本文主要是介绍Python运维学习Day02-subprocess/threading/psutil,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
文章目录
- 1. 检测网段在线主机
- 2. 获取系统变量的模块 psutil
1. 检测网段在线主机
import subprocessdef checkIP(ip):cmd = f'ping -n 1 -w 1 {ip}'null = open('nlll',mode='wb')status = subprocess.call(cmd,shell=True,stdout=null,stderr=null)if status == 0:print(f"主机[{ip}]在线")null.close()if __name__ == '__main__':for i in range(1,255,1):ip = f"192.169.3.{i}"checkIP(ip)运行结果:
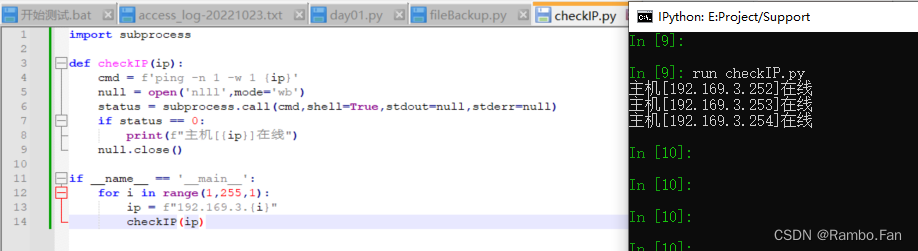
我们看看 subprocess.call的用法
In [10]: subprocess.call??
Signature: subprocess.call(*popenargs, timeout=None, **kwargs)
Source:
def call(*popenargs, timeout=None, **kwargs):"""Run command with arguments. Wait for command to complete ortimeout, then return the returncode attribute.The arguments are the same as for the Popen constructor. Example:retcode = call(["ls", "-l"])"""with Popen(*popenargs, **kwargs) as p:try:return p.wait(timeout=timeout)except: # Including KeyboardInterrupt, wait handled that.p.kill()# We don't call p.wait() again as p.__exit__ does that for us.raise
File: c:\users\thinkpad\appdata\local\programs\python\python39\lib\subprocess.py
Type: function该函数运行一条带参数的命令,返回值执行命令的返回码,运行时发现如此串联运行太慢了,我们修改下代码让其并行运行。
import subprocess
import threadingdef checkIP(ip):cmd = f'ping -n 1 -w 1 {ip}'null = open('nlll',mode='wb')status = subprocess.call(cmd,shell=True,stdout=null,stderr=null)if status == 0:print(f"主机[{ip}]在线")null.close()if __name__ == '__main__':for i in range(1,255,1):ip = f"192.169.3.{i}"ping_threading = threading.Thread(target=checkIP,args=(ip,))ping_threading.start()
我们看一下threading.Thread的用法
In [12]: threading.Thread??
Init signature:
threading.Thread(group=None,target=None,name=None,args=(),kwargs=None,*,daemon=None,
)
Source:
class Thread:"""A class that represents a thread of control.This class can be safely subclassed in a limited fashion. There are two waysto specify the activity: by passing a callable object to the constructor, orby overriding the run() method in a subclass."""_initialized = Falsedef __init__(self, group=None, target=None, name=None,args=(), kwargs=None, *, daemon=None):"""This constructor should always be called with keyword arguments. Arguments are:*group* should be None; reserved for future extension when a ThreadGroupclass is implemented.*target* is the callable object to be invoked by the run()method. Defaults to None, meaning nothing is called.*name* is the thread name. By default, a unique name is constructed ofthe form "Thread-N" where N is a small decimal number.*args* is the argument tuple for the target invocation. Defaults to ().*kwargs* is a dictionary of keyword arguments for the targetinvocation. Defaults to {}.If a subclass overrides the constructor, it must make sure to invokethe base class constructor (Thread.__init__()) before doing anythingelse to the thread."""assert group is None, "group argument must be None for now"if kwargs is None:kwargs = {}self._target = targetself._name = str(name or _newname())self._args = argsself._kwargs = kwargsif daemon is not None:self._daemonic = daemonelse:self._daemonic = current_thread().daemonself._ident = Noneif _HAVE_THREAD_NATIVE_ID:self._native_id = Noneself._tstate_lock = Noneself._started = Event()self._is_stopped = Falseself._initialized = True# Copy of sys.stderr used by self._invoke_excepthook()self._stderr = _sys.stderrself._invoke_excepthook = _make_invoke_excepthook()# For debugging and _after_fork()_dangling.add(self)def _reset_internal_locks(self, is_alive):# private! Called by _after_fork() to reset our internal locks as# they may be in an invalid state leading to a deadlock or crash.self._started._at_fork_reinit()if is_alive:# bpo-42350: If the fork happens when the thread is already stopped# (ex: after threading._shutdown() has been called), _tstate_lock# is None. Do nothing in this case.if self._tstate_lock is not None:self._tstate_lock._at_fork_reinit()self._tstate_lock.acquire()else:# The thread isn't alive after fork: it doesn't have a tstate# anymore.self._is_stopped = Trueself._tstate_lock = Nonedef __repr__(self):assert self._initialized, "Thread.__init__() was not called"status = "initial"if self._started.is_set():status = "started"self.is_alive() # easy way to get ._is_stopped set when appropriateif self._is_stopped:status = "stopped"if self._daemonic:status += " daemon"if self._ident is not None:status += " %s" % self._identreturn "<%s(%s, %s)>" % (self.__class__.__name__, self._name, status)def start(self):"""Start the thread's activity.It must be called at most once per thread object. It arranges for theobject's run() method to be invoked in a separate thread of control.This method will raise a RuntimeError if called more than once on thesame thread object."""if not self._initialized:raise RuntimeError("thread.__init__() not called")if self._started.is_set():raise RuntimeError("threads can only be started once")with _active_limbo_lock:_limbo[self] = selftry:_start_new_thread(self._bootstrap, ())except Exception:with _active_limbo_lock:del _limbo[self]raiseself._started.wait()def run(self):"""Method representing the thread's activity.You may override this method in a subclass. The standard run() methodinvokes the callable object passed to the object's constructor as thetarget argument, if any, with sequential and keyword arguments takenfrom the args and kwargs arguments, respectively."""try:if self._target:self._target(*self._args, **self._kwargs)finally:# Avoid a refcycle if the thread is running a function with# an argument that has a member that points to the thread.del self._target, self._args, self._kwargs
...
File: c:\users\thinkpad\appdata\local\programs\python\python39\lib\threading.py
Type: type
Subclasses: Timer, _MainThread, _DummyThread, HistorySavingThread
这里着重讲下几个重要参数和start方法
target: 一个回调函数,将会运行run()方法。
args: 元组对象,回调函数target的参数
start: 开始激活线程
2. 获取系统变量的模块 psutil
查看当前用户的名称,和开机时间
In [14]: import psutil as psIn [15]: ps.users()
Out[15]: [suser(name='ThinkPad', terminal=None, host=None, started=1698541200.6304576, pid=None)]In [16]: ps.users()[0]
Out[16]: suser(name='ThinkPad', terminal=None, host=None, started=1698541200.6304576, pid=None)In [17]: ps.users()[0].started
Out[17]: 1698541200.6304576In [18]: import datetimeIn [19]: t = ps.users()[0].startedIn [20]: datetime.datetime.fromtimestamp(t)
Out[20]: datetime.datetime(2023, 10, 29, 9, 0, 0, 630458)获取电脑cpu核数
In [23]: ps.cpu_count()
Out[23]: 8In [24]: ps.cpu_count??
Signature: ps.cpu_count(logical=True)
Source:
def cpu_count(logical=True):"""Return the number of logical CPUs in the system (same asos.cpu_count() in Python 3.4).If *logical* is False return the number of physical cores only(e.g. hyper thread CPUs are excluded).Return None if undetermined.The return value is cached after first call.If desired cache can be cleared like this:>>> psutil.cpu_count.cache_clear()"""if logical:ret = _psplatform.cpu_count_logical()else:ret = _psplatform.cpu_count_cores()if ret is not None and ret < 1:ret = Nonereturn ret
File: c:\users\thinkpad\envs\support\lib\site-packages\psutil\__init__.py
Type: function
这里默认是获取的逻辑核,如果要获取是物理核数,需要加上参数logical=False
In [25]: ps.cpu_count(logical=False)
Out[25]: 4获取boot开机时间
In [29]: ps.boot_time??
Signature: ps.boot_time()
Source:
def boot_time():"""Return the system boot time expressed in seconds since the epoch."""# Note: we are not caching this because it is subject to# system clock updates.return _psplatform.boot_time()
File: c:\users\thinkpad\envs\support\lib\site-packages\psutil\__init__.py
Type: functionIn [30]: b = ps.boot_time()In [31]: b
Out[31]: 1698541187.1580527In [32]: datetime.datetime.fromtimestamp(b)
Out[32]: datetime.datetime(2023, 10, 29, 8, 59, 47, 158053)
获取电脑内存信息
In [36]: ps.virtual_memory()
Out[36]: svmem(total=17048784896, available=10635776000, percent=37.6, used=6413008896, free=10635776000)In [37]: ps.virtual_memory??
Signature: ps.virtual_memory()
Source:
def virtual_memory():"""Return statistics about system memory usage as a namedtupleincluding the following fields, expressed in bytes:- total:total physical memory available.- available:the memory that can be given instantly to processes without thesystem going into swap.This is calculated by summing different memory values dependingon the platform and it is supposed to be used to monitor actualmemory usage in a cross platform fashion.- percent:the percentage usage calculated as (total - available) / total * 100- used:memory used, calculated differently depending on the platform anddesigned for informational purposes only:macOS: active + wiredBSD: active + wired + cachedLinux: total - free- free:memory not being used at all (zeroed) that is readily available;note that this doesn't reflect the actual memory available(use 'available' instead)Platform-specific fields:- active (UNIX):memory currently in use or very recently used, and so it is in RAM.- inactive (UNIX):memory that is marked as not used.- buffers (BSD, Linux):cache for things like file system metadata.- cached (BSD, macOS):cache for various things.- wired (macOS, BSD):memory that is marked to always stay in RAM. It is never moved to disk.- shared (BSD):memory that may be simultaneously accessed by multiple processes.The sum of 'used' and 'available' does not necessarily equal total.On Windows 'available' and 'free' are the same."""global _TOTAL_PHYMEMret = _psplatform.virtual_memory()# cached for later use in Process.memory_percent()_TOTAL_PHYMEM = ret.totalreturn ret
File: c:\users\thinkpad\envs\support\lib\site-packages\psutil\__init__.py
Type: functionIn [38]:获取cpu性能,上下文切换,硬件中断,软件中断,系统调用
In [42]: ps.cpu_stats()
Out[42]: scpustats(ctx_switches=217425683, interrupts=185259877, soft_interrupts=0, syscalls=753877621)In [43]: ps.cpu_stats??
Signature: ps.cpu_stats()
Source:
def cpu_stats():"""Return CPU statistics."""return _psplatform.cpu_stats()
File: c:\users\thinkpad\envs\support\lib\site-packages\psutil\__init__.py
Type: function
```这篇关于Python运维学习Day02-subprocess/threading/psutil的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




