本文主要是介绍day09-IO-字符流其它流,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
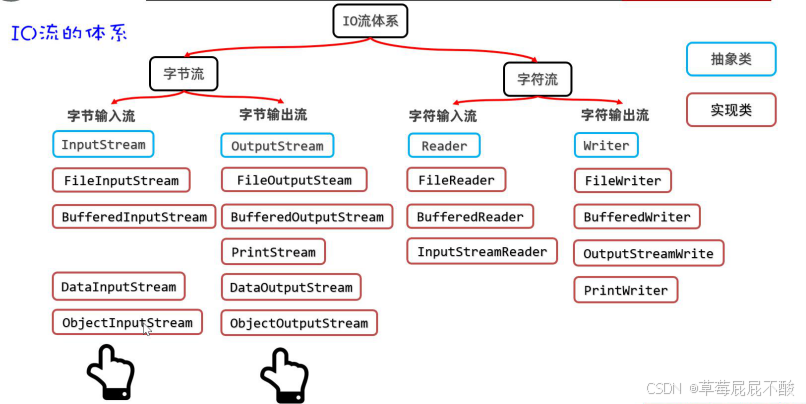
一、字符流
字符流(只能做文本文件的处理)字符输入流 Reader--FileReader字符输出流 Writer--FileWriter 使用文件字符输入流的好处:读取中文不会出现乱码问题
1.1 字符输入流
| 构造器 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public FileReader (File file) | 创建字符输入流管道与源文件接通 |
| public FileReader(String pathname) | 创建字符输入流管道与源文件接通 |
| 方法名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public int read() (每次读一个) | 每次读取一个字符返回,如果发现没有数据可读会返回-1. |
public class Demo1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {// 1.创建对象//方式一:
// File file = new File("day09-code/a-1.txt");
// FileReader reader = new FileReader(file);//方式二:FileReader reader = new FileReader("day09-code/a-1.txt");// 2.读数据//2.1 定义一个变量int read;//2.2写while循环,读取一次返回值设置到变量。判断!=-1while ((read = reader.read())!=-1){System.out.print((char) read);}
// int read = reader.read();
// System.out.println((char) read);
// int read1 = reader.read();
// System.out.println((char) read1);
// int read2 = reader.read();
// System.out.println((char) read2);
// int read3 = reader.read();
// System.out.println(read3);//3.关闭流reader.close();}
}| 方法名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public int read(char[] buffer)(每次读多个) | 每次用一个字符数组去读取数据,返回字符数组读取了多少个字符,如果发现没有数据可读会返回-1. |
public class Demo2 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{//1.创建对象FileReader reader = new FileReader("day09-code/a-1.txt");//2.读数据:一次读多个char[] chars = new char[3];//2.1 定义一个变量,记录每次读取的字符个数int len;//2.2 写while循环,读取一次返回值设置到变量。判断!=-1while((len = reader.read(chars)) != -1){System.out.println("读取长度" + len + ",内容:" + new String(chars,0,len));//3.关闭流reader.close();}}
}1.2 字符输出流
注意:字符输出流写出数据后,必须刷新流(flush)或者关闭流(close),写出的数据才会生效,原因是有缓存区如果要换行, 需要输出"\r\n"字符串
| 构造器 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public FileWriter(File file) | 创建字节输出流管道与源文件对象接通 |
| public FileWriter(String filepath) | 创建字节输出流管道与源文件路径接通 |
| public FileWriter(File file,boolean append) | 创建字节输出流管道与源文件对象接通,可追加数据 |
| public FileWriter(String filepath,boolean append) | 创建字节输出流管道与源文件路径接通,可追加数据 |
| 方法名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| void write(int c) | 写一个字符 |
| void write(String str) | 写一个字符串 |
| void write(String str, int off, int len) | 写一个字符串的一部分 |
| void write(char[] cbuf) | 写入一个字符数组 |
| void write(char[] cbuf, int off, int len) | 写入字符数组的一部分 |
字符输出流写出数据后,必须刷新流(flush)或者关闭流(close),写出的数据才会生效,原因是有缓存区。
| 方法名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public void flush() throws IOException | 刷新流,就是将内存中缓存的数据立即写到文件中去生效! |
| public void close() throws IOException | 关闭流的操作,包含了刷新! |
public class Demo3 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{// 1.创建文件输出流FileWriter writer = new FileWriter("day09-code/a-2.txt");//2.IO操作// 2.1 写一个字符writer.write(98);//写入换行writer.write("\r\n");
//2.2 写一个字符串writer.write("你会不会突然的出现,在对面街角咖啡店");writer.write("\r\n");
// 2.3 写一个字符串的一部分writer.write("在对面街角咖啡店", 5, 3);writer.write("\r\n");
// 2.4 写一个字符数组char[] chars ={'多','么','想','和','你','见','一','面'};writer.write(chars);writer.write("\r\n");
// 2.5 写一个字符数组的一部分writer.write(chars,5,3);//3.关闭流writer.close();//包含flush//writer.flush();// 刷新}
}二、缓冲流
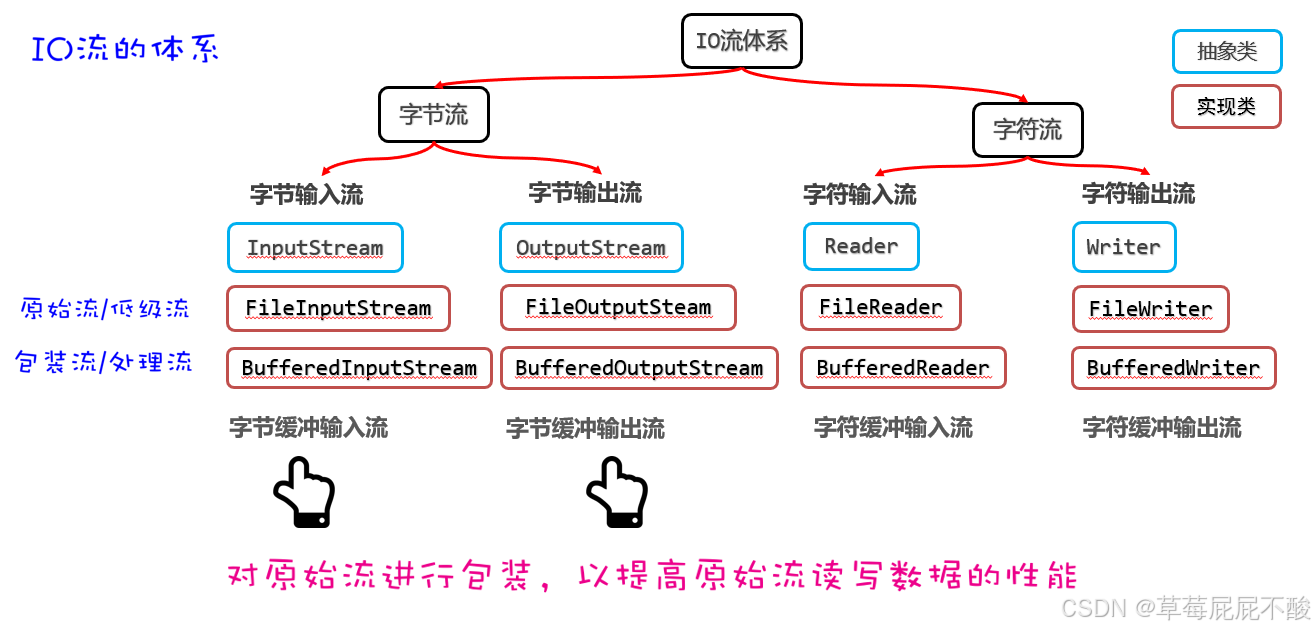
2.1 字节缓冲流
字节缓冲流自带8KB缓冲区, 减少了内存和硬盘之间的交互,从而提高原始流读、写数据的性能
| 构造器 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public BufferedInputStream(InputStream is) | 把低级的字节输入流包装成一个高级的缓冲字节输入流,从而提高读数据的性能 |
| public BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream os) | 把低级的字节输出流包装成一个高级的缓冲字节输出流,从而提高写数据的性能 |
//把a-2.txt复制一份到同一个文件夹下,命名为a-3.txt
public class Demo1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {//创建字节缓冲流FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("D:\\develop_tools\\JAVA\\itheima\\code\\advenceSE-code\\day09-code\\a-2.txt");BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\\develop_tools\\JAVA\\itheima\\code\\advenceSE-code\\day09-code\\a-3.txt");BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
//IO操作int len;byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];while((len = bis.read(bytes)) != -1){bos.write(bytes,0,len);}
//关闭流bos.close();fos.close();bis.close();fis.close();
}
}2.2 字符缓冲流
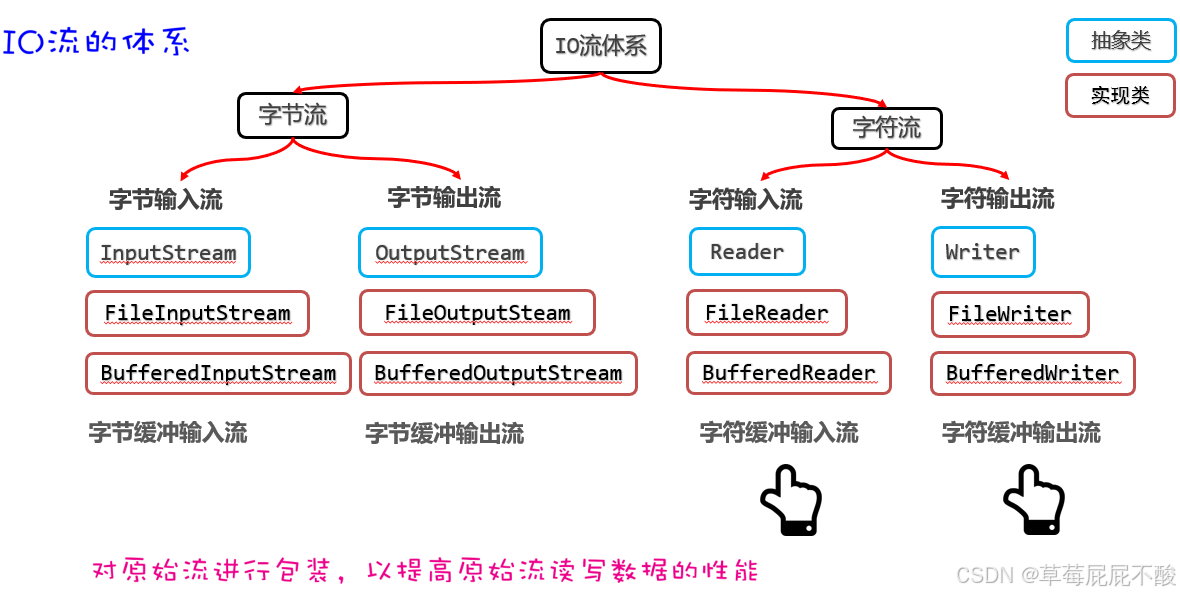
BufferedReader字符缓冲输入流
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public BufferedReader(Reader r) | 把低级的字符输入流包装成字符缓冲输入流管道,从而提高字符输入流读字符数据的性能 |
| public String readLine() | 读取一行数据返回,如果没有数据可读了,会返回null |
//读取b-3.txt的内容
public class Demo3 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {//1.创建BufferedReader对象BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("day09-code/b-3.txt"));
//2.IO操作// String str = reader.readLine();// System.out.println(str);
//2.1 定义一个字符变量String str;//2.2while循环,读取一行,赋值变量,判定变量不等于Nullwhile ((str = reader.readLine())!=null){System.out.println(str);}
//3.关闭流reader.close();}
}BufferedWriter字符缓冲输出流
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public BufferedWriter(Writer r) | 把低级的字符输出流包装成一个高级的缓冲字符输出流,从而提高字符输出流写数据的性能 |
| public void newLine() | 换行 |
public static void main2(String[] args) throws Exception {//1.创建BufferedWriter对象BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("day09-code/b-4.txt"));//2.IO操作writer.write("hello");writer.newLine();writer.write("world");writer.write("\r\n");writer.write("java");
//3.关闭流writer.close();
}练习:读取b-3.txt的内容,写入b-4.txt
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {//1.创建BufferedReader对象和BufferedWriter对象BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("day09-code/b-3.txt"));BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("day09-code/b-4.txt"));//2.IO操作//逐行读取内容String str;while ((str = reader.readLine())!= null){//逐行写入writer.write(str);//换行writer.newLine();}//3.关闭流writer.close();reader.close();
}三、转换流
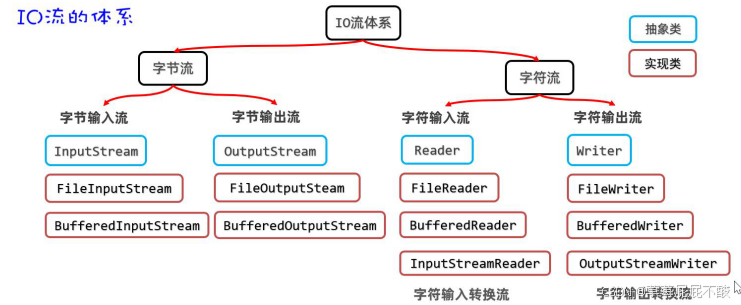
问题描述:当程序使用的编码跟操作文档的编码不一致时,会出现乱码问题此时可以使用字符转换流它的思路是: 先获取文件的原始字节流,再将其按真实的字符集编码转成字符输入流,这样字符输入流中的字符就不乱码了
InputStreamReader字符输入转换流
好处:可以解决字符流读取不同编码乱码的问题 public InputStreamReader(InputStream is,String charset):可以指定编码把原始字节流转换成字符流,如此字符流中的字符不乱码
| 构造器 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public InputStreamReader (InputStream is ,String charset) | 把原始的字节输入流,按照指定字符集编码转成字符输入流 |
public class Demo1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {//需求: 从c-1.txt读取内容//1.建文件字节输入流FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("day09-code/c-1.txt");//2.创建字符输入转换流InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis, "GBK");//3.字符输入转化流包装为字符输出缓冲流BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(isr);//4.读取数据String str = reader.readLine();System.out.println(str);//5.关闭流reader.close();isr.close();fis.close();}
}OutputStreamWriter字符输出转换流
作用:可以控制写出去的字符使用什么字符集编码。 获取字节输出流,再按照指定的字符集编码将其转换成字符输出流,以后写出去的字符就会用该字符集编码了。
| 构造器 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream os,String charset) | 可以把原始的字节输出流,按照指定编码转换成字符输出流 |
public class Demo2 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {//需求: 向c-2.txt写出内容, 字符集为GBK//1.建文件字节输入流FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("day09-code/c-1.txt");//2.创建字符输入转换流OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(fos, "GBK");//3.字符输入转化流包装为字符输出缓冲流BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(osw);//4.写入数据writer.write("你好");writer.newLine();writer.write("世界");//5.关闭流writer.close();osw.close();fos.close();}
}四、打印流
打印流可以实现更方便、更高效的打印数据出去,能实现打印啥出去就是啥出去。

| 构造器 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public PrintStream(OutputStream/File/String) | 打印流直接通向字节输出流/文件/文件路径 |
| public PrintWriter(OutputStream/Writer/File/String) | 打印流直接通向字符输出流/文件/文件路径 |
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public void println(Xxx xx) | 打印任意类型的数据出去 |
| public void write(int/byte[]/byte[]一部分) | 可以支持写字节数据出去(PrintStream) |
| public void write(int/String/char[]/..) | 可以支持写字符数据出去(PrintWriter) |
PrintStream和PrintWriter的区别打印数据的功能上是一样的:都是使用方便,性能高效PrintStream继承自字节输出流OutputStream,因此支持写字节数据的方法PrintWriter继承自字符输出流Writer,因此支持写字符数据出去
public class Demo1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {//PrintStream 字节打印流PrintStream printStream = new PrintStream("day09-code/d-1.txt");printStream.println("hello");printStream.println(97);printStream.println(true);printStream.write(97);//共性从父类继承(字节或字节数组)printStream.close();
//PrintWriter 字符打印流PrintWriter printWriter = new PrintWriter("day09-code/d-2.txt");printWriter.println("hello");printWriter.println(97);printWriter.println(true);printWriter.write("abc");//共性从父类继承(字符串)printWriter.close();}
}五、数据流
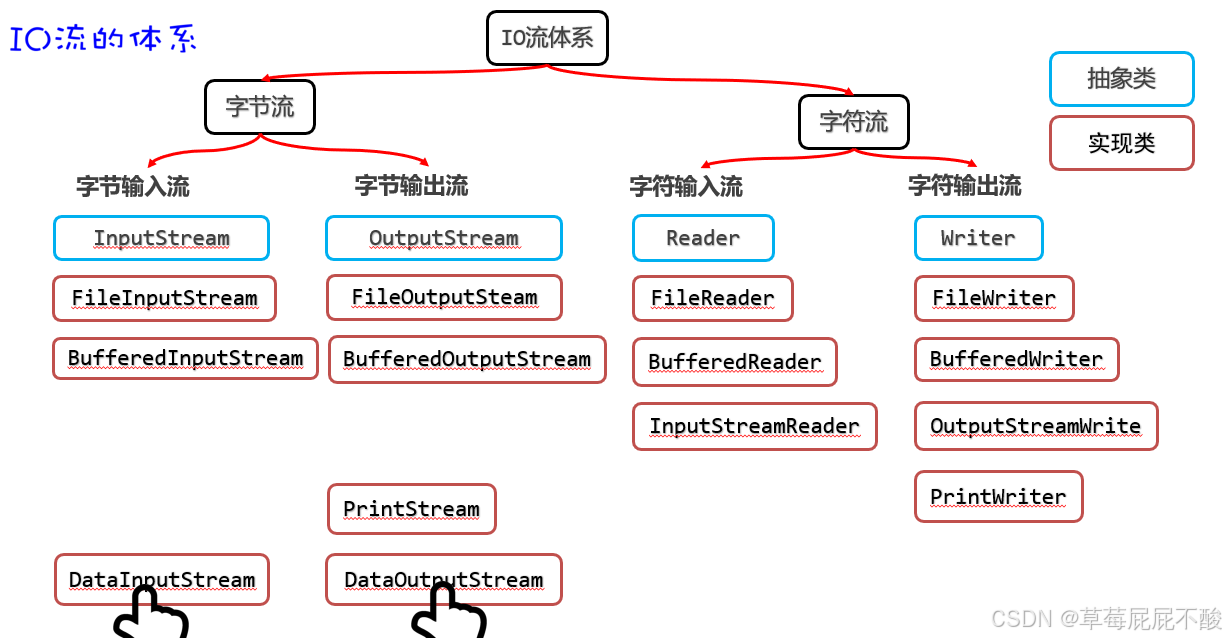
为了保存数据而用的一种数据流, 数据流输出的数据不是给人看的,是为了保存 数据输出流输出的数据,只能通过数据输入流读回程序
DataOutputStream数据输出流
允许把数据和其类型一并写出去
| 构造器 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public DataOutputStream(OutputStream out) | 创建新数据输出流包装基础的字节输出流 |
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public final void writeByte(int v) throws IOException | 将byte类型的数据写入基础的字节输出流 |
| public final void writeInt(int v) throws IOException | 将int类型的数据写入基础的字节输出流 |
| public final void writeDouble(Double v) throws IOException | 将double类型的数据写入基础的字节输出流 |
| public final void writeUTF(String str) throws IOException | 将字符串数据以UTF-8编码成字节写入基础的字节输出流 |
| public void write(int/byte[]/byte[]一部分) | 支持写字节数据出去 |
DataInputStream数据输入流
用于读取数据输出流写出去的数据
| 构造器 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public DataInputStream(InputStream is) | 创建新数据输入流包装基础的字节输入流 |
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Public final byte readByte() throws IOException | 读取字节数据返回 |
| public final int readInt() throws IOException | 读取int类型的数据返回 |
| public final double readDouble() throws IOException | 读取double类型的数据返回 |
| public final String readUTF() throws IOException | 读取字符串数(UTF-8)据返回 |
| public int readInt()/read(byte[]) | 支持读字节数据进来 |
public class Demo1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {//创建数据输出流,写出数据到文件DataOutputStream dataOutputStream = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("day09-code/e-1.txt"));//IO 操作dataOutputStream.writeByte(100);dataOutputStream.writeDouble(99.9);dataOutputStream.writeInt(100);dataOutputStream.writeUTF("你好");//关闭dataOutputStream.close();
//创建数据输入流,读取数据到程序DataInputStream dataInputStream = new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream("day09-code/e-1.txt"));//IO操作byte readByte = dataInputStream.readByte();System.out.println(readByte);double readDouble = dataInputStream.readDouble();System.out.println(readDouble);int readInt = dataInputStream.readInt();System.out.println(readInt);String readUTF = dataInputStream.readUTF();System.out.println(readUTF);//关闭dataInputStream.close();
}
}六、序列化流
ObjectOutputStream对象字节输出流
可以把Java对象进行序列化:把Java对象存入到文件中去。
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public ObjectOutputStream(OutputStream out) | 创建对象字节输出流,包装基础的字节输出流 |
| public final void writeObject(Object o) throws IOException | 把对象写出去 |
ObjectInputStream对象字节输出入流
可以把Java对象进行反序列化:把存储在文件中的Java对象读入到内存中来。
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public ObjectInputStream (InputStream is) | 创建对象字节输入流,包装基础的字节输入流 |
| public final Object readObject() | 把存储在文件中的Java对象读出来 |
注意对象如果要参与序列化,必须实现序列化接口(java.io.Serializable)
public class Demo1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {//0. 准备一个Student对象Student student = new Student("张三", 18);//将学生对象存入文件ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("day09-code/stu.txt"));//将数据粗人文件oos.writeObject(student);//关闭流oos.close();
//从文件中读取学生对象//创建对象字节输入流,包装基础的字节输入流ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("day09-code/stu.txt"));//读取数据Student stu = (Student)ois.readObject();System.out.println(stu);//关闭流ois.close();
}
}对象存储用一个ArrayList集合存储多个对象,然后直接对集合进行序列化即可 注意:ArrayList集合已经实现了序列化接口!
public class Demo2 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {//0. 准备一个Student对象的集合List<Student> students = new ArrayList<>();students.add(new Student("张三", 18));students.add(new Student("李四", 19));students.add(new Student("王五", 20));
//1. 序列化(f-1.txt)ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("day09-code/f-1.txt"));//写入文件oos.writeObject(students);//关闭oos.close();
//2. 反序列化(f-1.txt)ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("day09-code/f-1.txt"));//读取数据List<Student> studentList = ( List<Student>)ois.readObject();System.out.println(studentList);//关闭ois.close();
}
}1、对象序列化的含义是什么?怎么实现对象序列化?需要注意什么?
把对象数据存入到文件中去
对象字节输出流ObjectOutputStream
public void writeObject(Object obj)
对象必须实现序列化接口
2、 对象反序列化的含义是什么?怎么实现对象反序列化?
把对象数据存入到文件中去。
对象字节输入流ObjectInputStream
public Object readObject()
七、释放资源的方式

public class Demo1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {FileInputStream fis = null;FileOutputStream fos= null;
try {//1. 创建文件字节输入流、输出流fis = new FileInputStream("D:/upload/other/duotai1.wmv");fos = new FileOutputStream("D:/upload/other/duotai2.wmv");
//2. 使用输入流读取内容,使用输出流写出内容byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];int len = 0;while ((len = fis.read(bytes)) != -1) {fos.write(bytes, 0, len);}}catch (Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}finally {//3. 关闭流try {fos.close();}catch (Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}try {fis.close();}catch (Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}}}
}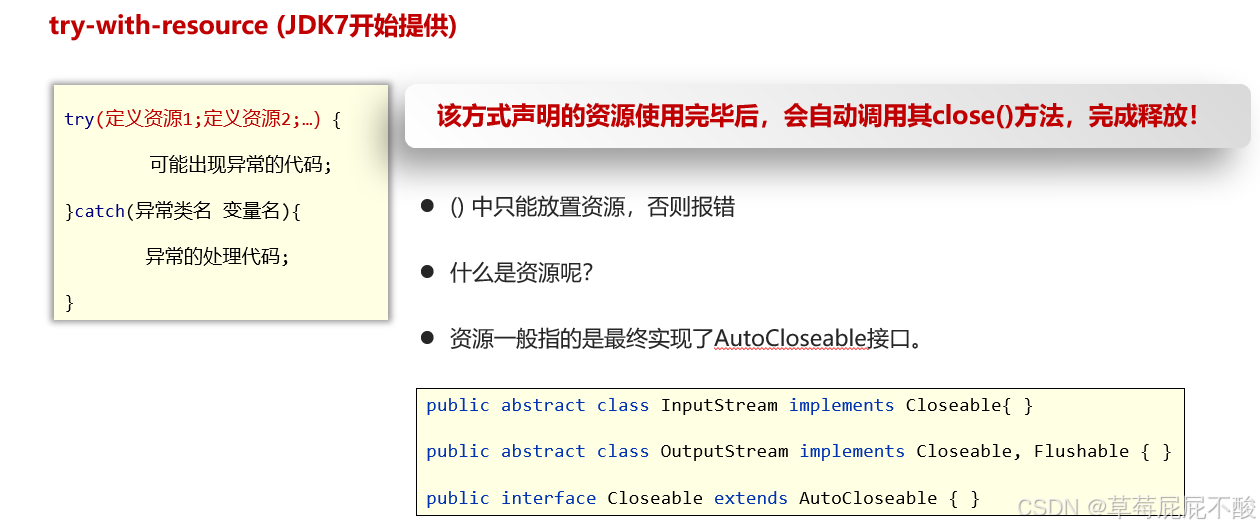
public class Demo2 {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
try(//1. 创建文件字节输入流、输出流FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("D:/upload/other/duotai1.wmv");FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("D:/upload/other/duotai2.wmv");){//2. 使用输入流读取内容,使用输出流写出内容byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];int len = 0;while ((len = fis.read(bytes)) != -1) {fos.write(bytes, 0, len);}}catch (Exception e){e.printStackTrace();}}
} /*
finally相关面试题1. try-catch-finally 中哪个部分可以省略? finally2. final,finally和finalize的区别3. 关于finally在try-catch中的执行顺序当try和catch代码块中有return语句时,finally仍然会被执行执行try或catch代码块中的return语句之前,都会先执行finally语句finally代码块中的return语句一定会执行无论在finally代码块中是否有返回值,返回值都不会改变,仍然是执行finally代码块之前的值
*/
public class Demo3 {public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println(m1());//System.out.println(m2());//System.out.println(m3());//System.out.println(m4());
}
//当try和catch代码块中有return语句时,finally仍然会被执行//执行try或catch代码块中的return语句之前,都会先执行finally语句public static int m1() {try {return 1;} finally {System.out.println("执行finally模块");}}//运行结果:执行finally模块// 1
public static int m2() {try {int a = 8 / 0;return 1;} catch (Exception e) {return 2;} finally {System.out.println("执行finally模块");}}//运行结果:执行finally模块// 2
//finally代码块中的return语句一定会执行public static int m3() {try {int a = 8 / 0;return 1;} catch (Exception e) {return 2;} finally {System.out.println("执行finally模块");return 0;}}//运行结果:执行finally模块// 0
//无论在finally代码块中是否有返回值,返回值都不会改变,仍然是执行finally代码块之前的值public static int m4() {int result = 0;try {return result;} finally {System.out.println("执行finally模块");result = 1;}}//运行结果:执行finally模块// 0
}
八、IO框架
框架的形式一般是将类、接口等编译成class文件形式,再压缩成一个jar包发行(供别人使用) Commons-io是Apache开源基金组织提供的一组关于IO操作的小框架,目的是提高IO相关操作开发的效率 使用步骤1、在模块下新建Directory文件夹,名字叫libs2、将准备好的jar包复制到lib文件夹3、对着lib目录右键Add as Library..添加到项日环境中4、修改eveL改为moduLe Librar5、在需要使用的地方直接调用即可
| FileUtils类提供的部分方法展示 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public static void copyFile(File srcFile, File destFile) | 复制文件 |
| public static void copyDirectory(File srcDir, File destDir) | 复制文件夹 |
| public static void deleteDirectory(File directory) | 删除文件夹 |
| public static String readFileToString(File file, String encoding) | 读数据 |
| public static void writeStringToFile(File file, String data, String charname, boolean append) | 写数据 |
| IOUtils类提供的部分方法展示 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public static int copy(InputStream inputStream, OutputStream outputStream) | 复制文件 |
| public static int copy(Reader reader, Writer writer) | 复制文件 |
| public static void write(String data, OutputStream output, String charsetName) | 写数据 |
public class Demo1 {public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {//FileUtils:文件操作的工作类// public static void copyFile(File数据源,File目的地) 复制文件FileUtils.copyFile(new File("D:\\aa-Test\\3-字符输入流.wmv"),new File("D:\\aa-Test\\2-字符输入流.wmv"));// public static void copyDirectory(File 数据源,File目的地) 复制文件夹FileUtils.copyDirectory(new File("D:\\aa-Test\\bb"),new File("D:\\aa-Test\\cc"));// public static void deleteDirectory(File 目标文件夹) 删除文件夹(有内容也直接删)FileUtils.deleteDirectory(new File("D:\\aa-Test\\cc"));// public static String readFileToString(File 数据源,String encoding) 读数据String string = FileUtils.readFileToString(new File("D:\\aa-Test\\bb\\b.txt"), "UTF-8");System.out.println(string);// public static void writeStringToFile(File file,String data,String encoding, Boolean append) 写数据FileUtils.writeStringToFile(new File("D:\\aa-Test\\bb\\b.txt"),"hello world", "UTF-8", true);//工具类IOUtils类// public static int copy(InputStream inputStream, OutputStream outputStream) 复制文件IOUtils.copy(new FileInputStream("D:\\aa-Test\\bb\\b.txt"),new FileOutputStream("D:\\aa-Test\\bb\\b1.txt"));// public static int copy(Reader reader, Writer writer) 复制文件FileReader reader = new FileReader("D:\\aa-Test\\bb\\b.txt");FileWriter writer = new FileWriter("D:\\aa-Test\\bb\\b2.txt");IOUtils.copy(reader, writer);writer.close();reader.close();// public static void write(String data, OutputStream output, String charsetName) 写数据IOUtils.write("hello world",new FileOutputStream("D:\\aa-Test\\bb\\b3.txt"),"UTF-8");}
}
这篇关于day09-IO-字符流其它流的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!









