本文主要是介绍【MySQL通关之旅】从山脚到山顶(傲视群雄版),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
查
基本查询 select
查询指定 name,age 字段并返回
select name,age from 表名
查询所有字段并返回
select * from 表名
查询指定 name,age 字段并起别名(姓名,性别) 返回
select name as ‘姓名’,age as ‘性别’ from 表名
去除某字段重复记录
select distinct 字段名 from 表名
基本查询 where
语法 select 字段名 from 表名
where筛选条件
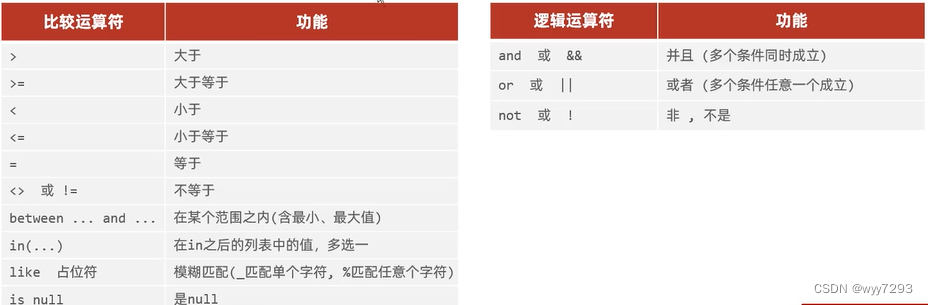
查询在某个范围之间的(包含最小和最大)
select * from 表名 where 字段名
between23 and 35查询年龄是23,24,25的数据
select * from 表名 where age = 23 or age = 24 or age = 25
select * from 表名 where agein(23,24,25)
查询姓名是两个字
select * from 表名 where name like ‘__’
查询姓名第一个字是张
select * from 表名 where name like ‘张%’
查询姓名最后一个字是张
select * from 表名 where name like ‘%张’
查询姓名中包含建
select * from 表名 where name like ‘%建%’
聚合函数
分组查询 group by
语法
- 在查询字段中只能使用分组字段和聚合函数
- 在分组后还要价筛选条件不能使用where,得使用having
查询入职时间在 ‘2023-05-20’ 之前的员工,并对职位
分组,获取员工数量>=2的职位
select 职位字段,count(*) from 表名 where create_time <= ‘2023-05-20’ group by 职位字段 having count(*) >=2
where与having区别
- 执行时机不同:where是分组之前进行过滤,不满足where条件,不参与分组,而having是分组之后对结果进行过滤
- 判断条件不同: where不能对聚合函数进行判断,而having可以。
- 执行顺序: where > 聚合函数 > having
扩展 if(条件表达式,true取值,false取值)select if(性别字段 == 0,‘女’,‘男’) as ‘age’,count(*) as ‘count’ from 表名 where create_time <= ‘2023-05-20’ group by 性别字段 having count >=2
扩展 (case 字段名 when 1 then '一' when 2 then '二' else '三' end)select (case 分组字段 when 1 then 班主任’ when 2 then ‘讲师’ when 3 then '学工主管 when 4 then ‘教研主管’ else ‘未分配职位’ end) as ‘职位’,count(*) from 表名 group by 分组字段;
排序查询 order by
排序方式order by 后面只能跟asc(升序) 或者desc(降序)根据入职时间进行降序排序,如果入职时间相等就对更新时间进行降序排序
select * from 表名 order by create_time desc,update_time desc
注意
- 如果是多字段排序,当第一个字段值相同时,才会根据第二个字段进行排序
分页查询
注意
- limit 起始索引从0开始
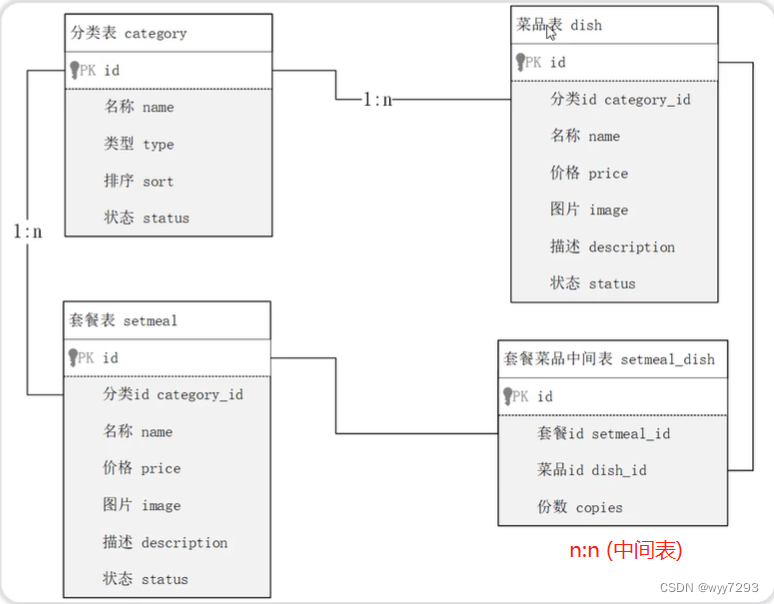
多表查询
多表具有三种关系
- 一对一
- 在任意一方中添加外键,关联另一方的主键
- 一对多
- 在多一方中添加外键,关联另一方的主键
- 多对多
- 添加中间表来关联,中间表中应至少有两个外键,来关联两张表的主键
内连接
根据入职时间进行降序排序,如果入职时间相等就对更新时间进行降序排序
select * from 表名 order by create_time desc,update_time desc
- 隐式内连接 查询员工姓名以及所属的部门 -> 消除笛卡尔积
- select 员工表.name,部门表.name from 员工表,部门表 where 员工表.部门表id = 部门表.id
起别名select a.name,b.name from 员工表 a,部门表 b where a.部门表id = b.id- 显式内连接 查询员工姓名以及所属的部门 -> 消除笛卡尔积
- select 员工表.name,部门表.name from 员工表 [inner] join 部门表 on 员工表.部门表id = 部门表.id
起别名select a.name,b.name from 员工表 a [inner] join 部门表 b on a.部门表id = b.id
外连接
左连接(以左边为准) 右连接(以右边为准)
- 左外连接 查询员工表 员工姓名以及所属的部门 (此时已左边员工表为准)
起别名select a.name,b.name from 员工表 as aleft[outer]join部门表 as bonwhere a.部门表id = b.id- 右外连接 查询部门表 员工姓名以及所属的部门 (此时已右边部门表为准)
起别名select a.name,b.name from 员工表 as aright[outer]join部门表 as bonwhere a.部门表id = b.id
案例
- 查询价格低于10元的菜品的名称 、价格及其菜品的所属分类
select d.name,d.price,c.name from dish as d left join category as c on where d.category_id = c.id and d.price < 10;- 查询所有价格在10元(含)到50元(含)之同 且 状态为”起售”的菜品,展示出菜品的名称、价格 及其菜品的分类名称即使求品没有分类 ,也需要将菜品查询出来)
select d.name,d.price,c.name from dish as d left join category as c on where d.category_id = c.id and d.price between 10 and 50 and d.status = 1;- 查询每个分类下最贵的菜品,展示出分类的名称、最贵的菜品的价格
select c.name,max(d.price) from category as c left join dish as d on where d.category_id = c.id group by c.name;- 查询各个分类下菜品状态为’起售’, 并且该分类下菜品总数大于等于3的分类名称
select c.name,count(*) as ct from dish as d left join category as c on where d.category_id = c.id and d.status = 1 group by c.name having ct >= 3;- 查询出"商务套餐A" 中包含哪些菜品(菜品名称、价格、份数)
select s.name,s.price,d.name,d.price,sd.copies from setmeal as s ,setmeal_dish as sd, dish as d where s.id = sd.setmeal_id and sd.dish_id = d.id and s.name = ‘商务套餐A’;- 查询出低于菜品平均价格的菜品信息
select * from dish shere price < (select avg(price) from dish);
这篇关于【MySQL通关之旅】从山脚到山顶(傲视群雄版)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!