本文主要是介绍Java宝藏实验资源库(5)字符流,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
一、实验目的
- 掌握输入输出流的基本概念。
- 掌握字符流处理类的基本结构。
- 掌握使用字符流进行输入输出的基本方法。
二、实验内容、过程及结果
**12.12 (Reformat Java source code) Write a program that converts the Java source
code from the next-line brace style to the end-of-line brace style. For example,
the following Java source in (a) uses the next-line brace style. Your program
converts it to the end-of-line brace style in (b).
HexFormatException
VideoNote
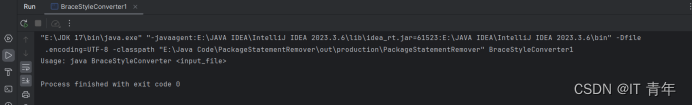
Your program can be invoked from the command line with the Java source
code file as the argument. It converts the Java source code to a new format. For
example, the following command converts the Java source-code file Test.java
to the end-of-line brace style.
java Exercise12_12 Test.java
* * 12.12(重新格式化Java源代码)编写一个程序转换Java源代码从下一行大括号样式到行尾大括号样式的代码。
例如,下面(a)中的Java源代码使用了下一行大括号样式。你的程序将其转换为(b)中的行尾大括号样式。
可以使用Java源代码从命令行调用您的程序代码文件作为参数。它将Java源代码转换为新的格式。为到行尾大括号样式。
java练习12_12测试
运行代码如下 :
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;public class BraceStyleConverter {public static void main(String[] args) {if (args.length == 0) {System.out.println("Usage: java BraceStyleConverter <input_file>");return;}String inputFile = args[0];String outputFile = "converted_" + inputFile;try (BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(inputFile));FileWriter writer = new FileWriter(outputFile)) {String line;boolean insideBlock = false;while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {line = line.trim();if (line.startsWith("{")) {insideBlock = true;}if (insideBlock) {writer.write(line);if (line.endsWith("}")) {writer.write("\n");insideBlock = false;} else {writer.write(" ");}} else {writer.write(line + "\n");}}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("Conversion completed. Output written to " + outputFile);}
}运行结果
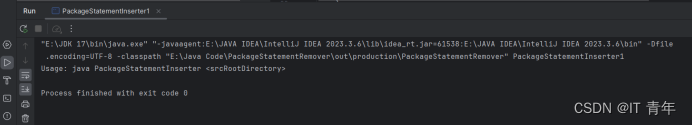
**12.18 (Add package statement) Suppose you have Java source files under the direc
tories chapter1, chapter2, . . . , chapter34. Write a program to insert the
statement package chapteri; as the first line for each Java source file under
the directory chapteri. Suppose chapter1, chapter2, . . . , chapter34
are under the root directory srcRootDirectory. The root directory and
chapteri directory may contain other folders and files. Use the following
command to run the program:
java Exercise12_18 srcRootDirectory
* * 12.18(添加包语句)假设在目录下有Java源文件托利党第一章,第二章……, chapter34。编写一个程序来插入语句包章节;作为下面每个Java源文件的第一行目录章。假设第一章,第二章,…, chapter34都在根目录srcRootDirectory下。根目录和Chapteri目录可能包含其他文件夹和文件。使用以下命令命令运行程序:
java Exercise12_18 srcRootDirectory
运行代码如下 :
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;public class PackageStatementInserter {public static void main(String[] args) {if (args.length == 0) {System.out.println("Usage: java PackageStatementInserter <srcRootDirectory>");return;}String srcRootDirectory = args[0];insertPackageStatements(srcRootDirectory);System.out.println("Package statements inserted successfully.");}public static void insertPackageStatements(String srcRootDirectory) {File rootDir = new File(srcRootDirectory);if (!rootDir.exists() || !rootDir.isDirectory()) {System.out.println("Invalid source root directory.");return;}File[] chapterDirs = rootDir.listFiles(File::isDirectory);if (chapterDirs == null) {System.out.println("No subdirectories found in the source root directory.");return;}for (File chapterDir : chapterDirs) {File[] javaFiles = chapterDir.listFiles((dir, name) -> name.toLowerCase().endsWith(".java"));if (javaFiles == null) {continue; // Skip directories without Java files}for (File javaFile : javaFiles) {try {insertPackageStatement(javaFile);} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}private static void insertPackageStatement(File javaFile) throws IOException {String originalFilePath = javaFile.getAbsolutePath();String tempFilePath = originalFilePath + ".tmp";try (BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(originalFilePath));FileWriter writer = new FileWriter(tempFilePath)) {// Insert package statement as the first lineString packageStatement = getPackageStatement(javaFile);if (packageStatement != null) {writer.write(packageStatement + "\n");}// Copy the rest of the fileString line;while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {writer.write(line + "\n");}}// Replace the original file with the modified temp filejavaFile.delete();new File(tempFilePath).renameTo(new File(originalFilePath));}private static String getPackageStatement(File javaFile) throws IOException {String chapterName = javaFile.getParentFile().getName(); // Assumes chapter directories are named appropriatelyString packageName = "chapter" + chapterName; // Adjust as needed based on your directory structurereturn "package " + packageName + ";";}
}运行结果
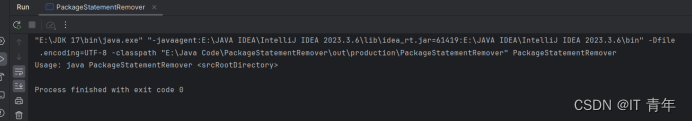
**12.20 (Remove package statement) Suppose you have Java source files under the directories chapter1, chapter2, . . . , chapter34. Write a program to remove the statement package chapteri; in the first line for each Java source file under the directory chapteri. Supposechapter1, chapter2, . . . , chapter34 are under the root directory srcRootDirectory. The root directory and chapteri directory may contain other folders and files. Use the following command to run the program:
java Exercise12_20 srcRootDirectory
* * 12.20(删除包语句)假设Java源文件在目录chapter1, chapter2,…, chapter34。编写程序…删除语句包章节;在每个Java的第一行中目录chapteri下的源文件。假设第一,第二章,……、chapter34都在根目录srcRootDirectory下。根目录和chapteri目录可能包含其他文件夹和文件。使用执行以下命令运行程序:
java Exercise12_20 srcRootDirectory
运行代码如下 :
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;public class PackageStatementRemover {public static void main(String[] args) {if (args.length == 0) {System.out.println("Usage: java PackageStatementRemover <srcRootDirectory>");return;}String srcRootDirectory = args[0];removePackageStatements(srcRootDirectory);System.out.println("Package statements removed successfully.");}public static void removePackageStatements(String srcRootDirectory) {File rootDir = new File(srcRootDirectory);if (!rootDir.exists() || !rootDir.isDirectory()) {System.out.println("Invalid source root directory.");return;}File[] chapterDirs = rootDir.listFiles(File::isDirectory);if (chapterDirs == null) {System.out.println("No subdirectories found in the source root directory.");return;}for (File chapterDir : chapterDirs) {File[] javaFiles = chapterDir.listFiles((dir, name) -> name.toLowerCase().endsWith(".java"));if (javaFiles == null) {continue; // Skip directories without Java files}for (File javaFile : javaFiles) {try {removePackageStatement(javaFile);} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}}}private static void removePackageStatement(File javaFile) throws IOException {String originalFilePath = javaFile.getAbsolutePath();String tempFilePath = originalFilePath + ".tmp";try (BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(originalFilePath));FileWriter writer = new FileWriter(tempFilePath)) {// Skip the first line (package statement)reader.readLine(); // Assuming the first line is always the package statement// Copy the rest of the fileString line;while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {writer.write(line + "\n");}}// Replace the original file with the modified temp filejavaFile.delete();new File(tempFilePath).renameTo(new File(originalFilePath));}
}运行结果
三、实验结论
通过本次实验实践了字符流输入输出功能的知识和操作,得到了调用子功能包时一定要注重效率,感悟到对程序的底层逻辑一定要了解,不能一味地求速学,该精学时还得筑牢基础。
![]() 结语
结语
喜欢的事情就要做到极致
决不能半途而废
!!!

这篇关于Java宝藏实验资源库(5)字符流的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





