本文主要是介绍cpp primer笔记090-动态内存,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
- shared_ptr和unique_ptr都支持的操作,加上shared_ptr独有的操作
![![[Pasted image 20230923103844.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/74898ba9734a43ea9a52db3fbb57cf5a.png)
![![[Pasted image 20230923103855.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/de63ddf298af496c95532a9b89ecabe0.png)
- 每个shared_ptr都有一个关联的计数器,通常称其为引用计数,当调用了shared_ptr的构造函数时就会递增,当调用析构函数时就会递减,一旦一个shared_ptr的计数器为0的时候,它就会自动释放自己所管理的对象。
#include <iostream> #include <fstream> #include <array> #include <vector> #include <string> #include <exception> #include <algorithm> #include <stack> #include <deque> #include <numeric> #include <memory> int main() {std::shared_ptr<int> ptr1 = std::make_shared<int>(10);std::cout << ptr1.unique() << " " << ptr1.use_count() << std::endl;std::shared_ptr<int> ptr2 = std::make_shared<int>(10);std::cout << ptr1.unique() << " " << ptr1.use_count() << std::endl; std::shared_ptr<int> ptr3(ptr1); std::cout << ptr1.unique() << " " << ptr1.use_count() << std::endl;
}
cpp
1 1
1 1
0 2
```
-
如果想让STL的容器产生类似于shared_ptr指针的效果,可以进行下面的操作:(如果一个shared_ptr指向的对象的引用次数为0,则该对象会被销毁)
#include <iostream> #include <fstream> #include <array> #include <vector> #include <string> #include <exception> #include <algorithm> #include <deque> #include <numeric> #include <memory> #include <initializer_list> #include <exception> class StrBlob { public:typedef std::vector<std::string>::size_type size_type;StrBlob() :data(std::make_shared<std::vector<std::string>>()) {};StrBlob(std::initializer_list<std::string> il) :data(std::make_shared<std::vector<std::string>>(il)) {};StrBlob(std::vector<std::string> vec) :data(std::make_shared<std::vector<std::string>>(vec)) {};~StrBlob() = default;size_type size() const;void push_back(const std::string& t);void pop_back();std::string front() const;std::string back() const;auto cbegin() -> decltype(std::cbegin(std::vector<std::string>()));auto cend() -> decltype(std::cend(std::vector<std::string>())); private:std::shared_ptr<std::vector<std::string>> data;void check(size_type i, const std::string& msg) const throw(const std::string&); }; std::vector<std::string>::size_type StrBlob::size() const {return data->size(); }void StrBlob::push_back(const std::string& t) {data->push_back(t); }void StrBlob::pop_back() {data->pop_back(); }std::string StrBlob::front() const {check(0, "front on empty StrBlob");return data->front(); }std::string StrBlob::back() const {check(0, "back on empty StrBlob");return data->back(); }void StrBlob::check(std::vector<std::string>::size_type i, const std::string& msg) const throw(const std::string&) {if (i >= data->size()){throw std::out_of_range(msg);} }auto StrBlob::cbegin() -> decltype(std::cbegin(std::vector<std::string>())) {return this->data->cbegin(); }auto StrBlob::cend() -> decltype(std::cend(std::vector<std::string>())) {return this->data->cend(); }int main() {StrBlob str1({ "123", "fsdf","zcxv" });StrBlob str2 = str1;str1.push_back("sdfsdfz");str1.~StrBlob();std::ostream_iterator<std::string> os(std::cout, " ");std::for_each(str2.cbegin(), str2.cend(), [&os](std::string val) { os = val; });return 0; }123 fsdf zcxv sdfsdfz -
智能指针不允许进行内置指针到智能指针间的隐式转换,只能显示转换。下面是shared_ptr和new结合使用的各种函数
#include <iostream> #include <fstream> #include <array> #include <vector> #include <string> #include <exception> #include <algorithm> #include <deque> #include <numeric> #include <memory> #include <initializer_list> #include <exception> std::shared_ptr<int> clone(int p) {//return new int(p);不能隐式转换return std::shared_ptr<int>(new int(p)); } int main() {std::shared_ptr<int> ptr1;std::shared_ptr<double> ptr2(new double(42));//可以通过构造函数转换//std::shared_ptr<int> ptr3 = new int(1024);不能隐式转换return 0; }![![[Pasted image 20230923144221.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/d41716db173f4496ad4abfa492eb9ead.png)
![![[Pasted image 20230923153455.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/f154a6beb43a43e1ba505b3a4faefee6.png)
![![[Pasted image 20230923161047.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/2cd190f68e844feaad5bd71d9c4757e0.png)
-
不要混用普通指针和智能指针,尽量都是用智能指针,如果混用二者会产生以下未定义行为。智能指针相对于普通指针的区别有当函数使用智能指针的时候,如果抛出异常,则栈解退的时候会自动调用析构函数释放内存,而使用普通指针的时候则不会delete掉
void process(std::shared_ptr<int> ptr) {; } int main() {std::shared_ptr<int> p(new int(42));process(p);int i = *p;std::cout << i << std::endl;int* x(new int(1024));//process(x); 不能将int*显式转换为一个shared_ptr<int>()类型的指针process(std::shared_ptr<int>(x));//如果将x显式类型转换,则可能导致x的内存被释放int j = *x;//未定义行为:x是一个悬空指针!std::cout << j << std::endl;return 0; }42 -572662307 -
unique_ptr操作,一般情况下是不允许拷贝unique_ptr,但是如果从函数返回一个unique_ptr值或者返回一个局部对象拷贝的情况下是允许的。
![![[Pasted image 20230923154021.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/f575fdf1966f40dca9ba29ad0aa61a49.png)
![![[Pasted image 20230923161112.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/817287cb8ef24524ad4d164a57319236.png)
#include <vector>#include <string>#include <exception>#include <algorithm>#include <deque>#include <numeric>#include <memory>#include <initializer_list>#include <exception>std::unique_ptr<std::string> clone1(std::string str){return std::unique_ptr<std::string>(new std::string(str));}std::unique_ptr<std::string> clone2(std::string str){std::unique_ptr<std::string> ret(new std::string(str));return ret;}int main(){std::unique_ptr<std::string> ptr1(new std::string("sjkdfskdf"));std::unique_ptr<std::string> ptr2(ptr1.release());std::unique_ptr<std::string> ptr3(new std::string("kxcnsd"));std::cout << *ptr2 << std::endl;ptr2.reset(ptr3.release());std::cout << *ptr2 << std::endl;return 0;}
-
weak_ptr的一些操作:
![![[Pasted image 20230923160922.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/c43a23a1351340fdb5706e5e03d854d7.png)
-
由于分配的内存并不是一个数组类型,因此不能对动态数组调用begin和end函数,也不能用范围for语句来处理动态数组中的元素,我们所说的动态数组并不是数组类型
-
指向数组的unique_ptr支持一下操作,由于shared_ptr不支持通过[]访问的操作,因此需要使用get函数。
![![[Pasted image 20230923163322.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/45a0008aaeff4b019aa827eb65bf2b5f.png)
#include <iostream>#include <fstream>#include <array>#include <vector>#include <string>#include <exception>#include <algorithm>#include <deque>#include <numeric>#include <memory>#include <initializer_list>#include <exception>int main(){std::unique_ptr<int[]> up(new int[10]);std::shared_ptr<int> sp(new int[10], [](int* p) {delete[] p; });for (size_t i = 0; i != 10; ++i){up[i] = i;*(sp.get() + i) = 2 * i;}for (size_t i = 0; i < 10; ++i){std::cout << up[i] << "/" << *(sp.get() + i) << " ";}return 0;}
- allocate的使用:
![![[Pasted image 20230923170327.png]]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/5687b9bc913745db90aca9b165a46d7b.png)
#include <iostream>#include <fstream>#include <array>#include <vector>#include <string>#include <exception>#include <algorithm>#include <deque>#include <numeric>#include <memory>#include <initializer_list>#include <exception>int main(){int n;std::allocator<std::string> alloc;//可以分配string内存的allocator对象std::cin >> n;auto const start = alloc.allocate(n);//分配十个内存,start是指向该内存开头的指针auto end = const_cast<decltype(alloc.allocate(n))>(start);//end即构造完成的内存的下一个位置alloc.construct(end++, 10, 'c');//构造一个含有10个c的字符串alloc.construct(end++, "sdfksd");//构造一个sdfksd的字符串for (auto it = start; it != end; ++it){std::cout << *it << " ";//输出已经构造的空间的字符串}std::cout << std::endl;alloc.destroy(--end);//重置一个已经构造的空间,但是并不会销毁for (auto it = start; it != end; ++it){std::cout << *it << " ";}alloc.deallocate(start, n);//销毁所有已分配的空间return 0;}
5cccccccccc sdfksdcccccccccc
![[Pasted image 20230923171456.png]]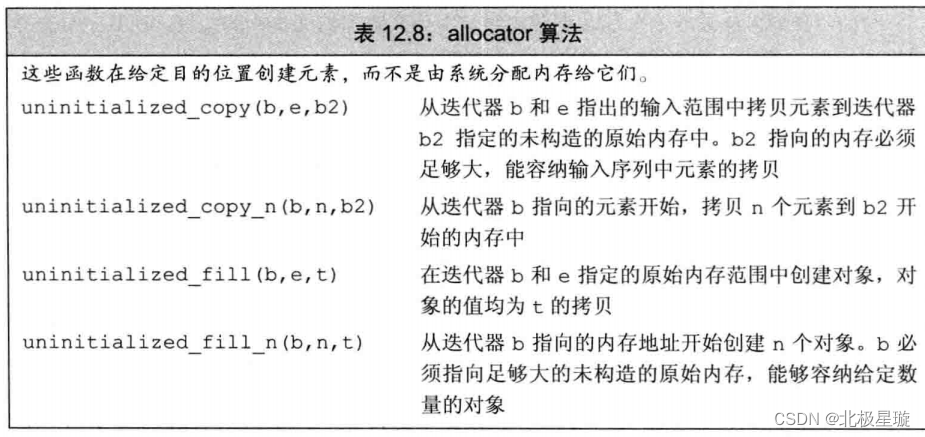
#include <iostream>#include <fstream>#include <array>#include <vector>#include <string>#include <exception>#include <algorithm>#include <deque>#include <numeric>#include <memory>#include <initializer_list>#include <exception>int main(){std::allocator<int> a,b;auto beginPtrA = a.allocate(10);auto beginPtrB = b.allocate(10);std::uninitialized_fill_n(beginPtrA, 10, 5);for (size_t i = 0; i < 10; ++i){std::cout << *(beginPtrA + i) << " ";}std::cout << std::endl;std::uninitialized_copy_n(beginPtrA, 10, beginPtrB);for (size_t i = 0; i < 10; ++i){std::cout << *(beginPtrA + i) << " ";}return 0;}
5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5
5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5
- 智能指针shared_ptr和unique_ptr重载删除器,都可以用普通函数,仿函数和未捕获任何类型的lambda表达式,但是unique需要传递一个函数指针
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1 #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <memory> #include <deque> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> #include <functional> void deleter(int* x) {std::cout << "普通函数删除器" << std::endl;delete[] x; } class Deleter { public:void operator() (int* x) {std::cout << "仿函数删除器" << std::endl;delete[] x;} };int main() {std::shared_ptr<int> shPtr1(new int[5], deleter);std::shared_ptr<int> shPtr2(new int[2], std::function<void(int*)>(Deleter()));std::shared_ptr<int> shPtr3(new int[7], [](int* x) {std::cout << "lambda表达式删除器" << std::endl;delete[] x;});std::unique_ptr<int[], std::function<void(int*)>> unPtr1(new int[5], deleter);std::unique_ptr<int[], std::function<void(int*)>> unPtr2(new int[6], std::function<void(int*)>(Deleter()));std::unique_ptr<int[], std::function<void(int*)>> unPtr3(new int[7], [](int* x) {std::cout << "lambda表达式删除器" << std::endl;delete[] x;});return 0; }
这篇关于cpp primer笔记090-动态内存的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






