本文主要是介绍Flink的处理函数——processFunction,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
目录
一、处理函数概述
二、Process函数分类——8个
(1)ProcessFunction
(2)KeyedProcessFunction
(3)ProcessWindowFunction
(4)ProcessAllWindowFunction
(5)CoProcessFunction
(6)ProcessJoinFunction
(7)BroadcastProcessFunction
(8)KeyedBroadcastProcessFunction
三、KeyedProcessFunction案例
1.运行processElement方法中的事件时间
(1)输入数据
2.运行processElement方法中的处理时间
(1)先输入一条数据
(2)再快速输入两条数据
3.运行processElement方法中的水位线
(1)输入数据
4.总结:
四、应用案例——求TopN
(一)思路一:hashmap
(二)思路二:keyby
(三)思路三:使用侧输出流——推荐
一、处理函数概述
在Flink更底层,我们可以不定义任何具体的算子(比如map,filter,或者window),而只是提炼出一个统一的“处理”(process)操作——它是所有转换算子的一个概括性的表达,可以自定义处理逻辑,所以这一层接口就被叫作“处理函数”(process function)。
二、Process函数分类——8个
Flink提供了8个不同的处理函数:
(1)ProcessFunction
最基本的处理函数,基于DataStream直接调用.process()时作为参数传入。
(2)KeyedProcessFunction
对流按键分区后的处理函数,基于KeyedStream调用.process()时作为参数传入。要想使用定时器,比如基于KeyedStream。
(3)ProcessWindowFunction
开窗之后的处理函数,也是全窗口函数的代表。基于WindowedStream调用.process()时作为参数传入。
(4)ProcessAllWindowFunction
同样是开窗之后的处理函数,基于AllWindowedStream调用.process()时作为参数传入。
(5)CoProcessFunction
合并(connect)两条流之后的处理函数,基于ConnectedStreams调用.process()时作为参数传入。关于流的连接合并操作,我们会在后续章节详细介绍。
(6)ProcessJoinFunction
间隔连接(interval join)两条流之后的处理函数,基于IntervalJoined调用.process()时作为参数传入。
(7)BroadcastProcessFunction
广播连接流处理函数,基于BroadcastConnectedStream调用.process()时作为参数传入。这里的“广播连接流”BroadcastConnectedStream,是一个未keyBy的普通DataStream与一个广播流(BroadcastStream)做连接(conncet)之后的产物。关于广播流的相关操作,我们会在后续章节详细介绍。
(8)KeyedBroadcastProcessFunction
按键分区的广播连接流处理函数,同样是基于BroadcastConnectedStream调用.process()时作为参数传入。与BroadcastProcessFunction不同的是,这时的广播连接流,是一个KeyedStream与广播流(BroadcastStream)做连接之后的产物。
三、KeyedProcessFunction案例
基于keyBy之后的KeyedStream,直接调用.process()方法,这时需要传入的参数就是KeyedProcessFunction的实现类。
stream.keyBy( t -> t.f0 ).process(new MyKeyedProcessFunction())类似地,KeyedProcessFunction也是继承自AbstractRichFunction的一个抽象类,与ProcessFunction的定义几乎完全一样,区别只是在于类型参数多了一个K,这是当前按键分区的key的类型。同样地,我们必须实现一个.processElement()抽象方法,用来处理流中的每一个数据;另外还有一个非抽象方法.onTimer(),用来定义定时器触发时的回调操作。
代码示例:
import com.atguigu.bean.WaterSensor;
import com.atguigu.split.WaterSensorMapFunction;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.time.DateFormatUtils;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.eventtime.WatermarkStrategy;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.TimerService;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.KeyedStream;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.SingleOutputStreamOperator;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.StreamExecutionEnvironment;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.KeyedProcessFunction;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.windowing.ProcessWindowFunction;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.windowing.assigners.TumblingEventTimeWindows;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.windowing.time.Time;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.windowing.windows.TimeWindow;
import org.apache.flink.util.Collector;import java.time.Duration;public class KeyedProcessTimerDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();env.setParallelism(1);SingleOutputStreamOperator<WaterSensor> sensorDS = env.socketTextStream("node141", 9999).map(new WaterSensorMapFunction());WatermarkStrategy<WaterSensor> watermarkStrategy = WatermarkStrategy.<WaterSensor>forBoundedOutOfOrderness(Duration.ofSeconds(3)) // 乱序// 提取watermark的时间戳.withTimestampAssigner((element, recordTimestamp) ->element.getTs() * 1000L);SingleOutputStreamOperator<WaterSensor> sensorDSWithWatermark = sensorDS.assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(watermarkStrategy);KeyedStream<WaterSensor, String> sensorKS = sensorDSWithWatermark.keyBy(WaterSensor::getId);// key 输入的类型 输出的类型SingleOutputStreamOperator<String> process = sensorKS.process(new KeyedProcessFunction<String, WaterSensor, String>() {/*** 来一条数据调用一次* @param value* @param ctx* @param out* @throws Exception*/@Overridepublic void processElement(WaterSensor value, Context ctx, Collector<String> out) throws Exception {//获取当前数据的keyString currentKey = ctx.getCurrentKey();// TODO 1.定时器注册TimerService timerService = ctx.timerService();// 1、事件时间的案例
// Long currentEventTime = ctx.timestamp(); // 数据中提取出来的事件时间
// timerService.registerEventTimeTimer(5000L);
// System.out.println("当前key=" + currentKey + ",当前时间=" + currentEventTime + ",注册了一个5s的定时器");// 2、处理时间的案例long currentTs = timerService.currentProcessingTime();timerService.registerProcessingTimeTimer(currentTs + 5000L);System.out.println("当前key=" + currentKey + ",当前时间=" + currentTs + ",注册了一个5s后的定时器");// 3、获取 process的 当前watermark
// long currentWatermark = timerService.currentWatermark();
// System.out.println("当前数据=" + value + ",当前watermark=" + currentWatermark);// 注册定时器: 处理时间、事件时间
// timerService.registerProcessingTimeTimer();
// timerService.registerEventTimeTimer();// 删除定时器: 处理时间、事件时间
// timerService.deleteEventTimeTimer();
// timerService.deleteProcessingTimeTimer();// 获取当前时间进展: 处理时间-当前系统时间, 事件时间-当前watermark
// long currentTs = timerService.currentProcessingTime();
// long wm = timerService.currentWatermark();}/*** TODO 2.时间进展到定时器注册的时间,调用该方法* @param timestamp 当前时间进展,就是定时器被触发时的时间* @param ctx 上下文* @param out 采集器* @throws Exception*/@Overridepublic void onTimer(long timestamp, OnTimerContext ctx, Collector<String> out) throws Exception {super.onTimer(timestamp, ctx, out);String currentKey = ctx.getCurrentKey();System.out.println("key=" + currentKey + "现在时间是" + timestamp + "定时器触发");}});process.print();env.execute();}
}1.运行processElement方法中的事件时间
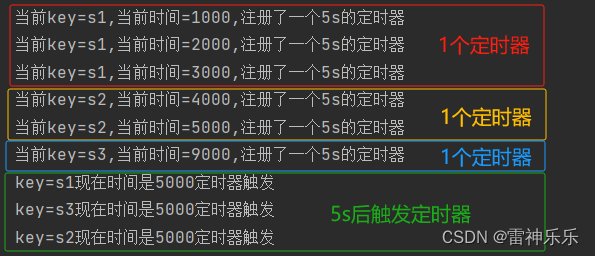
// 1、事件时间的案例
Long currentEventTime = ctx.timestamp(); // 数据中提取出来的事件时间
timerService.registerEventTimeTimer(5000L);
System.out.println("当前key=" + currentKey + ",当前时间=" + currentEventTime + ",注册了一个5s的定时器");(1)输入数据
[root@node141 ~]# nc -lk 9999
s1,1,1
s1,2,2
s1,3,3
s2,4,4
s2,5,5
s3,9,9
运行结果:注册定时器后,5s后触发
2.运行processElement方法中的处理时间
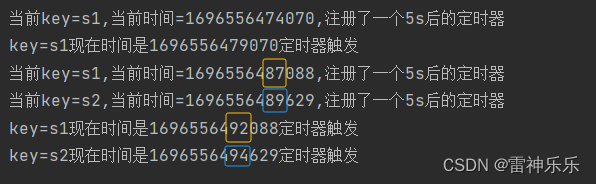
// 2、处理时间的案例
long currentTs = timerService.currentProcessingTime();
timerService.registerProcessingTimeTimer(currentTs + 5000L);
System.out.println("当前key=" + currentKey + ",当前时间=" + currentTs + ",注册了一个5s后的定时器");(1)先输入一条数据
[root@node141 ~]# nc -lk 9999
s1,1,1
运行结果:相差5s

(2)再快速输入两条数据
[root@node141 ~]# nc -lk 9999
s1,1,1
s1,2,2
s2,2,2
运行结果:相差5s,5s后定时器触发
3.运行processElement方法中的水位线
// 3、获取 process的 当前watermark
long currentWatermark = timerService.currentWatermark();
System.out.println("当前数据=" + value + ",当前watermark=" + currentWatermark);(1)输入数据
[root@node141 ~]# nc -lk 9999
s1,1,1
s1,5,5
s1,9,9运行结果:
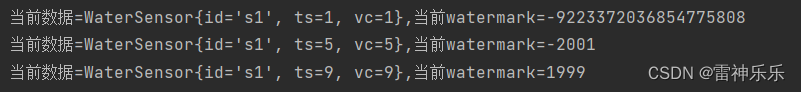
数据经过map算子,然后再到process方法中。
当第一条数据输入时,进入map时的watermark是1s-3s-1ms=-2001ms,数据随后进入process方法,调用了processElement方法,在processElement方法中获取当前的watermark,此时-2001ms这一watermark还没有进入process中,所以当前process的watermark是long的最小值;
第一条数据处理完成后,第二条继续输入到map中,此时process中的watermark变为-2001ms,而map中的watermark是5s-3s-1ms=1999ms,同样,数据再进入process中,调用processElement方法,此时1999ms这一watermark仍然还没有进入process中,所以当前process中的watermark是之前的-2001ms;
第二条数据处理完成后,第三条数据继续输入到map中,此时process中的watermark变为1999ms,而map中的watermark是9s-3s-1ms=5999ms,同样,数据再进入process中,调用processElement方法,此时5999ms这一watermark也没有来得及进入process中,所以当前process中的watermark是之前的1999ms。
4.总结:
TODO 定时器
1、keyed才有
2、事件时间定时器,通过watermark来触发的
watermark >= 注册的时间
注意: watermark = 当前最大事件时间 - 等待时间 -1ms, 因为 -1ms,所以会推迟一条数据
比如, 5s的定时器,
如果 等待=3s, watermark = 8s - 3s -1ms = 4999ms,不会触发5s的定时器
需要 watermark = 9s -3s -1ms = 5999ms ,才能去触发 5s的定时器
3、在process中获取当前watermark,显示的是上一次的watermark
==> 因为process还没接收到这条数据对应生成的新watermark
四、应用案例——求TopN
(一)思路一:hashmap
使用所有数据到一起,用hashmap来存储,key=vc,value=count值
import com.atguigu.bean.WaterSensor;
import com.atguigu.split.WaterSensorMapFunction;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.time.DateFormatUtils;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.eventtime.WatermarkStrategy;
import org.apache.flink.api.java.tuple.Tuple2;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.SingleOutputStreamOperator;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.StreamExecutionEnvironment;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.windowing.ProcessAllWindowFunction;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.windowing.assigners.SlidingEventTimeWindows;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.windowing.time.Time;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.windowing.windows.TimeWindow;
import org.apache.flink.util.Collector;import java.time.Duration;
import java.util.*;public class TopNDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();env.setParallelism(1);SingleOutputStreamOperator<WaterSensor> sensorDS = env.socketTextStream("node141", 9999).map(new WaterSensorMapFunction()).assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(WatermarkStrategy.<WaterSensor>forBoundedOutOfOrderness(Duration.ofSeconds(3)) // 乱序.withTimestampAssigner((element, recordTimestamp) ->element.getTs() * 1000L));// 最近10s=窗口长度 每5s输出=滑动步长// TODO 思路一:使用所有数据到一起,用hashmap来存储,key=vc,value=count值sensorDS.windowAll(SlidingEventTimeWindows.of(Time.seconds(10), Time.seconds(5))).process(new MyTopNPawf()).print();env.execute();}public static class MyTopNPawf extends ProcessAllWindowFunction<WaterSensor, String, TimeWindow> {@Overridepublic void process(ProcessAllWindowFunction<WaterSensor, String, TimeWindow>.Context context, Iterable<WaterSensor> elements, Collector<String> out) throws Exception {// 定义一个hashmap用来存,key=vc,value=count值Map<Integer, Integer> vcCountMap = new HashMap<>();// 1.遍历数据,统计各个vc出现的次数for (WaterSensor element : elements) {Integer vc = element.getVc();if (vcCountMap.containsKey(vc)) {// 1.1 key存在,不是这个key的第一条数据,直接累加vcCountMap.put(vc, vcCountMap.get(vc) + 1);} else {// 1.2 如果key不存在,则初始化vcCountMap.put(vc, 1);}}// 2.对count值进行排序,利用list来实现排序List<Tuple2<Integer, Integer>> datas = new ArrayList<>();// 2.1 对list进行排序,根据count值进行降序for (Integer vc : vcCountMap.keySet()) {datas.add(Tuple2.of(vc, vcCountMap.get(vc)));}// count值相减datas.sort((o1, o2) -> o2.f1 - o1.f1);// 3.取出count最大的2个vcStringBuffer outStr = new StringBuffer();outStr.append("\n=======================\n");for (int i = 0; i < Math.min(2, datas.size()); i++) {Tuple2<Integer, Integer> vcCount = datas.get(i);outStr.append("窗口开始时间:" + DateFormatUtils.format(context.window().getStart(), "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS"));outStr.append("\n");outStr.append("top:" + (i + 1));outStr.append("\n");outStr.append("vc=" + vcCount.f0);outStr.append("\n");outStr.append("count=" + vcCount.f1);outStr.append("\n");outStr.append("窗口结束时间:" + DateFormatUtils.format(context.window().getEnd(), "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS\n"));}outStr.append("\n=======================\n");// 输出out.collect(outStr.toString());}}
}输入数据:
[root@node141 ~]# nc -lk 9999
s1,1,1
s1,2,1
s1,3,3
s1,6,1
s1,8,2
s1,9,3
s1,10,2
s1,11,1
s1,13,2运行结果:
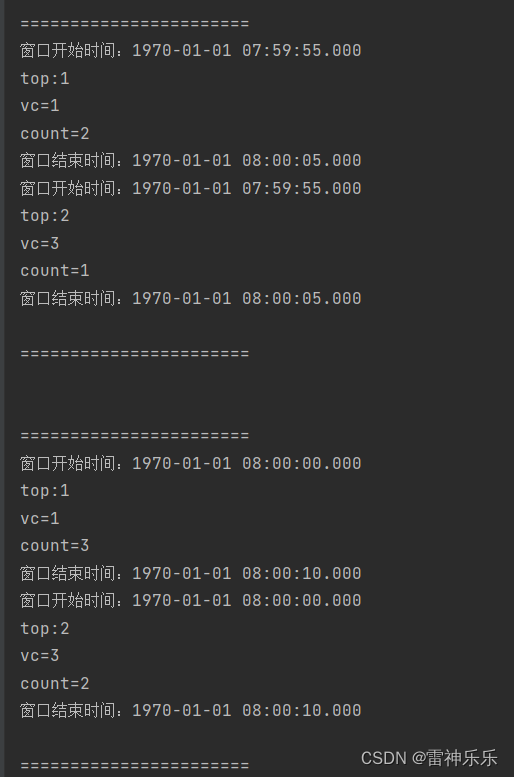
思路一不推荐,因为要将数据攒到一起才会计算,效果不好。
(二)思路二:keyby
代码思路:
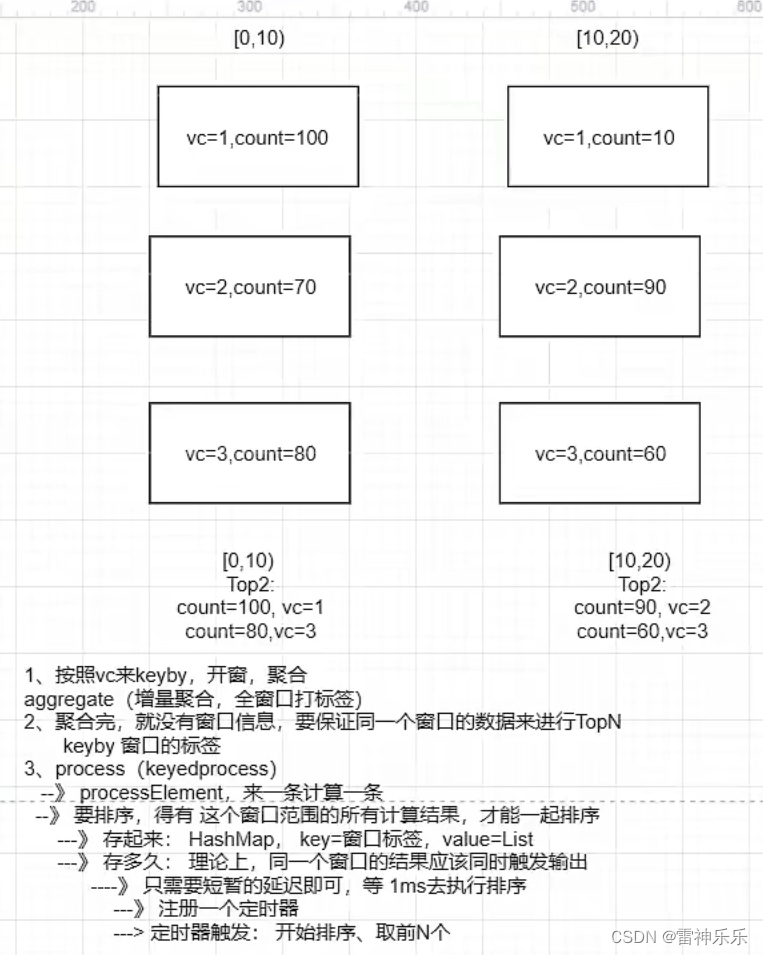
实现步骤:
1、按照vc做keyby,开窗,分别count
==》 增量聚合,计算 count
==》 全窗口,对计算结果 count值封装 , 带上 窗口结束时间的 标签
==》 为了让同一个窗口时间范围的计算结果到一起去
2、对同一个窗口范围的count值进行处理: 排序、取前N个
=》 按照 windowEnd做keyby
=》 使用process, 来一条调用一次,需要先存,分开存,用HashMap进行存储,key=windowEnd,value=List
=》 使用定时器,对 存起来的结果 进行 排序、取前N个
import com.atguigu.bean.WaterSensor;
import com.atguigu.split.WaterSensorMapFunction;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.time.DateFormatUtils;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.eventtime.WatermarkStrategy;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.AggregateFunction;
import org.apache.flink.api.java.tuple.Tuple3;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.SingleOutputStreamOperator;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.StreamExecutionEnvironment;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.KeyedProcessFunction;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.windowing.ProcessWindowFunction;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.windowing.assigners.SlidingEventTimeWindows;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.windowing.time.Time;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.windowing.windows.TimeWindow;
import org.apache.flink.util.Collector;import java.time.Duration;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;public class KeyedProcessFunctionTopNDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();env.setParallelism(1);SingleOutputStreamOperator<WaterSensor> sensorDS = env.socketTextStream("node141", 9999).map(new WaterSensorMapFunction()).assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(WatermarkStrategy.<WaterSensor>forBoundedOutOfOrderness(Duration.ofSeconds(3)) // 乱序.withTimestampAssigner((element, recordTimestamp) ->element.getTs() * 1000L));// 最近10s=窗口长度 每5s输出=滑动步长// TODO 使用keyedProcessFunction实现// 1.按照vc分组、开窗、聚合(增量计算+全量打标签)// 开窗聚合后,就是普通的流,没有了窗口信息,需要自己打上窗口的标记 windowEndSingleOutputStreamOperator<Tuple3<Integer, Integer, Long>> windowAgg = sensorDS.keyBy(WaterSensor::getVc).window(SlidingEventTimeWindows.of(Time.seconds(10), Time.seconds(5))).aggregate(new VcCountAgg(),new WindowResult());// 2.按照窗口标签(窗口结束时间)keyby,保证同一个窗口时间范围的结果,到一起去,排序、取TopNwindowAgg.keyBy(r -> r.f2).process(new TopN(2)).print();env.execute();}public static class VcCountAgg implements AggregateFunction<WaterSensor, Integer, Integer> {@Overridepublic Integer createAccumulator() {return 0;}@Overridepublic Integer add(WaterSensor value, Integer accumulator) {return accumulator + 1;}@Overridepublic Integer getResult(Integer accumulator) {return accumulator;}@Overridepublic Integer merge(Integer a, Integer b) {return null;}}/*** 泛型如下:* 第一个:输入类型=增量函数的输出 count值,Integer* 第二个:输出类型=Tuple3<vc,count,windowEnd>,带上 窗口结束时间的标签* 第三个:key的类型:vc,Integer* 第四个:窗口类型*/public static class WindowResult extends ProcessWindowFunction<Integer, Tuple3<Integer, Integer, Long>, Integer, TimeWindow> {@Overridepublic void process(Integer key, Context context, Iterable<Integer> elements, Collector<Tuple3<Integer, Integer, Long>> out) throws Exception {// 迭代器里面只有一条数据,next一次即可Integer count = elements.iterator().next();long windowEnd = context.window().getEnd();out.collect(Tuple3.of(key, count, windowEnd));}}/*** 泛型如下:* 第一个:key的类型,是windowEnd* 第二个:输入的类型,三元组Tuple3<vc,count,windowEnd>,带上 窗口结束时间的标签* 第三个:打印输出结果*/public static class TopN extends KeyedProcessFunction<Long, Tuple3<Integer, Integer, Long>, String> {private Map<Long, List<Tuple3<Integer, Integer, Long>>> dataListMap;// 要取的top数量private int threshold;public TopN(int threshold) {this.threshold = threshold;dataListMap = new HashMap<>();}@Overridepublic void processElement(Tuple3<Integer, Integer, Long> value, KeyedProcessFunction<Long, Tuple3<Integer, Integer, Long>, String>.Context ctx, Collector<String> out) throws Exception {// 进入这个方法,只是一条数据,要排序,必须等数据到齐才行,将不同窗口的数据用hashmap分开存起来,// todo 1.存到hashmap中 注意此时的key是窗口的结束时间Long windowEnd = value.f2;if (dataListMap.containsKey(windowEnd)) {// 1.1 包含vc,不是该vc的第一条,直接添加到list中List<Tuple3<Integer, Integer, Long>> dataList = dataListMap.get(windowEnd);dataList.add(value);// 也就是说只需要把value的值添加到dataListMap中即可} else {// 1.2 不包含,是该vc的第一条,需要初始化listList<Tuple3<Integer, Integer, Long>> dataList = new ArrayList<>();dataList.add(value);dataListMap.put(windowEnd, dataList);}// todo 2.注册一个定时器,windowEnd+1ms即可// 同一个窗口范围,应该同时输出ctx.timerService().registerEventTimeTimer(windowEnd + 1);}@Overridepublic void onTimer(long timestamp, KeyedProcessFunction<Long, Tuple3<Integer, Integer, Long>, String>.OnTimerContext ctx, Collector<String> out) throws Exception {super.onTimer(timestamp, ctx, out);// 定时器触发,同一个窗口范围的计算结果攒齐了,开始 排序、取TopNLong windowEnd = ctx.getCurrentKey();// 1.排序List<Tuple3<Integer, Integer, Long>> dataList = dataListMap.get(windowEnd);dataList.sort((o1, o2) -> o2.f1 - o1.f1);// 2.取TopNStringBuffer outStr = new StringBuffer();outStr.append("\n=======================\n");for (int i = 0; i < Math.min(threshold, dataList.size()); i++) {Tuple3<Integer, Integer, Long> vcCount = dataList.get(i);outStr.append("top:" + (i + 1));outStr.append("\n");outStr.append("vc=" + vcCount.f0);outStr.append("\n");outStr.append("count=" + vcCount.f1);outStr.append("\n");outStr.append("窗口结束时间:" + DateFormatUtils.format(vcCount.f2, "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS" + "\n"));outStr.append("=======================\n");}// 用完的List,及时清理dataList.clear();// 输出out.collect(outStr.toString());}}
}输入数据:
[root@node141 ~]# nc -lk 9999
s1,1,1
s1,2,2
s1,8,1
s1,10,1运行结果:
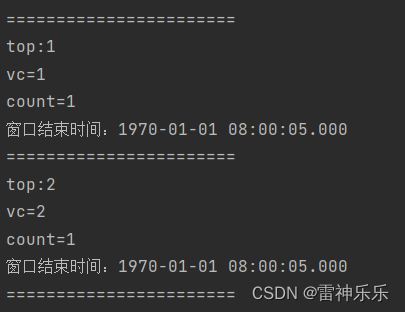
(三)思路三:使用侧输出流——推荐
import com.atguigu.bean.WaterSensor;
import com.atguigu.split.WaterSensorMapFunction;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.eventtime.WatermarkStrategy;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.typeinfo.Types;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.SingleOutputStreamOperator;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.StreamExecutionEnvironment;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.KeyedProcessFunction;
import org.apache.flink.util.Collector;
import org.apache.flink.util.OutputTag;import java.time.Duration;public class SideOutputDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();env.setParallelism(1);SingleOutputStreamOperator<WaterSensor> sensorDS = env.socketTextStream("node141", 9999).map(new WaterSensorMapFunction()).assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(WatermarkStrategy.<WaterSensor>forBoundedOutOfOrderness(Duration.ofSeconds(3)) // 乱序.withTimestampAssigner((element, recordTimestamp) ->element.getTs() * 1000L));OutputTag<String> warnTag = new OutputTag<>("warn", Types.STRING);SingleOutputStreamOperator<WaterSensor> process = sensorDS.keyBy(WaterSensor::getId).process(new KeyedProcessFunction<String, WaterSensor, WaterSensor>() {@Overridepublic void processElement(WaterSensor value, KeyedProcessFunction<String, WaterSensor, WaterSensor>.Context ctx, Collector<WaterSensor> out) throws Exception {// 使用侧输出流告警if (value.getVc() > 10) {ctx.output(warnTag, "当前水位=" + value.getVc() + ",大于阈值10!!!");}// 主流正常发送数据out.collect(value);}});process.print("主流");process.getSideOutput(warnTag).printToErr("warn");env.execute();}
}输入数据:
[root@node141 ~]# nc -lk 9999
s1,1,5
s1,10,1
s1,6,11
s1,7,20
运行结果:
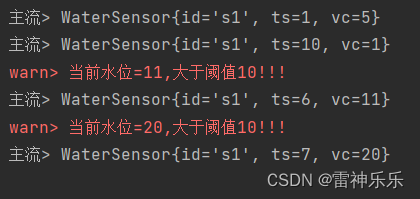
这篇关于Flink的处理函数——processFunction的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





