本文主要是介绍python circular doubly linked list,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
python的双向链表
- 需求
- 码
- 番外
最近写装饰器看了 functools.lru_cache 的源码1,里面发现了这样的代码:
root = [] # root of the circular doubly linked listroot[:] = [root, root, None, None] # initialize by pointing to self
类似的代码之前在 collections.OrderedDict 的源码里见过,之前也写过相关文章2 ,但再看依然理解不深,于是今天再来聊聊这个。
需求
-
lru_cache
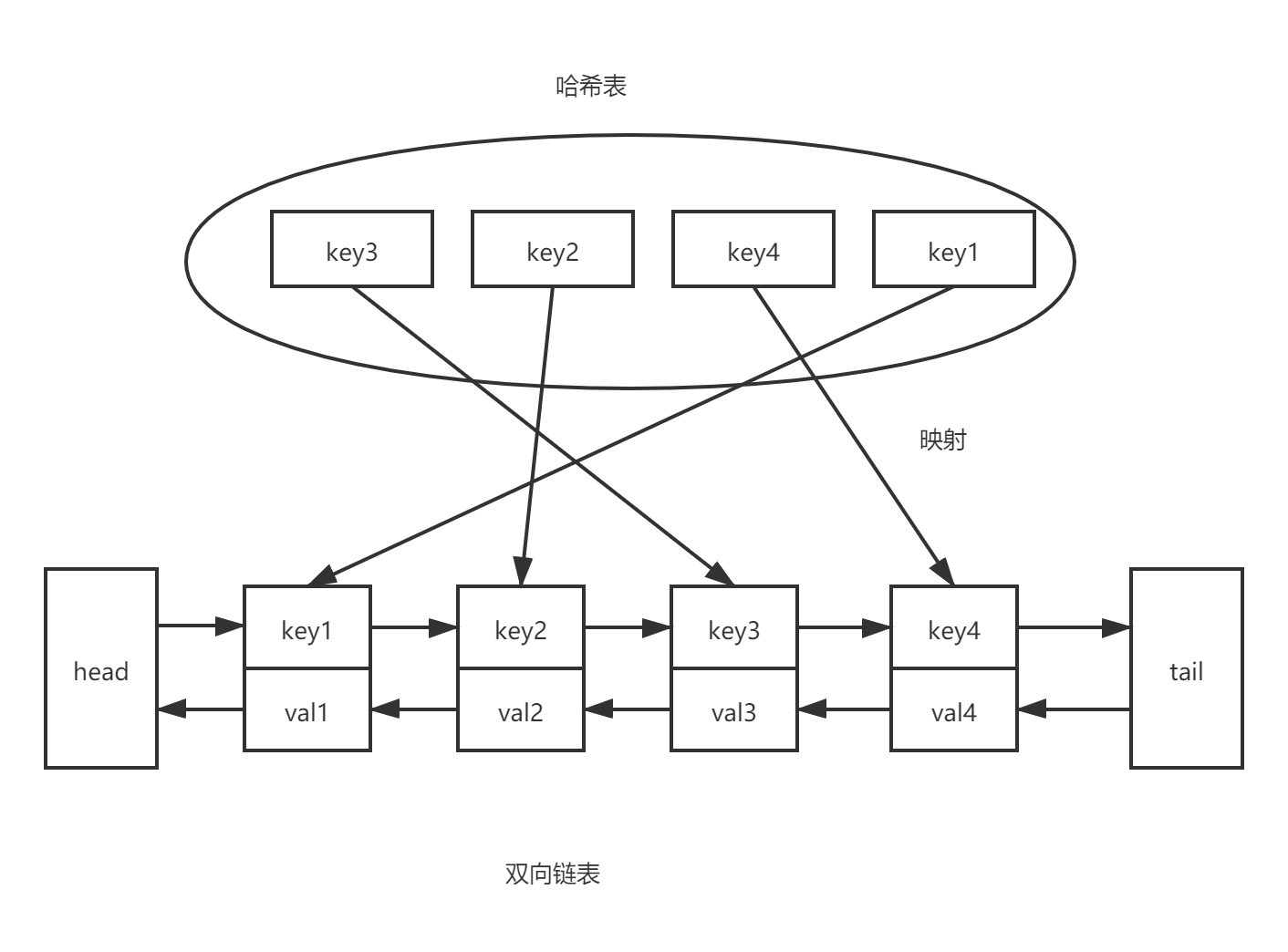
首先是记录和调整顺序(插入移动删除),由双向链表来实现;其次是通过键查询到值,由哈希表来实现。
-
OrderedDict
先讲个题外话,虽然自 Python 3.7 之后,字典的顺序会确保为插入顺序,但是 OrderedDict 并没有被干掉,搜了下只发现了这个答案3,它谈到了
OrderedDict.move_to_end()和比较相等时的顺序敏感性。
那么 OrderedDict 需要啥呢,本质上和上面一样,哈希表查找快,但是数据无固定顺序;链表有顺序之分,插入删除快,但是查找慢,结合一下就是哈希双向链表。
码
因为经常需要对队头和队尾进行操作,为了简化算法,设置一个哨兵节点 root
PREV, NEXT, KEY, RESULT = 0, 1, 2, 3 # names for the link fieldsroot = [] # root of the circular doubly linked listroot[:] = [root, root, None, None] # initialize by pointing to self
root[PERV] 表示队尾的节点, root[NEXT] 表示队头的节点。
下面是一些操作
# 添加节点到队尾
# Put result in a new link at the front of the queue.
last = root[PREV]
link = [last, root, key, result]
last[NEXT] = root[PREV] = cache[key] = link# 移动节点到队尾
# Move the link to the front of the circular queue
link_prev, link_next, _key, result = link
link_prev[NEXT] = link_next
link_next[PREV] = link_prev
last = root[PREV]
last[NEXT] = root[PREV] = link
link[PREV] = last
link[NEXT] = root# 删除头节点并添加节点到队尾 这里把要删除的节点的key/result清空 变成新的哨兵节点
# 旧哨兵节点直接存入添加节点的key/result
# Use the old root to store the new key and result.
oldroot = root
oldroot[KEY] = key
oldroot[RESULT] = result
# Empty the oldest link and make it the new root.
# Keep a reference to the old key and old result to
# prevent their ref counts from going to zero during the
# update. That will prevent potentially arbitrary object
# clean-up code (i.e. __del__) from running while we're
# still adjusting the links.
root = oldroot[NEXT]
oldkey = root[KEY]
oldresult = root[RESULT]
root[KEY] = root[RESULT] = None
# Now update the cache dictionary.
del cache[oldkey]
# Save the potentially reentrant cache[key] assignment
# for last, after the root and links have been put in
# a consistent state.
cache[key] = oldroot
关于 collections.OrderedDict 为什么舍弃掉这种写法,而使用了节点类和弱引用,我想就是因为 OrderedDict 里面有一些删除操作,在循环引用下可能会有内存的问题。
可以看到 lru_cache 装饰器里没有删除单个节点的操作,当缓存数量达到 maxsize 时,优化的算法没有先删除再添加,而是修改节点然后移动哨兵节点的位置。
番外
对函数传入的参数做哈希可以参考源码这部分,当然参数必须是可哈希的
class _HashedSeq(list):""" This class guarantees that hash() will be called no more than onceper element. This is important because the lru_cache() will hashthe key multiple times on a cache miss."""__slots__ = 'hashvalue'def __init__(self, tup, hash=hash):self[:] = tupself.hashvalue = hash(tup)def __hash__(self):return self.hashvaluedef _make_key(args, kwds, typed,kwd_mark = (object(),),fasttypes = {int, str},tuple=tuple, type=type, len=len):"""Make a cache key from optionally typed positional and keyword argumentsThe key is constructed in a way that is flat as possible rather thanas a nested structure that would take more memory.If there is only a single argument and its data type is known to cacheits hash value, then that argument is returned without a wrapper. Thissaves space and improves lookup speed."""# All of code below relies on kwds preserving the order input by the user.# Formerly, we sorted() the kwds before looping. The new way is *much*# faster; however, it means that f(x=1, y=2) will now be treated as a# distinct call from f(y=2, x=1) which will be cached separately.key = argsif kwds:key += kwd_markfor item in kwds.items():key += itemif typed:key += tuple(type(v) for v in args)if kwds:key += tuple(type(v) for v in kwds.values())elif len(key) == 1 and type(key[0]) in fasttypes:return key[0]return _HashedSeq(key)
最后贴两篇也是分析 lru_cache 源码的文章4 5,别人都会实现双向链表,我好菜呜呜呜~
其他存替换策略(cache replacement policies)6
https://github.com/python/cpython/blob/main/Lib/functools.py#L427 ↩︎
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41967784/article/details/105370492 ↩︎
https://stackoverflow.com/a/50872567 ↩︎
https://blog.51cto.com/nu1l/3584159 ↩︎
https://www.cnblogs.com/TM0831/p/13268327.html ↩︎
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cache_replacement_policies ↩︎
这篇关于python circular doubly linked list的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!



