本文主要是介绍SS-nbt和FCB模块实现,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
目录
- 前言
- LEDNet中的SS-nbt模块
- LRNNET中的FCB模块
前言

论文链接:LRNNET - 轻量级实时语义分割算法
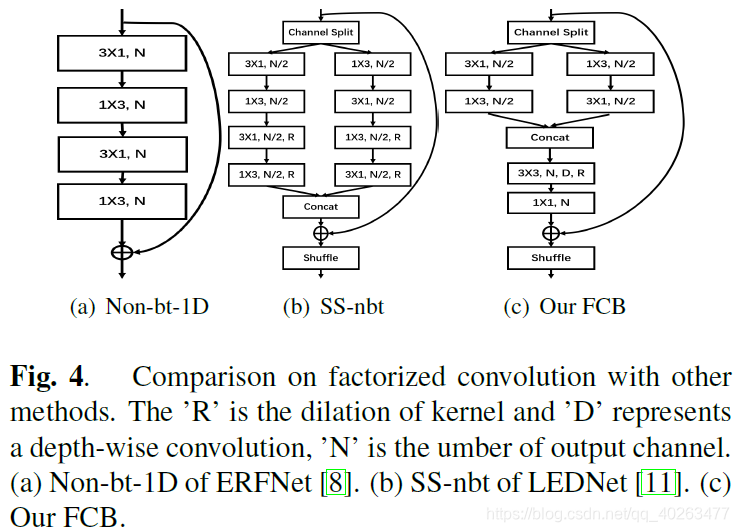
LEDNet中的SS-nbt模块
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
def Split(x):c = int(x.size()[1])c1 = round(c * 0.5)x1 = x[:, :c1, :, :].contiguous()x2 = x[:, c1:, :, :].contiguous()return x1, x2 def Merge(x1,x2):return torch.cat((x1,x2),1) def Channel_shuffle(x, groups):batchsize, num_channels, height, width = x.data.size()channels_per_group = num_channels // groups#reshapex = x.view(batchsize, groups,channels_per_group, height, width)x = torch.transpose(x, 1, 2).contiguous()#flattenx = x.view(batchsize, -1, height,width)return xclass SS_nbt_module(nn.Module):def __init__(self, chann, dropprob, dilated): super().__init__()oup_inc = chann//2#dwself.conv3x1_1_l = nn.Conv2d(oup_inc, oup_inc, (3,1), stride=1, padding=(1,0), bias=True)self.conv1x3_1_l = nn.Conv2d(oup_inc, oup_inc, (1,3), stride=1, padding=(0,1), bias=True)self.bn1_l = nn.BatchNorm2d(oup_inc, eps=1e-03)self.conv3x1_2_l = nn.Conv2d(oup_inc, oup_inc, (3,1), stride=1, padding=(1*dilated,0), bias=True, dilation = (dilated,1))self.conv1x3_2_l = nn.Conv2d(oup_inc, oup_inc, (1,3), stride=1, padding=(0,1*dilated), bias=True, dilation = (1,dilated))self.bn2_l = nn.BatchNorm2d(oup_inc, eps=1e-03)#dwself.conv3x1_1_r = nn.Conv2d(oup_inc, oup_inc, (3,1), stride=1, padding=(1,0), bias=True)self.conv1x3_1_r = nn.Conv2d(oup_inc, oup_inc, (1,3), stride=1, padding=(0,1), bias=True)self.bn1_r = nn.BatchNorm2d(oup_inc, eps=1e-03)self.conv3x1_2_r = nn.Conv2d(oup_inc, oup_inc, (3,1), stride=1, padding=(1*dilated,0), bias=True, dilation = (dilated,1))self.conv1x3_2_r = nn.Conv2d(oup_inc, oup_inc, (1,3), stride=1, padding=(0,1*dilated), bias=True, dilation = (1,dilated))self.bn2_r = nn.BatchNorm2d(oup_inc, eps=1e-03) self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)self.dropout = nn.Dropout2d(dropprob)# self.channel_shuffle = PermutationBlock(2)def forward(self, x):residual = xx1, x2 = Split(x)output1 = self.conv3x1_1_l(x1)output1 = self.relu(output1)output1 = self.conv1x3_1_l(output1)output1 = self.bn1_l(output1)output1_mid = self.relu(output1)output2 = self.conv1x3_1_r(x2)output2 = self.relu(output2)output2 = self.conv3x1_1_r(output2)output2 = self.bn1_r(output2)output2_mid = self.relu(output2)output1 = self.conv3x1_2_l(output1_mid)output1 = self.relu(output1)output1 = self.conv1x3_2_l(output1)output1 = self.bn2_l(output1)output2 = self.conv1x3_2_r(output2_mid)output2 = self.relu(output2)output2 = self.conv3x1_2_r(output2)output2 = self.bn2_r(output2)if (self.dropout.p != 0):output1 = self.dropout(output1)output2 = self.dropout(output2)out = Merge(output1, output2)out = F.relu(residual + out)# out = self.channel_shuffle(out) ### channel shuffleout = Channel_shuffle(out, 2) ### channel shufflereturn out# return ### channel shuffle
if __name__ == '__main__':ss_nbt = SS_nbt_module(256, 0.2, 6).cuda()input = torch.randn([1, 256, 14, 14]).cuda()y = ss_nbt(input)print(y.shape)
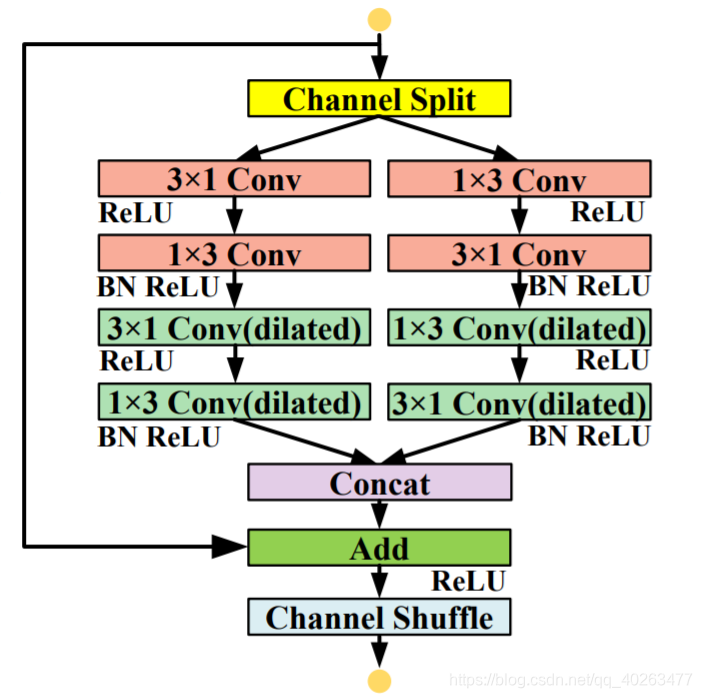
LRNNET中的FCB模块
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
def Split(x):c = int(x.size()[1])c1 = round(c * 0.5)x1 = x[:, :c1, :, :].contiguous()x2 = x[:, c1:, :, :].contiguous()return x1, x2 def Merge(x1,x2):return torch.cat((x1,x2),1) def Channel_shuffle(x, groups):batchsize, num_channels, height, width = x.data.size()channels_per_group = num_channels // groups#reshapex = x.view(batchsize, groups,channels_per_group, height, width)x = torch.transpose(x, 1, 2).contiguous()#flattenx = x.view(batchsize, -1, height,width)return xclass FCB_module(nn.Module):def __init__(self, chann, dropprob, dilated): super().__init__()oup_inc = chann//2#dwself.conv3x1_1_l = nn.Conv2d(oup_inc, oup_inc, (3,1), stride=1, padding=(1,0), bias=True)self.conv1x3_1_l = nn.Conv2d(oup_inc, oup_inc, (1,3), stride=1, padding=(0,1), bias=True)self.bn1_l = nn.BatchNorm2d(oup_inc, eps=1e-03)#dwself.conv3x1_1_r = nn.Conv2d(oup_inc, oup_inc, (3,1), stride=1, padding=(1,0), bias=True)self.conv1x3_1_r = nn.Conv2d(oup_inc, oup_inc, (1,3), stride=1, padding=(0,1), bias=True)self.bn1_r = nn.BatchNorm2d(oup_inc, eps=1e-03)#dsself.conv3x3 = nn.Conv2d(chann, chann, (3,3), stride=1, padding=(1*dilated, 1*dilated), bias=True, dilation = (dilated, dilated))self.conv1x1 = nn.Conv2d(chann, chann, (1,1), stride=1)self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(chann, eps=1e-03) self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)self.dropout = nn.Dropout2d(dropprob)# self.channel_shuffle = PermutationBlock(2)def forward(self, x):residual = xx1, x2 = Split(x)output1 = self.conv3x1_1_l(x1)output1 = self.relu(output1)output1 = self.conv1x3_1_l(output1)output1 = self.bn1_l(output1)output1_mid = self.relu(output1)output2 = self.conv1x3_1_r(x2)output2 = self.relu(output2)output2 = self.conv3x1_1_r(output2)output2 = self.bn1_r(output2)output2_mid = self.relu(output2)if (self.dropout.p != 0):output1_mid = self.dropout(output1_mid)output2_mid = self.dropout(output2_mid) output = Merge(output1_mid, output2_mid)output = F.relu(output)output = self.conv3x3(output)output = self.relu(output)output = self.conv1x1(output)output = self.bn2(output)output = F.relu(residual + output)# out = self.channel_shuffle(out) ### channel shuffleoutput = Channel_shuffle(output, 2) ### channel shufflereturn output# return ### channel shuffle
if __name__ == '__main__':fcb = FCB_module(256, 0.2, 6).cuda()input = torch.randn([1, 256, 14, 14]).cuda()y = fcb(input)print(y.shape)
这篇关于SS-nbt和FCB模块实现的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






