本文主要是介绍链表收尾(8.2),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
例题解析
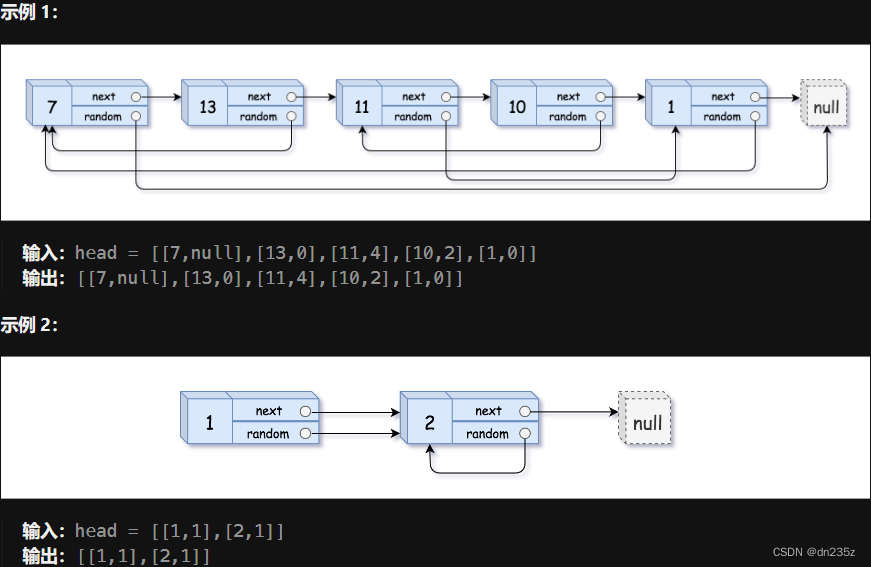
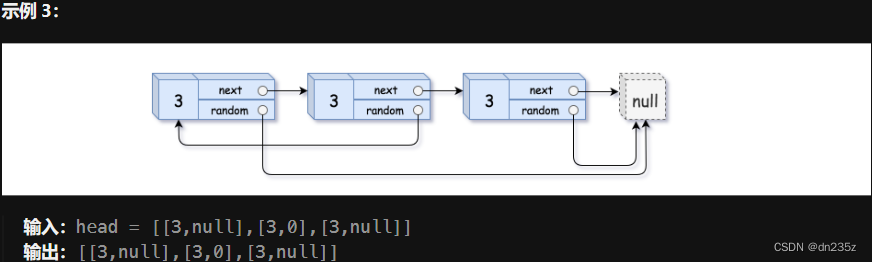
138. 随机链表的复制 - 力扣(LeetCode)
1.拷贝节点插入原节点的后面(核心)
这样做的目的是方便找 random 节点,知道原节点可以找 random,知道上一个 random 可以找下一个 random 。
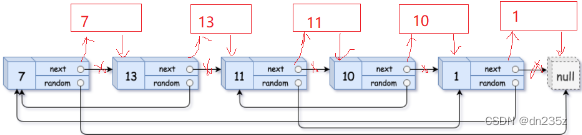
struct Node* cur=head;while(cur){//通过一前一后两个指针来插入节点struct Node* next=cur->next;struct Node* copy=(struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));copy->val=cur->val;//链接cur->next=copy;copy->next=next;//cur移动cur=next;}2.放置每个拷贝节点的 random
我们可以通过原节点的 random 轻松找到拷贝的 random
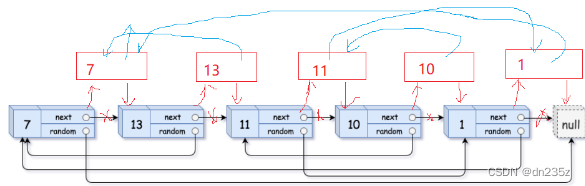
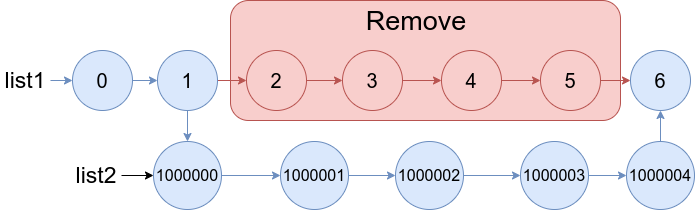
cur=head;//放置拷贝节点的randomwhile(cur){//从cur的下一个节点开始遍历struct Node* copy=cur->next;//如果原节点的random为空,拷贝节点的random也为空if(cur->random==NULL){copy->random=NULL;}else//否则拷贝节点的random等于原节点的random的拷贝节点{copy->random=cur->random->next;}//cur后移动一位cur=copy->next;}3.将拷贝节点与原链表解开,尾插到一起,并恢复原链表的链接
cur=head;
//创建新链表的头尾节点便于插入struct Node* copyhead=NULL,*copytail=NULL;while(cur){struct Node* copy=cur->next;struct Node* next=copy->next;//copy节点尾插到新链表if(copyhead==NULL){copy= copyhead=copytail;}else{copytail->next=copy;copytail=copytail->next;}//恢复原节点cur->next=next;cur=next;}完整代码:
/*** Definition for a Node.* struct Node {* int val;* struct Node *next;* struct Node *random;* };*/struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head) {//拷贝节点到原节点的后面struct Node* cur=head;while(cur){//通过一前一后两个指针来插入节点struct Node* next=cur->next;struct Node* copy=(struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));copy->val=cur->val;//链接cur->next=copy;copy->next=next;//cur移动cur=next;}cur=head;//放置拷贝节点的randomwhile(cur){//从cur的下一个节点开始遍历struct Node* copy=cur->next;//如果原节点的random为空,拷贝节点的random也为空if(cur->random==NULL){copy->random=NULL;}else//否则拷贝节点的random等于原节点的random的拷贝节点{copy->random=cur->random->next;}//cur后移动一位cur=copy->next;}cur=head;//创建新链表的头尾节点便于插入struct Node* copyhead=NULL,*copytail=NULL;while(cur){struct Node* copy=cur->next;struct Node* next=copy->next;//copy节点尾插到新链表if(copytail==NULL){copyhead=copytail=copy;}else{copytail->next=copy;copytail=copytail->next;}//恢复原节点cur->next=next;cur=next;}return copyhead;
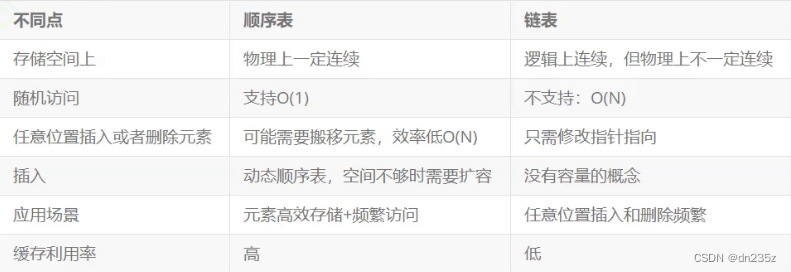
}4.顺序表和链表的区别
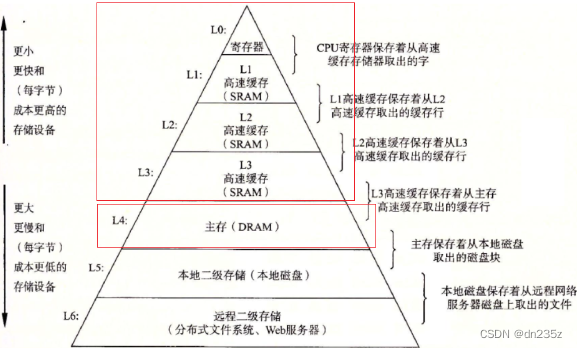
拓展学习:
这篇关于链表收尾(8.2)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!