本文主要是介绍LabVIEW在打开一个新的引用,提示内存已满,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
LabVIEW在打开一个新的引用,提示内存已满
运行LabVIEW代码时,收到错误2 LabVIEW:内存已满。错误发生于创建一个VI的新引用时,例如(获取通知器,获取队列,打开VI引用,.NET构造函数节点,打开/创建/替换文件等)。为什么会收到此错误,如何避免?
解答: LabVIEW使用有限量的内存来存储每种类型的引用。因此,对于每种类型的引用,同时打开的数量被限制为1048575。因此,当到达这个数量后,任何在内存中创建新引用的框图函数可能会返回此错误。

编辑切换为居中
添加图片注释,不超过 140 字(可选)
这表示代码中的引用泄漏。引用没有正确关闭,并且最终1048575个同一类型的引用同时打开。尝试打开第1048576个引用时会出现此错误。要防止达到引用限制,请修改应用程序,以便在引用不再使用时使用相应的VI(例如释放通知器,释放队列,关闭引用等)来关闭引用。
Closing References in LabVIEW
Whenyou open a reference to an application, project, VI, or other reference source,LabVIEW allocates memory to store that reference. To free up the space inmemory where LabVIEW stored the reference source, you must close the reference.It is always safe to close a reference when you no longer need it. You can usethe Close Reference function (linked below) to close a reference.
VI Server References
VIServer references are reference types found under the SelectClass»VI Server shortcut menu item that appears when youright-click a property or invoke node, as shown in the following block diagram.VI Server references include references to applications, projects, libraries,controls, VIs, and so on.
编辑切换为居中
添加图片注释,不超过 140 字(可选)
Knowingwhen to close a VI Server reference and when you can safely leave a referenceopen can be difficult. However, unless you are certain you can safely leave areference open, always close references when you no longer need them.
Reference Functions
Ifyou open a reference using an Open VI Reference function, New VI function, orsimilar function, LabVIEW creates a new reference every time LabVIEW calls thereferenced VI. Close these references each time you open them to avoid creatingadditional memory allocations for each reference.
Multiple Calls toProperty and Invoke Nodes
WhenLabVIEW calls a Property or Invoke Node multiple times, LabVIEW does notprovide any method for checking whether LabVIEW returns the exact samereference for each call or allocates a new reference for each call. In thefollowing example, LabVIEW calls a Property Node multiple times, but providesno way of knowing whether the property will return the same reference each timeLabVIEW calls it.

编辑
添加图片注释,不超过 140 字(可选)
Becauseyou cannot be sure that LabVIEW does not create a new reference allocation foreach call, close these references, as shown in the following block diagram, toavoid any potential reference leaks.

编辑
添加图片注释,不超过 140 字(可选)
Reference Leaks
Ifyou do not close a reference, your application is susceptible to referenceleaks that can use up memory and slow the execution time of the application.LabVIEW automatically closes a reference when the top-level VI that opened thereference goes idle, but if the application runs for extended periods of time,the effects of reference leaks gradually increase.
Usethe following guidelines to determine which VI is a top-level VI:
§If theRun VI method runs a VI, that VI is a separate top-level VI.
§If a CallBy Reference node calls a VI, that VI is considered a subVI of the calling VIunless the VI being called is a remote VI.
§If aStart Asynchronous Call function makes a call-and-forget VI call, that VI is aseparate top-level VI.
§If aStart Asynchronous Call function makes a call-and-collect VI call, that VI isconsidered a subVI of the calling VI.
Tip Youcan use the Call Chain function (linked below) to identify the top-level VIunless you use a Start Asynchronous Call function to call the VI.
Referenceleaks to larger sources, such as VIs, projects, libraries, and so on, have agreater impact on memory usage and execution speed than references to smallersources, such as controls or objects within a VI. For example, if LabVIEW leaksa control reference, LabVIEW stores refnums and related control data in memory.However, if LabVIEW leaks a VI reference, LabVIEW stores a whole VI in memory.
IfLabVIEW leaks a VI reference, your program may behave incorrectly if you expectLabVIEW to unload the VI and reset the state of the VI for the next call. Toavoid reference leaks, close all references when you no longer need them.
Note Ifyou attempt to close a project reference, LabVIEW may not remove the project inmemory even if you close all references to that project because either theProject Explorer window is open or a library reference that contains theproject is open. You can use the Close method (linked below) to close allreferences to all items in a project.
Exceptions
ImplicitReferences and Unwired Property and Invoke Nodes
Althoughyou should usually close references when you no longer need them, you can leaveimplicit references and references returned in the referenceout terminal of unwired property and invoke nodes open,shown below, because a Close Reference function does not actually close thesereferences or remove the target objects from memory.

编辑
添加图片注释,不超过 140 字(可选)
Leaving these references open also creates a slightlycleaner block diagram by not cluttering the code with a Close Referencefunction.
Closing VIReferences that Have Child Object References
Youcan close child object references when you no longer need them, but closing theparent VI reference automatically closes child object references of that VI.However, if you close the parent VI reference before LabVIEW calls a childobject reference, the child object reference may become invalid. Make sure towire block diagram objects so each function executes in the order you want.
Inthe following example, if you close the VI reference immediately after LabVIEWopens the VI reference, the front panel reference may become invalid beforeLabVIEW can get the class name.

编辑
添加图片注释,不超过 140 字(可选)
Closethe VI reference only when you no longer need the front panel reference to makesure the front panel reference remains valid, as shown in the following blockdiagram.

编辑
添加图片注释,不超过 140 字(可选)
Inthe previous example, you do not need to close the front panel referencebecause the front panel reference closes when you close the VI reference.However, if you close the front panel reference, you must do so before closingthe VI reference. Otherwise, LabVIEW may return an error when LabVIEW attemptsto close the front panel reference.
Asynchronous Behavior of the CloseReference Function
Whenyou close a reference using the Close Reference function, LabVIEW closes andinvalidates the refnum immediately. However, LabVIEW does not alwaysimmediately dispose of the object in memory. LabVIEW may dispose of the objectwhen LabVIEW calls the Close function or anytime after LabVIEW calls the Closefunction.
Inthe following example, the Open VI Reference function loads the target VI intomemory. LabVIEW closes the reference after getting the name of the target VI.In this example, LabVIEW may dispose of the target VI in memory when LabVIEWcalls the Close function or LabVIEW may dispose of the target VIasynchronously.
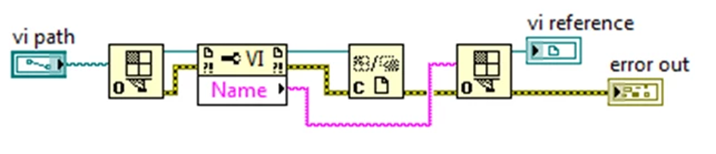
编辑切换为居中
添加图片注释,不超过 140 字(可选)
Inthe previous example, closing the VI reference immediately before or inparallel to the second Open VI Reference function creates a race condition.LabVIEW may dispose of the target VI in memory before the second Open VIReference function can open a reference to the target VI. However, LabVIEW alsomay keep the target VI in memory long enough for the second Open VI Referencefunction to call the target VI.
Tip Youcan use the All VIs in Memory property to display and monitor when a VI leavesmemory.
LabVIEW、LabVIEW开发、LabVIEW编程、LabVIEW程序
上文中提到的例子和资料,均在word中的附件里,可点击下载。进一步了解,可联系们。
LabVIEW在打开一个新的引用,提示内存已满 - 北京瀚文网星科技有限公司 (bjcyck.com)
这篇关于LabVIEW在打开一个新的引用,提示内存已满的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





