本文主要是介绍java集合--千锋教育,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
文章目录
- 集合
- 一、集合概念
- Collection体系
- 父接口
- List
- List 实现类
- 泛型 参数化类型
- 泛型类
- 泛型接口
- 泛型方法
- 转换异常 正常类
- Set集合
- 实现类
- HashSet
- TreeSet
- Map
- 实现类
- HashMap
- Hashtable
- TreeMap
- Collections
集合
一、集合概念
- 概念:对象的容器,定义了对多个对象进行操作的常用方法 可实现数组的功能
- 和数组的区别:
- 数组长度固定 集合不固定
- 数组可以存储基本类型和引用类型 集合只能存放引用类型
Collection体系
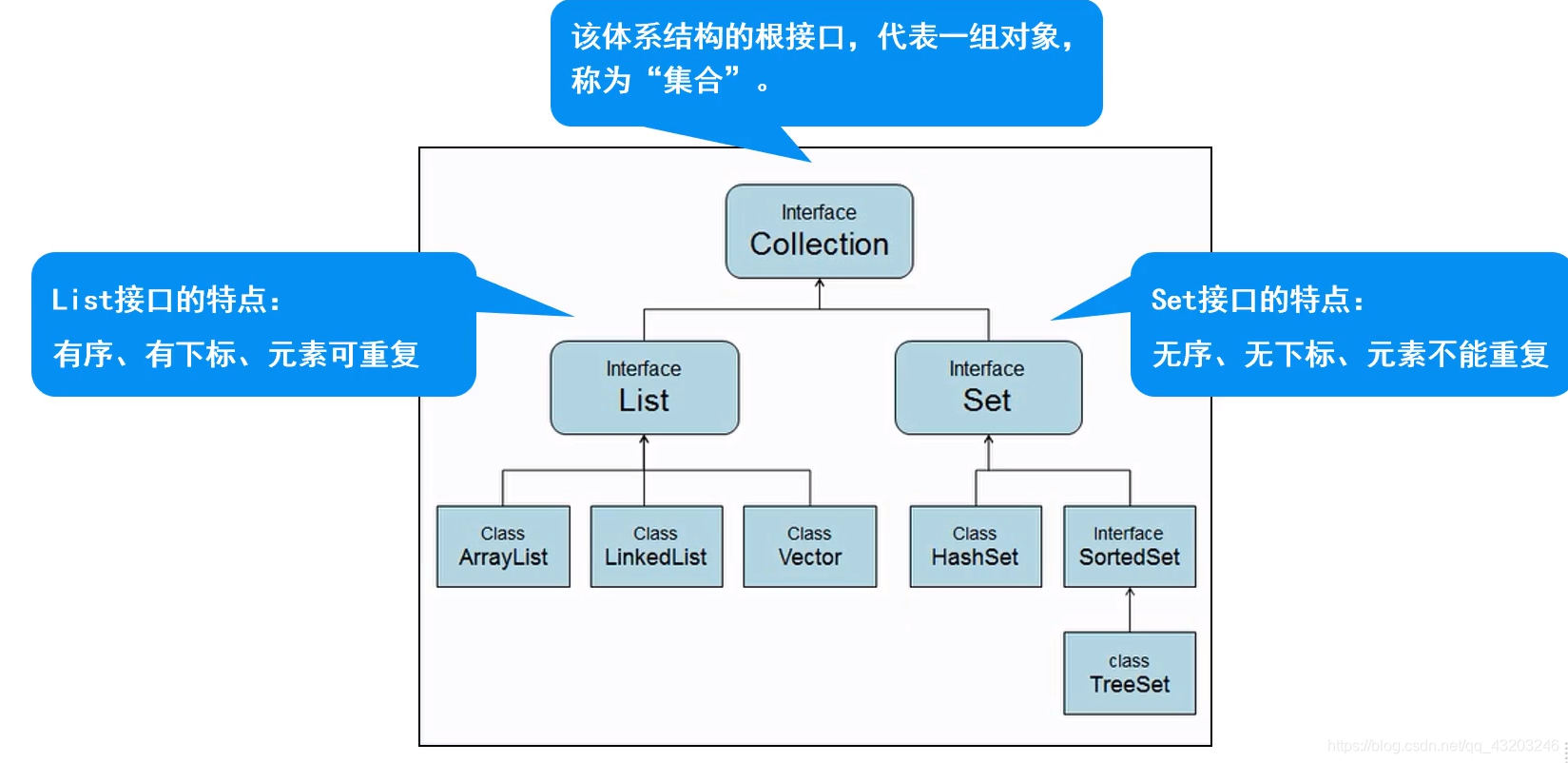
父接口
- 特点: 代表一组任意类型的对象,无序、无下标、不能重复
- 方法:
- boolean add(Object obj) //添加一个对象
- boolean addAll(Collection c)//将一个集合中的所有对象添加到此集合中
- void clear()//清空此集合中的所有对象
- boolean contains(Object o)//检查此集合是否包含o对象
- boolean equals(Object o)//判断此对象 是否与指定对象 相等
- boolean isEmpty()//判断此集合是否为空
- boolean remove (Object o) //在此集合中移除o对象
- int size()//返回此集合中的元素个数
- Object[] toArray()//将此集合转为数组
- Iterator iterator()//迭代
package Collection;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;public class Demo01 {public static void main(String[] args) {Collection collection =new ArrayList();//添加元素collection.add("香蕉");collection.add("橘子");collection.add("火龙果");//打印集合元素及个数System.out.println("元素个数为:"+collection.size());System.out.println(collection);//遍历//1.增强for Collection不能使用下标System.out.println("====================");for(Object object:collection){System.out.println(object);}//2.迭代器 专门用来遍历集合System.out.println("======迭代器=======");Iterator it =collection.iterator();while(it.hasNext()){//hasNext()判断下一个元素是否存在String str = (String)it.next();//next()返回下一个元素System.out.println(str);//collection.remove(str);//遍历时不能用remove方法移除//it.remove();//可用迭代器remove移除}//判断System.out.println(collection.isEmpty());System.out.println(collection.contains("西瓜"));//移除元素collection.remove("橘子");System.out.println("元素个数为:"+collection.size());System.out.println(collection);//清空collection.clear();System.out.println("元素个数为:"+collection.size());System.out.println(collection);}
}
元素个数为:3
[香蕉, 橘子, 火龙果]
====================
香蕉
橘子
火龙果
======迭代器=======
香蕉
橘子
火龙果
false
false
元素个数为:2
[香蕉, 火龙果]
元素个数为:0
[]
package Collection;public class Student {private String name;private int age;public Student(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Student{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +'}';}
}
package Collection;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;public class Demo02 {public static void main(String[] args) {//新建Collection对象Collection collection = new ArrayList();Student s1 = new Student("陈壹",21);Student s2 = new Student("陈贰",22);Student s3 = new Student("陈叁",21);//添加数据collection.add(s1);collection.add(s2);collection.add(s3);collection.add(s3);System.out.println("元素个数为:"+collection.size());System.out.println(collection.toString());//删除//collection.remove(new Student("陈壹",21));new 对象不会删除原来列表collection.remove(s3);//没有移除全部s3 删除一个System.out.println("元素个数为:"+collection.size());System.out.println(collection.toString());//遍历//1.增强forfor(Object object : collection){Student s = (Student)object;System.out.println(s.toString());}//2.迭代器Iterator iterator= collection.iterator();while(iterator.hasNext()){Student s = (Student)iterator.next();iterator.remove();System.out.println(s.toString());}System.out.println(collection.toString());//remove 删除完毕//判断System.out.println(collection.contains(s1));System.out.println(collection.isEmpty());}
}
元素个数为:4
[Student{name='陈壹', age=21}, Student{name='陈贰', age=22}, Student{name='陈叁', age=21}, Student{name='陈叁', age=21}]
元素个数为:3
[Student{name='陈壹', age=21}, Student{name='陈贰', age=22}, Student{name='陈叁', age=21}]
Student{name='陈壹', age=21}
Student{name='陈贰', age=22}
Student{name='陈叁', age=21}
Student{name='陈壹', age=21}
Student{name='陈贰', age=22}
Student{name='陈叁', age=21}
[]
false
true
List
- 特点:有序 有下表 元素可以重复
- 方法
- void add(int index , Object o)//在index处插入对象o
- boolean addAll(int index,Collection c)//将一个集合中的元素添加到index处
- Object get(int index)//返回集合中指定位置的元素
- LIst subList (int fromIndex ,int toIndex)//返回fromIndex 到toIndex的元素
package List;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ListIterator;public class List01 {public static void main(String[] args) {//创建集合List list =new ArrayList<>();//1.添加元素list.add("小米");list.add("三星");list.add("苹果");list.add("华为");System.out.println("元素个数为:"+list.size());System.out.println(list.toString());//2.删除元素//list.remove("三星");list.remove(0);System.out.println("元素个数为:"+list.size());System.out.println(list.toString());//3.遍历//1.for循环System.out.println("=========1.for=========");for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {System.out.println(list.get(i));}//2.增强forSystem.out.println("==========增强for=====");for (Object object: list){System.out.println(object);}//迭代器System.out.println("==========迭代器======");Iterator it=list.iterator();while (it.hasNext()){String s = (String)it.next();System.out.println(s.toString());}//list迭代器 可以前向 后向 遍历 可以增改System.out.println("=========list迭代器======");ListIterator lit =list.listIterator();System.out.println("=====从前往后========");while(lit.hasNext()){System.out.println(lit.nextIndex()+":"+lit.next());}System.out.println("======从后往前====");while(lit.hasPrevious()){System.out.println(lit.previousIndex()+":"+lit.previous());}}
}
元素个数为:4
[小米, 三星, 苹果, 华为]
元素个数为:3
[三星, 苹果, 华为]
=========1.for=========
三星
苹果
华为
==========增强for=====
三星
苹果
华为
==========迭代器======
三星
苹果
华为
=========list迭代器======
=====从前往后========
0:三星
1:苹果
2:华为
======从后往前====
2:华为
1:苹果
0:三星
package List;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;public class List02 {public static void main(String[] args) {List list =new ArrayList<>();//添加数字list.add(10);list.add(20);list.add(30);list.add(40);list.add(50);list.add(60);list.add(70);System.out.println("列表元素为:"+list.size());System.out.println(list.toString());//删除元素list.remove(6);System.out.println("列表元素为:"+list.size());System.out.println(list.toString());//通过元素值移除元素 二种方法list.remove((Object)60);System.out.println("列表元素为:"+list.size());System.out.println(list.toString());list.remove(new Integer(50));//Collection类中 Student 不能通过new Student 删除 为什么???? 因为 对equals定义不同 Student 是通过地址判断 需重写成判断name age 才可以这样删除System.out.println("列表元素为:"+list.size());System.out.println(list.toString());//补充 subList 含头不含尾System.out.println(list.subList(1,3));}
}
列表元素为:7
[10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70]
列表元素为:6
[10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60]
列表元素为:5
[10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
列表元素为:4
[10, 20, 30, 40]
[20, 30]
List 实现类
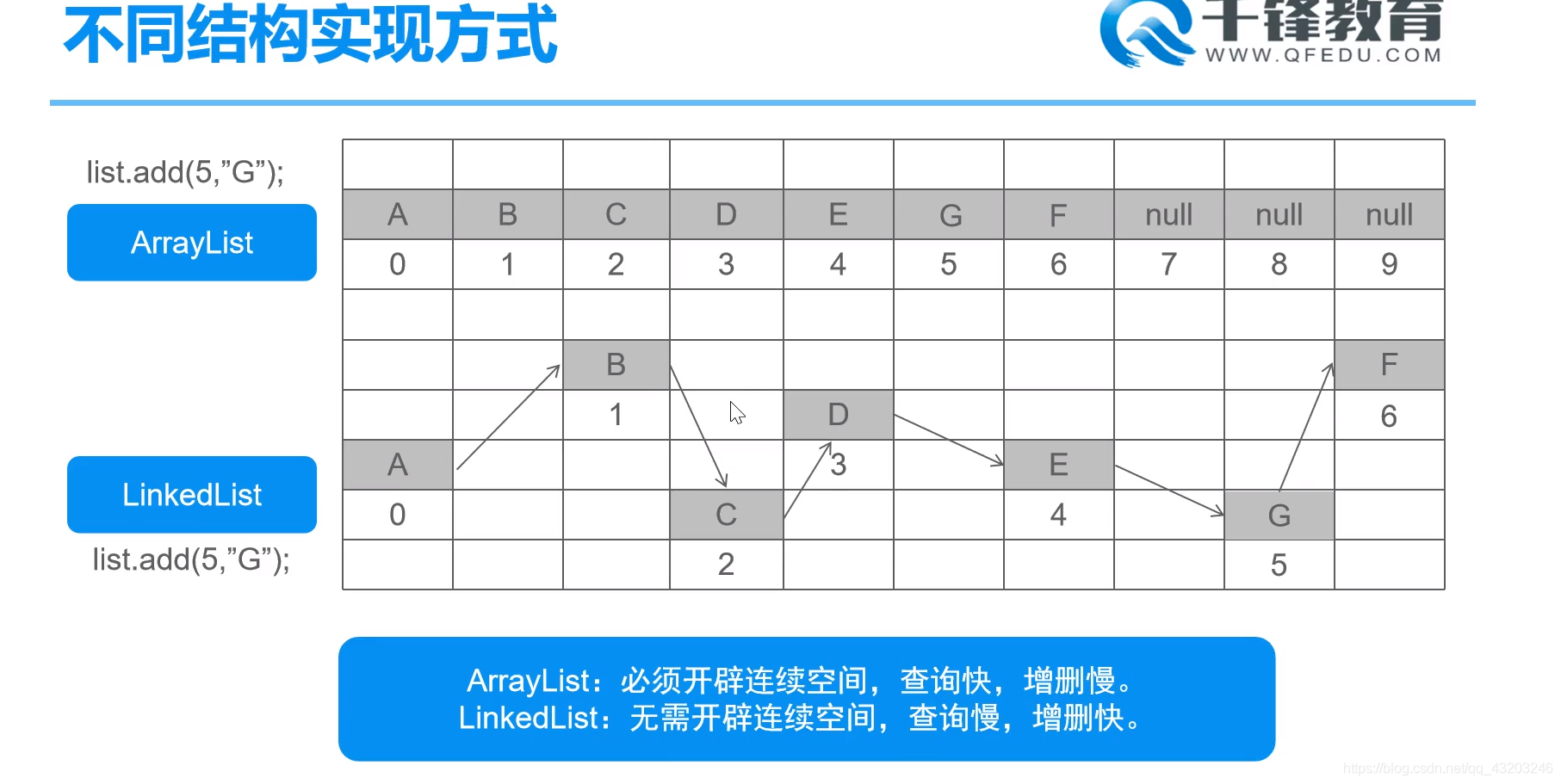
- ArrayList:
- 数组结构实现 查询快 增删慢
- 运行效率快 线程不安全
- Vector(了解):
- 数组结构实现 查询快 增删慢
- 运行效率慢 线程安全
- LinkedList:
- 链表结构实现 增删快 查询慢
Arraylist: 储存结构-- 数组
package Collection;import java.util.Objects;public class Student {private String name;private int age;public Student(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Student{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +'}';}@Override/*public boolean equals(Object o) {if (this == o) return true;if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;Student student = (Student) o;return age == student.age &&Objects.equals(name, student.name);*/public boolean equals(Object o) {if(this==o){return true;}if(this==null){return false;}if(o instanceof Student){Student s = (Student)o;if (this.name.equals(s.getName()) && this.age==s.getAge()){return true;}}return false;}
}
package Arraylist;import Collection.Student;import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.ListIterator;public class Demo01 {public static void main(String[] args) {///创建集合ArrayList<Object> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();//添加元素Student s1 = new Student("刘德华",59);Student s2 = new Student("郭富城",55);Student s3 = new Student("黎明",54);Student s4 = new Student("张学友",59);arrayList.add(s1);arrayList.add(s2);arrayList.add(s3);arrayList.add(s4);arrayList.add(s4);System.out.println("元素个数为:"+arrayList.size());System.out.println(arrayList.toString());//删除元素arrayList.remove(new Student("张学友",59));//重写equals方法 可以删除System.out.println("元素个数为:"+arrayList.size());System.out.println(arrayList.toString());//遍历元素//1.增强forSystem.out.println("==========增强for===========");for (Object object:arrayList) {Student s =(Student)object;System.out.println(s.toString());}//2.下标 forSystem.out.println("========普通for==============");for (int i = 0; i < arrayList.size(); i++) {System.out.println(arrayList.get(i));}//3.迭代器// Iterator 迭代器System.out.println("==============Iteraor迭代器===========");Iterator it =arrayList.iterator();while(it.hasNext()){Student s =(Student)it.next();System.out.println(s.toString());}//ListIterator 迭代器System.out.println("==============ListIterator 前向迭代器===========");ListIterator lit = arrayList.listIterator();while(lit.hasNext()){Student s =(Student)lit.next();System.out.println(s.toString());}System.out.println("==============ListIterator 后向迭代器===========");while(lit.hasPrevious()){Student s =(Student)lit.previous();System.out.println(s.toString());}//判断System.out.println(arrayList.contains(s1));System.out.println(arrayList.contains(new Student("郭富城",55)));//重写 equals}
}
元素个数为:5
[Student{name='刘德华', age=59}, Student{name='郭富城', age=55}, Student{name='黎明', age=54}, Student{name='张学友', age=59}, Student{name='张学友', age=59}]
元素个数为:4
[Student{name='刘德华', age=59}, Student{name='郭富城', age=55}, Student{name='黎明', age=54}, Student{name='张学友', age=59}]
==========增强for===========
Student{name='刘德华', age=59}
Student{name='郭富城', age=55}
Student{name='黎明', age=54}
Student{name='张学友', age=59}
========普通for==============
Student{name='刘德华', age=59}
Student{name='郭富城', age=55}
Student{name='黎明', age=54}
Student{name='张学友', age=59}
==============Iteraor迭代器===========
Student{name='刘德华', age=59}
Student{name='郭富城', age=55}
Student{name='黎明', age=54}
Student{name='张学友', age=59}
==============ListIterator 前向迭代器===========
Student{name='刘德华', age=59}
Student{name='郭富城', age=55}
Student{name='黎明', age=54}
Student{name='张学友', age=59}
==============ListIterator 后向迭代器===========
Student{name='张学友', age=59}
Student{name='黎明', age=54}
Student{name='郭富城', age=55}
Student{name='刘德华', age=59}
true
true
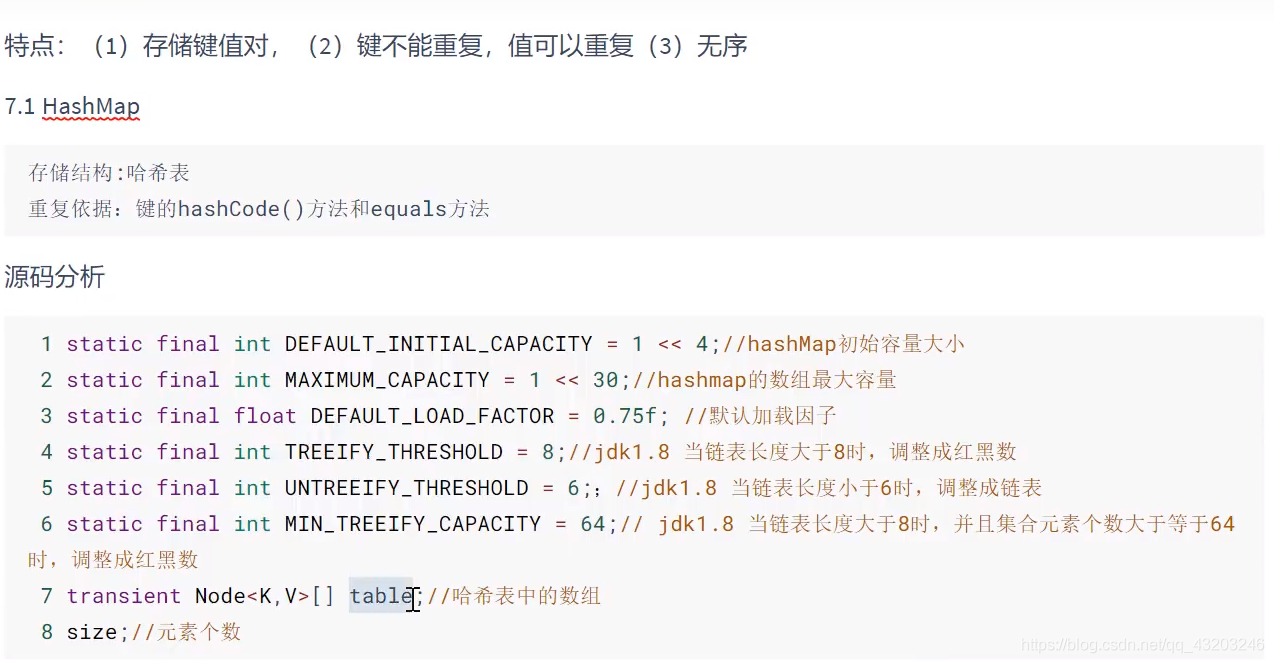
源码分析
默认容量: DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10 注意:如果没有向集合中添加元素 默认为0 添加任意元素 则为10 到达极限是 扩容为原来的1.5倍
存放元素的数组 elementData
实际元素个数 size
add()方法:
源码
public boolean add(E e) {ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!elementData[size++] = e;return true;
}private static int calculateCapacity(Object[] elementData, int minCapacity) {if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);}return minCapacity;}private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity));}private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {modCount++;// overflow-conscious codeif (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)grow(minCapacity);}private void grow(int minCapacity) {// overflow-conscious codeint oldCapacity = elementData.length;int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)newCapacity = minCapacity;if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);}Vector: 数组
package Vector;import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.Vector;public class Demo0 {public static void main(String[] args) {//创建集合Vector<Object> vector = new Vector<>();//添加元素vector.add("香蕉");vector.add("橘子");vector.add("芒果");vector.add("西瓜");System.out.println("元素个数为:"+vector.size());System.out.println(vector.toString());//遍历元素 枚举法 增强for等也可以Enumeration elements = vector.elements();while(elements.hasMoreElements()){String s = (String) elements.nextElement();System.out.println(s);}//判断System.out.println(vector.contains("西瓜"));System.out.println(vector.isEmpty());//其他方法System.out.println(vector.firstElement());System.out.println(vector.lastElement());System.out.println(vector.elementAt(0));//删除元素vector.remove(0);System.out.println(vector.toString());vector.remove("西瓜");System.out.println(vector.toString());vector.clear();System.out.println(vector.toString());}
}
元素个数为:4
[香蕉, 橘子, 芒果, 西瓜]
香蕉
橘子
芒果
西瓜
true
false
香蕉
西瓜
香蕉
[橘子, 芒果, 西瓜]
[橘子, 芒果]
[]
LinkedList:
package LinkerList;import Collection.Student;import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.ListIterator;public class Demo00 {public static void main(String[] args) {//创建集合LinkedList linkedlist = new LinkedList<>();//添加元素Student s1 = new Student("刘德华",59);Student s2 = new Student("郭富城",55);Student s3 = new Student("黎明",54);Student s4 = new Student("张学友",59);linkedlist.add(s1);linkedlist.add(s2);linkedlist.add(s3);linkedlist.add(s4);System.out.println("元素个数:"+linkedlist.size());System.out.println(linkedlist.toString());//遍历//2.1forSystem.out.println("=========for============");for (int i = 0; i < linkedlist.size(); i++) {System.out.println(linkedlist.get(i));}//2.2增强forSystem.out.println("=======增强for============");for (Object obj : linkedlist){Student s =(Student) obj;System.out.println(s.toString());}//2.3迭代器System.out.println("==========迭代器==========");Iterator it = linkedlist.iterator();while(it.hasNext()){Student s =(Student)it.next();System.out.println(s.toString());}//2.4LiseIterator 迭代器System.out.println("========LiseIterator 迭代器=============");ListIterator lit = linkedlist.listIterator();while(lit.hasNext()) {Student s = (Student) lit.next();System.out.println(s.toString());}//判断System.out.println(linkedlist.contains(s1));System.out.println(linkedlist.isEmpty());//获取linkedlist.get(0);//删除linkedlist.remove(0);System.out.println(linkedlist.toString());linkedlist.remove(new Student("郭富城",55));System.out.println(linkedlist.toString());linkedlist.clear();System.out.println(linkedlist.toString());}
}
元素个数:4
[Student{name='刘德华', age=59}, Student{name='郭富城', age=55}, Student{name='黎明', age=54}, Student{name='张学友', age=59}]
=========for============
Student{name='刘德华', age=59}
Student{name='郭富城', age=55}
Student{name='黎明', age=54}
Student{name='张学友', age=59}
=======增强for============
Student{name='刘德华', age=59}
Student{name='郭富城', age=55}
Student{name='黎明', age=54}
Student{name='张学友', age=59}
==========迭代器==========
Student{name='刘德华', age=59}
Student{name='郭富城', age=55}
Student{name='黎明', age=54}
Student{name='张学友', age=59}
========LiseIterator 迭代器=============
Student{name='刘德华', age=59}
Student{name='郭富城', age=55}
Student{name='黎明', age=54}
Student{name='张学友', age=59}
true
false
[Student{name='郭富城', age=55}, Student{name='黎明', age=54}, Student{name='张学友', age=59}]
[Student{name='黎明', age=54}, Student{name='张学友', age=59}]
[]
泛型 参数化类型
<T。。。>类型占位符 表示一种引用类型
- 好处
- 提高代码的重用性
- 防止类型转换异常,提高代码安全性
泛型类
语法 : 类名后加<T,E,K…> T类型占位符 是一种引用类型 可以编写多个
package Mygeneric;public class Mygeneric<T> {//使用泛型//1.创建变量T t;//2.方法参数public void show(T t){// T t =new T(); 不可new对象 因为无法确定T的类型this.t = t;System.out.println(t);}//3.泛型作为方法的返回值public T getT(){return t;}
}
package Mygeneric;import com.sun.org.glassfish.external.amx.AMX;public class TestGeneric {public static void main(String[] args) {//泛型为引用类型 不同泛型类型之间不能相互赋值Mygeneric<String> mg1 = new Mygeneric<String>();mg1.show("生活");System.out.println(mg1.t);String S = mg1.getT();Mygeneric<Integer> mg2 = new Mygeneric<Integer>();mg2.show(150);System.out.println(mg2.t);Integer i1 = mg2.getT();//Mygeneric<String> mg1=mg2; 错误}
}
生活
生活
150
150
泛型接口
接口
package Mygeneric;public interface MyInterface <T>{public static String name= "泛型";T show(T t);
}
实现类
1.实现时声明类型
package Mygeneric;public class MyInterface01 implements MyInterface<String> {@Overridepublic String show(String s ) {System.out.println(s);System.out.println();return s;}
}
2.调用时声明类型
package Mygeneric;public class MyInterface02 <T> implements MyInterface<T>{@Overridepublic T show(T t) {System.out.println(t);return t;}
}
测试类
package Mygeneric;public class MyTest {public static void main(String[] args) {MyInterface01 interface01 = new MyInterface01();interface01.show("花好月圆");System.out.println(MyInterface.name);MyInterface02<Integer> interface02 = new MyInterface02<Integer>();interface02.show(1314);}
}
花好月圆泛型
泛型
1314
泛型方法
public class MyGenericMethod {public <T> T show (T t){System.out.println("泛型方法"+t);return t;}
}MyGenericMethod genericMethod = new MyGenericMethod();genericMethod.show("huhuhu");//无需声明 类型 根据输入参数决定genericMethod.show(200);genericMethod.show(3.14);
泛型方法huhuhu
泛型方法200
泛型方法3.14
转换异常 正常类
需要判断数据类型能否转换
package Mygeneric;import java.util.ArrayList;public class Demo0 {public static void main(String[] args) {ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList();arrayList.add("huahua");arrayList.add("gugu");arrayList.add(120);arrayList.add(520);for (Object obj:arrayList) {String s =(String) obj;System.out.println(s);}}}
huahua
gugu
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ClassCastException: java.lang.Integer cannot be cast to java.lang.Stringat Mygeneric.Demo0.main(Demo0.java:13)
使用泛型 使集合元素为统一类型 避免强类型转换异常
import java.util.ArrayList;public class Demo0 {public static void main(String[] args) {ArrayList<String> arrayList = new ArrayList<String>();arrayList.add("huahua");arrayList.add("gugu");//arrayList.add(120);//arrayList.add(520);for (String str:arrayList) {System.out.println(str);}}
}
使用泛型约束后 int类型元素就无法添加到集合了 避免使用强类型转换
Set集合
- 无序 无下标 元素不可重复
package Set;import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.util.*;public class Demo01 {public static void main(String[] args) {//创建集合Set<String> set = new HashSet<>();//添加元素set.add("华为");set.add("小米");set.add("三星");set.add("苹果");set.add("魅族");System.out.println("元素个数为:"+set.size());System.out.println(set.toString());//遍历//1.增强forfor (String str:set) {System.out.println(str);}//迭代器System.out.println("==========迭代器=========");Iterator it = set.iterator();while(it.hasNext()){String s =(String)it.next();System.out.println(s);}//判断System.out.println(set.contains("小米"));System.out.println(set.isEmpty());//删除set.remove("三星");System.out.println(set.toString());set.clear();System.out.println(set.toString());}
}
元素个数为:5
[苹果, 华为, 魅族, 小米, 三星]
苹果
华为
魅族
小米
三星
==========迭代器=========
苹果
华为
魅族
小米
三星
true
false
[苹果, 华为, 魅族, 小米]
[]实现类
- HashSet
- TreeSet
HashSet
- 基于HashSet计算元素存放位置
- 当存入元素的哈希码相同时,会调用equals进行确认,若结果为true 则拒绝后者加入
存储位置 哈希表(数组加链表+红黑树)
package Set.HashSet;import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;public class Demo01 {public static void main(String[] args) {//创建集合HashSet<String> hashSet = new HashSet<String>();//添加元素hashSet.add("刘亦菲");hashSet.add("杨幂");hashSet.add("刘诗诗");hashSet.add("唐嫣");hashSet.add("赵丽颖");//hashSet.add("赵丽颖");重复 不再添加System.out.println("元素个数为:"+hashSet.size());System.out.println(hashSet.toString());//遍历System.out.println("=======增强for==========");for (String str:hashSet) {System.out.println(str);}//迭代器System.out.println("============迭代器===========");Iterator it = hashSet.iterator();while (it.hasNext()){System.out.println(it.next());}//判断System.out.println(hashSet.contains("杨幂"));System.out.println(hashSet.isEmpty());//删除元素hashSet.remove("赵丽颖");System.out.println(hashSet.toString());hashSet.clear();System.out.println(hashSet.toString());}
}
元素个数为:5
[赵丽颖, 杨幂, 唐嫣, 刘亦菲, 刘诗诗]
=======增强for==========
赵丽颖
杨幂
唐嫣
刘亦菲
刘诗诗
============迭代器===========
赵丽颖
杨幂
唐嫣
刘亦菲
刘诗诗
true
false
[杨幂, 唐嫣, 刘亦菲, 刘诗诗]
[]
储存过程
(1)根据hashcode 计算保存的位置,如果此位置为空 则直接保存 非空 则第二步
(2)执行equals方法 如果equals方法为true 认为重复 false则链表
package Set.HashSet;import java.util.Objects;public class Person {private String name;private int age;public Person() {}public Person(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}@Overridepublic boolean equals(Object o) {if (this == o) return true;if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;Person person = (Person) o;return age == person.age &&Objects.equals(name, person.name);}@Overridepublic int hashCode() {return Objects.hash(name, age);}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Person{" +"name='" + name + '\'' +", age=" + age +'}';}
}
package Set.HashSet;import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Iterator;public class Demo02 {public static void main(String[] args) {HashSet<Person> hashSet = new HashSet<Person>();Person p1 = new Person("刘亦菲",33);Person p2 = new Person("杨幂",34);Person p3 = new Person("唐嫣",37);Person p4 = new Person("刘诗诗",33);Person p5 = new Person("赵丽颖",33);hashSet.add(p1);hashSet.add(p2);hashSet.add(p3);hashSet.add(p4);hashSet.add(p5);hashSet.add(new Person("赵丽颖",33));//重写后 由name age决定hashcodeSystem.out.println("元素个数为:"+hashSet.size());System.out.println(hashSet.toString());//遍历System.out.println("==========增强for==========");for (Person person:hashSet) {System.out.println(person.toString());}System.out.println("=========迭代器=====");Iterator it =hashSet.iterator();while(it.hasNext()){System.out.println(it.next());}//判断System.out.println(hashSet.contains(p2));System.out.println(hashSet.contains(new Person("赵丽颖", 33)));System.out.println(hashSet.isEmpty());//删除hashSet.remove(p5);System.out.println(hashSet.toString());hashSet.clear();System.out.println(hashSet.toString());}
}
元素个数为:5
[Person{name='赵丽颖', age=33}, Person{name='刘诗诗', age=33}, Person{name='刘亦菲', age=33}, Person{name='杨幂', age=34}, Person{name='唐嫣', age=37}]
==========增强for==========
Person{name='赵丽颖', age=33}
Person{name='刘诗诗', age=33}
Person{name='刘亦菲', age=33}
Person{name='杨幂', age=34}
Person{name='唐嫣', age=37}
=========迭代器=====
Person{name='赵丽颖', age=33}
Person{name='刘诗诗', age=33}
Person{name='刘亦菲', age=33}
Person{name='杨幂', age=34}
Person{name='唐嫣', age=37}
true
true
false
[Person{name='刘诗诗', age=33}, Person{name='刘亦菲', age=33}, Person{name='杨幂', age=34}, Person{name='唐嫣', age=37}]
[]
TreeSet
- 基于排列顺序实现元素不可重复
- 实现SortedSet接口 对集合元素自动排序
- 元素对象的类型必须实现Comparable接口,指定排列顺序
- 通过
- CompareTo方法确认是否是重复元素
package Set.TreeSet;import Set.HashSet.Person;import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.TreeSet;public class DEmo01 {public static void main(String[] args) {//创建集合TreeSet<Person> set = new TreeSet<>();//添加元素Person p1 = new Person("刘亦菲",33);Person p2 = new Person("杨幂",34);Person p3 = new Person("唐嫣",37);Person p4 = new Person("刘诗诗",33);Person p5 = new Person("赵丽颖",33);set.add(p1);//添加时 Person类必须实现Comparable接口set.add(p2);set.add(p3);set.add(p4);set.add(p5);System.out.println("元素个数:"+set.size());System.out.println(set.toString());//删除 removeset.remove(p5);System.out.println("元素个数:"+set.size());System.out.println(set.toString());//遍历System.out.println("=======增强for=====");for (Person person: set) {System.out.println(person);}System.out.println("======迭代器==========");Iterator it = set.descendingIterator();//倒序while (it.hasNext()){System.out.println(it.next());}//判断System.out.println(set.contains(p1));System.out.println(set.isEmpty());}
}
元素个数:5
[Person{name='刘亦菲', age=33}, Person{name='刘诗诗', age=33}, Person{name='唐嫣', age=37}, Person{name='杨幂', age=34}, Person{name='赵丽颖', age=33}]
元素个数:4
[Person{name='刘亦菲', age=33}, Person{name='刘诗诗', age=33}, Person{name='唐嫣', age=37}, Person{name='杨幂', age=34}]
=======增强for=====
Person{name='刘亦菲', age=33}
Person{name='刘诗诗', age=33}
Person{name='唐嫣', age=37}
Person{name='杨幂', age=34}
======迭代器==========
Person{name='杨幂', age=34}
Person{name='唐嫣', age=37}
Person{name='刘诗诗', age=33}
Person{name='刘亦菲', age=33}
true
false
还有一种定制比较器Comparator 不需要对对象类实现Comparable
package Set.TreeSet;import Set.HashSet.Person;import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.TreeSet;public class DEMO02 {public static void main(String[] args) {TreeSet<Person> set = new TreeSet<>(new Comparator<Person>() {@Overridepublic int compare(Person o1, Person o2) {int n1 = o1.getName().compareTo(o2.getName());int n2 = o1.getAge()-o2.getAge();return n1==0?n2:n1;}});Person p1 = new Person("刘亦菲",33);Person p2 = new Person("杨幂",34);Person p3 = new Person("唐嫣",37);Person p4 = new Person("刘诗诗",33);Person p5 = new Person("赵丽颖",33);set.add(p1);//添加时 Person类必须实现Comparable接口set.add(p2);set.add(p3);set.add(p4);set.add(p5);System.out.println("元素个数:"+set.size());System.out.println(set.toString());}
}
元素个数:5
[Person{name='刘亦菲', age=33}, Person{name='刘诗诗', age=33}, Person{name='唐嫣', age=37}, Person{name='杨幂', age=34}, Person{name='赵丽颖', age=33}]
package Set.TreeSet;import sun.reflect.generics.tree.Tree;import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.TreeSet;public class Demo03 {public static void main(String[] args) {TreeSet<String> treeSet = new TreeSet<>(new Comparator<String>() {@Overridepublic int compare(String o1, String o2) {int n1= o1.length()-o2.length();int n2 = o1.compareTo(o2);return n1==0?n2:n1;}});//添加元素treeSet.add("qingdao");treeSet.add("zaozhuang");treeSet.add("tengzhou");treeSet.add("nanjing");treeSet.add("jinan");System.out.println("城市个数为:"+treeSet.size());System.out.println(treeSet.toString());//遍历//增强forSystem.out.println("=======增强for=========");for (String str:treeSet) {System.out.println(str);}//迭代System.out.println("==========迭代器=====");Iterator iterator = treeSet.descendingIterator();while (iterator.hasNext()){System.out.println(iterator.next());}//判断System.out.println(treeSet.contains("jinan"));System.out.println(treeSet.isEmpty());//删除System.out.println(treeSet.remove("jinan"));treeSet.clear();}
}
城市个数为:5
[jinan, nanjing, qingdao, tengzhou, zaozhuang]
=======增强for=========
jinan
nanjing
qingdao
tengzhou
zaozhuang
==========迭代器=====
zaozhuang
tengzhou
qingdao
nanjing
jinan
true
false
true
Map
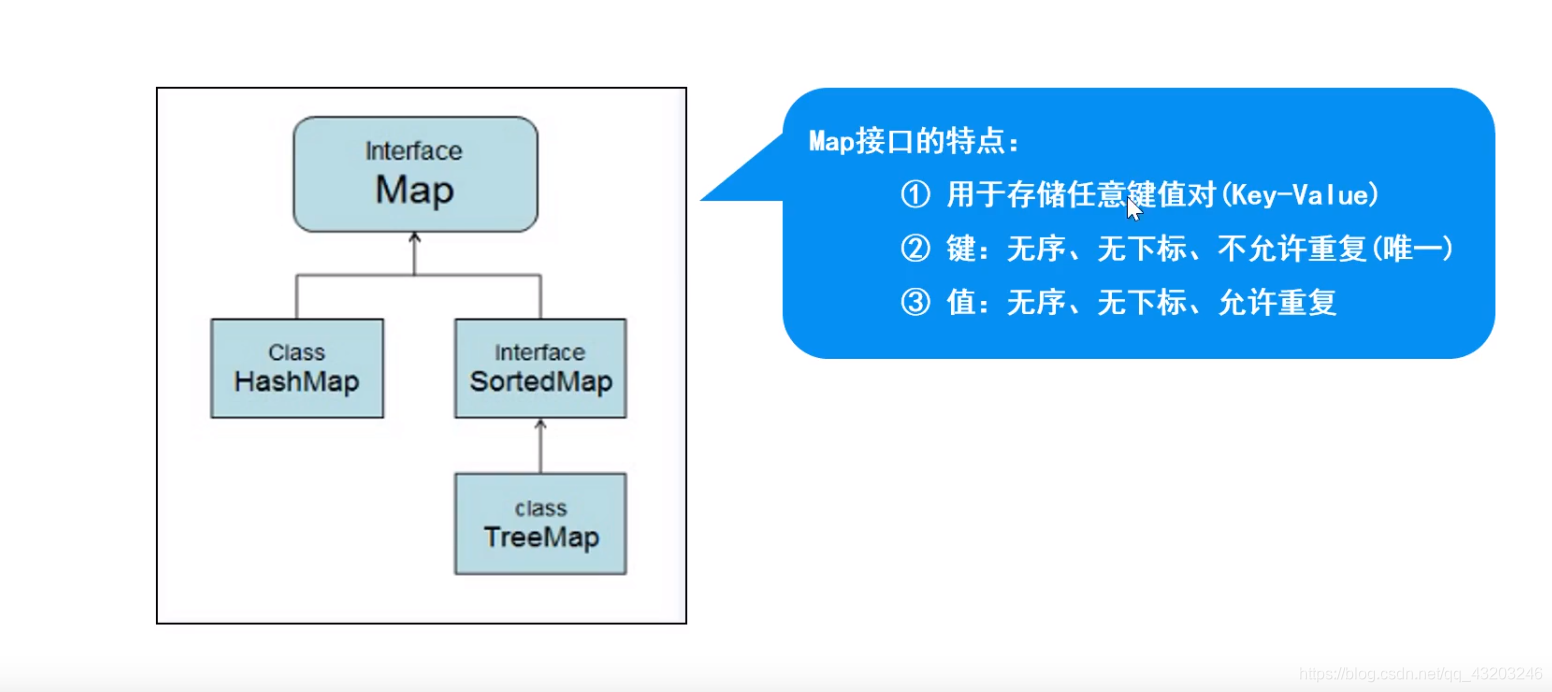
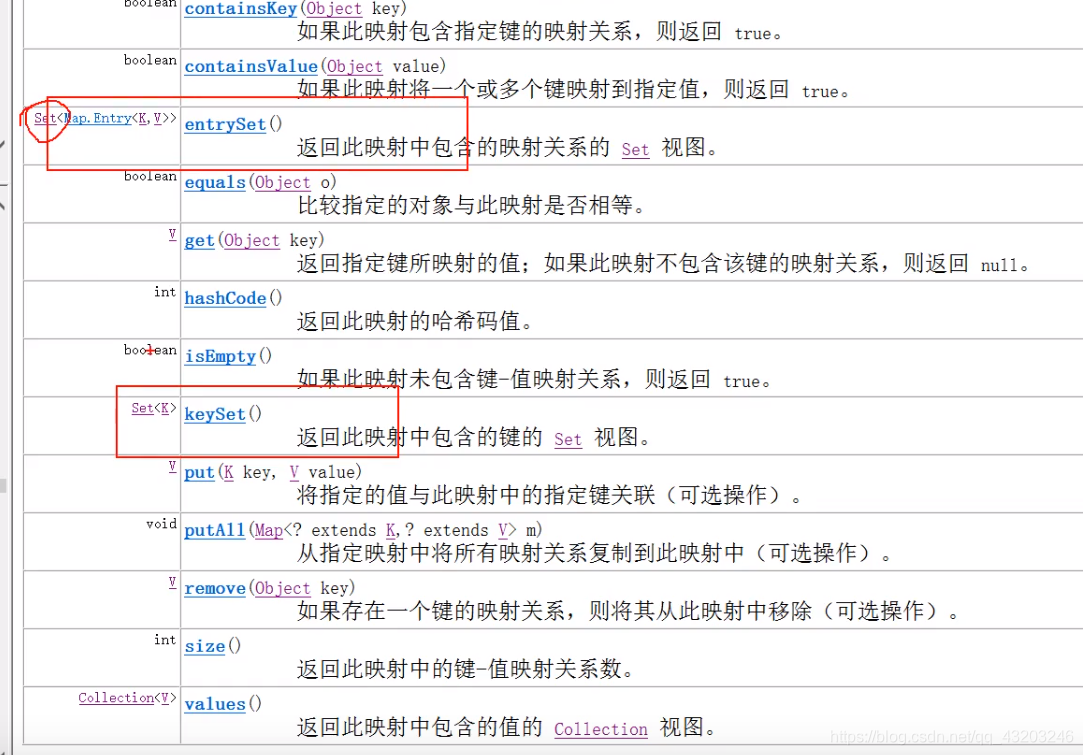
Map:
- 存储键值对
- 键不能重复,值可以重复
- 无序
package Map;import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;public class Demo0 {public static void main(String[] args) {//添加元素Map<String,String> map =new HashMap<>();map.put("没头脑","不高兴");map.put("汤姆","杰瑞");map.put("喜羊羊","美羊羊");map.put("喜羊羊","灰太狼");map.put("虹猫","蓝兔");System.out.println("键值对个数:"+map.size());System.out.println(map.toString());Map<String,String> map2 =new HashMap<>();map2.putAll(map);//复制全部System.out.println("键值对个数:"+map2.size());System.out.println(map2.toString());//判断System.out.println(map.containsKey("没头脑"));//判断是否包含键System.out.println(map.containsValue("蓝兔"));//判断是否包含值System.out.println(map.isEmpty());//迭代System.out.println( "=============keyset迭代========");for (String key:map.keySet()) {System.out.println(key+"-->"+map.get(key));}//entryset迭代System.out.println("============entryset迭代=============");//Set<Map.Entry<String,String>> entry=map.entrySet();for(Map.Entry<String,String> entry:map.entrySet()){System.out.println(entry);}//视图System.out.println(map.entrySet());//返回映射对System.out.println(map.keySet());//返回键System.out.println(map.values());//返回值//其他System.out.println(map.get("汤姆"));//返回键对应值}
}
键值对个数:4
{虹猫=蓝兔, 没头脑=不高兴, 喜羊羊=灰太狼, 汤姆=杰瑞}
键值对个数:4
{虹猫=蓝兔, 没头脑=不高兴, 喜羊羊=灰太狼, 汤姆=杰瑞}
true
true
false
=============keyset迭代========
虹猫-->蓝兔
没头脑-->不高兴
喜羊羊-->灰太狼
汤姆-->杰瑞
============entryset迭代=============
虹猫=蓝兔
没头脑=不高兴
喜羊羊=灰太狼
汤姆=杰瑞
[虹猫=蓝兔, 没头脑=不高兴, 喜羊羊=灰太狼, 汤姆=杰瑞]
[虹猫, 没头脑, 喜羊羊, 汤姆]
[蓝兔, 不高兴, 灰太狼, 杰瑞]
杰瑞
实现类
HashMap
默认容量16 0.75 扩容
package Map.HashMap;import java.util.Objects;public class Student {private String name;private int StuTo;public Student(String name, int stuTo) {this.name = name;StuTo = stuTo;}public Student() {}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getStuTo() {return StuTo;}public void setStuTo(int stuTo) {StuTo = stuTo;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Student{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + ", StuTo=" + StuTo + '}';}@Overridepublic boolean equals(Object o) {if (this == o) return true;if (!(o instanceof Student)) return false;Student student = (Student) o;return StuTo == student.StuTo &&Objects.equals(name, student.name);}@Overridepublic int hashCode() {return Objects.hash(name, StuTo);}
}
package Map.HashMap;import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;public class Demo00 {public static void main(String[] args) {//创建集合HashMap<Student, String> students = new HashMap<Student, String>();//添加元素Student s1 = new Student("周杰伦",20200001);Student s2 = new Student("林俊杰",20200002);Student s3 = new Student("王力宏",20200003);Student s4 = new Student("张杰",20200004);Student s5 = new Student("薛之谦",20200005);students.put(s1,"屋顶");students.put(s2,"一眼万年");students.put(s3,"真的爱你");students.put(s4,"天下");students.put(s5,"其实");students.put(new Student("薛之谦",20200005),"其实");//重写hashcode和equals后 由name StuTo判断相等System.out.println("歌手与其作品:"+students.size());System.out.println(students.toString());//无序排列//迭代System.out.println("==========keySet=======");for (Student student:students.keySet()) {System.out.println(student+"-->"+students.get(student));}System.out.println("=========EntrySet=============");for (Map.Entry<Student,String> entry: students.entrySet()){System.out.println(entry);}//判断System.out.println(students.containsKey(s1));System.out.println(students.containsValue("认真的雪"));//删除System.out.println(students.remove(s1));//删除键 返回值System.out.println(students.toString());//无序排列System.out.println(students.remove(s2,"江南"));System.out.println(students.remove(s2,"一眼万年"));students.clear();System.out.println(students.toString());//无序排列}
}
歌手与其作品:5
{Student{name='张杰', StuTo=20200004}=天下, Student{name='周杰伦', StuTo=20200001}=屋顶, Student{name='林俊杰', StuTo=20200002}=一眼万年, Student{name='薛之谦', StuTo=20200005}=其实, Student{name='王力宏', StuTo=20200003}=真的爱你}
==========keySet=======
Student{name='张杰', StuTo=20200004}-->天下
Student{name='周杰伦', StuTo=20200001}-->屋顶
Student{name='林俊杰', StuTo=20200002}-->一眼万年
Student{name='薛之谦', StuTo=20200005}-->其实
Student{name='王力宏', StuTo=20200003}-->真的爱你
=========EntrySet=============
Student{name='张杰', StuTo=20200004}=天下
Student{name='周杰伦', StuTo=20200001}=屋顶
Student{name='林俊杰', StuTo=20200002}=一眼万年
Student{name='薛之谦', StuTo=20200005}=其实
Student{name='王力宏', StuTo=20200003}=真的爱你
true
false
屋顶
{Student{name='张杰', StuTo=20200004}=天下, Student{name='林俊杰', StuTo=20200002}=一眼万年, Student{name='薛之谦', StuTo=20200005}=其实, Student{name='王力宏', StuTo=20200003}=真的爱你}
false
true
{}
刚创建hashmap table=null size=0 传入一个元素后 size=1<<4(16)
当传输到16*0.75=12时 扩容到原来2倍64 以此类推

Hashtable
properties
TreeMap
package Map.TreeMap;import Map.HashMap.Student;import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.TreeMap;public class Demo00 {public static void main(String[] args) {//创建集合 用定制比较器 或使类实现 ComparableTreeMap<Student, String> students = new TreeMap<>(new Comparator<Student>() {@Overridepublic int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {int n1 = o1.getName().compareTo(o2.getName());int n2 = o1.getStuTo()-o2.getStuTo();return n1==0?n2:n1;}});Student s1 = new Student("周杰伦",20200001);Student s2 = new Student("林俊杰",20200002);Student s3 = new Student("王力宏",20200003);Student s4 = new Student("张杰",20200004);Student s5 = new Student("薛之谦",20200005);students.put(s1,"屋顶");students.put(s2,"一眼万年");students.put(s3,"真的爱你");students.put(s4,"天下");students.put(s5,"其实");students.put(new Student("薛之谦",20200005),"其实");//重写hashcode和equals后 由name StuTo判断相等System.out.println("歌手与其作品:"+students.size());System.out.println(students.toString());//无序排列//迭代System.out.println("=======keySet()=========");for (Student key:students.keySet()) {System.out.println(key+"----------"+students.get(key));}System.out.println("============entrySet()===========");for(Map.Entry<Student,String> entry: students.entrySet()){System.out.println(entry.getKey()+"------"+entry.getValue());}///判断System.out.println(students.containsKey(s1));System.out.println(students.containsValue("认真的雪"));System.out.println(students.isEmpty());//移除students.remove(s1);System.out.println("歌手与其作品:"+students.size());students.clear();System.out.println("歌手与其作品:"+students.size());}
}
歌手与其作品:5
{Student{name='周杰伦', StuTo=20200001}=屋顶, Student{name='张杰', StuTo=20200004}=天下, Student{name='林俊杰', StuTo=20200002}=一眼万年, Student{name='王力宏', StuTo=20200003}=真的爱你, Student{name='薛之谦', StuTo=20200005}=其实}
=======keySet()=========
Student{name='周杰伦', StuTo=20200001}----------屋顶
Student{name='张杰', StuTo=20200004}----------天下
Student{name='林俊杰', StuTo=20200002}----------一眼万年
Student{name='王力宏', StuTo=20200003}----------真的爱你
Student{name='薛之谦', StuTo=20200005}----------其实
============entrySet()===========
Student{name='周杰伦', StuTo=20200001}------屋顶
Student{name='张杰', StuTo=20200004}------天下
Student{name='林俊杰', StuTo=20200002}------一眼万年
Student{name='王力宏', StuTo=20200003}------真的爱你
Student{name='薛之谦', StuTo=20200005}------其实
true
false
false
歌手与其作品:4
歌手与其作品:0
Collections
package Collections;import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.util.*;public class Demo01 {public static void main(String[] args) {List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();//添加元素list.add(20);list.add(6);list.add(12);list.add(25);list.add(30);System.out.println("元素个数:" + list.size());System.out.println(list.toString());//排列Collections.sort(list);System.out.println(list.toString());//二叉树查找 排序之后int s = Collections.binarySearch(list, 20);//存在返回索引值 不存在为负System.out.println(s);//倒序Collections.reverse(list);System.out.println(list);//乱序Collections.shuffle(list);System.out.println(list);//copy复制List<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList();for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {list1.add(0);}Collections.copy(list1,list);//IndexOutOfBoundsException 要求复制的列表大小一致System.out.println(list1);//其他//list转为数组System.out.println("===list转为数组===");Integer[] array = list.toArray(new Integer[0]);//参数小于list元素个数时 得到的数组大小为list.size 大于则为参数大小 其余以null填充System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));System.out.println(array.length);//数组转为列表System.out.println("====数组转为列表========");String[] singer= {"邓紫棋","毛不易","廖俊涛"};//数组转为的列表为受限列表 不能添加或删除List list2= Arrays.asList(singer);System.out.println(list2);//基本类型转换时 需要用包装类型//int[] i1= {10,20,100,200};//List<int> list3 =Arrays.asList(i1); 报错Integer[] i1= {10,20,100,200};List<Integer> list3 =Arrays.asList(i1);System.out.println(list3);}
}
元素个数:5
[20, 6, 12, 25, 30]
[6, 12, 20, 25, 30]
2
[30, 25, 20, 12, 6]
[20, 25, 6, 30, 12]
[20, 25, 6, 30, 12]
===list转为数组===
[20, 25, 6, 30, 12]
5
====数组转为列表========
[邓紫棋, 毛不易, 廖俊涛]
[10, 20, 100, 200
数组特点:大小固定,只能存储相同数据类型的数据
集合特点:大小可动态扩展,可以存储各种类型的数据
这篇关于java集合--千锋教育的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





