本文主要是介绍34. 二叉树中和为某一值的路径,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
comments: true
difficulty: 中等
edit_url: https://github.com/doocs/leetcode/edit/main/lcof/%E9%9D%A2%E8%AF%95%E9%A2%9834.%20%E4%BA%8C%E5%8F%89%E6%A0%91%E4%B8%AD%E5%92%8C%E4%B8%BA%E6%9F%90%E4%B8%80%E5%80%BC%E7%9A%84%E8%B7%AF%E5%BE%84/README.md
面试题 34. 二叉树中和为某一值的路径
题目描述
给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个整数目标和 targetSum ,找出所有 从根节点到叶子节点 路径总和等于给定目标和的路径。
叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:
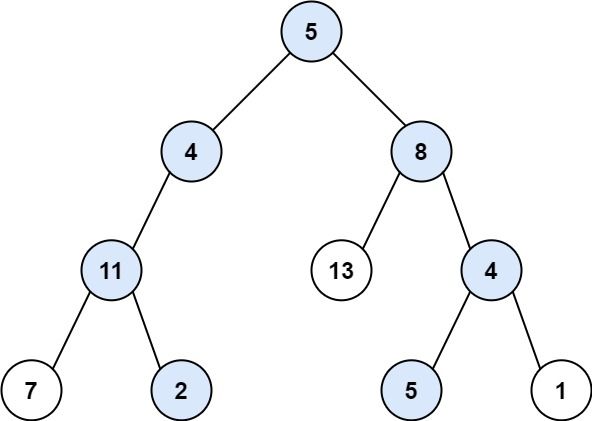
输入:root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,5,1], targetSum = 22 输出:[[5,4,11,2],[5,8,4,5]]
示例 2:
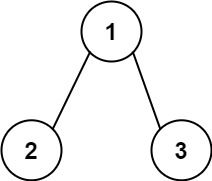
输入:root = [1,2,3], targetSum = 5 输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:root = [1,2], targetSum = 0 输出:[]
提示:
- 树中节点总数在范围
[0, 5000]内 -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000-1000 <= targetSum <= 1000
注意:本题与主站 113 题相同:https://leetcode.cn/problems/path-sum-ii/
解法
方法一:递归
从根节点开始,递归遍历每个节点,每次递归时,将当前节点值加入到路径中,然后判断当前节点是否为叶子节点,如果是叶子节点并且路径和等于目标值,则将该路径加入到结果中。如果当前节点不是叶子节点,则递归遍历其左右子节点。递归遍历时,需要将当前节点从路径中移除,以确保返回父节点时路径刚好是从根节点到父节点。
时间复杂度 O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O(n2),空间复杂度 O ( n ) O(n) O(n)。其中 n n n 是二叉树的节点数。
Python3
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:def pathSum(self, root: TreeNode, target: int) -> List[List[int]]:def dfs(root, s):if root is None:return#加入节点的同时,检查路径是否满足t.append(root.val)s -= root.valif root.left is None and root.right is None and s == 0:#root不能为空ans.append(t[:]) #t会动态改变dfs(root.left, s)dfs(root.right, s)t.pop() #这种写法,回溯时不需要s+=root.valans = []t = []dfs(root, target)return ans
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = Noneclass Solution(object):def findPath(self, root, sum):""":type root: TreeNode:type sum: int:rtype: List[List[int]]"""def dfs(root):nonlocal sif root is None:returnt.append(root.val)s-=root.valif root.left is None and root.right is None and s==0:ans.append(t[:])dfs(root.left)dfs(root.right)t.pop()s+=root.valans = []t=[]s=sumdfs(root)return ans
Java
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* public class TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode left;* TreeNode right;* TreeNode() {}* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {* this.val = val;* this.left = left;* this.right = right;* }* }*/
class Solution {private List<Integer> t = new ArrayList<>();private List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int target) {dfs(root, target);return ans;}private void dfs(TreeNode root, int s) {if (root == null) {return;}t.add(root.val);s -= root.val;if (root.left == null && root.right == null && s == 0) {ans.add(new ArrayList<>(t));}dfs(root.left, s);dfs(root.right, s);t.remove(t.size() - 1);}
}
C++
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* struct TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode *left;* TreeNode *right;* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int target) {vector<vector<int>> ans;vector<int> t;function<void(TreeNode * root, int s)> dfs = [&](TreeNode* root, int s) {if (!root) {return;}t.push_back(root->val);s -= root->val;if (!root->left && !root->right && !s) {ans.push_back(t);}dfs(root->left, s);dfs(root->right, s);t.pop_back();};dfs(root, target);return ans;}
};
Go
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* type TreeNode struct {* Val int* Left *TreeNode* Right *TreeNode* }*/
func pathSum(root *TreeNode, target int) (ans [][]int) {t := []int{}var dfs func(*TreeNode, int)dfs = func(root *TreeNode, s int) {if root == nil {return}t = append(t, root.Val)s -= root.Valif root.Left == nil && root.Right == nil && s == 0 {ans = append(ans, slices.Clone(t))}dfs(root.Left, s)dfs(root.Right, s)t = t[:len(t)-1]}dfs(root, target)return
}
TypeScript
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* class TreeNode {* val: number* left: TreeNode | null* right: TreeNode | null* constructor(val?: number, left?: TreeNode | null, right?: TreeNode | null) {* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)* }* }*/function pathSum(root: TreeNode | null, target: number): number[][] {const ans: number[][] = [];const t: number[] = [];const dfs = (root: TreeNode | null, s: number): void => {if (!root) {return;}const { val, left, right } = root;t.push(val);s -= val;if (!left && !right && s === 0) {ans.push([...t]);}dfs(left, s);dfs(right, s);t.pop();};dfs(root, target);return ans;
}
Rust
// Definition for a binary tree node.
// #[derive(Debug, PartialEq, Eq)]
// pub struct TreeNode {
// pub val: i32,
// pub left: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// pub right: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,
// }
//
// impl TreeNode {
// #[inline]
// pub fn new(val: i32) -> Self {
// TreeNode {
// val,
// left: None,
// right: None
// }
// }
// }
use std::cell::RefCell;
use std::rc::Rc;
impl Solution {fn dfs(root: &Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>,mut target: i32,t: &mut Vec<i32>,ans: &mut Vec<Vec<i32>>,) {if let Some(node) = root.as_ref() {let node = node.borrow();t.push(node.val);target -= node.val;if node.left.is_none() && node.right.is_none() && target == 0 {ans.push(t.clone());}Self::dfs(&node.left, target, t, ans);Self::dfs(&node.right, target, t, ans);t.pop();}}pub fn path_sum(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, target: i32) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {let mut ans = vec![];Self::dfs(&root, target, &mut vec![], &mut ans);ans}
}
JavaScript
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)* }*/
/*** @param {TreeNode} root* @param {number} target* @return {number[][]}*/
var pathSum = function (root, target) {const ans = [];const t = [];const dfs = (root, s) => {if (!root) {return;}const { val, left, right } = root;t.push(val);s -= val;if (!left && !right && !s) {ans.push([...t]);}dfs(left, s);dfs(right, s);t.pop();};dfs(root, target);return ans;
};
C#
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* public class TreeNode {* public int val;* public TreeNode left;* public TreeNode right;* public TreeNode(int val=0, TreeNode left=null, TreeNode right=null) {* this.val = val;* this.left = left;* this.right = right;* }* }*/
public class Solution {private List<IList<int>> ans = new List<IList<int>>();private List<int> t = new List<int>();public IList<IList<int>> PathSum(TreeNode root, int target) {dfs(root, target);return ans;}private void dfs(TreeNode root, int s) {if (root == null) {return;}t.Add(root.val);s -= root.val;if (root.left == null && root.right == null && s == 0) {ans.Add(new List<int>(t));}dfs(root.left, s);dfs(root.right, s);t.RemoveAt(t.Count - 1);}
}
Swift
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* public class TreeNode {* public var val: Int* public var left: TreeNode?* public var right: TreeNode?* public init() { self.val = 0; self.left = nil; self.right = nil; }* public init(_ val: Int) { self.val = val; self.left = nil; self.right = nil; }* public init(_ val: Int, _ left: TreeNode?, _ right: TreeNode?) {* self.val = val* self.left = left* self.right = right* }* }*/class Solution {private var t = [Int]()private var ans = [[Int]]()func pathSum(_ root: TreeNode?, _ target: Int) -> [[Int]] {dfs(root, target)return ans}private func dfs(_ root: TreeNode?, _ s: Int) {guard let root = root else {return}t.append(root.val)let remainingSum = s - root.valif root.left == nil && root.right == nil && remainingSum == 0 {ans.append(Array(t))}dfs(root.left, remainingSum)dfs(root.right, remainingSum)t.removeLast()}
}
这篇关于34. 二叉树中和为某一值的路径的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





