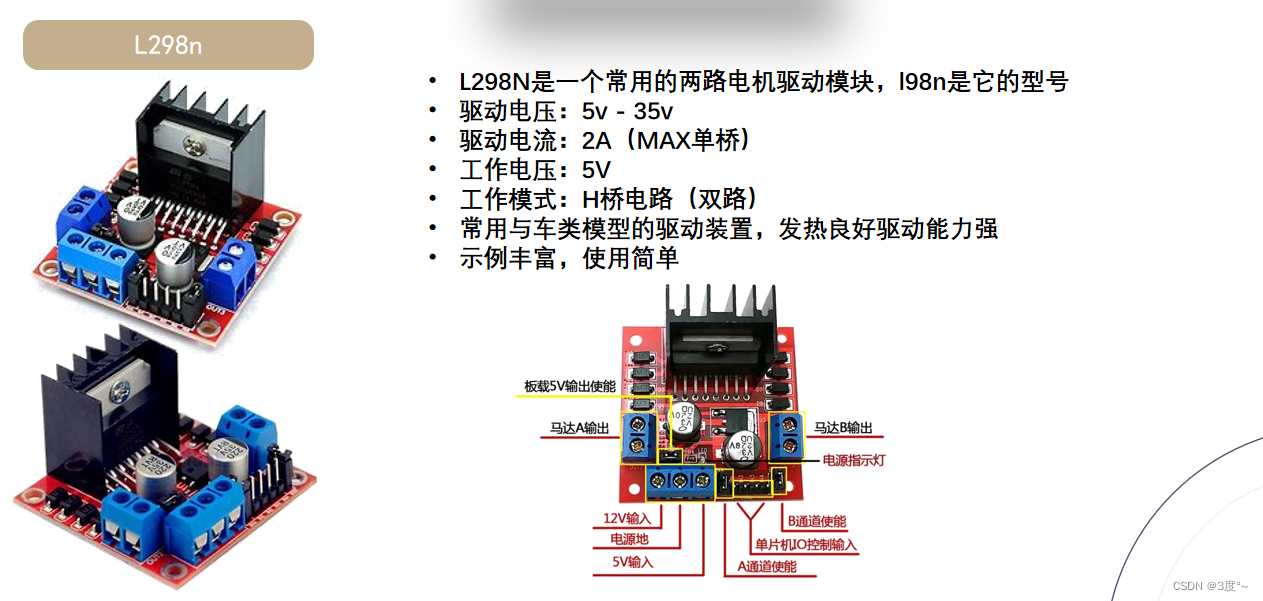
当电源<12v的时候,板载5v输出使能跳线帽不用拔掉,>12v可以拔掉,再找一个5v电源给板子供电
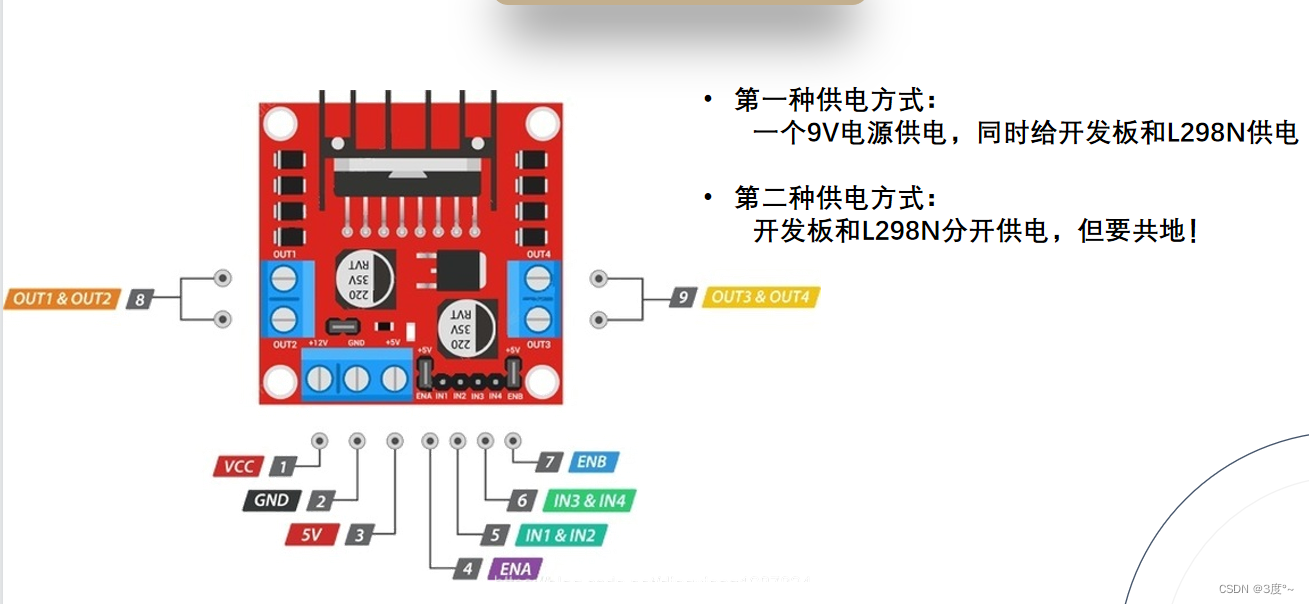
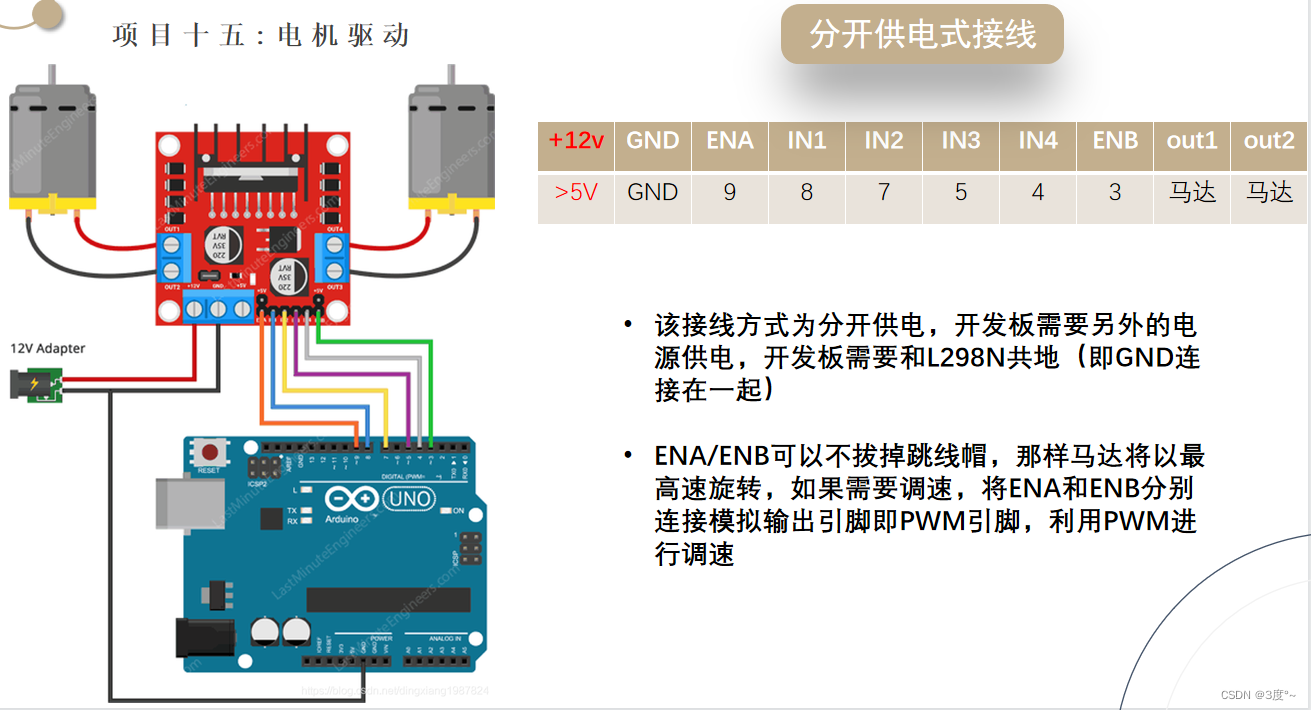
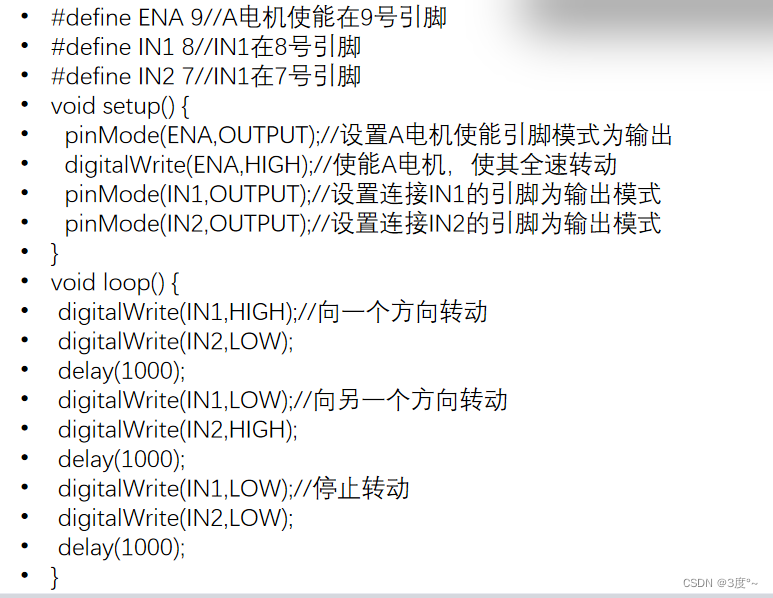
L9110电机驱动
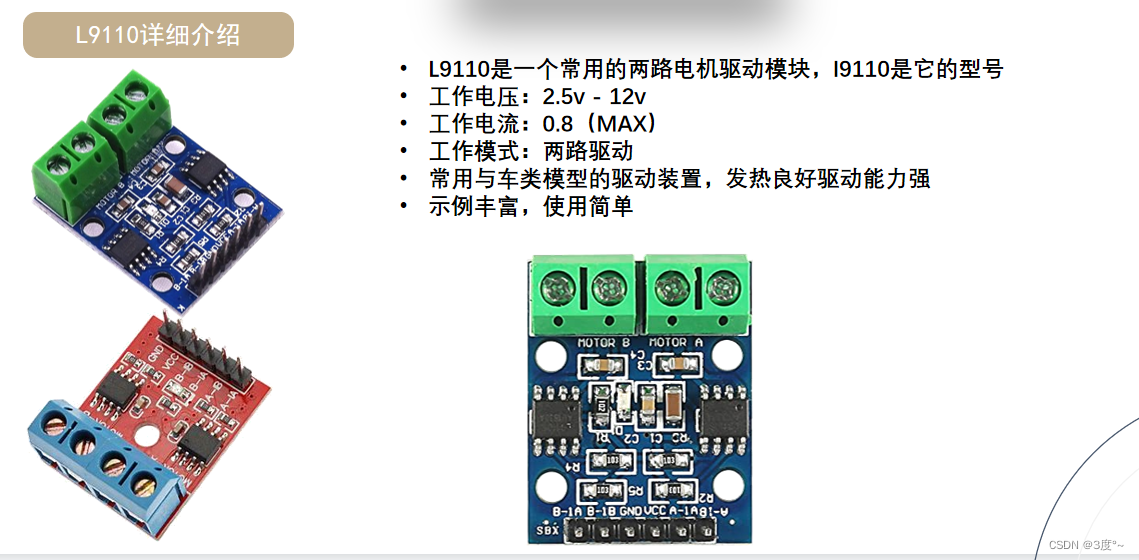
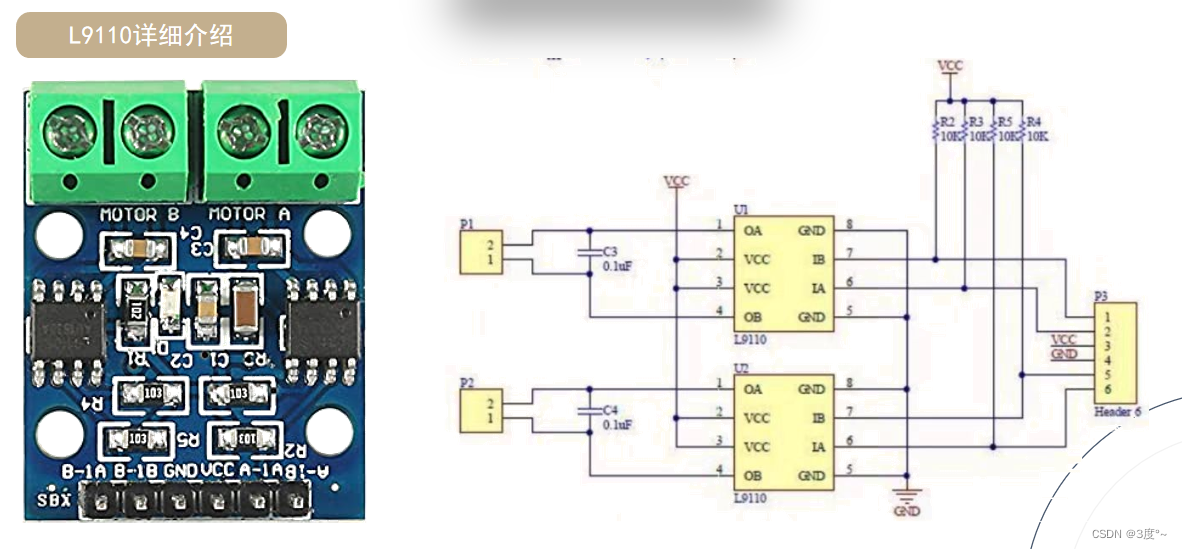
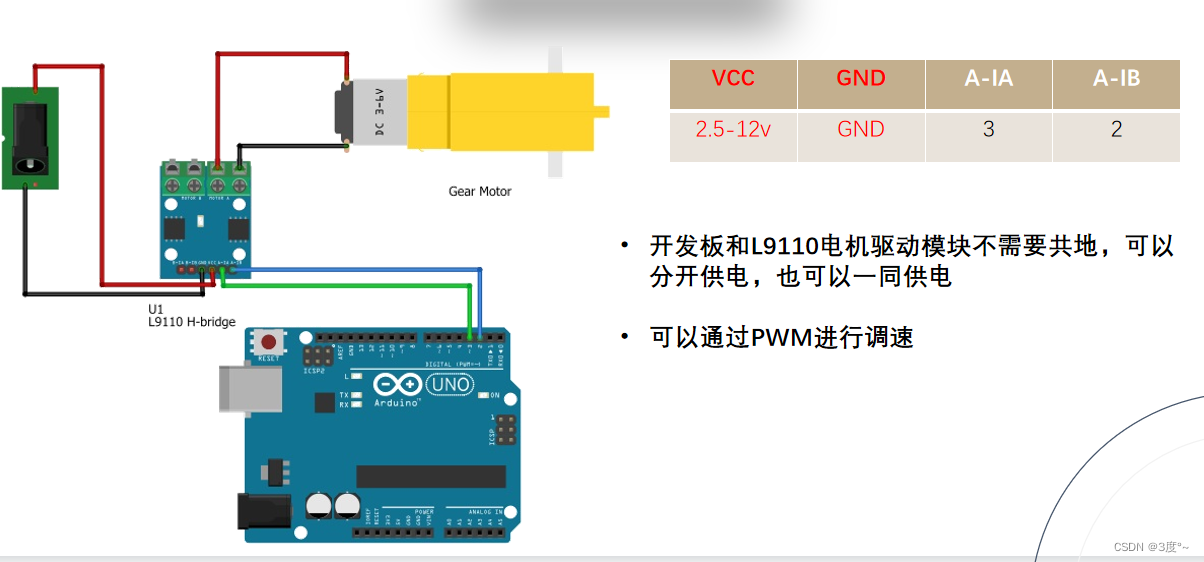

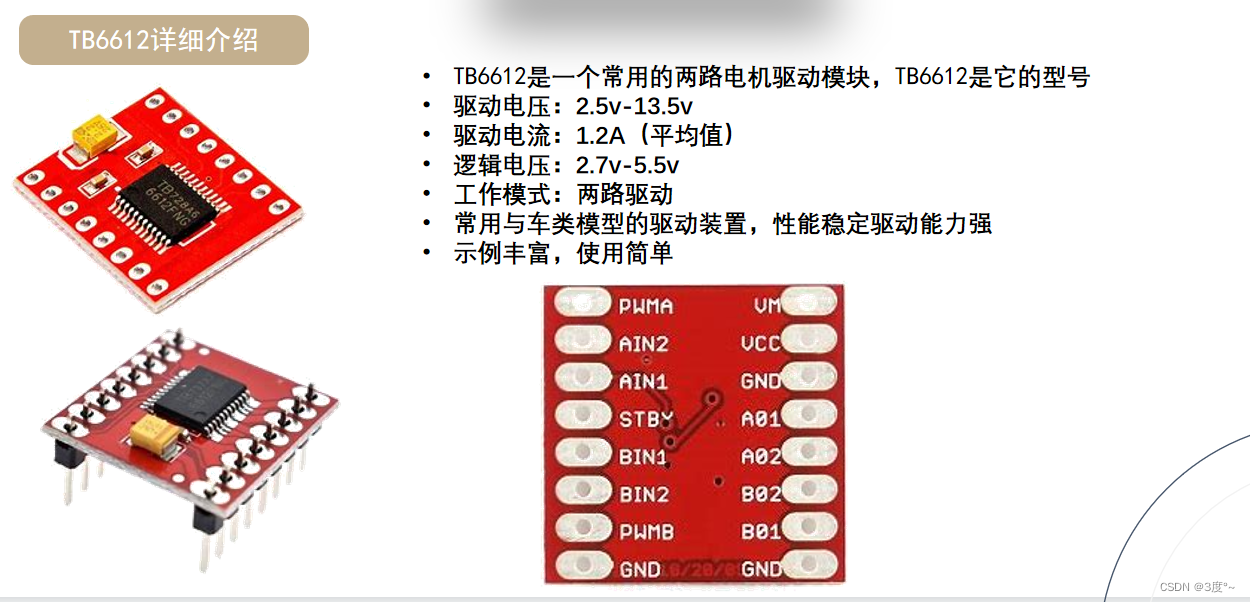
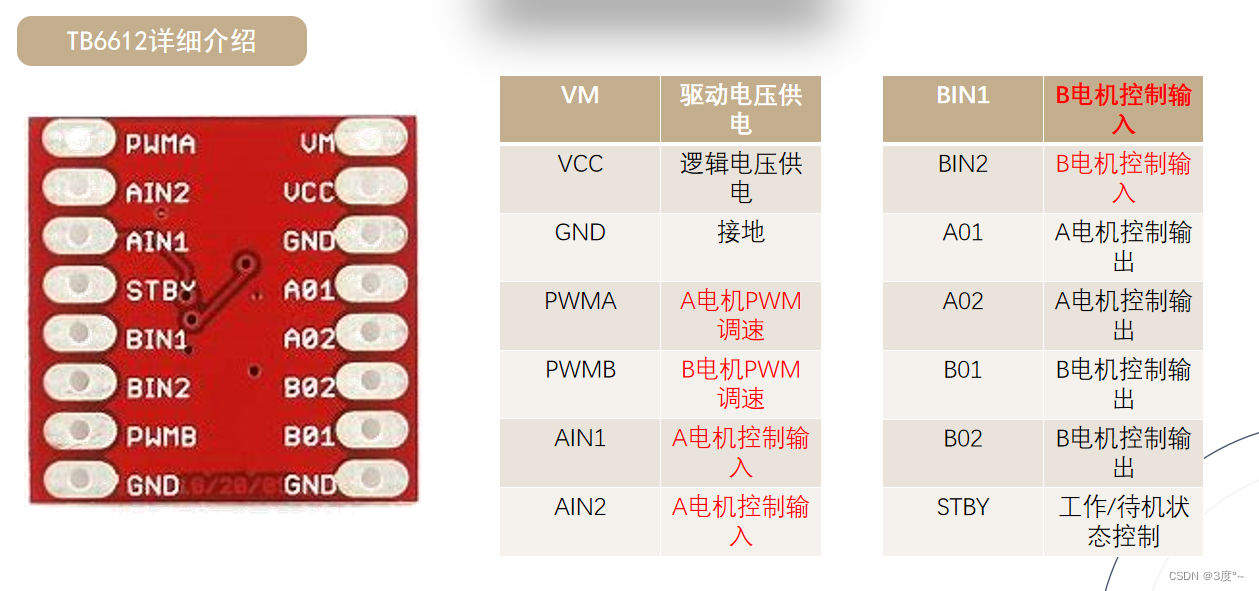
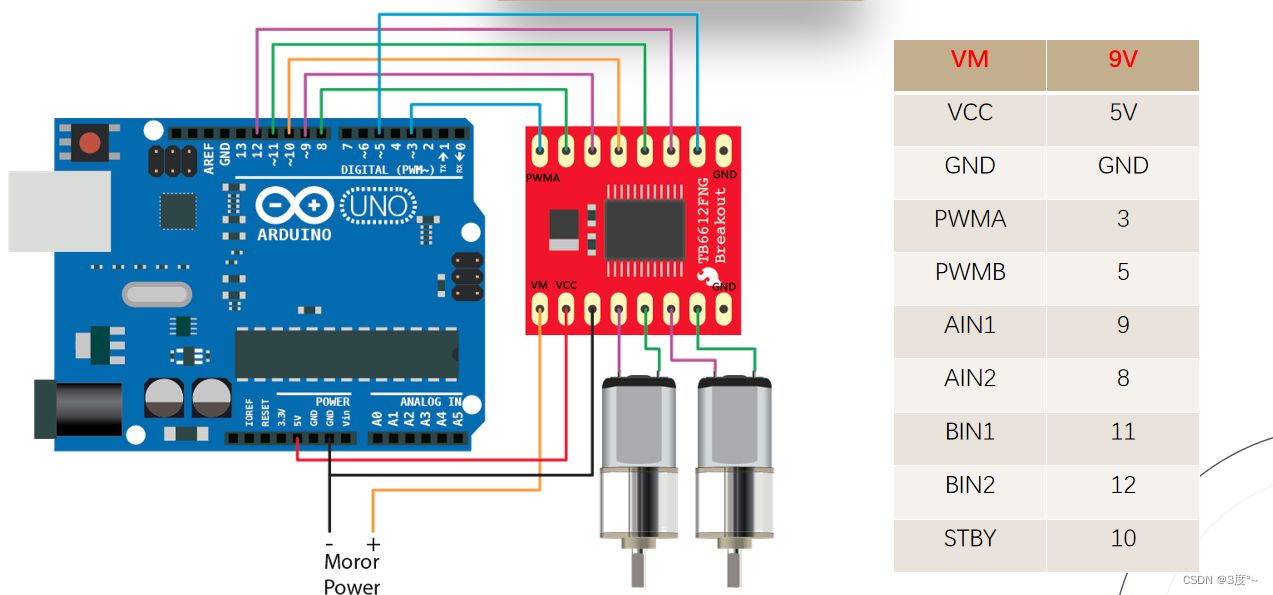
TB6612电机驱动

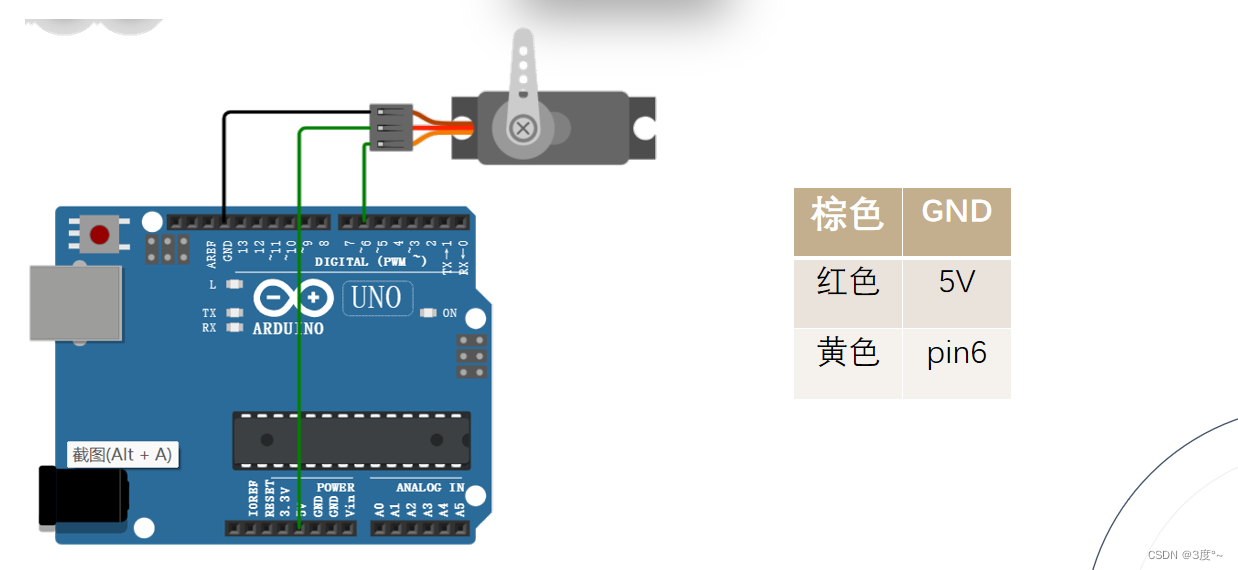
舵机使用


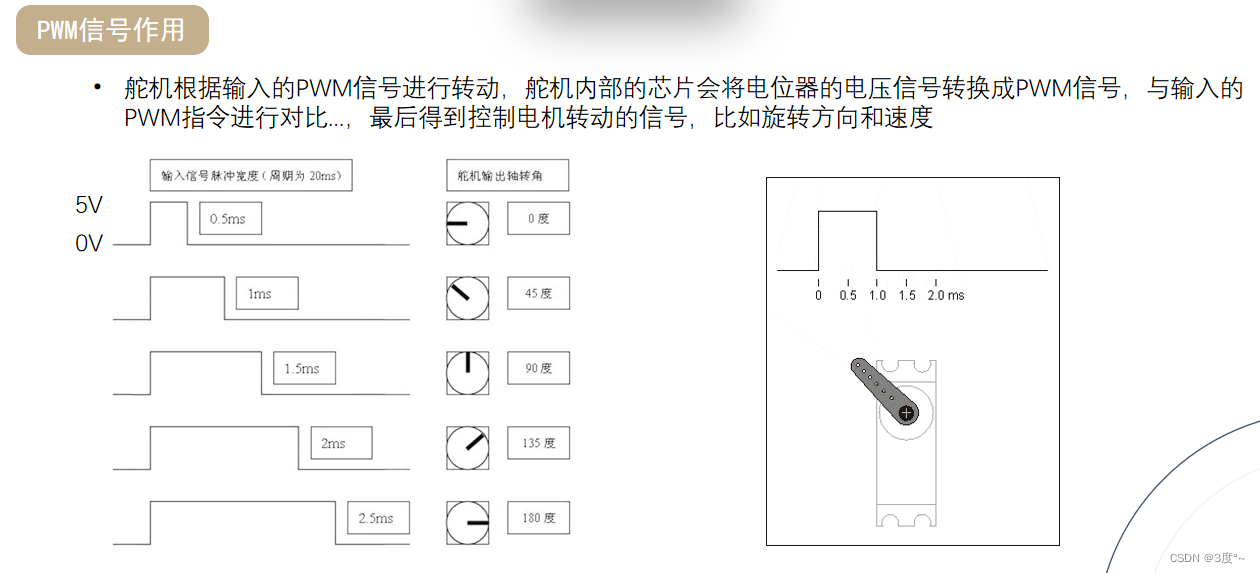



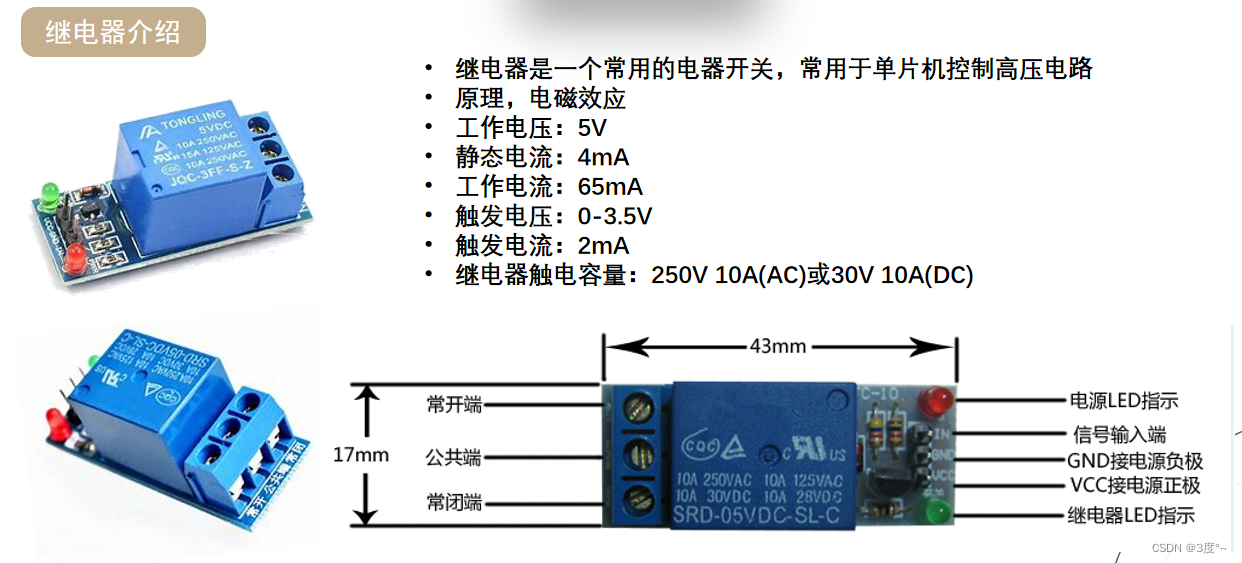
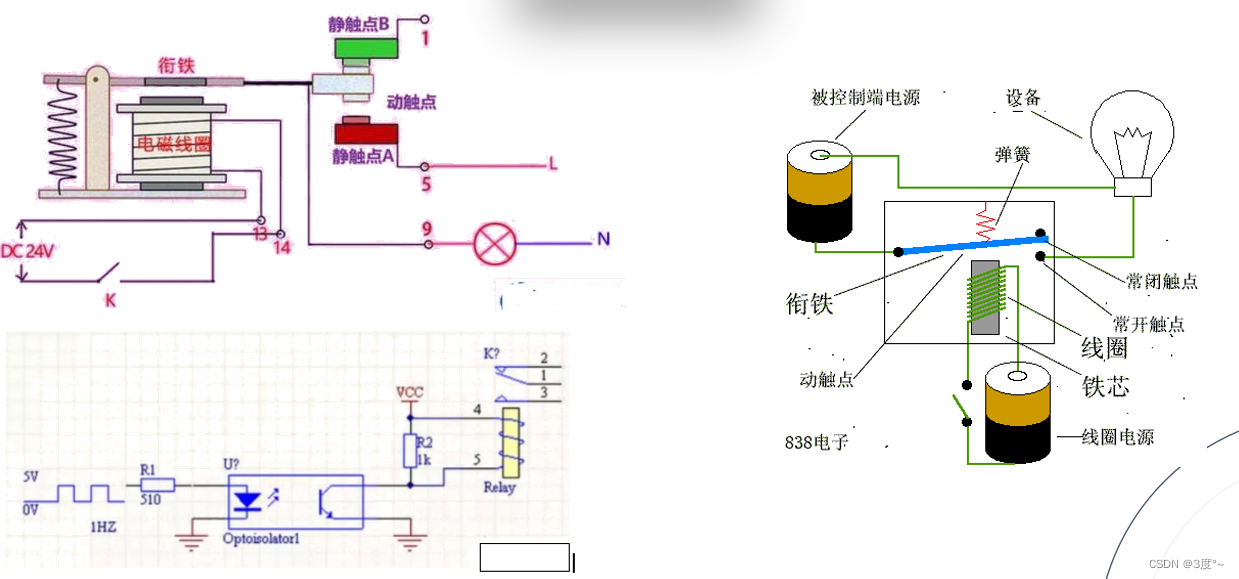
继电器使用
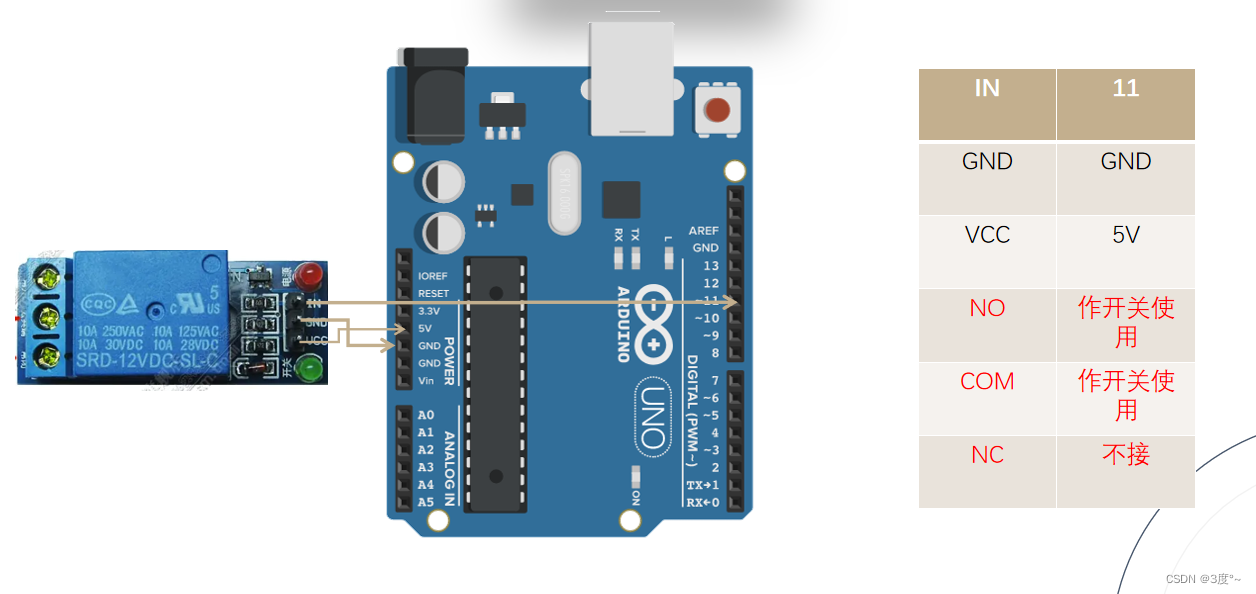

#define IN 11//设置信号触发引脚void setup() {
pinMode(IN,OUTPUT);//设置引脚模式为输出
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite(IN,LOW);//低电平触发
delay(3000);
digitalWrite(IN,HIGH);
delay(3000);
}这篇关于Arduino学习(B站up张居正)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!