本文主要是介绍Linux中shell的执行流控制,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
目录
一、for语句
1、for语句的基本格式
2、示例
二、条件语句
1、while…do语句
2、until…do语句
3、if …then语句
4、示例
三、case语句
四、expect应答语句
1、固定答案
2、将expect与bash环境结合
3、示例
五、终止语句
一、for语句
- 作用:为循环执行动作
- for语句结构
for 定义变量
do 使用变量,执行动作
done 结束标志1、for语句的基本格式
格式一:全部列出,依次循环
for HOST in 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
doecho $HOST
done格式二:连续数字,依次循环
for HOST in {1..10}
doecho $HOST
done格式三:连续数字,用seq方式指定间隔,依次循环
for HOST in $(seq 1 2 10)
doecho $HOST
done格式四:for循环语句
for ((HOST=0;HOST<10;HOST++))
doecho $HOST
done2、示例
[ -z "$*" ] && {echo is null !!exit
}[ ! -e "$*" ] &>/dev/null &&{echo is not file !!exit
}||{for name in `cat $*`douseradd $name | echo $name is create !!done
}
二、条件语句
1、while…do语句
作用:条件为真时执行动作
语句结构:
while true
do
done2、until…do语句
作用:条件为假时执行动作
语句结构:
until false
do
done3、if …then语句
作用:多次判定条件执行动作
语句结构:
if
then
elif
then
...
else
fi4、示例
check_file.sh
please input filename: file
file is not exist
file is file
file is direcory 此脚本会一直询问直到用户输入exit为止
while true
read -p "Please input filename: " FILE
doif [ $FILE = "exit" ]thenecho "bye !!!"exitelif [ ! -e "$FILE" ]thenecho "Error: $FILE is not exist !!!"elif [ -f "$FILE" ]thenecho "$FILE is a file"elif [ -d "$FILE" ]thenecho "$FILE is a directory"fi
done 
三、case语句
作用:符合哪个条件时执行相应的动作,对于同级别的条件,执行效率更高,点名机制;而if语句判定时为从上到下判定,更适合不同级别的条件。
语句结构:
case $1 inword1|WORD1)action1;;word2|WORD2)action2;;*)action3
esac四、expect应答语句
作用:针对一些需要根据问题输入答案的命令,如ssh远程连接时,需要输入密码,第一次连接还需要输入yes等,问题不同,答案也不同。
- 为模拟此类问题,设定一个问题脚本,并给予执行权限
问题脚本:
read -p "what's your name:" NAME
read -p "How old are you: " AGE
read -p "Which objective: " OBJ
read -p "Are you ok? " OK
echo $NAME is $AGE\'s old study $OBJ feel $OK
执行问题脚本时,需要一个一个输入答案,也可以选择多行输入EOF,提前把答案写入,但如果问题发生变化,就会回答错误,此时就需要使用expect来根据问题进行回答。

应答脚本:
注意:系统默认没有expect,需要安装,expect有自己的独立环境,创建应答脚本answer.exp时要监控问题脚本
1、固定答案
\r:换行,exp_continue:没有遇到问题的关键字时,继续按expect执行
yum install expect -y
vim answer.exp#!/usr/bin/expect
spawn sh /mnt/yyl.sh
expect {"name" { send "yyl\r";exp_continue }"old" { send "22\r";exp_continue }"objective" { send "linux\r";exp_continue }"ok" { send "ok\r" }
}
expect eof 
2、将expect与bash环境结合
#!/bin/bash
/usr/bin/expect <<EOF
spawn /mnt/yyl.sh #yyl.sh 权限给
expect {"name" { send "$1\r";exp_continue }"old" { send "$2\r";exp_continue }"objective" { send "$3\r";exp_continue }"ok" { send "$4\r" }
}
expect eof
EOF
3、示例
host_list.sh 检测172.25.254.1-172.25.254.10网络是否开启 如果网络正常请生成解析列表hosts_list 格式如下 ip 主机名称 例如:172.25.254.1为开启状态主机名为westos_student1.westos.org hosts_list中 172.25.254.1 westos_student1.westos.org
#!/bin/bash
SSH_hostname()
{
/usr/bin/expect <<EOF
spawn ssh -l root $1 hostname
expect {"yes/no" { send "yes\r";exp_continue }"password" { send "123456\r" }
}
expect eof
EOF
}
for IP in 192.168.67.110
doping -c1 -w1 $IP &> /dev/null && {echo -e "$IP\t`SSH_hostname $IP | sed -n '$p'`" >> /mnt/hosts_list}
done 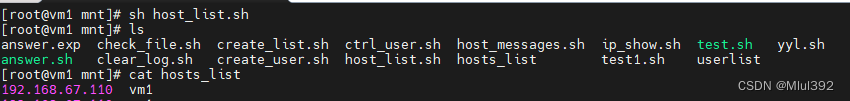
五、终止语句
continue | 终止当前循环提前进入下个循环 |
break | 终⽌当前所在语句所有动作进⾏语句外的其他动作 |
exit | 退出脚本 |
这篇关于Linux中shell的执行流控制的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






