本文主要是介绍一笔画路径生成(c/c++),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
一笔画 路径生成(c++)
练习图的遍历、回溯
新建一个OnePen类;
使用setNodeNum()方法设置节点数量;
使用setNodeJoin()设置节点连线;
执行drawLine()方法即可得出该图的一笔画路线;
- main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "OnePen.h"void test01()
{OnePen op;op.setNodeNum(4);op.setNodeJoin(1, 2);op.setNodeJoin(1, 3);op.setNodeJoin(2, 3);op.setNodeJoin(2, 4);op.printTable();op.drawLine();
}void test02()
{OnePen op;op.setNodeNum(5);op.setNodeJoin(1, 4);op.setNodeJoin(1, 5);op.setNodeJoin(2, 4);op.setNodeJoin(2, 5);op.setNodeJoin(3, 4);op.setNodeJoin(3, 5);op.setNodeJoin(4, 5);op.printTable();op.drawLine();
}int main()
{test02();system("pause");return 0;
}
- OnePen.h
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>class OnePen
{
private:struct node // 节点{int data; // 数据域bool flag; // 标记(1已使用0未使用)node* next; // 下一个};node* nodeArray; // 节点数组int nodeNum; // 节点数量std::vector<int> path; // 路径bool checkAlone();bool sign(int p1, int p2, int flag);bool endCheck();int draw(int p);
public:OnePen();void setNodeNum(int num);void setNodeJoin(int begin, int end);void printTable();void drawLine();
};
- OnePen.cpp
#include "OnePen.h"// 构造函数,初始化成员变量
OnePen::OnePen()
{this->nodeNum = 0;this->nodeArray = NULL;
}// 设置节点数量,并生成初始数组
void OnePen::setNodeNum(int num)
{if (num <= 1){std::cout << "节点数必须大于 1。" << std::endl;}else{this->nodeNum = num;this->nodeArray = new node[num];for (int i = 0; i < num; i++){this->nodeArray[i].data = i;this->nodeArray[i].flag = false;this->nodeArray[i].next = NULL;}}
}// 连接节点
void OnePen::setNodeJoin(int begin, int end)
{// 首尾不能相同if (begin == end){std::cout << "首尾节点不能相同,请重新确认!";std::cout <<"(Error: .setNodeJoin(" << begin << "," << end << ");)" << std::endl;return;}// 其中一节点不存在bool beginExist = false, endExist = false;for (int i = 0; i < this->nodeNum; i++){// 数据存储节点是从0开始,但是从用户角度节点是从1开始,所以需要-1if (this->nodeArray[i].data == begin - 1)beginExist = true;if (this->nodeArray[i].data == end - 1)endExist = true;}if (!beginExist || !endExist){std::cout << "节点不存在,请重新确认!";std::cout << "(Error: .setNodeJoin(" << begin << "," << end << ");)" << std::endl;return;}// 找到 begin 节点的最后一个邻接节点,然后插入新的邻接节点node* beginNode = &this->nodeArray[begin - 1]; // begin节点while (NULL != beginNode->next){if (beginNode->next->data == end - 1){// 已存在从 begin -> end 的路线break;}beginNode = beginNode->next;}if (beginNode->next == NULL){node* temp = new node;temp->data = end - 1;temp->flag = 0;temp->next = NULL;beginNode->next = temp;}// 找到 end 节点的最后一个邻接节点,然后插入新的邻接节点node* endNode = &this->nodeArray[end - 1]; // end节点while (NULL != endNode->next){if (endNode->next->data == begin - 1){// 已存在从 end -> begin 的路线break;}endNode = endNode->next;}if (endNode->next == NULL){node* temp = new node;temp->data = begin - 1;temp->flag = 0;temp->next = NULL;endNode->next = temp;}
}// 输出邻接表
void OnePen::printTable()
{std::cout << "当前邻接表为:" << std::endl;std::cout << "-----------------------------" << std::endl;for (int i = 0; i < this->nodeNum; i++){std::cout << this->nodeArray[i].data + 1 << " | ";node* temp = this->nodeArray[i].next;while (temp != NULL){std::cout << " ->" << temp->data + 1;temp = temp->next;}std::cout << std::endl;}std::cout << "-----------------------------\n" << std::endl;
}// 检查是否存在独立的点(即出度和入度皆为0)
bool OnePen::checkAlone()
{for (int i = 0; i < this->nodeNum; i++){if (this->nodeArray[i].next == NULL){return true;}}return false;
}// 设置标记(p1->p2 的 flag 设置为 flag)
bool OnePen::sign(int p1, int p2, int flag)
{node* it = this->nodeArray[p1].next;while (it != NULL){if (it->data == p2){it->flag = flag;return true;}it = it->next;}return false;
}// 最终检查(邻接表的全部flag都为1即返回true)
bool OnePen::endCheck()
{node* temp;for (int i = 0; i < this->nodeNum; i++){temp = this->nodeArray[i].next;while (NULL != temp){if (temp->flag == 0){return false;}temp = temp->next;}}return true;
}// 开始画线
void OnePen::drawLine()
{// 检查是否存在独立的点if (this->checkAlone()){std::cout << "- 单独的节点:\n\n>>> ";for (int i = 0; i < this->nodeNum; i++){if (this->nodeArray[i].next == NULL){std::cout << this->nodeArray[i].data << "\t";}}std::cout << "\n\n- 请将全部节点连接!\n" << std::endl;return;}// 统计有多少种方法int count = 1;// 从每个节点为初始节点依次走一次for (int i = 0; i < this->nodeNum; i++){// 将全部标签置0for (int j = 0; j < this->nodeNum; j++){node* t = this->nodeArray[j].next;while (t != NULL){t->flag = 0;t = t->next;}}// 将路径清空this->path.clear();// 开始画线draw(i),其中i为初始节点,返回结果为是否走得通if (this->draw(i)){std::cout << "-----------------------------" << std::endl;std::cout << ">>> 第 " << count << " 种解法:\n>>> ";count++;for (int i = 0; i < this->path.size(); i++){if (i == 0)std::cout << this->path[i];elsestd::cout << " ->" << this->path[i];}std::cout << "\n" << std::endl;}}
}// 以point节点为开始节点走下一步
int OnePen::draw(int point)
{// 当前节点添加到路径(由于存储和显示不同,所以+1)this->path.push_back(point + 1);// 完成(到该点已经全部路线都走完了就逐层返回1)if (this->endCheck()){return 1;}node* past = new node; // 走过节点列表(已经走过并且走不通)node* last = past; // 走过节点列表 的最后一个节点(方便添加新的节点)int peerNode = -1; // 目标节点(将要走的节点,初始化为不可能的-1)node* it = this->nodeArray[point].next; // 当前节点的第一个邻接点// 找到下一个要走的节点,并且标记while (it != NULL){if (it->flag == 0) // 尚未走过的目标节点{peerNode = it->data; // 记录目标节点it->flag = 1; // 标记目标节点past->data = peerNode; // 目标节点加入past列表past->next = NULL;break;}it = it->next;}// 此路不通(遍历完当前节点的所有邻接点都没找到flag=0的节点即无路可走了)if (it == NULL){return 0;}// 将目标节点到当前节点的线标记this->sign(peerNode, point, 1);// 开始递归,如果递归结果返回0(即此路不通)开始进入循环找新的目标节点while (!this->draw(peerNode)){// 进入循环证明当前past列表的最新元素走不通,移除this->path.pop_back();// 1. 将刚刚走过的标记取消(让其他节点可以走)this->sign(point, peerNode, 0);this->sign(peerNode, point, 0);// 2. 找到一个节点需要即不在past列表里,并且flag为0it = this->nodeArray[point].next;while (it != NULL){if (it->flag == 0){bool b = true; // 检查这个节点是否存在past列表(1这个节点能走,0这个节点不能走)// 遍历走过列表node* ps = past;while (ps != NULL){// 如果当前节点存在走过列表里面,这个节点不能走if (it->data == ps->data){b = false;break;}ps = ps->next;}// 找到目标节点if (b){peerNode = it->data;// 添加到走过列表node* past2 = new node;past2->data = peerNode;past2->next = NULL;last->next = past2; // 添加到past列表的最后last = past2; // last指向past列表的最后元素// 标记(当前节点到目标节点的路线已使用)this->sign(point, peerNode, 1);this->sign(peerNode, point, 1);// 退出循环break;}}it = it->next;}// 3. 遍历完邻接点也没找到可用的节点,没有可以走的路线了,此路不通if (it == NULL){return 0;}}
}
-
测试(上面的main.cpp的test02函数)
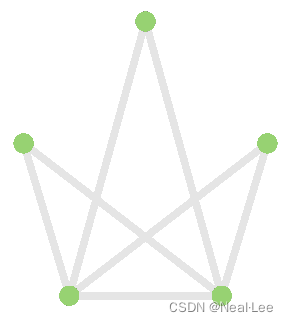
-
执行结果
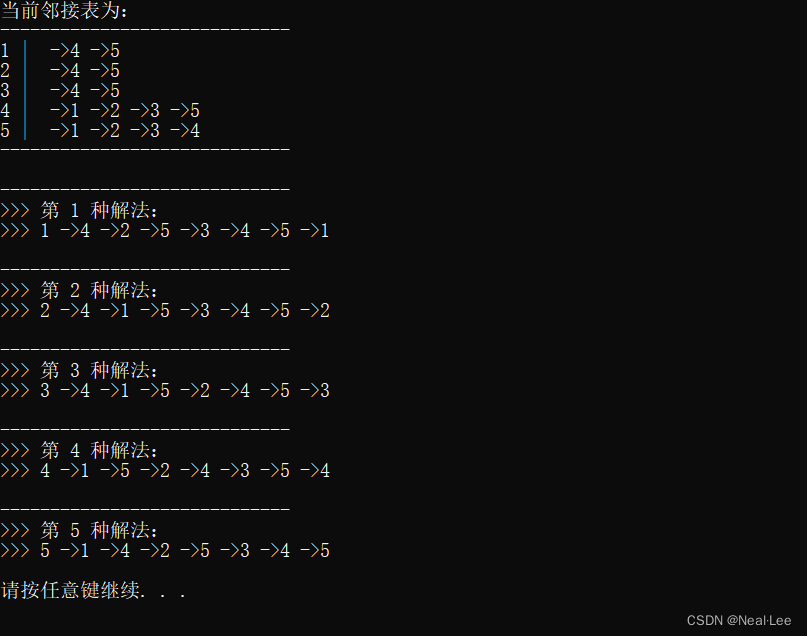
这篇关于一笔画路径生成(c/c++)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!







