本文主要是介绍Android 13 - Media框架(4)- MediaPlayerService,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
MediaPlayerService是android的多媒体框架的核心服务之一,该服务存储有android平台所支援的编解码器信息,管理所有通过MediaPlayer创建的播放器实例,起着承上启下的作用,这一节我们将了解MediaPlayerService中的内容。
1、libmedia
上一篇笔记中我们了解了 MediaPlayer native 实现,这个实现在源码中位于 frameworks/av/media/libmedia,libmedia也是多媒体框架的核心库之一,这里我们来看看libmedia到底包含哪些东西。
libmedia底下的内容大致可以分为四类:
- Java类的native实现,例如:
mediaplayer.cppmediarecorder.cppMediaScanner.cpp,分别对应MediaPlayer.javaMediaRecorder.javaMediaScanner.java; - binder service所需要的文件,这类可以分为两小类:
- aidl文件,编译时直接生成bp/bn文件,例如
IMediaExtractorService.aidl; - 手动实现的bp/bn文件,例如
IMediaPlayerService.cpp
- aidl文件,编译时直接生成bp/bn文件,例如
- binder service中传输对象所需的文件,例如
IMediaPlayer.cppIMediaExtractor.cppIDataSource.cppIMediaCodecList.cpp,这些对象将在service进程中创建,通过binder传输给client进行,供client使用; - 其他工具类,例如
MediaCodecInfo.cppMediaCodecBuffer.cppOMXBuffer.cpp
为什么有的 binder service 用 aidl 生成相关 bp/bn 文件,有的却手动实现呢?大致浏览 aidl 文件可以发现,需要传递的类型已经使用 aidl 定义过了或者是基础类型;手动编写的文件例如 IMediaPlayer.cpp 需要传递比较复杂的类型,例如 KeyedVector 等,如果要用 aidl 编写会很麻烦。
我们这一篇要了解的 MediaPlayerService 部分源码就在 libmedia 之中。
2、MediaPlayerService
MediaPlayerService 启动文件位于 frameworks/av/media/mediaserver/main_mediaserver.cpp,这个进程名为 mediaserver ,除了有 MediaPlayerService 这个服务外,还有包含有一个资源管理服务 ResourceManagerService,这里我们不做研究。
MediaPlayerService 在 ServiceManager 中注册的名字是 media.player,平时我会将 MediaPlayerService mediaserver media.player 看作是一个东西。
接下来从 IMediaPlayerService.h 中来看 MediaPlayerService 会为我们提供什么服务:
class IMediaPlayerService: public IInterface
{
public:virtual sp<IMediaRecorder> createMediaRecorder(const android::content::AttributionSourceState &attributionSource) = 0;virtual sp<IMediaPlayer> create(const sp<IMediaPlayerClient>& client,audio_session_t audioSessionId = AUDIO_SESSION_ALLOCATE,const android::content::AttributionSourceState &attributionSource =android::content::AttributionSourceState()) = 0;virtual sp<IMediaCodecList> getCodecList() const = 0;
};
MediaPlayerService 主要提供了三个服务createMediaRecorder create 和 getCodecList,我们主要了解后面两个服务。
2.1、getCodecList
sp<IMediaCodecList> MediaPlayerService::getCodecList() const {return MediaCodecList::getLocalInstance();
}
第一次调用getCodecList 会去加载 Codec 信息,信息来自于两个地方:
- OmxInfoBuilder.cpp :从OMX service获取硬件编解码组件信息
- Codec2InfoBuilder.cpp :从注册文件获取软件编解码组件信息,文件包括
media_codecs.xmlmedia_codecs_c2.xmlmedia_codecs_performance.xml,前两个文件一般包含有所有的 code type,最后一个文件包含 codec 对应的性能信息。
所有加载到的信息以 MediaCodecInfo 的形式存储在 MediaCodecList 中,我们可以调用 MediaCodecList 的 findCodecByType findCodecByName findMatchingCodecs 来查找想要的 codec 组件。
以下是从虚拟设备中的 vendor/etc/media_codecs_google_video.xml 截取到的 h265 decoder的信息
<MediaCodec name="OMX.google.hevc.decoder" type="video/hevc"><!-- profiles and levels: ProfileMain : MainTierLevel51 --><Limit name="size" min="2x2" max="2048x2048" /><Limit name="alignment" value="2x2" /><Limit name="block-size" value="8x8" /><Limit name="block-count" range="1-139264" /><Limit name="blocks-per-second" range="1-2000000" /><Limit name="bitrate" range="1-10000000" /><Limit name="performance-point-1920x1080" value="30" /><Feature name="adaptive-playback" /></MediaCodec>
以下是从 vendor/etc/media_codecs_performance.xml 截取到的 performance 信息
<MediaCodec name="OMX.google.hevc.decoder" type="video/hevc" update="true"><!-- 4 runs, min 754 max 817 gmean 775 --><Limit name="measured-frame-rate-352x288" range="754-817" /><!-- 4 runs, min 323 max 394 gmean 373 --><Limit name="measured-frame-rate-640x360" range="323-394" /><!-- 4 runs, min 349 max 372 gmean 358 --><Limit name="measured-frame-rate-720x480" range="349-372" /><!-- 4 runs, min 144 max 157 gmean 151 --><Limit name="measured-frame-rate-1280x720" range="144-157" /><!-- 4 runs, min 74 max 85 gmean 80 --><Limit name="measured-frame-rate-1920x1080" range="74-85" /></MediaCodec>
以下是 dumpsys media.player 获取到的部分 codec 信息:
Media type 'video/hevc':Decoder "OMX.google.hevc.decoder" supportsaliases: []attributes: 0: [encoder: 0,vendor: 0,software-only: 0,hw-accelerated: 0 ]owner: "default"rank: 528profile/levels: [1/65536 (Main/Main 5.1),4/65536 (MainStill/Main 5.1) ]colors: [0x7f420888 (YUV420Flexible),0x13 (YUV420Planar) ]details: AMessage(what = 0x00000000) = {string alignment = "2x2"string bitrate-range = "1-10000000"string block-count-range = "1-139264"string block-size = "8x8"string blocks-per-second-range = "1-2000000"int32_t feature-adaptive-playback = 0string measured-frame-rate-1280x720-range = "144-157"string measured-frame-rate-1920x1080-range = "74-85"string measured-frame-rate-352x288-range = "754-817"string measured-frame-rate-640x360-range = "323-394"string measured-frame-rate-720x480-range = "349-372"string performance-point-1920x1080-range = "30-30"string size-range = "2x2-2048x2048"}
我们可以从信息中看到mime type,codec name,是否为 encoder, 是否是vendor实现,是否是硬件加速,owner 为 default 表示是OMX组件,c2 software codec 的 owner 为 codec2::software。
MediaCodecInfo 中还可以包含其他信息,比如 FEATURE_TUNNELED_PLAYBACK 等,我们可以调用 getCapabilitiesFor 获取指定 codec 的编解码能力。
2.2、create
status_t MediaPlayer::setDataSource(const sp<IMediaHTTPService> &httpService,const char *url, const KeyedVector<String8, String8> *headers)
{ALOGV("setDataSource(%s)", url);status_t err = BAD_VALUE;if (url != NULL) {const sp<IMediaPlayerService> service(getMediaPlayerService());if (service != 0) {sp<IMediaPlayer> player(service->create(this, mAudioSessionId, mAttributionSource));if ((NO_ERROR != doSetRetransmitEndpoint(player)) ||(NO_ERROR != player->setDataSource(httpService, url, headers))) {player.clear();}err = attachNewPlayer(player);}}return err;
}
MediaPlayer native 对象会在 setDataSource 时获取 MediaPlayerService 并且调用 create 方法创建一个远程的 player 实例,接着调用该实例的 setDataSource 方法。
先看 create:
sp<IMediaPlayer> MediaPlayerService::create(const sp<IMediaPlayerClient>& client,audio_session_t audioSessionId, const AttributionSourceState& attributionSource)
{// 给创建的 client 进行编号int32_t connId = android_atomic_inc(&mNextConnId);AttributionSourceState verifiedAttributionSource = attributionSource;verifiedAttributionSource.pid = VALUE_OR_FATAL(legacy2aidl_pid_t_int32_t(IPCThreadState::self()->getCallingPid()));verifiedAttributionSource.uid = VALUE_OR_FATAL(legacy2aidl_uid_t_int32_t(IPCThreadState::self()->getCallingUid()));// 创建 clientsp<Client> c = new Client(this, verifiedAttributionSource, connId, client, audioSessionId);// 添加 client 到 mediaplayerservice wp<Client> w = c;{Mutex::Autolock lock(mLock);mClients.add(w);}// 返回 client 到 mediaPlayer nativereturn c;
}
create 方法会传入 MediaPlayer Native 对象的远程代理用于 Callback ,这里要注意,传进来的是MediaPlayer Native 对象的一个强引用,MediaPlayerService 回传给 MediaPlayer Native 的也是一个强引用,这里出现循环引用,所以我们要注意释放的流程是怎么样的。

create 方法还会将创建的 Client 对象的弱引用传递给 MediaPlayerService,这里的传递仅仅供 dumpsys media.player 使用,我们来看看会 dump 出什么:
generic_x86:/ # dumpsys media.playerClientpid(4130), connId(7323), status(0), looping(false)NuPlayerstate(5), atEOS(0), looping(0), autoLoop(0)mime(video/avc)decoder(OMX.android.goldfish.h264.decoder)resolution(1920 x 1080)numFramesTotal(388), numFramesDropped(0), percentageDropped(0.00%)mime(audio/mp4a-latm)decoder(c2.android.aac.decoder)AudioOutputstream type(3), left - right volume(1.000000, 1.000000)msec per frame(0.022676), latency (531)aux effect id(0), send level (0.000000)AudioTrack::dumpid(279) status(0), state(0), session Id(2793), flags(0)stream type(3), left - right volume(1.000000, 1.000000)format(0x1), channel mask(0x3), channel count(2)sample rate(44100), original sample rate(44100), speed(1.000000)frame count(22448), req. frame count(22448)notif. frame count(11224), req. notif. frame count(0), req. notif. per buff(0)latency (531), selected device Id(0), routed device Id(2)output(13) AF latency (22) AF frame count(976) AF SampleRate(44100)17 registered handlers:34: CCodecWatchdog: 2124 messages processed37487: MediaClock: 0 messages processed37488: NuPlayerDriver Looper: 3 messages processed37489: http live: 1 messages processed37490: http live: 3 messages processed37997: MediaClock: 395 messages processed37998: NuPlayerDriver Looper: 36 messages processed37999: http live: 1 messages processed38000: http live: 24 messages processed38002: Fetcher: 25 messages processed38003: NuPlayerRenderer: 934 messages processed38004: NPDecoder: 288 messages processed38005: NPDecoder-CL: 106 messages processed38006: NPDecoder-CL: 396 messages processed38007: NPDecoder: 1174 messages processed38008: CodecLooper: 1240 messages processed38009: NPDecoder-CL: 1969 messages processed
可以看到有调用 MediaPlayerService 的进程 id,使用的 Player 类型,audio/video mime 和 codec type,一些播放器信息(当前的状态,解出的帧数,丢弃的帧数等), audio的相关信息,还有所有的Handler,其注册的Looper以及处理消息的数量。以后如果播放器出现异常可以将这些信息dump下来看看。
2.3、MediaPlayerFactory
MediaPlayerService 的构造函数会初始化 MediaPlayerFactory,里面注册有平台上所有的播放器,如果我们要添加一个新的播放器,那么除了要继承于 MediaPlayerInterface/MediaPlayerHWInterface 实现MediaPlayerBase 接口外,还要实现一个新的 IFactory 并且注册到 MediaPlayerFactory 中。
MediaPlayerService::MediaPlayerService()
{ALOGV("MediaPlayerService created");mNextConnId = 1;MediaPlayerFactory::registerBuiltinFactories();
}
使用是先调用 getPlayerType 获取合适的 player 类型:
static player_type getPlayerType(const sp<IMediaPlayer>& client, const char* url);
再调用 createPlayer,用获取到的 player 类型创建一个对应的实例:
static sp<MediaPlayerBase> createPlayer(player_type playerType, const sp<MediaPlayerBase::Listener> &listener, pid_t pid);
3、MediaPlayerService::Client
MediaPlayerService::Client 的接口可以在 IMediaPlayer.h 中查询。
我们继续来看 setDataSource :
status_t MediaPlayerService::Client::setDataSource(const sp<IMediaHTTPService> &httpService,const char *url,const KeyedVector<String8, String8> *headers)
{ALOGV("setDataSource(%s)", url);if (url == NULL)return UNKNOWN_ERROR;// 检查网络权限if ((strncmp(url, "http://", 7) == 0) ||(strncmp(url, "https://", 8) == 0) ||(strncmp(url, "rtsp://", 7) == 0)) {if (!checkPermission("android.permission.INTERNET")) {return PERMISSION_DENIED;}}// 获取player类型player_type playerType = MediaPlayerFactory::getPlayerType(this, url);// create player and setAudioSinksp<MediaPlayerBase> p = setDataSource_pre(playerType);if (p == NULL) {return NO_INIT;}// 调用 player 的 setDataSource 并且将 player 存储到 Client 中return mStatus =setDataSource_post(p, p->setDataSource(httpService, url, headers));
}
- 根据 url 判断是否需要网络权限;
- 使用 MediaPlayerFactory 判断要创建哪一个 player;
- 根据获取到的播放器类型来创建播放器;
a. 检查 media.extractor 服务并监听死亡通知;
b. 检查 IOmx 服务并监听死亡通知;
c. 监听 Codec2 服务的死亡通知;
d. 用 audioSessionId 创建 AudioOutput,调用 player 的 setAudioSink; - 调用 player 的 setDataSource 方法;
到这里播放器的创建就完成了,由于涉及的类比较多,这里贴一张图来表现他们的层次关系:
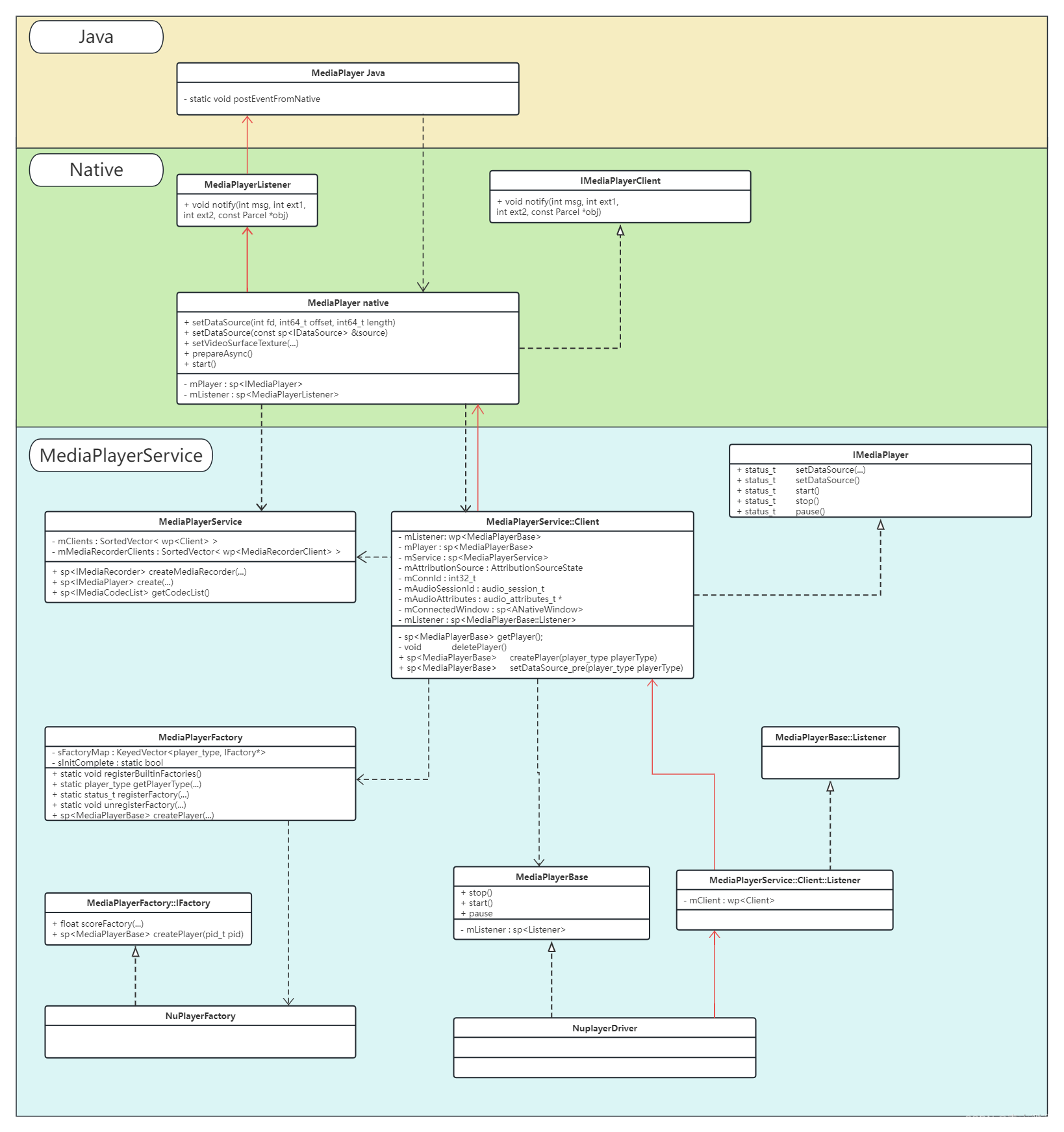
图中黑色箭头表示调用关系,红色的箭头表示消息上抛过程,一连串的调用之后,最后到达 NuPlayer,后面我们将了解它的结构与实现;
4、MediaPlayer::reset
reset 的目的是销毁用 MediaPlayerService 创建的 IMediaPlayer 本地对象,上一篇笔记中我们了解 reset 过程分为3步,这里我们再回顾一下:
- 调用
IMediaPlayer的 reset 方法; - 调用
IMediaPlayer的 disconnect 方法; - 销毁
IMediaPlayer。
IMediaPlayer reset 核心是调用 MediaPlayerBase 的 reset 方法:
status_t MediaPlayerService::Client::reset()
{ALOGV("[%d] reset", mConnId);mRetransmitEndpointValid = false;sp<MediaPlayerBase> p = getPlayer();if (p == 0) return UNKNOWN_ERROR;return p->reset();
}
IMediaPlayer disconnect 做的事情会比较多:
- 清除上层传下来的 MediaPlayer native对象,防止出现循环引用导致资源无法释放;
- 清除 mPlayer 中的内容,这里 MediaPlayerBase并不会销毁;
- 清除 MediaPlayerBase 的 callback;
- 调用 MediaPlayerBase 的 reset(reset方法核心就是这个);
- 走出 disconnect 作用域,销毁 MediaPlayerBase;
void MediaPlayerService::Client::disconnect()
{ALOGV("disconnect(%d) from AttributionSource %s", mConnId,mAttributionSource.toString().c_str());// grab local reference and clear main reference to prevent future// access to objectsp<MediaPlayerBase> p;{Mutex::Autolock l(mLock);p = mPlayer;// 1 清除上层传下来的 MediaPlayer native对象mClient.clear();// 2 清除 Client mPlayer中的内容mPlayer.clear();}// clear the notification to prevent callbacks to dead client// and reset the player. We assume the player will serialize// access to itself if necessary.if (p != 0) {// 3 清除 MediaPlayerBase 中的 callbackp->setNotifyCallback(0);
#if CALLBACK_ANTAGONIZERALOGD("kill Antagonizer");mAntagonizer->kill();
#endif// 4 调用 MediaPlayerBase 中的 resetp->reset();}{Mutex::Autolock l(mLock);disconnectNativeWindow_l();}IPCThreadState::self()->flushCommands();// 5 销毁 MediaPlayerBase
}
析构函数会再次尝试调用 disconnect 销毁内部的 MediaPlayerBase 对象,然后移除 MediaPlayerService 记录的 Client 实例。
MediaPlayerService::Client::~Client()
{ALOGV("Client(%d) destructor AttributionSource = %s", mConnId,mAttributionSource.toString().c_str());mAudioOutput.clear();wp<Client> client(this);disconnect();mService->removeClient(client);if (mAudioAttributes != NULL) {free(mAudioAttributes);}mAudioDeviceUpdatedListener.clear();
}
至此 MediaPlayer Native 对象中的 mPlayer 就释放完成了,如果还要继续使用该MediaPlayer实例,需要重新调用 setDataSource 让 MediaPlayerService 重新创建本地实例。
5、MediaPlayer.release
Java 有一个api release,用意是释放MediaPlayer Native对象,JNI结构实现如下:
- MediaPlayer 强引用计数减一;
- 调用disconnect,这在上一节已经进行了了解,释放 MediaPlayerService 中的实例;
- 走出函数作用域,销毁MediaPlayer对象;
static void
android_media_MediaPlayer_release(JNIEnv *env, jobject thiz)
{ALOGV("release");decVideoSurfaceRef(env, thiz);// 1 强引用计数减一sp<MediaPlayer> mp = setMediaPlayer(env, thiz, 0);if (mp != NULL) {// this prevents native callbacks after the object is releasedmp->setListener(0);// 2 调用disconnectmp->disconnect();
MediaPlayer 析构函数仍会尝试调用一次 disconnect 去释放远程资源:
MediaPlayer::~MediaPlayer()
{ALOGV("destructor");if (mAudioAttributesParcel != NULL) {delete mAudioAttributesParcel;mAudioAttributesParcel = NULL;}AudioSystem::releaseAudioSessionId(mAudioSessionId, (pid_t)-1);disconnect();IPCThreadState::self()->flushCommands();
}
到这里MediaPlayer Native对象资源释放完毕,MediaPlayer Java对象就无法再使用了。如果还想使用MediaPlayer 需要重新 new 一个对象,它的构造函数会重新创建一个 native 对象。
这篇关于Android 13 - Media框架(4)- MediaPlayerService的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






