本文主要是介绍Spring繁华的AOP王国---第一讲,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
Spring繁华的AOP王国---第一讲
- 为什么需要AOP
- AOP国家的公民
- JoinPoint
- PointCut
- PointCut表达式
- pointcut运算
- Advice
- beforeAdvice
- AfterAdvice
- aroundAdvice
- Introduction
- Aspect
- 织入和织入器
- 目标对象
- AOP王国底层运行机制
- 代理模式
- 静态代理
- 动态代理
- 动态字节码生成
- Spring aop 一世
- Spring aop中的Joinpoint
- Spring aop中的PointCut
- 常见的PointCut
- NameMatchMethodPointcut
- JdkRegexpMethodPointcut
- AnnotationMatchingPointcut
- ComposablePointcut
- ControlFlowPointcut
- 扩展pointcut
- 自定义StaticMethodMatcherPointcut
- 自定义DynamicMethodMatcherPointcut
- IOC容器中的pointcut
- Spring AOP中的Adivce
- per-class类型的Advice
- before advice
- ThrowsAdvice
- AfterReturningAdvice
- Around Advice
- per-instance类型的Advice
- Introduction
- DelegatingIntroductionInterceptor
- DelegatePerTargetObjectIntroductionInterceptor
- Spring AOP中的Aspect
- PointcutAdvisor
- DefaultPointcutAdvisor
- NameMatchMethodPointcutAdvisor
- RegexpMethodPointcutAdvisor
- DefaultBeanFactoryPointcutAdvisor
- IntroductionAdvisor分支
- Ordered作用
为什么需要AOP
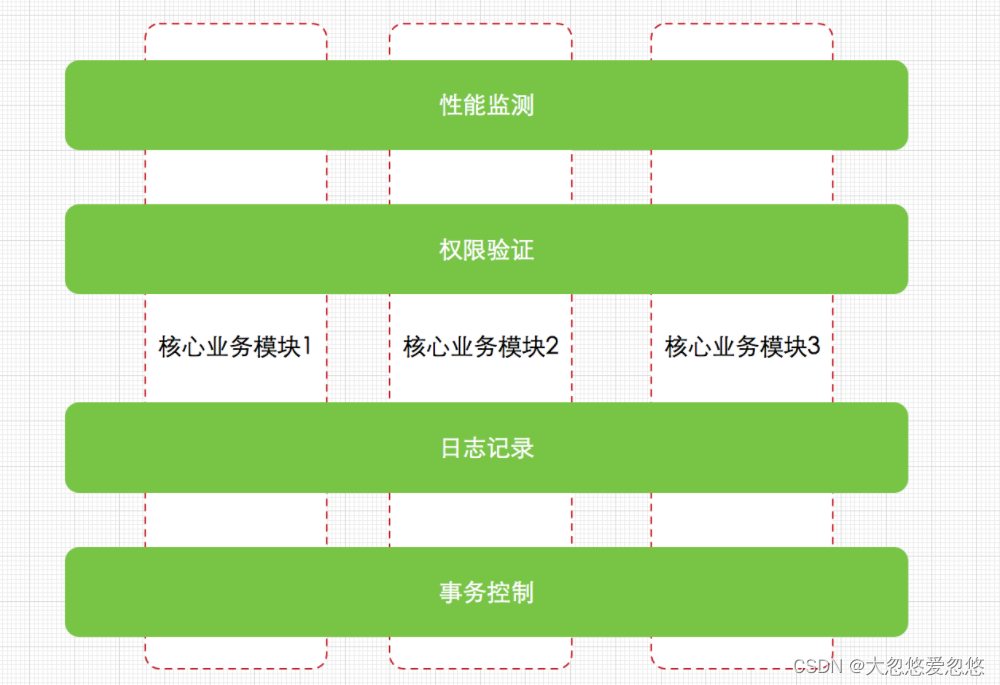
我相信上面这张图已经可以很好的说明AOP的作用了,为什么需要AOP?
如果不通过aop,那么类似于上面这些功能,就需要耦合到代码中去,如果使用了aop,那么我们在业务代码中是看不到上面这些功能的实现语句的,这样就进行了解耦,并且仿佛这些功能是自动被横切到业务逻辑中去的一样,非常神奇。
AOP国家的公民
JoinPoint
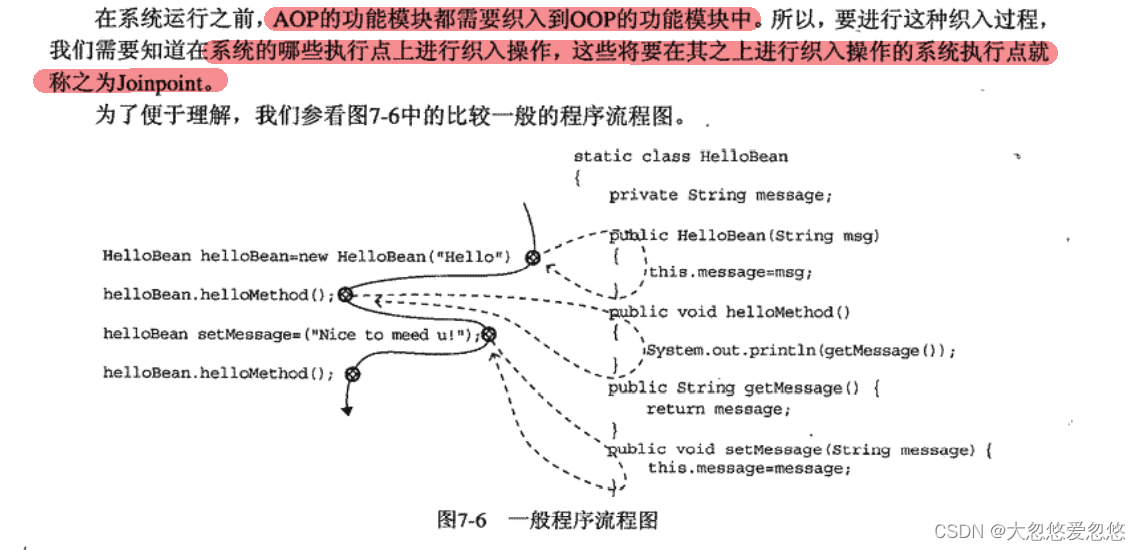
OOP:面向对象编程
AOP:面向切面编程



JoinPoint总结就是横切逻辑的织入点,这里织入点可以是构造方法,普通方法,字段,类初始化。但是并不是每个AOP具体的实现都支持上面这些织入点,大多都支持部分。
PointCut

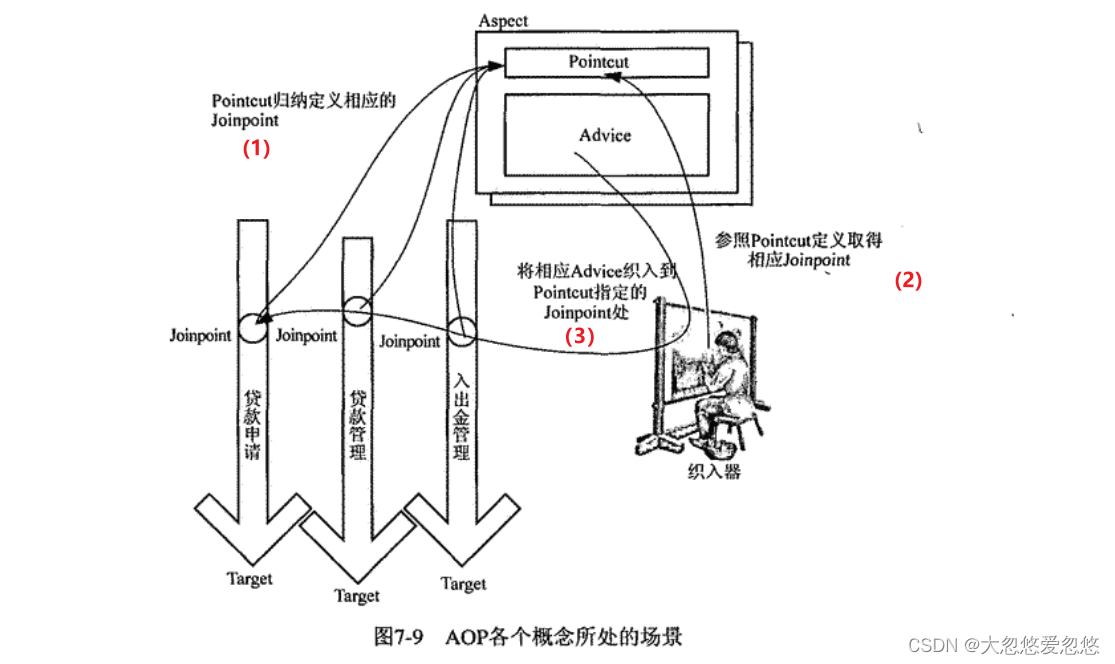
PointCut规定哪些织入点需要进行横切操作,然后这些织入点将被进行横切逻辑织入
PonitCut指定的这一组切入点就是一组JoinPoint
PointCut表达式

最后一点相信大家只要使用过spring aop aspectj实现的小伙伴都深有体会,即通过aspectj的表达式指定一个需要横切的范围,符合这些条件的方法都将被进行横切逻辑的织入
pointcut运算
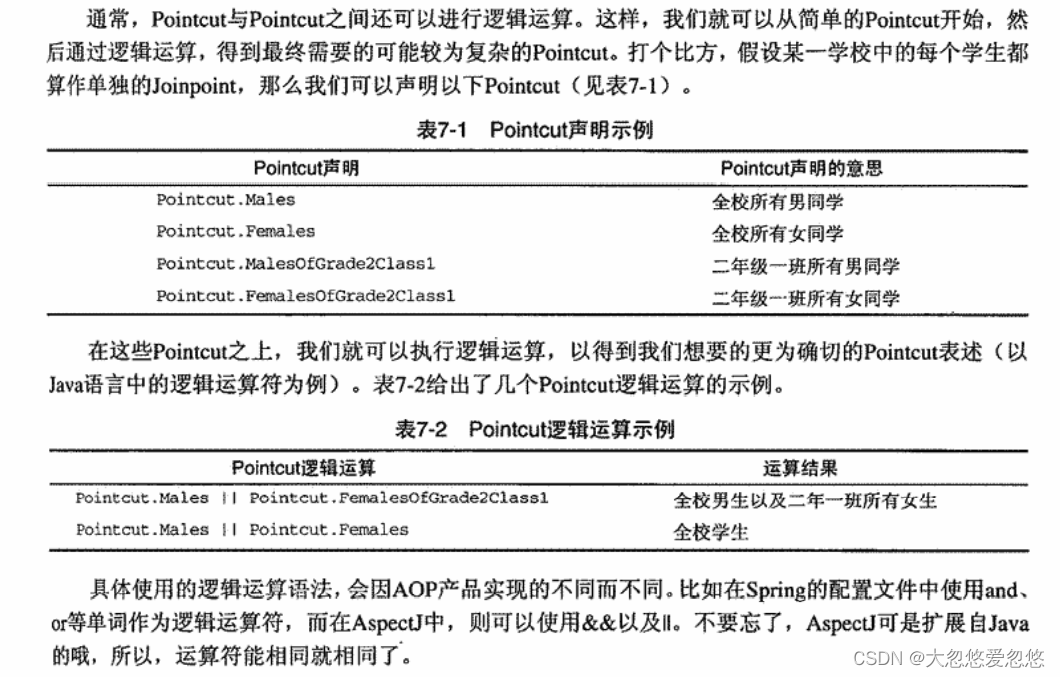
不知道各位在使用spring aop的过程中是否使用过pointcut的运算功能,就是其实求并集或者交集,即扩大或者缩小范围
Advice

Advice就是具体要织入进去的横切逻辑,被织入的切入点称为JointPoint,该切入点由PointCut指定,不知道各位明白没有
beforeAdvice

大家可以联系spring aop aspectj的实现进行理解,但是不要将aop等同于spring aop aspectj.两者一个是抽象,一个是具体实现
AfterAdvice


aroundAdvice

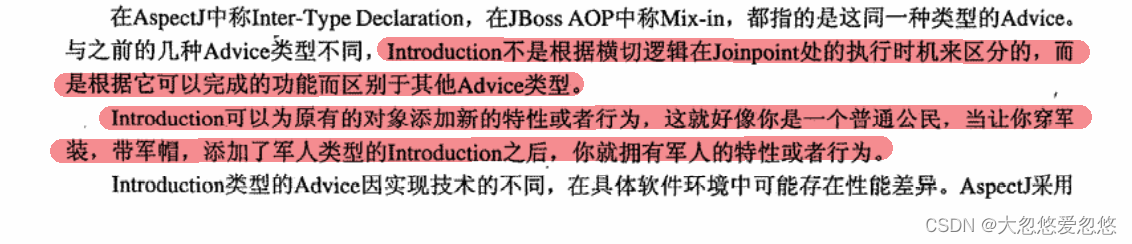
Introduction

Aspect

AspectJ风格定义的AspectJ声明
这里使用的是AspectJ的编译器对下面这个类进行的编译,然后再将编译生成的字节码对应被横切的java类源码中
public aspect MyAspectJDemo {/*** 定义切点,日志记录切点*/pointcut recordLog():call(* HelloWord.sayHello(..));/*** 定义切点,权限验证(实际开发中日志和权限一般会放在不同的切面中,这里仅为方便演示)*/pointcut authCheck():call(* HelloWord.sayHello(..));/*** 定义前置通知!*/before():authCheck(){System.out.println("sayHello方法执行前验证权限");}/*** 定义后置通知*/after():recordLog(){System.out.println("sayHello方法执行后记录日志");}
}
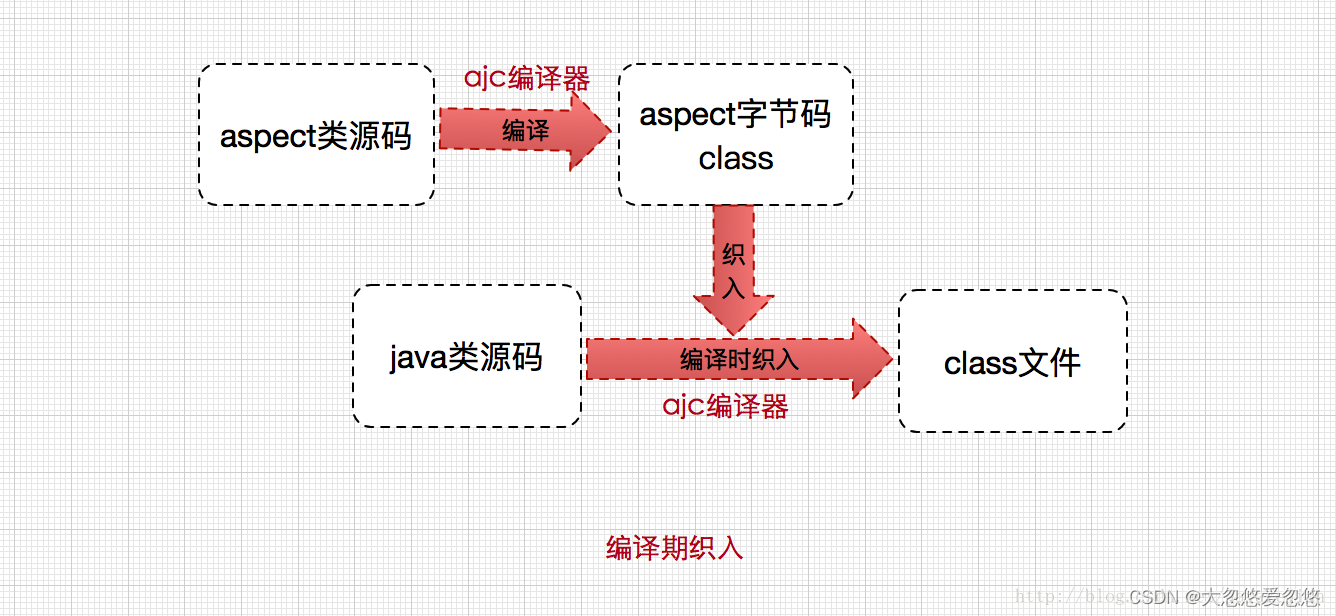
关于ajc编译器,是一种能够识别aspect语法的编译器,它是采用java语言编写的,由于javac并不能识别aspect语法,便有了ajc编译器,注意ajc编译器也可编译java文件。

织入和织入器
有诗句云,“一桥飞架南北,天堑变通途”,织入(Weaving)过程就是“飞架”AOP和OOP的那座桥,只有经过织入过程之后,以Aspect模块化的横切关注点才会集成到OOP的现存系统中。而完成织入过程的那个“人”就称之为织入器(Weaver)啦!
AspectJ有专门的编译器来完成织入操作,即ajc,所以ajc就是AspectJ完成织入的织入器;JBossAOP采用自定义的类加载器来完成最终织入,那么这个自定义的类加载器就是它的织入器;SpringAOP使用一组类来完成最终的织入操作,ProxyFactory类则是Spring AOP中最通用的织入器。总之,Java平台各AOP实现的织入器形式不一而足,唯一相同的就是它们的职责,即完成横切关注点逻辑到系统的最终织入。
目标对象

AOP王国底层运行机制
Spring AOP属于第二代AOP,采用动态代理机制和字节码生成技术实现,与最初Aspect采用编译器将横切逻辑织入目标对象不同,动态代理机制和字节码生成都是在运行期间为目标对象生成一个代理对象,而将横切逻辑织入到这个代理对象中,系统最终使用的是织入了横切逻辑的代理对象,而不是真正的目标对象。
为了理解这种差别以及最终可以达到的效果,我们有必要先从动态代理机制的根源----代理模式开始说起…
代理模式
之前在写设计模式专栏的时候,也写过一篇代理模式的介绍,感兴趣的童鞋可以了解一下:
代理模式
揭开动态代理的神秘面纱
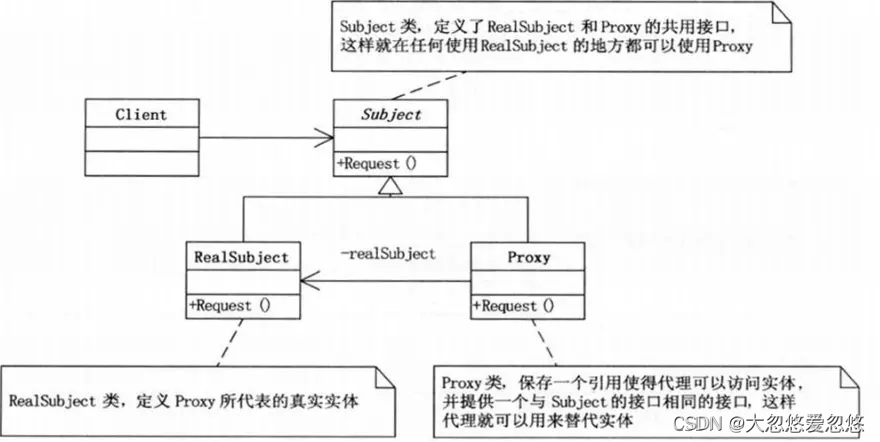
静态代理
这里给出静态代理的一个简单的小例子:
public class Request {public void doGet() throws InterruptedException {System.out.println("处理请求中...");Thread.sleep(new Random().nextInt(10));}
}
public class RequestProxy extends Request{private Request request;public RequestProxy(Request request) {this.request = request;}@Overridepublic void doGet() throws InterruptedException {long start = System.currentTimeMillis();request.doGet();long end = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println("当前请求耗时为: "+String.valueOf(end-start)+"毫秒");}
}public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {//没有被静态代理的类Request request=new Request();request.doGet();//被静态代理的类Request requestProxy=new RequestProxy(request);requestProxy.doGet();}
}

这个例子应该很容易看懂,这就对静态代理也就不过多介绍了,重点是对下面的动态代理进行介绍。
静态代理的缺点很明显: 虽然我们这里的Joinpoint相同(request()方法的执行),但是对应的目标对象类型是不一样的,针对不一样的目标对象类型,我们要为其单独实现一个代理对象,而实际上,这些代理对象所有添加的横切逻辑是一样的,当系统中存在大量符合Pointcut匹配条件的目标对象时,我们就需要为这些对象创建大量的代理对象,显然这是绝对行不通的!
动态代理
下面我们用JDK动态代理来实现一下上面的例子:
public interface IRequest {public void doGet() throws InterruptedException ;
}
public class Request implements IRequest{@Overridepublic void doGet() throws InterruptedException {System.out.println("处理请求中...");Thread.sleep(new Random().nextInt(10));}
}
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Request request=new Request();IRequest proxyInstance = (IRequest)Proxy.newProxyInstance(request.getClass().getClassLoader(),request.getClass().getInterfaces(),new InvocationHandler() {@Overridepublic Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {long start = System.currentTimeMillis();Object invoke = method.invoke(request, args);long end = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println("请求耗时为 :" + String.valueOf(end - start) + "毫秒");return invoke;}});proxyInstance.doGet();}
}


默认情况下,Spring AOP发现目标对象实现了相应的接口,则采用动态代理机制为其生成代理对象实例,而如果没有的话,则会尝试使用CGLIB代为完成
动态字节码生成
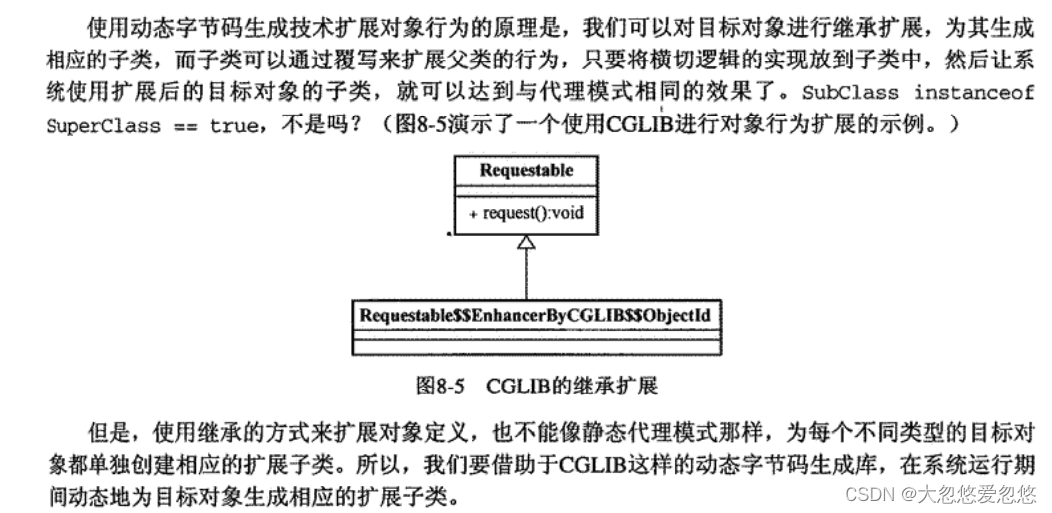
小例子:
public class Request{public void doGet() throws InterruptedException {System.out.println("处理请求中...");Thread.sleep(new Random().nextInt(10));}
}//实现MethodInterceptor接口
public class ProxyFactory implements MethodInterceptor
{//需要代理的目标对象private Object target;public ProxyFactory(Object target){this.target=target;}//获取代理对象的方法public Object getProxyInstance(){// 通过CGLIB动态代理获取代理对象的过程Enhancer enhancer=new Enhancer();// 设置enhancer对象的父类,因为Cglib是针对指定的类生成一个子类,所以需要指定父类enhancer.setSuperclass(target.getClass());//设置enhancer的回调对象enhancer.setCallback(this);// 创建代理对象return enhancer.create();}/*** @param o cglib生成的代理对象* @param method 被代理对象的方法* @param objects 传入方法的参数* @param methodProxy 代理的方法*/@Overridepublic Object intercept(Object o, Method method, Object[] objects,MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {long start = System.currentTimeMillis();//这里必须传入被代理的对象,否则会死循环//因为代理对象方法调用会触发拦截器Object ret= method.invoke(target, objects);long end = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println("请求耗时为 :" + String.valueOf(end - start) + "毫秒");return ret;}
}
public class Main {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {ProxyFactory proxyFactory=new ProxyFactory(new Request());Request proxyInstance = (Request) proxyFactory.getProxyInstance();proxyInstance.doGet();}
}
使用CGLIB对类进行扩展的唯一限制就是无法对final方法进行覆写
Spring aop 一世
Spring aop中的Joinpoint

Spring aop中的PointCut

public interface Pointcut {Pointcut TRUE = TruePointcut.INSTANCE;ClassFilter getClassFilter();MethodMatcher getMethodMatcher();
}

@FunctionalInterface
public interface ClassFilter {ClassFilter TRUE = TrueClassFilter.INSTANCE;boolean matches(Class<?> var1);
}

public interface MethodMatcher {MethodMatcher TRUE = TrueMethodMatcher.INSTANCE;boolean matches(Method var1, Class<?> var2);boolean isRuntime();boolean matches(Method var1, Class<?> var2, Object... var3);
}


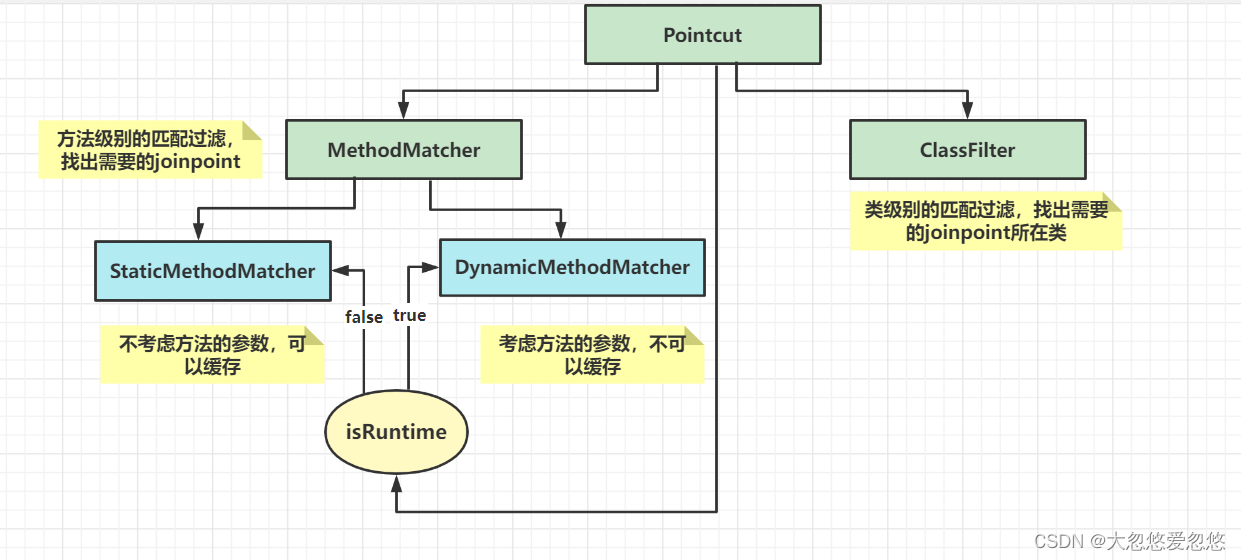

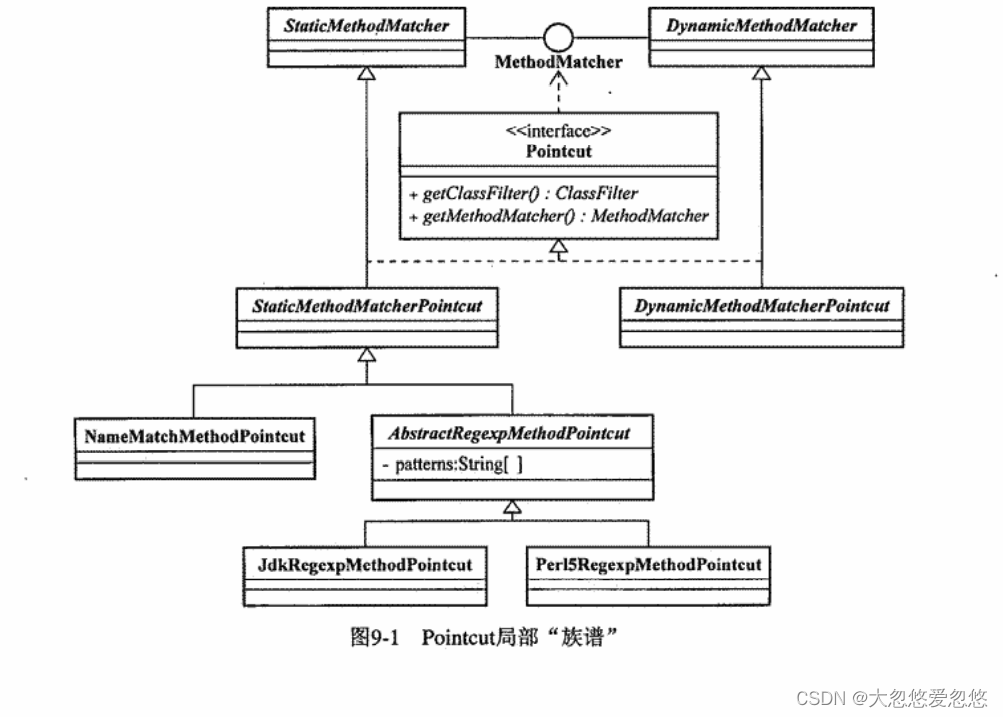
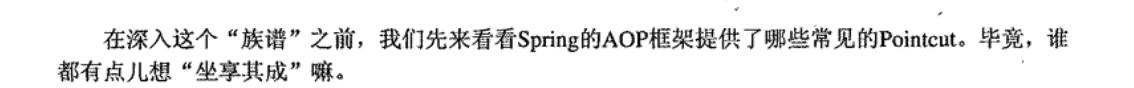
首先明确一点概念: PointCut是用来规定一组joinpoint的
常见的PointCut
NameMatchMethodPointcut
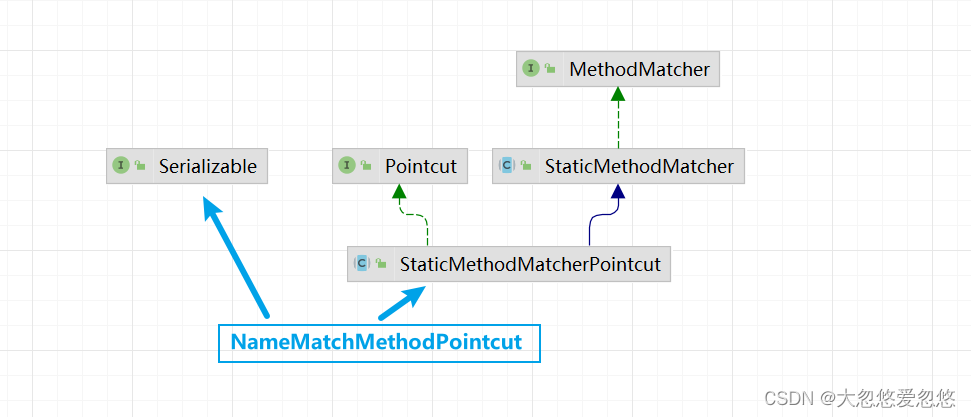

public class NameMatchMethodPointcut extends StaticMethodMatcherPointcut implements Serializable {private List<String> mappedNames = new ArrayList();public NameMatchMethodPointcut() {}public void setMappedName(String mappedName) {this.setMappedNames(mappedName);}public void setMappedNames(String... mappedNames) {this.mappedNames = new ArrayList(Arrays.asList(mappedNames));}public NameMatchMethodPointcut addMethodName(String name) {this.mappedNames.add(name);return this;}public boolean matches(Method method, Class<?> targetClass) {Iterator var3 = this.mappedNames.iterator();String mappedName;do {if (!var3.hasNext()) {return false;}mappedName = (String)var3.next();} while(!mappedName.equals(method.getName()) && !this.isMatch(method.getName(), mappedName));return true;}protected boolean isMatch(String methodName, String mappedName) {return PatternMatchUtils.simpleMatch(mappedName, methodName);}.....
}JdkRegexpMethodPointcut
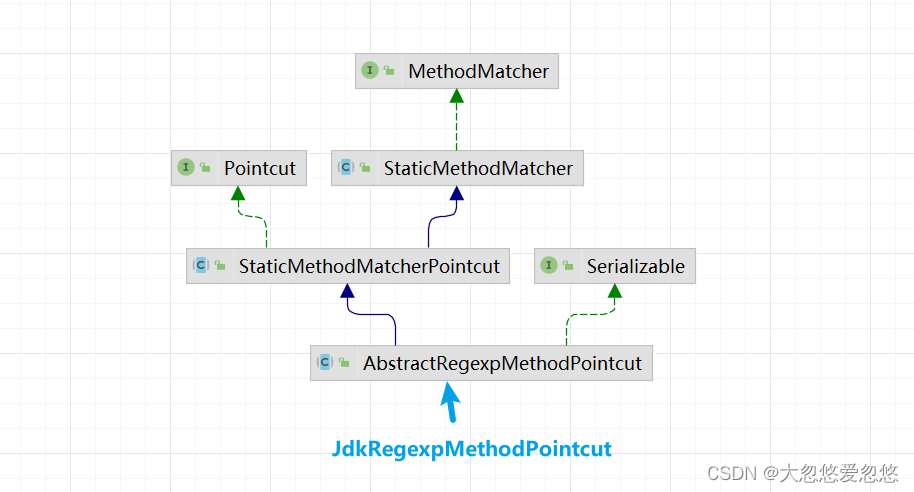



public class JdkRegexpMethodPointcut extends AbstractRegexpMethodPointcut {private Pattern[] compiledPatterns = new Pattern[0];private Pattern[] compiledExclusionPatterns = new Pattern[0];public JdkRegexpMethodPointcut() {}protected void initPatternRepresentation(String[] patterns) throws PatternSyntaxException {this.compiledPatterns = this.compilePatterns(patterns);}protected void initExcludedPatternRepresentation(String[] excludedPatterns) throws PatternSyntaxException {this.compiledExclusionPatterns = this.compilePatterns(excludedPatterns);}protected boolean matches(String pattern, int patternIndex) {Matcher matcher = this.compiledPatterns[patternIndex].matcher(pattern);return matcher.matches();}protected boolean matchesExclusion(String candidate, int patternIndex) {Matcher matcher = this.compiledExclusionPatterns[patternIndex].matcher(candidate);return matcher.matches();}private Pattern[] compilePatterns(String[] source) throws PatternSyntaxException {Pattern[] destination = new Pattern[source.length];for(int i = 0; i < source.length; ++i) {destination[i] = Pattern.compile(source[i]);}return destination;}
}AnnotationMatchingPointcut

@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface ClassLevelAnnotation { } @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
public @interface MethodLevelAnnotation { }

@ClassLevelAnnotation
public class TargetObject { @MethodLevelAnnotation public void method1() { System.out.println("target : method1"); } public void method2() { System.out.println("target : method2"); }
}


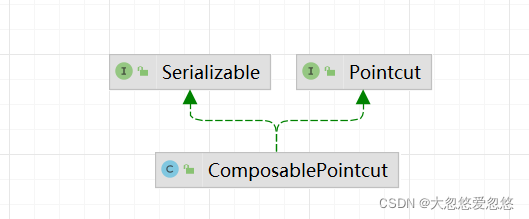
ComposablePointcut

ControlFlowPointcut



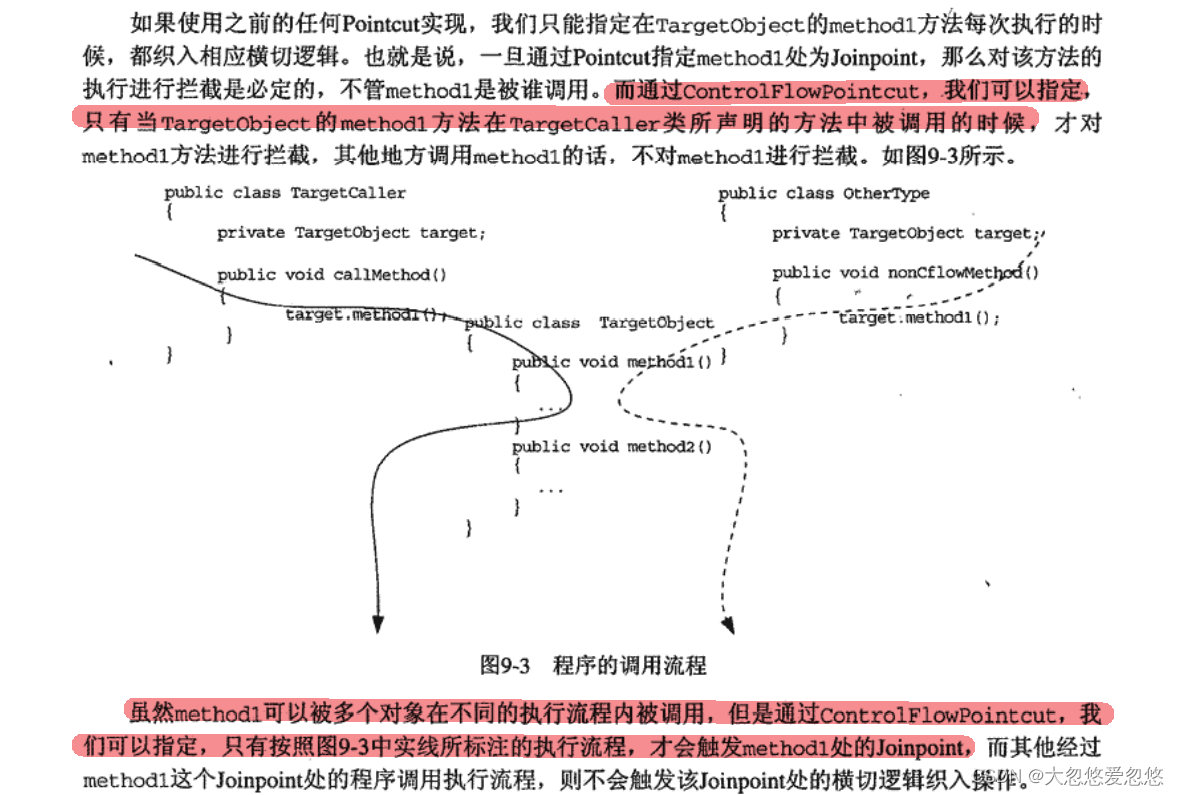
上面的pointcut对于方法的切入范围都相对来说比较宽泛,无法限制到只有方法在被指定类调用的时候,才会被织入切入的逻辑,而当前正在讲解的这个pointcut可以实现上面的需求



扩展pointcut

自定义StaticMethodMatcherPointcut


自定义DynamicMethodMatcherPointcut

IOC容器中的pointcut


Spring AOP中的Adivce
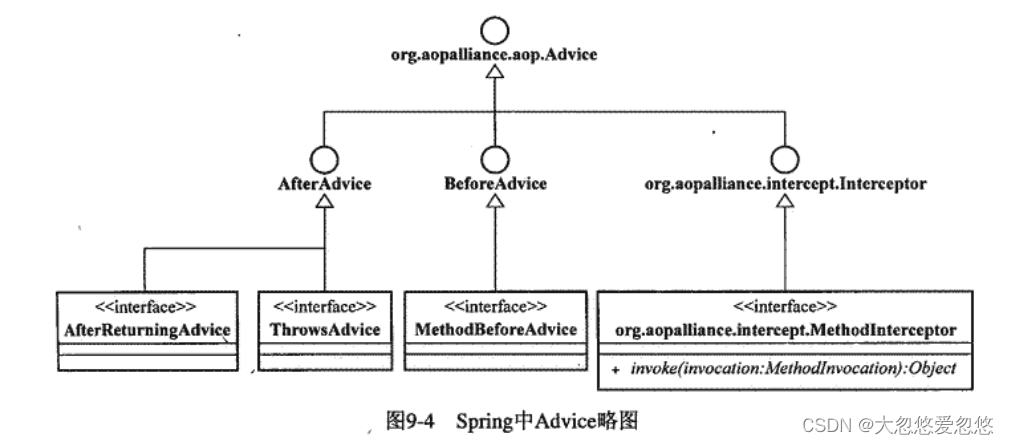
pointcut负责找到所有符合条件的joinpoint,然后由织入器将advice里面的横切逻辑织入到这些joinpoint中去


per-class类型的Advice


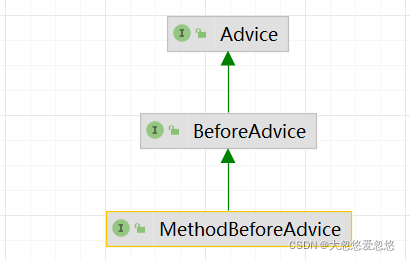
before advice


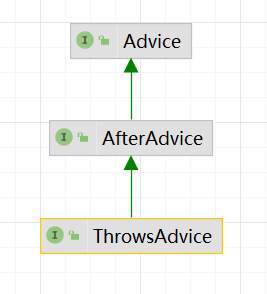
ThrowsAdvice



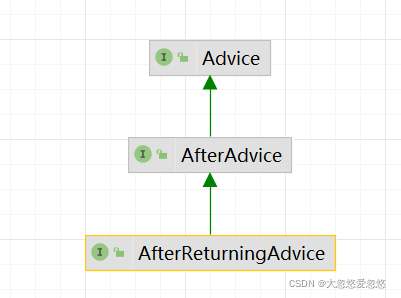
AfterReturningAdvice

public interface AfterReturningAdvice extends AfterAdvice {void afterReturning(@Nullable Object returnValue, Method method, Object[] args, @Nullable Object target) throws Throwable;
}

Around Advice
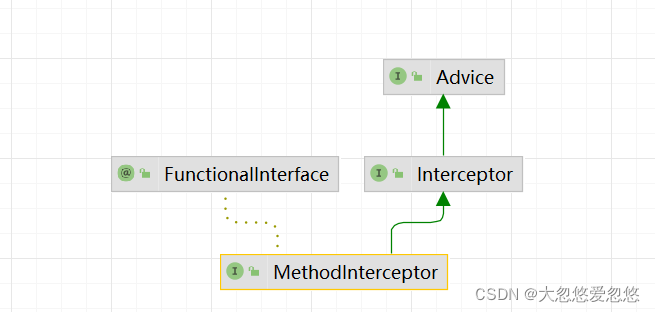

@FunctionalInterface
public interface MethodInterceptor extends Interceptor {@NullableObject invoke(@Nonnull MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable;
}


per-instance类型的Advice

Introduction

public interface IntroductionInterceptor extends MethodInterceptor, DynamicIntroductionAdvice {
}
public interface DynamicIntroductionAdvice extends Advice {boolean implementsInterface(Class<?> intf);
}
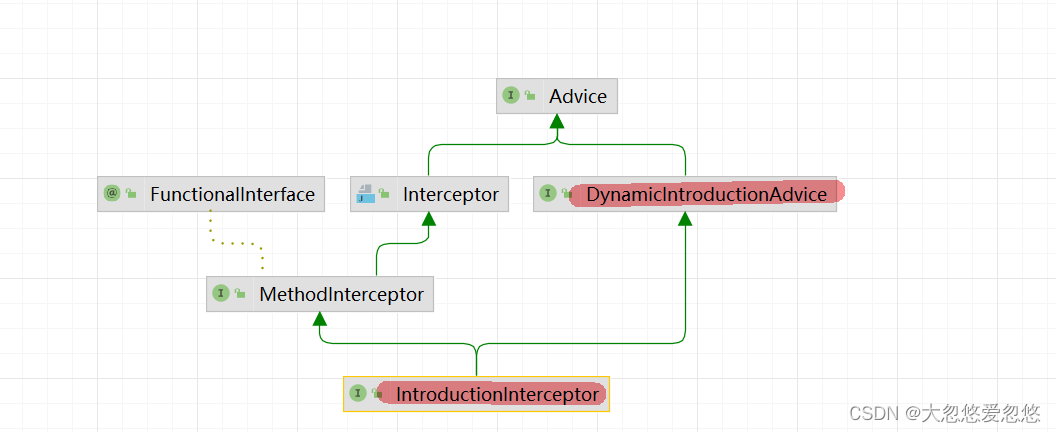


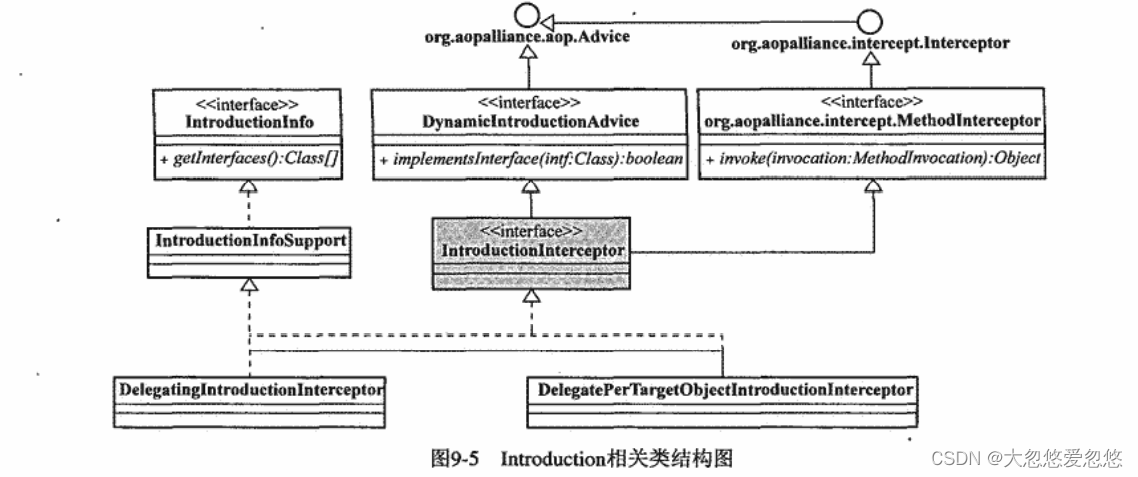

public interface IntroductionInfo {Class<?>[] getInterfaces();
}


DelegatingIntroductionInterceptor




DelegatePerTargetObjectIntroductionInterceptor



Spring AOP中的Aspect

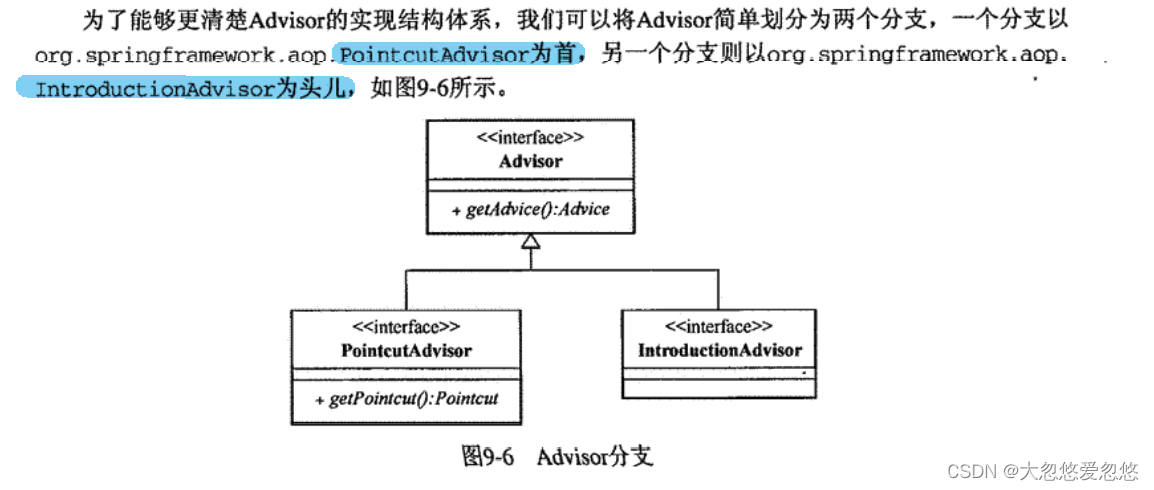
PointcutAdvisor

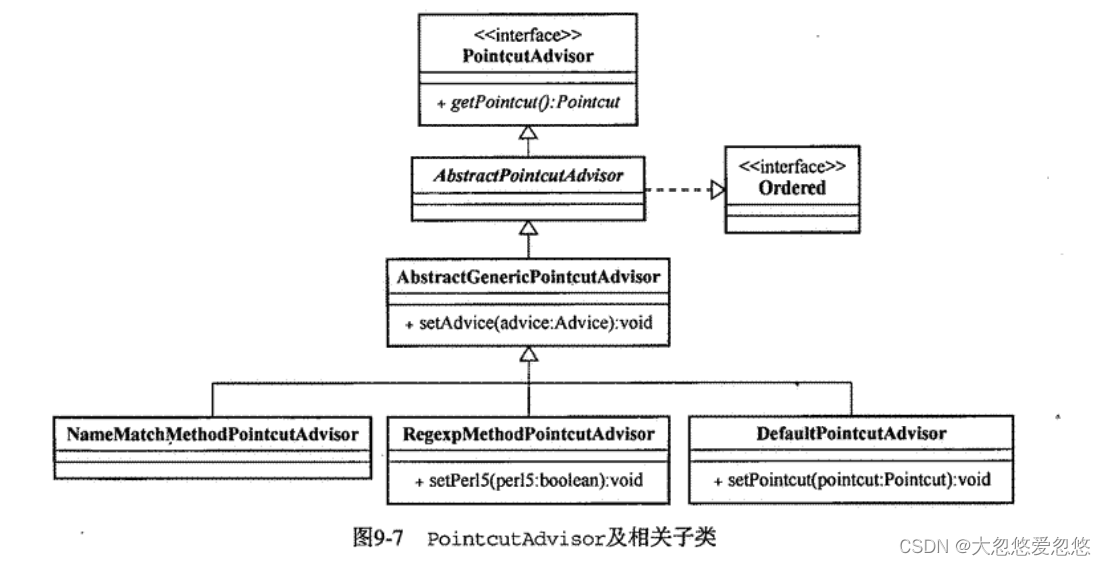

DefaultPointcutAdvisor
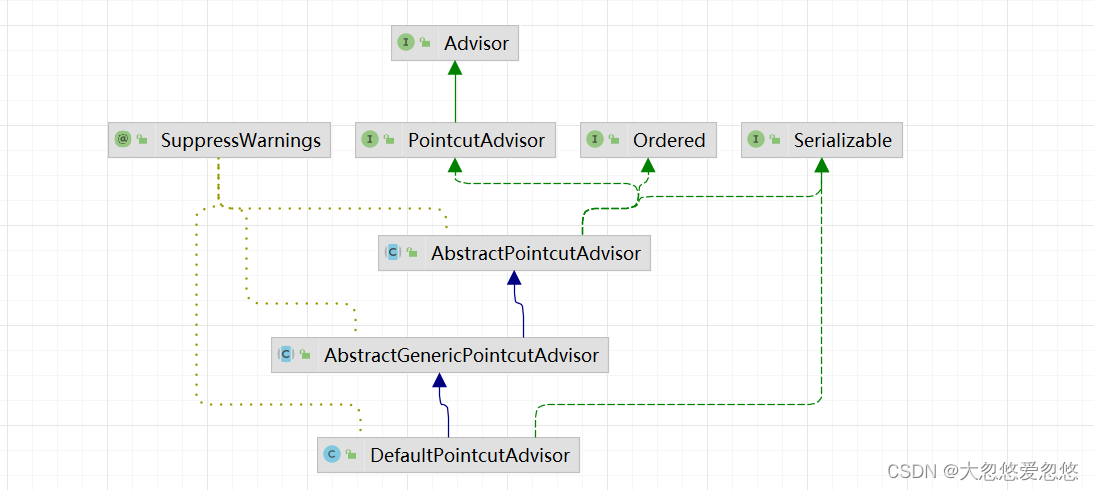
Generic: 通用的



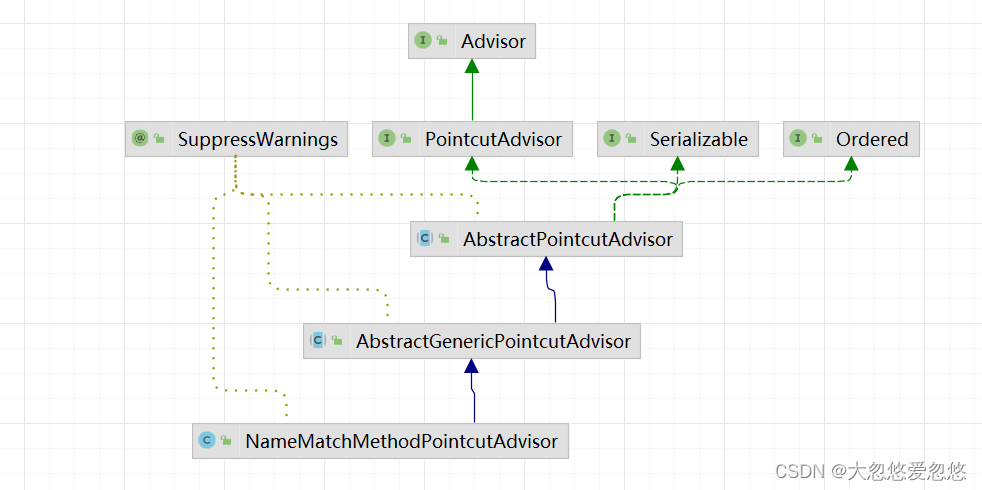
NameMatchMethodPointcutAdvisor


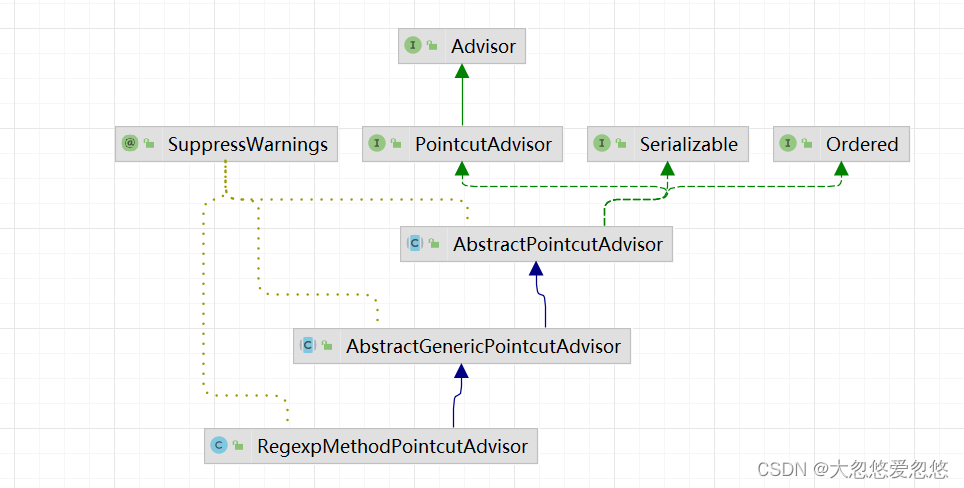
RegexpMethodPointcutAdvisor


DefaultBeanFactoryPointcutAdvisor
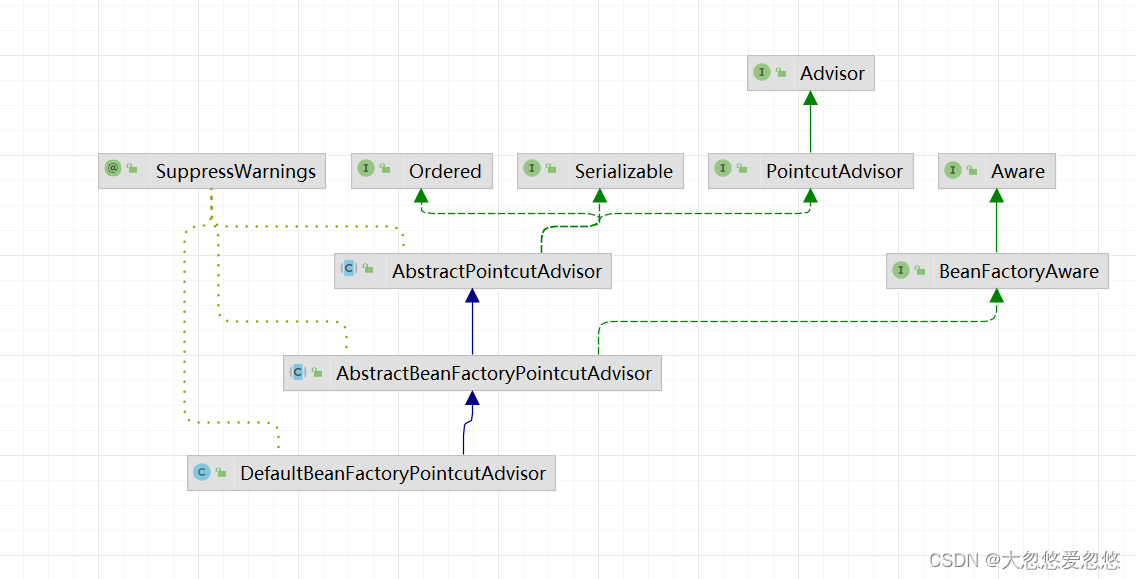


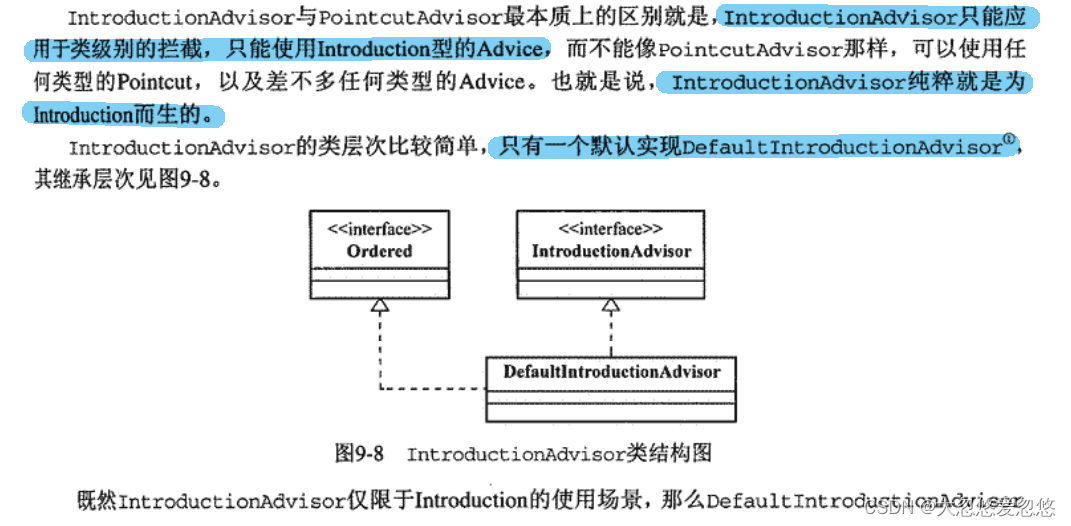
IntroductionAdvisor分支


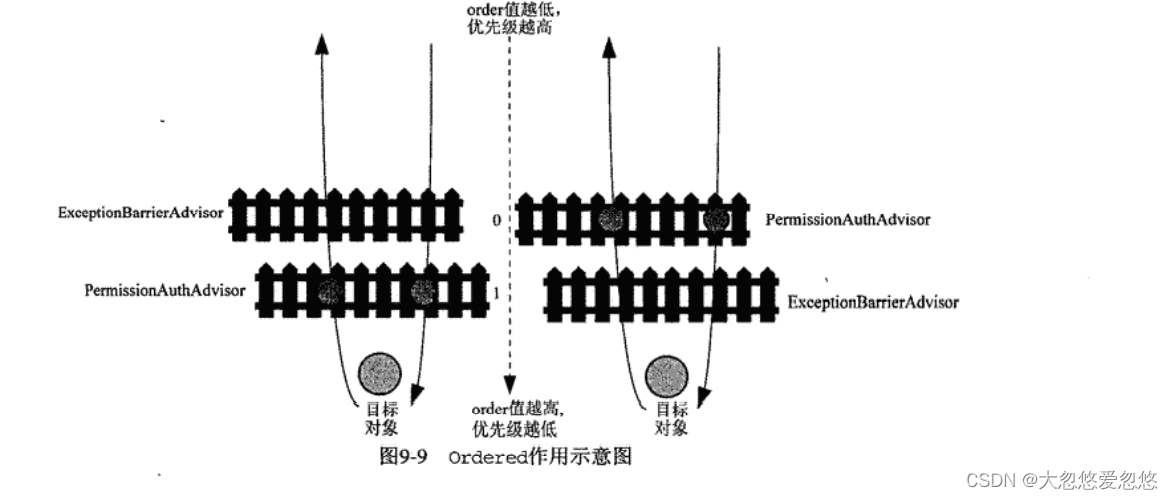
Ordered作用



这篇关于Spring繁华的AOP王国---第一讲的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






