本文主要是介绍Spring源码阅读之PropertySource,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
试问,一篇文章一半的字不认识,你能理解讲了什么故事吗?Spring中大部分的类你都陌生,你能读懂?顶多是死记硬背罢了!
本文带你了解Spring中的存储属性资源的类-PropertySource
最佳打开方式:自己一边手动翻看源码,一边对照阅读。文章中粘出的代码都很容易,慢慢啃,绝对有收获!
一、PropertySource
public abstract class PropertySource<T> {protected final String name;protected final T source;public String getName() {return this.name;}public T getSource() {return this.source;}public boolean containsProperty(String name) {return (getProperty(name) != null);}public abstract Object getProperty(String name);
}最上层的类PropertySource是一个抽象类,只有2个属性,name和泛型定义的source,而且是final标注的,表明赋值后不可修改。方法也很简单,用来获取属性。
下面是类关系图:
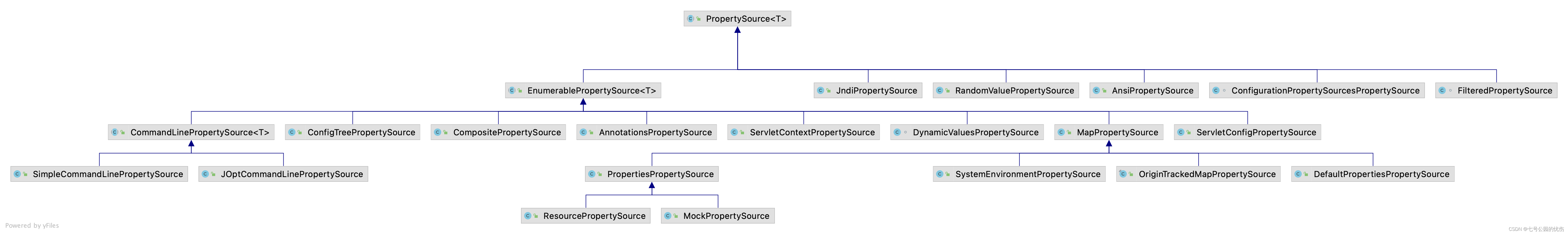
看着很复杂,但其实仔细看可以发现,以PropertySource为基础,一共能分为2部分:左边的EnumerablePropertySource为一部分,剩下右边的为一部分,接下来,我们来看看这两部分分别是干什么的。
二、右半部分
这部分是直接继承自PropertySource,而且没有子类,如下图中用红框圈出的部分:
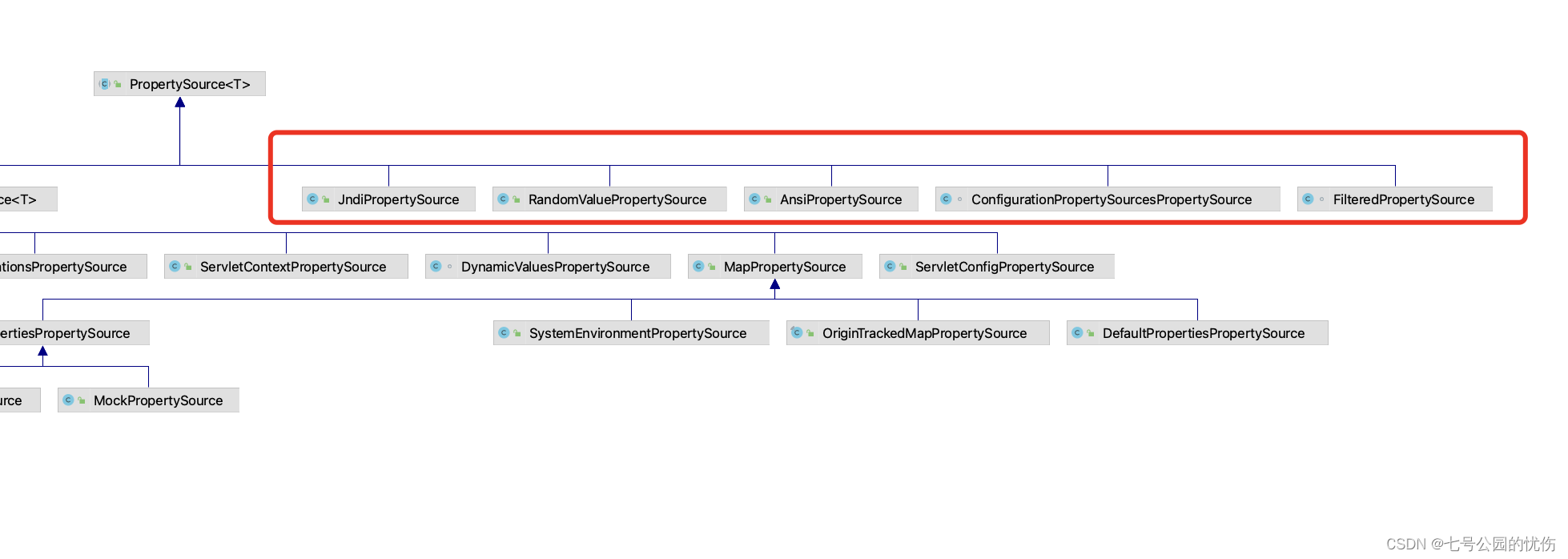
2.1 JndiPropertySource
该类的作用是从底层Spring JndLocatorDelegate读取属性,要查找的名称将自动以“java:comp/env/”作为前缀。
public class JndiPropertySource extends PropertySource<JndiLocatorDelegate> {public JndiPropertySource(String name) {this(name, JndiLocatorDelegate.createDefaultResourceRefLocator());}public JndiPropertySource(String name, JndiLocatorDelegate jndiLocator) {super(name, jndiLocator);}public Object getProperty(String name) {if (getSource().isResourceRef() && name.indexOf(':') != -1) {return null;}try {Object value = this.source.lookup(name);if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {logger.debug("JNDI lookup for name [" + name + "] returned: [" + value + "]");}return value;}catch (NamingException ex) {if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {logger.debug("JNDI lookup for name [" + name + "] threw NamingException " +"with message: " + ex.getMessage() + ". Returning null.");}return null;}}
}
JNDI即Java Naming and Directory Interface(JAVA命名和目录接口)。为开发人员提供了查找和访问各种命名和目录服务的通用、统一的接口。
2.2 RandomValuePropertySource
该类为任何以"random."开头的属性返回一个随机值,主要代码如下:
public class RandomValuePropertySource extends PropertySource<Random> {public static final String RANDOM_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "random";private static final String PREFIX = "random.";public RandomValuePropertySource() {this(RANDOM_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME);}public RandomValuePropertySource(String name) {super(name, new Random());}@Overridepublic Object getProperty(String name) {if (!name.startsWith(PREFIX)) {return null;}logger.trace(LogMessage.format("Generating random property for '%s'", name));return getRandomValue(name.substring(PREFIX.length()));}private Object getRandomValue(String type) {if (type.equals("int")) {return getSource().nextInt();}if (type.equals("long")) {return getSource().nextLong();}String range = getRange(type, "int");if (range != null) {return getNextIntInRange(Range.of(range, Integer::parseInt));}range = getRange(type, "long");if (range != null) {return getNextLongInRange(Range.of(range, Long::parseLong));}if (type.equals("uuid")) {return UUID.randomUUID().toString();}return getRandomBytes();}这里举几个例子来说明用法:
class test{public static void main(String[] args) {RandomValuePropertySource random = new RandomValuePropertySource();System.out.println(random.getProperty("random.int"));//生成int随机数System.out.println(random.getProperty("random.int(100,200)"));//指定范围System.out.println(random.getProperty("random.long"));//生成long随机数System.out.println(random.getProperty("random.long(200,300)"));//指定范围System.out.println(random.getProperty("random.uuid"));//生成随机uuid}
}
2.3 AnsiPropertySource
该类的作用是用来获取AnsiStyle形式的属性,使用的地方在SpringBoot的banner中。
代码如下:
public class AnsiPropertySource extends PropertySource<AnsiElement> {private static final Iterable<Mapping> MAPPINGS;static {List<Mapping> mappings = new ArrayList<>();mappings.add(new EnumMapping<>("AnsiStyle.", AnsiStyle.class));mappings.add(new EnumMapping<>("AnsiColor.", AnsiColor.class));mappings.add(new Ansi8BitColorMapping("AnsiColor.", Ansi8BitColor::foreground));mappings.add(new EnumMapping<>("AnsiBackground.", AnsiBackground.class));mappings.add(new Ansi8BitColorMapping("AnsiBackground.", Ansi8BitColor::background));mappings.add(new EnumMapping<>("Ansi.", AnsiStyle.class));mappings.add(new EnumMapping<>("Ansi.", AnsiColor.class));mappings.add(new EnumMapping<>("Ansi.BG_", AnsiBackground.class));MAPPINGS = Collections.unmodifiableList(mappings);}
}定义了颜色、字体风格、背景等。
使用的时候,在banner.txt中如下:
${AnsiColor.BRIGHT_YELLOW}${AnsiStyle.BOLD}
__ _ ___________ ___
\ \/ \/ /\____ \ \/ /\ / | |_> > <\/\_/ | __/__/\_ \|__| \/
${AnsiColor.CYAN}${AnsiStyle.BOLD}
:: Java :: (v${java.version})
:: Spring Boot :: (v${spring-boot.version})
${Ans那么启动的时候,解析过程会调用该类,结果如下:

3.3 ConfigurationPropertySourcesPropertySource
这个类没有特别的地方,是为了便于这些属性资源可以与PropertySolver一起使用或添加到 Environment中。
这个类后续讲 Environment和PropertySolver会说到。
3.4 FilteredPropertySource
这个类使用来过滤掉一些指定的属性,代码如下:
class FilteredPropertySource extends PropertySource<PropertySource<?>> {private final Set<String> filteredProperties;FilteredPropertySource(PropertySource<?> original, Set<String> filteredProperties) {super(original.getName(), original);this.filteredProperties = filteredProperties;}@Overridepublic Object getProperty(String name) {if (this.filteredProperties.contains(name)) {return null;}return getSource().getProperty(name);}
}该类支持把别的PropertySource传入,并且指定一个特定的集合,查询的时候,指定集合中的属性返回null。
三、左半部分
右半部分说完,我们来看左半部分,左边都是PropertySource的子类EnumerablePropertySource类的派生类,如下:

我们先来看EnumerablePropertySource,这个看名字含义是:可枚举的PropertySource,代码如下:
public abstract class EnumerablePropertySource<T> extends PropertySource<T> {public EnumerablePropertySource(String name, T source) {super(name, source);}protected EnumerablePropertySource(String name) {super(name);}@Overridepublic boolean containsProperty(String name) {return ObjectUtils.containsElement(getPropertyNames(), name);}public abstract String[] getPropertyNames();}
和名字一样,只是比父类多了一个抽象方法,用于获取source中的所有属性名字。
子类都很类似,都是获取属性的一些方法,我们这里主要讲一下MapPropertySource和他的子类。
3.1 MapPropertySource
该类作用和名字意思一样,指定了父类中T source中泛型类型,为map。实现了父类EnumerablePropertySource的方法,获取了map中key的集合。
public class MapPropertySource extends EnumerablePropertySource<Map<String, Object>> {public MapPropertySource(String name, Map<String, Object> source) {super(name, source);}@Override@Nullablepublic Object getProperty(String name) {return this.source.get(name);}@Overridepublic boolean containsProperty(String name) {return this.source.containsKey(name);}@Overridepublic String[] getPropertyNames() {return StringUtils.toStringArray(this.source.keySet());}}3.2 DefaultPropertiesPropertySource
该类是MapPropertySource的子类,类中与父类与众不同的方法都加了注释:
下面代码中出现的PropertySources和PropertySource不是一回事,和名字意思一样,PropertySources中包含了多个PropertySource。
public class DefaultPropertiesPropertySource extends MapPropertySource {public static final String NAME = "defaultProperties";//入参中的propertySource名字是否和当前类一样public static boolean hasMatchingName(PropertySource<?> propertySource) {return (propertySource != null) && propertySource.getName().equals(NAME);}//参数校验通过后,将入参source带入action中执行public static void ifNotEmpty(Map<String, Object> source, Consumer<DefaultPropertiesPropertySource> action) {if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(source) && action != null) {action.accept(new DefaultPropertiesPropertySource(source));}}//将给定的map添加到sources中,或者合sources中的名字为NAME的source合并public static void addOrMerge(Map<String, Object> source, MutablePropertySources sources) {if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(source)) {Map<String, Object> resultingSource = new HashMap<>();DefaultPropertiesPropertySource propertySource = new DefaultPropertiesPropertySource(resultingSource);if (sources.contains(NAME)) {mergeIfPossible(source, sources, resultingSource);sources.replace(NAME, propertySource);}else {resultingSource.putAll(source);sources.addLast(propertySource);}}}@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")private static void mergeIfPossible(Map<String, Object> source, MutablePropertySources sources,Map<String, Object> resultingSource) {PropertySource<?> existingSource = sources.get(NAME);if (existingSource != null) {Object underlyingSource = existingSource.getSource();if (underlyingSource instanceof Map) {resultingSource.putAll((Map<String, Object>) underlyingSource);}resultingSource.putAll(source);}}//将propertySources中名字为NAME("defaultProperties")的source移动到最后public static void moveToEnd(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {PropertySource<?> propertySource = propertySources.remove(NAME);if (propertySource != null) {propertySources.addLast(propertySource);}}}四、总结
通过这么多类的说明,大家应该对PropertySource有了深刻的理解,说白了就是对属性资源的操作类,Spring根据不同的使用场景实现了不同的类。
觉得有帮助的同学不妨点个赞吧!你的支持是我写作的最大动力,谢谢!
这篇关于Spring源码阅读之PropertySource的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




