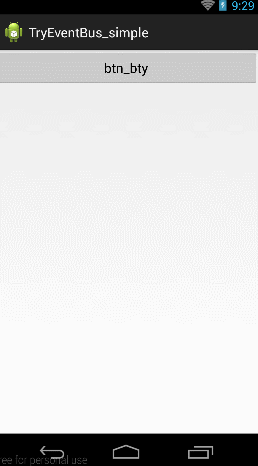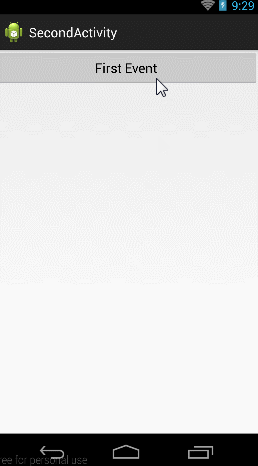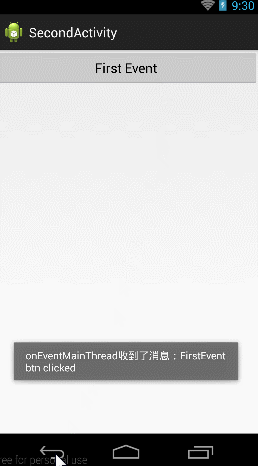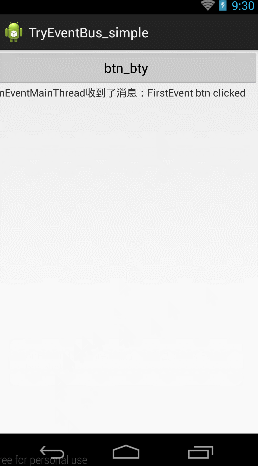本文主要是介绍EventBus使用(一),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
一、概述
EventBus是一款针对Android优化的发布/订阅事件总线。主要功能是替代Intent,Handler,BroadCast在Fragment,Activity,Service,线程之间传递消息.优点是开销小,代码更优雅。以及将发送者和接收者解耦。
1、下载EventBus的类库
源码:https://github.com/greenrobot/EventBus
2、基本使用
(1)自定义一个类,可以是空类,比如:
- public class AnyEventType {
- public AnyEventType(){}
- }
(2)在要接收消息的页面注册:
- eventBus.register(this);
(3)发送消息
- eventBus.post(new AnyEventType event);
(4)接受消息的页面实现(共有四个函数,各功能不同,这是其中之一,可以选择性的实现,这里先实现一个):
- public void onEvent(AnyEventType event) {}
- eventBus.unregister(this);
首先,在EventBus中,获取实例的方法一般是采用EventBus.getInstance()来获取默认的EventBus实例,当然你也可以new一个又一个,个人感觉还是用默认的比较好,以防出错。
二、实战
先给大家看个例子:
当击btn_try按钮的时候,跳到第二个Activity,当点击第二个activity上面的First Event按钮的时候向第一个Activity发送消息,当第一个Activity收到消息后,一方面将消息Toast显示,一方面放入textView中显示。
按照下面的步骤,下面来建这个工程:
1、基本框架搭建
想必大家从一个Activity跳转到第二个Activity的程序应该都会写,这里先稍稍把两个Activity跳转的代码建起来。后面再添加EventBus相关的玩意。
MainActivity布局(activity_main.xml)
- <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
- android:layout_width="match_parent"
- android:layout_height="match_parent"
- android:orientation="vertical">
- <Button
- android:id="@+id/btn_try"
- android:layout_width="match_parent"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:text="btn_bty"/>
- <TextView
- android:id="@+id/tv"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="match_parent"/>
- </LinearLayout>
- <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
- android:layout_width="match_parent"
- android:layout_height="match_parent"
- android:orientation="vertical"
- tools:context="com.harvic.try_eventbus_1.SecondActivity" >
- <Button
- android:id="@+id/btn_first_event"
- android:layout_width="match_parent"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:text="First Event"/>
- </LinearLayout>
- public class MainActivity extends Activity {
- Button btn;
- @Override
- protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
- super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
- setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
- btn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_try);
- btn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
- @Override
- public void onClick(View v) {
- // TODO Auto-generated method stub
- Intent intent = new Intent(getApplicationContext(),
- SecondActivity.class);
- startActivity(intent);
- }
- });
- }
- }
2、新建一个类FirstEvent
- package com.harvic.other;
- public class FirstEvent {
- private String mMsg;
- public FirstEvent(String msg) {
- // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
- mMsg = msg;
- }
- public String getMsg(){
- return mMsg;
- }
- }
3、在要接收消息的页面注册EventBus:
在上面的GIF图片的演示中,大家也可以看到,我们是要在MainActivity中接收发过来的消息的,所以我们在MainActivity中注册消息。
通过我们会在OnCreate()函数中注册EventBus,在OnDestroy()函数中反注册。所以整体的注册与反注册的代码如下:
- package com.example.tryeventbus_simple;
- import com.harvic.other.FirstEvent;
- import de.greenrobot.event.EventBus;
- import android.app.Activity;
- import android.content.Intent;
- import android.os.Bundle;
- import android.util.Log;
- import android.view.View;
- import android.widget.Button;
- import android.widget.TextView;
- import android.widget.Toast;
- public class MainActivity extends Activity {
- Button btn;
- TextView tv;
- @Override
- protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
- super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
- setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
- //注册EventBus
- EventBus.getDefault().register(this);
- btn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_try);
- tv = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.tv);
- btn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
- @Override
- public void onClick(View v) {
- // TODO Auto-generated method stub
- Intent intent = new Intent(getApplicationContext(),
- SecondActivity.class);
- startActivity(intent);
- }
- });
- }
- @Override
- protected void onDestroy(){
- super.onDestroy();
- EventBus.getDefault().unregister(this);//反注册EventBus
- }
- }
4、发送消息
发送消息是使用EventBus中的Post方法来实现发送的,发送过去的是我们新建的类的实例!
- EventBus.getDefault().post(new FirstEvent("FirstEvent btn clicked"));
完整的SecondActivity.Java的代码如下:
- package com.example.tryeventbus_simple;
- import com.harvic.other.FirstEvent;
- import de.greenrobot.event.EventBus;
- import android.app.Activity;
- import android.os.Bundle;
- import android.view.View;
- import android.widget.Button;
- public class SecondActivity extends Activity {
- private Button btn_FirstEvent;
- @Override
- protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
- super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
- setContentView(R.layout.activity_second);
- btn_FirstEvent = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_first_event);
- btn_FirstEvent.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
- @Override
- public void onClick(View v) {
- // TODO Auto-generated method stub
- EventBus.getDefault().post(
- new FirstEvent("FirstEvent btn clicked"));
- }
- });
- }
- }
5、接收消息
接收消息时,我们使用EventBus中最常用的onEventMainThread()函数来接收消息,具体为什么用这个,我们下篇再讲,这里先给大家一个初步认识,要先能把EventBus用起来先。
在MainActivity中重写onEventMainThread(FirstEvent event),参数就是我们自己定义的类:
在收到Event实例后,我们将其中携带的消息取出,一方面Toast出去,一方面传到TextView中;
- public void onEventMainThread(FirstEvent event) {
- String msg = "onEventMainThread收到了消息:" + event.getMsg();
- Log.d("harvic", msg);
- tv.setText(msg);
- Toast.makeText(this, msg, Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
- }
完整的MainActiviy代码如下:
- package com.example.tryeventbus_simple;
- import com.harvic.other.FirstEvent;
- import de.greenrobot.event.EventBus;
- import android.app.Activity;
- import android.content.Intent;
- import android.os.Bundle;
- import android.util.Log;
- import android.view.View;
- import android.widget.Button;
- import android.widget.TextView;
- import android.widget.Toast;
- public class MainActivity extends Activity {
- Button btn;
- TextView tv;
- @Override
- protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
- super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
- setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
- EventBus.getDefault().register(this);
- btn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_try);
- tv = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.tv);
- btn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
- @Override
- public void onClick(View v) {
- // TODO Auto-generated method stub
- Intent intent = new Intent(getApplicationContext(),
- SecondActivity.class);
- startActivity(intent);
- }
- });
- }
- public void onEventMainThread(FirstEvent event) {
- String msg = "onEventMainThread收到了消息:" + event.getMsg();
- Log.d("harvic", msg);
- tv.setText(msg);
- Toast.makeText(this, msg, Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
- }
- @Override
- protected void onDestroy(){
- super.onDestroy();
- EventBus.getDefault().unregister(this);
- }
- }
如果我的文章有帮到你,请关注哦。
源码地址:http://download.csdn.net/detail/harvic880925/8111357
请大家尊重原创者版权,转载请标明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/harvic880925/article/details/40660137 谢谢!
Android学习交流群:523487222
(如果您觉得有用,欢迎加入,一起学习进步)
点击链接加入群【Android学习群】

这篇关于EventBus使用(一)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!