本文主要是介绍AWS助理架构师认证培训 | EC2 Fundamentals,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
视频来源:B站《AWS 认证解决方案架构师 助理级 SAA-C03》
一边学习一边整理老师的课程内容及试验笔记,并与大家分享,侵权即删,谢谢支持!
附上汇总贴:AWS助理架构师认证培训 | 汇总_热爱编程的通信人的博客-CSDN博客
EC2 Basics
Amazon EC2
- EC2 is one of the most popular of AWS' offering
- EC2 = Elastic Compute Cloud = Infrastructure as a Service
- It mainly consists in the capability of:Renting virtual machines (EC2)Storing data on virtual drives (EBS)Distributing load across machines (ELB)Scaling the services using an auto-scaling group (ASG)
- Knowing EC2 is fundamental to understand how the Cloud works
EC2 sizing & configuration options
- Operating System (OS): Linux, Windows or Mac OS
- How much compute power & cores (CPU)
- How much random-access memory (RAM)
- How much storage space:Network-attached (EBS & EFS)hardware (EC2 Instance Store)
- Network card: speed of the card, Public IP address
- Firewall rules: security group
- Bootstrap script (configure at first launch): EC2 User Data
EC2 User Data
- lt is possible to bootstrap our instances using an EC2 User data script
- bootstrapping means launching commands when a machine starts
- That script is only run once at the instance first start
- EC2 user data is used to automate boot tasks such as:Installing updatesInstalling softwareDownloading common files from the internetAnything you can think of
- The EC2 User Data Script runs with the root user
EC2 instance types: example

t2.micro is part of the AWS free tier (up to 750 hours per month)
Create an EC2 Instance with EC2 User Data to have a Website Hands on
Hands-On: Launching an EC2 Instance running Linux
- We'll be launching our first virtual server using the AWS Console
- We'll get a first high-level approach to the various parameters
- We'll see that our web server is launched using EC2 user data
EC2 Instance Types Basics
EC2 Instance Types - Overview
- You can use different types of EC2 instances that are optimised for different use cases (https://aws.amazon.com/ec2/instance-types/)

- AWS has the following naming convention:
m5.2xlarge
- m: instance class
- 5: generation (AWS improves them over time)
- 2xlarge: size within the instance class
EC2 Instance Types - General Purpose
- Great for a diversity of workloads such as web servers or code repositories
- Balance between:ComputeMemoryNetworking
- In the course, we will be using the t2.micro which is a General Purpose EC2 instance

EC2 Instance Types - Compute Optimized
- Great for compute-intensive tasks that require high performance processors:Batch processing workloadsMedia transcodingHigh performance web serversHigh performance computing (HPC)Scientific modeling &machine learningDedicated gaming servers

EC2 Instance Types - Memory Optimized
- Fast performance for workloads that process large data sets in memory
- Use cases:High performance, relational/non-relational databases Distributed web scale cache stores In-memory databases optimized for BI (business intelligence)Applications performing real-time processing of big unstructured data

EC2 Instance Types - Storage Optimized
- Great for storage-intensive tasks that require high, sequential read and write access to large data sets on local storage
- Use cases:High frequency online transaction processing (OLTP) systemsRelational & NoSQL databasesCache for in-memory databases (for example, Redis)Data warehousing applicationsDistributed file systems

EC2 Instance Type: example

Security Groups & Classic Ports Overview
Introduction to Security Groups
- Security Groups are the fundamental of network security in AWS
- They control how traffic is allowed into or out of our EC2 Instances

- Security groups only contain allow rules
- Security groups rules can reference by IP or by security group
Security Groups Deeper Dive
- Security groups are acting as a "firewall" on EC2 instances
- They regulate:Access to PortsAuthorised IP ranges - IPv4 and IPv6Control of inbound network (from other to the instance)Control of outbound network (from the instance to other)
Security Groups Diagram

Security Groups Good to know
- Can be attached to multiple instances
- Locked down to a region/VPC combination
- Does live "outside" the EC2 - if traffic is blocked the EC2 instance won't see it
- It's good to maintain one separate security group for SSH access
- If your application is not accessible (timeout), then it's a security group issue
- lf your application gives a "connection refused" error, then it's an application error or it's not launched
- All inbound traffic is blocked by default
- All outbound traffic is authorised by default
Referencing other security groups Diaram

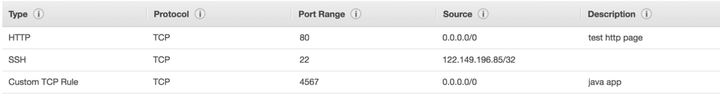
Classic Ports to know
- 22 = SSH (Secure Shell) - log into a Linux instance
- 21 = FTP (File Transfer Protocol) - upload files into a file share
- 22 = SFTP (Secure File Transfer Protocol) - upload files using SSH
- 80 = HTTP - access unsecured websites
- 443 = HTTPS - access secured websites
- 3389 = RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol) - log into a Windows instance
SSH Overview
SSH Summary Table

Which Lectures to watch
- Mac / Linux:SSH on Mac / Linux lecture
- Windows:Putty LectureIf Windows 10: SSH on Windows 10 lecture
- All:EC2 Instance Connect lecture
SSH troubleshooting
- Students have the most problems with SSH
- lf things don't work...Re-watch the lecture. You may have missed something Read the troubleshooting guide Try EC2 Instance Connect
- If one method works (SSH, Putty or EC2 Instance Connect) you're good
- If no method works, that's okay, the course won't use SSH much
How to SSH using Linux or MAC
How to SSH into your EC2 Instance Linux / Mac OS X
- We'll learn how to SSH into your EC2 instance using Linux / Mac
- SSH is one of the most important function. It allows you to control a remote machine, all using the command line.

How to SSH using Windows
How to SSH into your EC2 Instance Windows
- We'll learn how to SSH into your EC2 instance using Windows
- SSH is one of the most important function. It allows you to control a remote machine, all using the command line

- We will configure all the required parameters necessary for doing SSH on Windows using the free tool Putty
EC2 Instance Purchasing Options
EC2 Instances Purchasing Options
- On-Demand Instances - short workload, predictable pricing, pay by second
- Reserved (1 & 3 years)Reserved Instances - long workloadsConvertible Reserved Instances - long workloads with flexible instances
- Savings Plans (1 & 3 years) - commitment to an amount of usage, long workload
- Spot Instances - short workloads, cheap, can lose instances (less reliable)
- Dedicated Hosts - book an entire physical server, control instance placement
- Dedicated Instances - no other customers will share your hardware
- Capacity Reservations - reserve capacity in a specific AZ for any duration
EC2 On Demand
- Pay for what you use:Linux or Windows - billing per second, after the first minuteAll other operating systems - billing per hour
- Has the highest cost but no upfront payment
- No long-term commitment
- Recommended for short-term and un-interrupted workloads, where you can't predict how the application will behave
EC2 Reserved Instances
- Up to 72% discount compared to On-demand
- You reserve a specific instance attributes (Instance Type, Region, Tenancy, OS)
- Reservation Period - 1 year (+discount) or 3 years (+++discount)
- Payment Options - No Upfront (+), Partial Upfront (++), All Upfront (+++)
- Reserved Instance's Scope - Regional or Zonal (reserve capacity in an AZ)
- Recommended for steady-state usage applications (think database)
- You can buy and sell in the Reserved Instance Marketplace
- Convertible Reserved InstanceCan change the EC2 instance type, instance family, OS, scope and tenancy Up to 66% discount
EC2 Savings Plans
- Get a discount based on long-term usage (up to 72% - same as Rls)
- Commit to a certain type of usage ($ 10/hour for 1 or 3 years)
- Usage beyond EC2 Savings Plans is billed at the On-Demand price
- Locked to a specifc instance family & AWS region (e.g., M5 in us-east-1)
- Flexible across:Instance Size (e.g., m5.xlarge, m5.2xlarge)OS (e.g., Linux, Windows)Tenancy (Host, Dedicated, Default)
EC2 Spot Instances
- Can get a discount of up to 90% compared to On-demand
- Instances that you can "lose" at any point of time if your max price is less than the current spot price
- The MOST cost-efficient instances in AWS
- Useful for workloads that are resilient to failureBatch jobsData analysislmage processingAny distributed workloadsWorkloads with a flexible start and end time
- Not suitable for critical jobs or databases
EC2 Dedicated Hosts
- A physical server with EC2 instance capacity full dedicated to your use
- Allows you address compliance requirements an d use your existing server-bound software licenses (per-socket, per-core, pe-VM software licenses)
- Purchasing Options:On-demand - pay per second for active Dedicated HostReserved - 1 or 3 years (No Upfront, Partial Upfront, All Upfront)
- The most expensive option
- Useful for software that have complicated licensing model (BYOL - Bring Your Own License)
- Or for companies that have strong regulatory or compliance needs
EC2 Dedicated lnstances
- Instances run on hardware that's dedicated to you
- May share hardware with other instances in same account
- No control over instance placement (can move hardware after Stop/Start)

EC2 Capacity Reservations
- Reserve On-Demand instances capacity in a specifc AZ for any duration
- You always have access to EC2 capacity when you need it
- No time commitment (create/cancel anytime), no biling discounts
- Combine with Regional Reserved Instances and Savings Plans to benefit from billing discounts
- You're charged at On-Demand rate whether you run instances or not
- Suitable for short-term, uninterrupted workloads that needs to be in a specific AZ
Which purchasing option is right for me?
- On demand: coming and staying in resort whenever we like, we pay the full price
- Reserved: like planning ahead and if we plan to stay for along time, we may get a good discount
- Savings Plans: pay a certain amount per hour for certain period and stay in any room type (e.g., King, Suite, SeaView, ...)
- Spot instances: the hotel allows people to bid for the empty rooms and the highest bidder keeps the rooms. You can get kicked out at anytime
- Dedicated Hosts: We book an entire building of the resort
- Capacity Reservations: you book a room for a period with full price even you don't stay in it

Price Comparison Example - m4.large - us-east-1

Spot Instances & Spot Fleet
EC2 Spot Instance Requests
- Can get a discount of up to 90% compared to On-demand
- Define max spot price and get the instance while current spot price < maxThe hourly spot price varies based on offer and capacityIf the current spot price > your max price you can choose to stop or terminate your instance with a 2 minutes grace period.
- Other strategy: Spot Block"block" spot instance during a specified time frame (1 to 6 hours) without interruptions In rare situations, the instance may be reclaimed
- Used for batch jobs, data analysis, or workloads that are resilient to failures
- Not great for critical jobs or databases
EC2 Spot Instances Pricing

How to terminate Spot Instances?


Spot Fleets
- Spot Fleets = set of Spot Instances + (optional) On-Demand Instances
- The Spot Fleet will try to meet the target capacity with price constraints Define possible launch pools: instance type (m5.large), OS, Availabilty Zone Can have multiple launch pools, so that the fleet can chooseSpot Fleet stops launching instances when reaching capacity or max cost
- Strategies to allocate Spot Instances:lowest Price: from the pool with the lowest price (cost optimization, short workload)diversified: distributed across all pools (great for availability, long workloads)capacityOptimized: pool with the optimal capacity for the number of instances
- Spot Fleets allow us to automatically request Spot Instances with the lowest price
这篇关于AWS助理架构师认证培训 | EC2 Fundamentals的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!








