本文主要是介绍Android从零开始搭建MVVM架构(3)——ViewModel,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
ViewModel类是被设计用来以可感知生命周期的方式存储和管理 UI 相关数据,ViewModel中数据会一直存活即使 activity configuration发生变化。
ViewModel有什么优势?
1.数据持久化
activity 在销毁重建时,之前我们可以用 activity 的onSaveInstanceState()机制保存和恢复数据,但缺点很明显,onSaveInstanceState只适合保存少量的可以被序列化、反序列化的数据,假如我们需要保存是一个比较大的 bitmap list ,这种机制明显不合适。ViewModel 就可以解决这种问题。
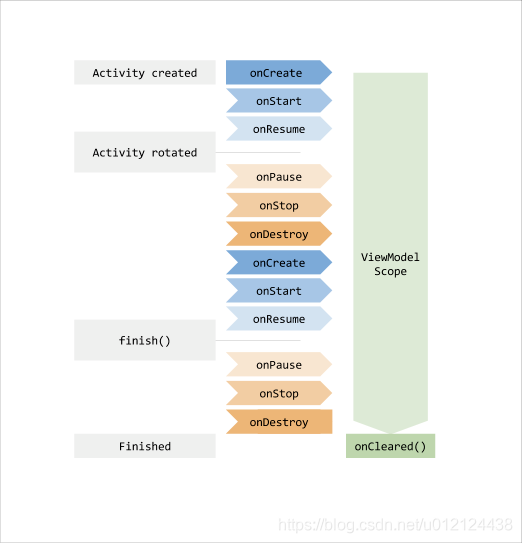
ViewModel 生命周期是贯穿整个 activity 生命周期,包括 Activity 因旋转造成的重创建,直到 Activity 真正意义上销毁后才会结束。
2.异步回调问题
app 需要频繁异步请求数据,比如调接口请求服务器数据。当然这些请求的回调都是相当耗时的,之前我们在 Activity 或 fragment里接收这些回调。所以不得不考虑潜在的内存泄漏情况,比如 Activity 被销毁后接口请求才返回。处理这些问题,会给我们增添好多复杂的工作。
但现在我们利用 ViewModel 处理数据回调,可以解决此问题。
3.分担 UI controller负担
从最早的 MVC 到目前流行的 MVP、MVVM,目的无非是 明确职责,分离 UI controller 负担。
UI controller 比如 Activity 、Fragment 是设计用来渲染展示数据、响应用户行为、处理系统的某些交互。如果再要求他去负责加载网络或数据库数据,会让其显得臃肿和难以管理。所以为了简洁、清爽、丝滑,我们可以分离出数据操作的职责给 ViewModel。
4、Fragments 间共享数据
比如在一个 Activity 里有多个fragment,这fragment 之间需要做某些交互。我之前的做法是接口回调,需要统一在 Activity 里管理,并且不可避免的 fragment 之间还得互相持有对方的引用。
那么用 ViewModel 是怎么样的呢(官网例子):
(activity 与其内部的 fragment 可以共用一个ViewModel)
public class SharedViewModel extends ViewModel {private final MutableLiveData<Item> selected = new MutableLiveData<Item>();public void select(Item item) {selected.setValue(item);}public LiveData<Item> getSelected() {return selected;}
}public class MasterFragment extends Fragment {private SharedViewModel model;public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);model = ViewModelProviders.of(getActivity()).get(SharedViewModel.class);itemSelector.setOnClickListener(item -> {model.select(item);});}
}public class DetailFragment extends Fragment {public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);SharedViewModel model = ViewModelProviders.of(getActivity()).get(SharedViewModel.class);model.getSelected().observe(this, { item ->// Update the UI.});}
}
好处如下:
1、Activity 不需要做任何事,甚至不知道这次交互,完美解耦。
2、Fragment 只需要 与ViewModel交互,不需要知道对方 Fragment 的状态甚至是否存在,更不需要持有其引用。所有当对方 Fragment 销毁时,不影响本身任何工作。
3、Fragment 生命周期互不影响,甚至 fragment 替换成其他的 也不影响这个系统的运作。
用法简介
ViewModel一般配合 LiveData 使用
1.获取 ViewModel 实例,通过提供的类ViewModelProviders:
MyViewModel model = ViewModelProviders.of(activity).get(MyViewModel.class);
或MyViewModel model = ViewModelProviders.of(fragment).get(MyViewModel.class);
或带有 Factory 的
MyViewModel model = ViewModelProviders.of(activity,factory).get(MyViewModel.class);
VM 内部操作:
public class MyViewModel extends ViewModel {private MutableLiveData<List<User>> users;public LiveData<List<User>> getUsers() {if (users == null) {users = new MutableLiveData<List<User>>();loadUsers();}return users;}private void loadUsers() {// Do an asynchronous operation to fetch users.}
}
然后,可在 activity 观察数据变化:
public class MyActivity extends AppCompatActivity {public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {// Create a ViewModel the first time the system calls an activity's onCreate() method.// Re-created activities receive the same MyViewModel instance created by the first activity.MyViewModel model = ViewModelProviders.of(this).get(MyViewModel.class);model.getUsers().observe(this, users -> {// update UI});}
}
源码分析原理
ViewModel 一般在 onCreate 里初始化。
1.实例化的代码
ViewModelProviders.of(activity,factory).get(MyViewModel.class)
1)首先是ViewModelProviders 的 of 方法:
@MainThreadpublic static ViewModelProvider of(@NonNull FragmentActivity activity) {initializeFactoryIfNeeded(checkApplication(activity));return new ViewModelProvider(ViewModelStores.of(activity), sDefaultFactory);}@MainThreadpublic static ViewModelProvider of(@NonNull FragmentActivity activity,@NonNull Factory factory) {checkApplication(activity);return new ViewModelProvider(ViewModelStores.of(activity), factory);}
参数有 activity 与 fragment 的我就只贴 activity 的了 ,重点看这里引出了一个 Factory,不带Factory的方法只是通过initializeFactoryIfNeeded初始化了一个sDefaultFactory(Factory的实现类):
/*** Implementations of {@code Factory} interface are responsible to instantiate ViewModels.*/public interface Factory {/*** Creates a new instance of the given {@code Class}.* <p>** @param modelClass a {@code Class} whose instance is requested* @param <T> The type parameter for the ViewModel.* @return a newly created ViewModel*/@NonNull<T extends ViewModel> T create(@NonNull Class<T> modelClass);}
只有一个 create 方法,用脚指头想想也知道肯定是用来初始化viewmodel的。先放着里等会用到再说。继续看 of 方法:
return new ViewModelProvider(ViewModelStores.of(activity), sDefaultFactory)
出现了两个新的类ViewModelProvider与ViewModelStores,先看ViewModelProvider:
public class ViewModelProvider {private static final String DEFAULT_KEY ="android.arch.lifecycle.ViewModelProvider.DefaultKey";private final Factory mFactory;private final ViewModelStore mViewModelStore;……@NonNull@MainThreadpublic <T extends ViewModel> T get(@NonNull String key, @NonNull Class<T> modelClass) {ViewModel viewModel = mViewModelStore.get(key);if (modelClass.isInstance(viewModel)) {//noinspection uncheckedreturn (T) viewModel;} else {//noinspection StatementWithEmptyBodyif (viewModel != null) {// TODO: log a warning.}}viewModel = mFactory.create(modelClass);mViewModelStore.put(key, viewModel);//noinspection uncheckedreturn (T) viewModel;}}
此类很简单 就是维护了 一个mFactory,一个新出现的类ViewModelStore,并提供了用mFactory和ViewModelStore生成 ViewModel 的 get 方法。哇,这里就已经看到 ViewModel 最终实例化的地方了,但是别着急还有好多东西呢。
再来看
ViewModelStores.of(activity)
/*** Factory methods for {@link ViewModelStore} class.*/
@SuppressWarnings("WeakerAccess")
public class ViewModelStores {private ViewModelStores() {}/*** Returns the {@link ViewModelStore} of the given activity.** @param activity an activity whose {@code ViewModelStore} is requested* @return a {@code ViewModelStore}*/@MainThreadpublic static ViewModelStore of(@NonNull FragmentActivity activity) {return holderFragmentFor(activity).getViewModelStore();}/*** Returns the {@link ViewModelStore} of the given fragment.** @param fragment a fragment whose {@code ViewModelStore} is requested* @return a {@code ViewModelStore}*/@MainThreadpublic static ViewModelStore of(@NonNull Fragment fragment) {return holderFragmentFor(fragment).getViewModelStore();}
}
只有两个 of 方法,holderFragmentFor为 HolderFragment 初始化的静态方法
public class HolderFragment extends Fragment {
……private ViewModelStore mViewModelStore = new ViewModelStore();public ViewModelStore getViewModelStore() {return mViewModelStore;}
……
}
没啥说的,看ViewModelStore:
public class ViewModelStore {private final HashMap<String, ViewModel> mMap = new HashMap<>();final void put(String key, ViewModel viewModel) {ViewModel oldViewModel = mMap.get(key);if (oldViewModel != null) {oldViewModel.onCleared();}mMap.put(key, viewModel);}final ViewModel get(String key) {return mMap.get(key);}/*** Clears internal storage and notifies ViewModels that they are no longer used.*/public final void clear() {for (ViewModel vm : mMap.values()) {vm.onCleared();}mMap.clear();}
}
很明显是一个用来存放 ViewModel 实例的类,内部维护了一个 HashMap 存放 ViewModel,
并提供了 get,put,clear方法。
至此ViewModelProviders of 做了哪些事情呢:
1、初始化了ViewModelProvider内部维护了 用于创建 VM 的 Factory,和用户存放 VM 的ViewModelStore;
2、初始化了 用来生成 ViewModel 的 Factory(默认为DefaultFactory);
3、通过ViewModelStores的静态方法实例化了 HolderFragment,并实例化了ViewModelStore
2、然后是ViewModelProvider的 get 方法:
ViewModelProviders.of(activity,factory).get(MyViewModel.class);@NonNull@MainThreadpublic <T extends ViewModel> T get(@NonNull String key, @NonNull Class<T> modelClass) {ViewModel viewModel = mViewModelStore.get(key);if (modelClass.isInstance(viewModel)) {//noinspection uncheckedreturn (T) viewModel;} else {//noinspection StatementWithEmptyBodyif (viewModel != null) {// TODO: log a warning.}}viewModel = mFactory.create(modelClass);mViewModelStore.put(key, viewModel);//noinspection uncheckedreturn (T) viewModel;}
逻辑不复杂,先看ViewModelStore是不是已经存了,没有的话就通过 factory 实例化, 并存到 ViewModelStore 中。
ViewModel 的死亡:
public abstract class ViewModel {/*** This method will be called when this ViewModel is no longer used and will be destroyed.* <p>* It is useful when ViewModel observes some data and you need to clear this subscription to* prevent a leak of this ViewModel.*/@SuppressWarnings("WeakerAccess")protected void onCleared() {}
}
Vm 只有一个onCleared方法,那么他是在何时调用的呢
这里就要介绍之前提到的 HolderFragment了:
public class HolderFragment extends Fragment {private static final String LOG_TAG = "ViewModelStores";private static final HolderFragmentManager sHolderFragmentManager = new HolderFragmentManager();/*** @hide*/@RestrictTo(RestrictTo.Scope.LIBRARY_GROUP)public static final String HOLDER_TAG ="android.arch.lifecycle.state.StateProviderHolderFragment";private ViewModelStore mViewModelStore = new ViewModelStore();public HolderFragment() {setRetainInstance(true);}@Overridepublic void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);sHolderFragmentManager.holderFragmentCreated(this);}@Overridepublic void onDestroy() {super.onDestroy();mViewModelStore.clear();}public ViewModelStore getViewModelStore() {return mViewModelStore;}static class HolderFragmentManager {private Map<Activity, HolderFragment> mNotCommittedActivityHolders = new HashMap<>();private Map<Fragment, HolderFragment> mNotCommittedFragmentHolders = new HashMap<>();……private static HolderFragment createHolderFragment(FragmentManager fragmentManager) {HolderFragment holder = new HolderFragment();fragmentManager.beginTransaction().add(holder, HOLDER_TAG).commitAllowingStateLoss();return holder;}HolderFragment holderFragmentFor(FragmentActivity activity) {FragmentManager fm = activity.getSupportFragmentManager();HolderFragment holder = findHolderFragment(fm);if (holder != null) {return holder;}holder = mNotCommittedActivityHolders.get(activity);if (holder != null) {return holder;}if (!mActivityCallbacksIsAdded) {mActivityCallbacksIsAdded = true;activity.getApplication().registerActivityLifecycleCallbacks(mActivityCallbacks);}holder = createHolderFragment(fm);mNotCommittedActivityHolders.put(activity, holder);return holder;}……
}
Vm 创建的时候提到过 实例化了一个 HolderFragment 。并且实例化的时候通过上面createHolderFragment 方法将其fragmentManager.beginTransaction().add(holder, HOLDER_TAG).commitAllowingStateLoss();
我们知道commit 之后 fragment 将会拥有灵魂,获得生命周期。再看其onDestroy方法里
调用了 mViewModelStore.clear();
public final void clear() {for (ViewModel vm : mMap.values()) {vm.onCleared();}mMap.clear();}
Google 充分利用了 fragment 生命周期的特性,使得 Vm 完成了 onCleared。Google 的 lifecycle 与 ViewModel 全都是利用 fragment 的一些特性去玩这些生命周期.
那么问题来了 为什么横竖屏切换 ViewModel 不会 onCleared?
看 HolderFragment 的构造方法里有个setRetainInstance(true);
注意
由于 ViewModel 生命周期可能长与 activity 生命周期,所以为了避免内存泄漏 Google 禁止在 ViewModel 中持有 Context 或 activity 或 view 的引用。如果非得使用Context ,可以继承AndroidViewModel 类中获取 ApplicationContext
public class AndroidViewModel extends ViewModel {@SuppressLint("StaticFieldLeak")private Application mApplication;public AndroidViewModel(@NonNull Application application) {mApplication = application;}/*** Return the application.*/@NonNullpublic <T extends Application> T getApplication() {//noinspection uncheckedreturn (T) mApplication;}
}
这篇关于Android从零开始搭建MVVM架构(3)——ViewModel的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





