本文主要是介绍php规范 psr,PHP中什么是PSR规范?,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
PHP中PSR规范指的是PHP标准规范,PSR是PHP Standard Recommendations的简写,是由PHP FIG组织制定的PHP规范,是PHP开发的实践标准。

PSR是PHP Standard Recommendations(PHP标准规范)的简写,是由PHP FIG组织制定的PHP规范,是PHP开发的实践标准。
PHP FIG,FIG 是 Framework Interoperability Group(框架可互用性小组)的缩写,由几位开源框架的开发者成立于 2009 年,从那开始也选取了很多其他成员进来(包括但不限于Laravel, Joomla, Drupal, Composer, Phalcon, Slim, Symfony, Zend Framework等),虽然不是「官方」组织,但也代表了大部分的 PHP 社区。
项目的目的在于:通过框架作者或者框架的代表之间讨论,以最低程度的限制,制定一个协作标准,各个框架遵循统一的编码规范,避免各家自行发展的风格阻碍了 PHP 的发展,解决这个程序设计师由来已久的困扰。
至今,php-fig已经发布了五个规范:PSR-0:自动加载标准,2014-10-21该标准已经被废弃,使用PSR-4替代,不再细讲
PSR-1:基本的编码风格
PSR-2:编码风格(更严格)
PSR-3:日志记录器接口
PSR-4:自动加载
PSR-1
PHP标签:
PHP代码必须放在<?php ?>标签或= ?>标签中。
编码:
PHP文件必须使用无BOM的UTF-8编码。
副作用:
一个PHP文件可以定义符号(比如类、函数、常量等),或者执行只有唯一副作用的操作(比如输出结果、处理数据等),但是不能同时做这两件事,尽量是一个PHP文件的功能单一。在操作的时候尽量把变量、类、函数的声明分开,通过include或require文件的方式来使用。
如下不符合规范:<?php
// 改变设置
ini_set('error_reporting', E_ALL);
// 加载文件
include "file.php";
// 打印输出
echo "\n";
// 声明
function foo()
{
// function body
}
符合规范如下:<?php
// 声明
function foo()
{
// function body
}
// 条件判断
if (! function_exists('bar')) {
function bar()
{
// function body
}
}
命名空间和类:
命名空间和类必须遵循PSR-4自动加载器标准。
类的名称:
每个类都有自己的命名空间,且都在顶级命名空间下,类名必须使用驼峰式(CamelCase)。
PHP 5.3 及以上,必须使用正式的命名空间,例如:<?php
// PHP 5.3 及以后
namespace Vendor\Model;
class Foo
{
}
PHP 5.3一下应该使用Vendor_开头的伪命名空间约定,例如:<?php
// PHP 5.3以下
class Vendor_Model_Foo
{
}
常量:
常量必须全部是用大写,并且使用下划线(_)分开。例如:<?php
namespace Vendor\Model;
class Foo
{
const VERSION = '1.0';
const DATE_APPROVED = '2012-06-01';
}
类的方法:
类的方法必须使用小写字母开头的驼峰式(camelCase)命名。
PSR-2
PSR-2是对PSR-1的PHP的扩充。
贯彻PSR-1:
使用PSR-2代码标准之前要先贯彻PSR-1的代码标准。
文件和代码行:
PHP文件必须使用Unix风格的换行符(LF, linefeed),最后要有一个空行,仅包含PHP代码的文件而且不能使用PHP关闭标签?>,每行代码不应该超过80个字符,每行末尾不能有空格,每行只能有一条语句,可以在适当的地方添加空行提高代码的阅读性。
不加上?>关闭标签,可以避免意料之外的输出错误,如果加上关闭标签,且在关闭标签后有空行,那么空行会被当成输出,导致意想不到的错误。
缩进:
必须以4个空格为缩进,不能使用制表符(Tab键)缩进。
在不同的编辑器中,空格的渲染效果基本一致,而制表符的宽度各有差异。
关键字:
PHP的关键字必须使用小写,而且true, false, 和 null也必须小写。
命名空间和use声明:
现在,namespace声明之后必须要有一个空行,而且use声明必须放在namespace之后,必须分别使用use引入命名空间,而且use后要有空行,例如:<?php
namespace Vendor\Package;
use FooClass;
use BarClass as Bar;
use OtherVendor\OtherPackage\BazClass;
// ... additional PHP code ...
类的继承和实现:
extends和implements关键字必须和类名在同一行,类、接口和Traits定义体的起始括号应该在类名之后新起一行,结束括号也必须新起一行,例如:<?php
namespace Vendor\Package;
use FooClass;
use BarClass as Bar;
use OtherVendor\OtherPackage\BazClass;
class ClassName extends ParentClass implements \ArrayAccess, \Countable
{
// constants, properties, methods
}
如果implements后面实现了很多接口导致一行很长,可以依次将需要的类另起新行并缩进4个空格,如下:<?php
namespace Vendor\Package;
use FooClass;
use BarClass as Bar;
use OtherVendor\OtherPackage\BazClass;
class ClassName extends ParentClass implements
\ArrayAccess,
\Countable,
\Serializable
{
// constants, properties, methods
}
可见性:
类中的每个属性和方法都要声明可见性,有public、private和protected,不能使用var关键词来声明,老版本的PHP会在私有属性前加上_,一行只能声明一个属性,例如:<?php
namespace Vendor\Package;
class ClassName
{
public $foo = null;
}
方法:
类中的所有方法也应该定义可见性,方法名后面不能有空格,方法体的括号位置和类定义体的括号位置一样,都要新起一行,结束括号也要新起一行。方法参数的起始圆括号之后没有空格,结束括号之前也没有空格,有多个参数是,每个参数的逗号后面加一个空格,例如:<?php
namespace Vendor\Package;
class ClassName
{
public function fooBarBaz($arg1, &$arg2, $arg3 = [])
{
// method body
}
}
如果参数比较多,需要换行时,可以如下:<?php
namespace Vendor\Package;
class ClassName
{
public function aVeryLongMethodName(
ClassTypeHint $arg1,
&$arg2,
array $arg3 = []
) {
// method body
}
}
abstract、final和static:
现在,abstract、final必须在可见性修饰符之前,static声明必须放在可见性修饰符之后,例如:<?php
namespace Vendor\Package;
abstract class ClassName
{
protected static $foo;
abstract protected function zim();
final public static function bar()
{
// method body
}
}
方法和函数的调用:
在调用方法和函数时,圆括号必须跟在函数名之后,函数的参数之间有一个空格:<?php
bar();
$foo->bar($arg1);
Foo::bar($arg2, $arg3);
如果参数比较多,一行放不下时,如下处理:<?php
$foo->bar(
$longArgument,
$longerArgument,
$muchLongerArgument
);
PHP的控制结构:
PHP的控制结构包括if、else、elseif、switch、case、while、do while、for、foreach、try和catch。如果这些关键词后面有一对原括号,开始括号前必须有一个空格,与方法和类的定义体不同,控制结构关键词后面的起始括号应该和控制结构关键词写在同一行,例如:<?php
$gorilla = new \Animals\Gorilla;
$ibis = new \Animals\StrawNeckedIbis;
if ($gorilla->isWake() === true) {
do {
$gorilla->beatChest();
} while ($ibis->isAsleep() === true);
$ibis->flyAway();
}
PHP闭包函数:
闭包函数在声明时,function关键词后必须有一个空格,同时use关键词前后也必须有一个空格。起始大括号不需要另起新行,详细的如下代码:<?php
$closureWithArgs = function ($arg1, $arg2) {
// body
};
$closureWithArgsAndVars = function ($arg1, $arg2) use ($var1, $var2) {
// body
};
闭包函数有多个参数时,处理方式和方法的参数一样:<?php
$longArgs_noVars = function (
$longArgument,
$longerArgument,
$muchLongerArgument
) {
// body
};
$noArgs_longVars = function () use (
$longVar1,
$longerVar2,
$muchLongerVar3
) {
// body
};
$longArgs_longVars = function (
$longArgument,
$longerArgument,
$muchLongerArgument
) use (
$longVar1,
$longerVar2,
$muchLongerVar3
) {
// body
};
$longArgs_shortVars = function (
$longArgument,
$longerArgument,
$muchLongerArgument
) use ($var1) {
// body
};
$shortArgs_longVars = function ($arg) use (
$longVar1,
$longerVar2,
$muchLongerVar3
) {
// body
};
注意:以上规则同样适用于将闭包作为函数或方法的参数,如下:<?php
$foo->bar(
$arg1,
function ($arg2) use ($var1) {
// body
},
$arg3
);
到2019-08-10,PSR-2已被官方废弃
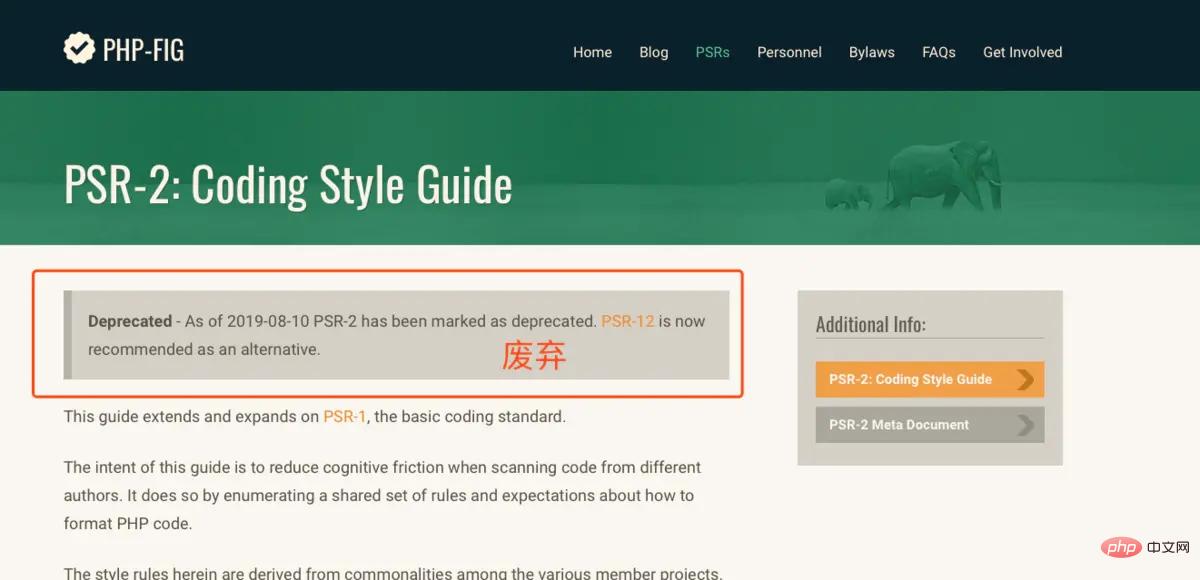
PSR-3
与PSR-1和PSR-2不同,PSR-3规定了一套通用的日志记录器接口(Psr\Log\LoggerInterface),为了符合PSR-3规范,框架必须实现该规范中的接口,这样可以更多的兼容第三方应用。PSR-3规范中包含了9个方法,每个方法都对应了RFC 5424协议的一个日志级别,而且都接受两个参数$message和$context,如下:<?php
namespace Psr\Log;
/**
* Describes a logger instance
*
* The message MUST be a string or object implementing __toString().
*
* The message MAY contain placeholders in the form: {foo} where foo
* will be replaced by the context data in key "foo".
*
* The context array can contain arbitrary data, the only assumption that
* can be made by implementors is that if an Exception instance is given
* to produce a stack trace, it MUST be in a key named "exception".
*
* See https://github.com/php-fig/fig-standards/blob/master/accepted/PSR-3-logger-interface.md
* for the full interface specification.
*/
interface LoggerInterface
{
/**
* System is unusable.
*
* @param string $message
* @param array $context
* @return void
*/
public function emergency($message, array $context = array());
/**
* Action must be taken immediately.
*
* Example: Entire website down, database unavailable, etc. This should
* trigger the SMS alerts and wake you up.
*
* @param string $message
* @param array $context
* @return void
*/
public function alert($message, array $context = array());
/**
* Critical conditions.
*
* Example: Application component unavailable, unexpected exception.
*
* @param string $message
* @param array $context
* @return void
*/
public function critical($message, array $context = array());
/**
* Runtime errors that do not require immediate action but should typically
* be logged and monitored.
*
* @param string $message
* @param array $context
* @return void
*/
public function error($message, array $context = array());
/**
* Exceptional occurrences that are not errors.
*
* Example: Use of deprecated APIs, poor use of an API, undesirable things
* that are not necessarily wrong.
*
* @param string $message
* @param array $context
* @return void
*/
public function warning($message, array $context = array());
/**
* Normal but significant events.
*
* @param string $message
* @param array $context
* @return void
*/
public function notice($message, array $context = array());
/**
* Interesting events.
*
* Example: User logs in, SQL logs.
*
* @param string $message
* @param array $context
* @return void
*/
public function info($message, array $context = array());
/**
* Detailed debug information.
*
* @param string $message
* @param array $context
* @return void
*/
public function debug($message, array $context = array());
/**
* Logs with an arbitrary level.
*
* @param mixed $level
* @param string $message
* @param array $context
* @return void
*/
public function log($level, $message, array $context = array());
}
关于message参数:
$message必须是一个字符串或者是含有__toString()方法的对象,$message应该包含占位符,例如{placeholder_name},占位符由{、占位符名称和}组成,不能包含空格,占位符名称可以由A-Z, a-z, 0-9, _组成,第三方实现可以用$context参数来替换占位符,占位符名称必须和$context数组的key对应。如下例子是使用$context中的值替换$message中的占位符:<?php
/**
* Interpolates context values into the message placeholders.
*/
function interpolate($message, array $context = array())
{
// build a replacement array with braces around the context keys
$replace = array();
foreach ($context as $key => $val) {
// check that the value can be casted to string
if (!is_array($val) && (!is_object($val) || method_exists($val, '__toString'))) {
$replace['{' . $key . '}'] = $val;
}
}
// interpolate replacement values into the message and return
return strtr($message, $replace);
}
// a message with brace-delimited placeholder names
$message = "User {username} created";
// a context array of placeholder names => replacement values
$context = array('username' => 'Bolivar');
// echoes "User Bolivar created"
echo interpolate($message, $context);
关于context参数:
$context是一个数组参数,用于构造复杂的日志消息,$context中的值不能抛出任何PHP异常或错误。如果$context中包含Exception对象,则该对象的key必须为exception。
PSR-3日志记录器的使用
推荐使用monolog/monolog,这样可以让我们不需要浪费更多的时间在编写一个日志记录器了。Monolog组建完全实现了PSR-3接口,而且便于使用自定义的消息格式化程序和处理程序扩展功能,通过Monolog可以把日志消息写入文本文件、系统日志和数据库中,还能通过电子邮件发送,并且还支持Slack和远程服务器。如下展示了如何设置Monolog,并把日志消息写入文本文件:use Monolog/Logger;
use Monolog/Handler/StreamHandler;
// 创建日志记录器
$log = new Logger('myApp');
$log->pushHandler(new StreamHandler('logs/development.log, Logger::DEBUG));
$log->pushHandler(new StreamHandler('logs/production.log', Logger::WARNING));
// 使用日志记录器
$log->debug("This is a debug message");
$log->warning("This is a warning message");
PSR-4
PSR-4规范描述了一个标准的自动加载器策略,指在运行时按需查找PHP类、接口或Traits。支持PSR-4自动加载器标准的PHP组建和框架,使用同一个自动加载器就能找到相关代码,然后将其载入PHP解释器。有了这个功能,就可以把现代PHP生态系统中很多客户操作的组件联系起来。
编写一个PSR-4自动加载器
PSR-4规范不要求改变代码的实现方式,只建议如何使用文件系统目录结构和PHP命名空间组织代码,PSR-4规范以来PHP命名空间和文件系统目录结构查找并加载PHP类、接口和Traits,这正是PSR-4的精髓所在。下面我们来自己手动实现一个PSR-4自动加载器:<?php
/**
* 使用SPL组册这个自动加载函数后,遇到下述代码时这个函数会尝试 从/path/to/project/src/Baz/Qux.php文件中加载\Foo\Bar\Baz\Qux类:
* new \Foo\Bar\Baz\Qux;
* @param string $class 完全限定的类名。
* @return void
**/
spl_autoload_register(function ($class) {
// 项目的命名空间前缀
$prefix = 'Foo\\Bar\\';
// 目录前缀对应的根目录
$base_dir = __DIR__ . '/src/';
// 判断传入的类是否使用了这个命名空间前缀
$len = strlen($prefix);
if (strncmp($prefix, $class, $len) !== 0) {
// 没有使用,交给注册的下一个自动加载器处理
return;
}
// 获取去掉前缀后的类名
$relative_class = substr($class, $len);
// 把命名空间前缀替换成根目录,
// 在去掉前缀的类名中,把命名空间分隔符替换成目录分隔符,
// 然后在后面加上.php
$file = $base_dir . str_replace('\\', '/', $relative_class) . '.php';
// 如果该文件存在,就将其导入
if (file_exists($file)) {
require $file;
}
});
更多相关知识,请访问 PHP中文网!!
本文原创发布php中文网,转载请注明出处,感谢您的尊重!
这篇关于php规范 psr,PHP中什么是PSR规范?的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




