本文主要是介绍Posix thread 多线程编程,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
====本文系本站原创,欢迎转载! 转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/yyplc====
用Posix thread进行多线程设计,就不怕跨平台了,因为很多OS都兼容Posix thread,如Linux/Windows等,甚至嵌入式系统上(如rt-thread)都支持posix thread API。线程有比进程体积小,速率高,速度快等优势。所以编程时,如果涉及到效率和速度时,采用pthread_create()一个线程总比fork()一个进程好些。
Posxi thread 线程操作主要有创建(creation),终止(termination),同步(joins,blocking),调度(scheduling),数据管理(datamanagement)和交互(interaction).
可以从以下线程框图了解线程的构架:
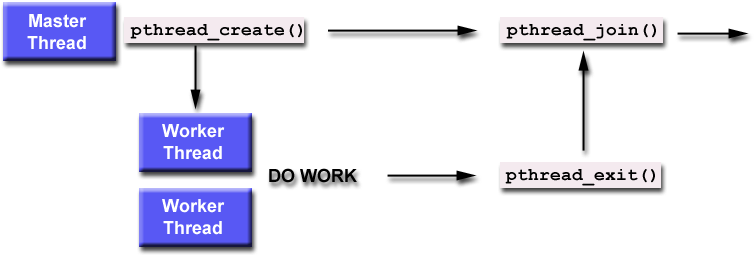
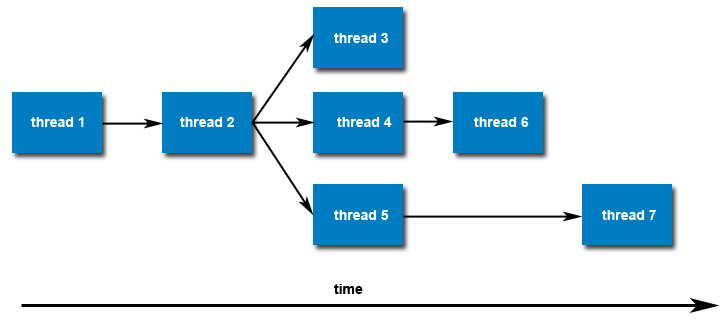
多线程间关系:
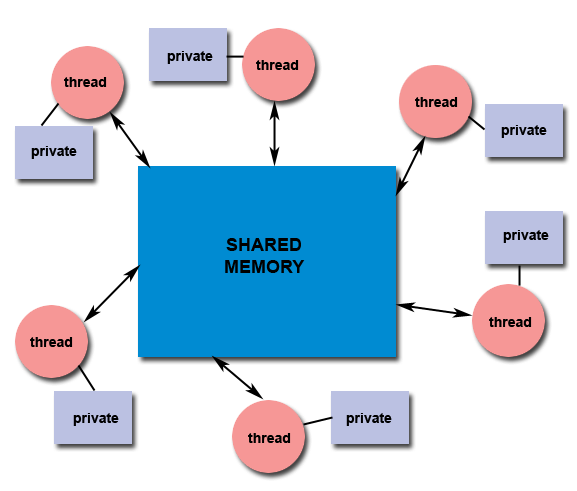
多线程间共享内存模型:
与普通的fork()进程不一样,线程很简单,线程并不需要维护线程列表,也不需要知道谁创建了它。以下是pthread_create()与fork()在各种平台上,性能的比较:
- The primary motivation for using Pthreads is to realize potential program performance gains.
- When compared to the cost of creating and managing a process, a thread can be created with much less operating system overhead. Managing threads requires fewer system resources than managing processes.
For example, the following table compares timingresults for the fork() subroutineand the pthread_create() subroutine.Timings reflect 50,000 process/thread creations, were performed with the time utility, and units are in seconds, nooptimization flags.
Note: don't expect the sytem and user times toadd up to real time, because these are SMP systems with multiple CPUs workingon the problem at the same time. At best, these are approximations run on localmachines, past and present.
| Platform | fork() | pthread_create() | ||||
| real | user | sys | real | user | sys | |
| Intel 2.8 GHz Xeon 5660 (12cpus/node) | 4.4 | 0.4 | 4.3 | 0.7 | 0.2 | 0.5 |
| AMD 2.3 GHz Opteron (16cpus/node) | 12.5 | 1.0 | 12.5 | 1.2 | 0.2 | 1.3 |
| AMD 2.4 GHz Opteron (8cpus/node) | 17.6 | 2.2 | 15.7 | 1.4 | 0.3 | 1.3 |
| IBM 4.0 GHz POWER6 (8cpus/node) | 9.5 | 0.6 | 8.8 | 1.6 | 0.1 | 0.4 |
| IBM 1.9 GHz POWER5 p5-575 (8cpus/node) | 64.2 | 30.7 | 27.6 | 1.7 | 0.6 | 1.1 |
| IBM 1.5 GHz POWER4 (8cpus/node) | 104.5 | 48.6 | 47.2 | 2.1 | 1.0 | 1.5 |
| INTEL 2.4 GHz Xeon (2 cpus/node) | 54.9 | 1.5 | 20.8 | 1.6 | 0.7 | 0.9 |
| INTEL 1.4 GHz Itanium2 (4 cpus/node) | 54.5 | 1.1 | 22.2 | 2.0 | 1.2 | 0.6 |
在同一个线程或进程中所创建的线程共同享有一样的地址空间。
线程间共享:
.进程指令(process instructions)
.大部分数据(most data)
.文件(descriptors)
.信号和信号句柄(signals and signal handlers)
.当前工作目录(current working directory)
.用户和组id(user and group id)
线程独自属性:
.线程id(thread id)
.寄存器(内容)和栈不同(set of registers,stack pointer)
.局部变量,返回地址(stack for local variables,return addresses)
.信号mask(signal mask)
.优先级(priority)
.返回值(return value errno)
主要的操作函数:
/*创建一个线程,成功返回0,失败返回error错误标志*/
- int pthread_create(pthread_t * thread, //thread :线程id, unsigned long intxi型
- const pthread_attr_t *attr, //attr: 线程属性参数,创建时将根据这个参数进行线程初始化
- void *(*start_routine)(void *), //start_routine:指向线程所调用的函数
- void *arg); //arg :线程传递参数
/* 终止线程,成功返回0,失败返回error错误 标志*/
- void pthread_exit(void *retval); //retval:返回值指针
/*等待直到id为th线程运行结束(合并一个线程的意思)*/
- int pthread_join(pthread_t th, void**thread_return); // th:线程id
- // thread_return :线程终止或取消时的返回值指针
/*获取当前线程id*/
- pthread_t pthread_self(void);
线程的同步机制:
.互斥量(mutexes)
.连接/合并(joins)
.条件变量(condition variables)
/*线程间互斥量操作函数,顾名思义*/
- int pthread_mutex_lock(pthread_mutex_t*mutex);//获取mutex,成功返0,失败返回错误标志,并阻塞当前线程
- intpthread_mutex_trylock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex); //同上,不同的是多了个try(也就是说先try一下)
- //如果在当前线程中,如果同一个互斥量已经被当前线程锁住,pthread_mutex_tyrlock将立即返回(成功).如果互斥量类型为:PTHREAD_MUTEX_RECURSIVE那么mutexlock count将自加一,然后立即返回(成功)
- int pthread_mutex_unlock(pthread_mutex_t*mutex); //释放一个mutex
实现原理:互斥量用于多线程对临界资源的访问,通过mutex lock count来判定是否锁住,初始值为0,当pthread_mutex_lock时mutex lock_count 自加,pthread_mutex_unlock时将mutex_lock_count自减。所以互斥量可用时mutex_lock_count = 0,对于一个临界资源,使用前应先lock,使用完后再unlock,如果使用不当,会有意外发生,但如果先unlock那么mutex_lock_count 自减1,说明改互斥量将可以同时使用2次了。
条件变量操作函数:
/*初始化一个条件变量cond(布尔型),成功返回0,失败返回error错误标志*/
- int pthread_cond_init(pthread_cond_t *restrictcond,
- const pthread_condattr_t*restrict attr);
/*销毁一个条件变量cond,成功返回0,失败返回error错误标志*/
- int pthread_cond_destroy(pthread_cond_t*cond);
/*释放一个互斥量且等待(即阻塞当前线程)一个条件变量cond为真,后再lock*/
- <pre name="code" class="cpp"> int pthread_cond_timedwait(pthread_cond_t*restrict cond, pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex,
- const struct timespec *restrictabstime);//等待条件变量cond是否为真,时限为abstime
- int pthread_cond_wait(pthread_cond_t*restrict cond,
- pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex); //等待条件cond是否为真,时限为cond真为止</pre>
- <pre></pre>
- <p></p>
- <p>/*释放条件变量cond,唤醒先前已被阻塞的线程*/ </p>
- <p></p>
- <pre name="code" class="cpp"> intpthread_cond_broadcast(pthread_cond_t *cond);//唤醒所有因条件变量cond而阻塞的线程
- intpthread_cond_signal(pthread_cond_t *cond);//唤醒一个因条件变量cond而阻塞的线程</pre><pre name="code" class="cpp"><p><span style="font-size:10px;"></span></p></pre>
- <p></p>
- <p>编程实例:</p>
- <p>完成一个有趣的游戏(类似抢板凳):主线程中创建线程1,然后线程1再创建2个线程2,3,线程2,3分别对一个计数器操作counter(初值为0),线程1每使用一次加3,线程2每使用一次加5,如果加到被15整除,那么counter加8,看哪个线程先加到9999,并计算自己使用了多少次计算器。先到者胜利,并打印出相应信息。</p>
- <p>实现代码:</p>
- <p></p>
- <pre name="code" class="cpp">#include<pthread.h>
- #include<stdlib.h>
- #include<unistd.h>
- #include<stdio.h>
- #defineCOUNTER_MAX 9999
- static intCOUNTER;
- struct RESULT {
- pthread_t tid;
- int cnt1;
- int cnt2;
- };
- static structRESULT res;
- staticpthread_mutex_t mux = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
- staticpthread_cond_t cond =PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;
- static void *thread2(void *arg)
- {
- int ret;
- printf("enter thread2, tid =%lu\n",pthread_self());
- sleep(1);
- for (;;) {
- pthread_mutex_lock(&mux);
- if(COUNTER >= COUNTER_MAX) {
- ret = pthread_cond_signal(&cond); //唤醒一个因条件变量cond而阻塞的线程
- if (ret) printf("error in thread2\n");
- res.tid = pthread_self();
- pthread_mutex_unlock(&mux); //释放mux
- pthread_exit(0);
- }
- printf(".");
- fflush(stdout);
- COUNTER += 3;
- if(COUNTER%15 == 0 && COUNTER) {
- COUNTER += 8;
- usleep(50*res.cnt1);
- }
- res.cnt1++;
- pthread_mutex_unlock(&mux);
- usleep(COUNTER);
- }
- }
- static void *thread3(void *arg)
- {
- int ret;
- printf("enter thread3, tid =%lu\n",pthread_self());
- sleep(1);
- for (;;) {
- pthread_mutex_lock(&mux);
- if(COUNTER >= COUNTER_MAX) {
- ret = pthread_cond_signal(&cond); //唤醒一个因条件变量cond而阻塞的线程
- if (ret) printf("error in thread3\n");
- res.tid = pthread_self();
- pthread_mutex_unlock(&mux); //释放mux
- pthread_exit(0);
- }
- printf("o");
- fflush(stdout);
- COUNTER += 5;
- if(COUNTER%15 == 0 && COUNTER) {
- COUNTER += 8;
- usleep(50*res.cnt2);
- }
- res.cnt2++;
- pthread_mutex_unlock(&mux);
- usleep(COUNTER);
- }
- }
- static void *thread1(void *arg)
- {
- int ret;
- pthread_t tid2,tid3;
- printf("starting...\n");
- pthread_mutex_lock(&mux);
- ret =pthread_create(&tid2,NULL,thread2,NULL);
- if (ret) {
- printf("create thread1 error\n");
- }
- ret =pthread_create(&tid3,NULL,thread3,NULL);
- if (ret) {
- printf("create thread2 error\n");
- }
- pthread_cond_wait(&cond,&mux); //释放mux,等待cond为真
- if (res.tid == tid2) {
- pthread_cancel(tid2);
- }
- else {
- pthread_cancel(tid3);
- }
- printf("\nget the winner:\n%s, tid= %lu,",(res.tid==tid2?"thread2":"thread3"),res.tid);
- printf("cnt1 = %d,cnt2 =%d\n",res.cnt1,res.cnt2);
- pthread_mutex_unlock(&mux);
- pthread_exit(0);
- }
- int main(void)
- {
- int ret;
- pthread_t tid1;
- ret =pthread_create(&tid1,NULL,thread1,NULL);
- if (ret) {
- printf("create thread1 error\n");
- }
- if (pthread_join(tid1,NULL)) { //等待thread1结束
- printf("error in thread1\n");
- }
- exit(0);
- }</pre>
- <p></p>
- <p>测试结果:</p>
- <p></p>
- <pre name="code" class="cpp">starting...
- enter thread3, tid= 3062217584
- enter thread2, tid= 3070610288
- thread2, tid =3070610288,cnt1 = 1046,cnt2 = 1072</pre>
- <p></p>
- <p align="LEFT" style="margin-bottom:0cm"><br>
- </p>
- <pre></pre>
- <pre></pre>
- <pre></pre>
- <pre></pre>
- <pre></pre>
- <pre></pre>
- <pre></pre>
- <pre></pre>
这篇关于Posix thread 多线程编程的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!



