本文主要是介绍最详细的JS学习笔记(连载)第二章、函数(this),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
9、this
全局中的this指向的是window,函数内的this也是指向window;对象方法中的this指向该方法。函数对象赋值给对象属性的时候,this指向的是该对象
var obj = {
name:'wyang'
}
function person(){
return this.name;
}
obj.sayNma = person;
obj.person(); //wyang
对象原型链上的this
var obj = {
sayPro:function(){
return '名字:'+this.name+'年龄:'+this.age;
}
}
var o = Object.create(obj);
o.name = 'wyang';
o.age = 26;
console.log(o.sayPro()); //名字:wyang年龄:26
(1)、全局的this(浏览器) 全局作用域下的this一般指向全局对象,浏览器汇总的全局对象就是window。

(2)、一般函数的this(浏览器)【重点】 全局作用域下直接调用f1(),this就仍然指向全局对象,浏览器中就是window,在node.js里面就是global对象。
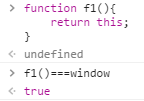
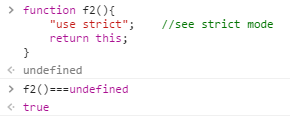
严格模式下直接调用f2(),this执行是undefined。
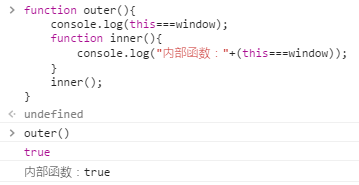
调用函数时,this被绑定到全局对象。如下内部函数调用时this也是绑定到全局对象window。
倘若语言设计正确,当内部函数被调用时,this应该仍然绑定到外部函数的this变量。这个设计错误的后果就是方法不能利用内部函数来帮助它工作,因为内部函数的this被绑定了错误的值,所以不能共享该方法对对象的访问权。
解决方案如下:定义一个变量that并给它赋值为this,那么内部函数就可以通过that访问到this。
//函数字面量创建add
var add=function(a,b){
return a+b;
}
var myObject = {
value: 0,
increment: function(inc) {
this.value += typeof inc === 'number' ? inc : 1;
}
}
myObject.increment();
document.writeln(myObject.value); //1
myObject.increment(2);
document.writeln(myObject.value); //3
//给myObject增加一个double方法
myObject.double=function(){
var that=this; //解决方法
var helper=function(){
that.value=add(that.value,that.value);
}
helper(); //以函数的形式调用helper
}
//以方法的形式调用double
myObject.double();
document.writeln(myObject.value); //6
(3)、作为对象方法的 函数的this【重点】 只要将函数作为对象的方法o.f,this就会指向这个对象o。
var o={ var o={prop:37};
prop:37, function independent(){
f:function(){ return this.prop;
return this.prop; }
} o.f=independent;
} console.log(o.f()); //37
console.log(o.f()); //37
在方法调用模式中this到对象的绑定发生在调用时,这个"超级"延迟绑定(very late binding)使得函数可以对this高度重用。【update20170306】
(4)、对象原型链上的this
对象o有个属性f。p是个空对象,并且p的原型指向o。给p添加2个属性a和b,再调用p.f()。调用p.f()的时候调用的是p的原型o上面的这样一个属性f。所以对象原型链上的this调用时指向的还是对象。
var o={
f:function(){
return this.a+this.b
}};
var p=Object.create(o);
p.a=1;
p.b=4;
console.log(p.f()); //5
(5)、get/set方法与this get set方法中的this一般也是指向get,set方法所在的对象。
function modulus(){
return Math.sqrt(this.re*this.re+this.im*this.im);
}
var o={
re:1,
im:-1,
get phase(){
return Math.atan2(this.im,this.re);
}
}
Object.defineProperty(o,'modulus',{
get:modulus,
enumerable:true,
configurable:true
})
console.log(o.phase,o.modulus); //-0.7853981633974483 1.4142135623730951
(6)、构造器中的this【重点】
如果在一个函数前面带上new来调用,那么背地里将会创建一个连接到该函数的prototype成员的新对象,同时this会绑定到那个新对象上。将MyClass作为了构造器来用。
function MyClass(){
this.a=37;
}
var o=new MyClass();
/*this指向空对象,并且这个空对象的原型指向MyClass.prototype,this作为返回值,因为没有return,所以对象o就会有属性a为37*/
console.log(o.a);//37
注意:return语句返回的是对象的话,将该对象作为返回值,所以下面a就是38。
function C2(){
this.a=37;
return {a:38};
}
o=new C2();
console.log(o.a);//38
(7)、call/apply方法与this【重点】
function add(c,d){
console.log(this.a+this.b+c+d);
}
var o={a:1,b:3};
//call调用 add.call(o,5,7); //16 //1+3+5+7=16
//apply调用 add.apply(o,[10,20]); //34 //1+3+10+20=34
应用
function bar(){
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(this));
}
bar.call(7); //[object Number]

call和apply如果this传入null或者undefined的话,this会指向全局对象,在浏览器里就是window。 如果是严格模式的话:传入this为null和undefined,那this就是null和undefined。
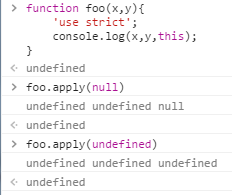
(8)、bind与this[ES5提供,IE9+才有] 想把某一个对象作为this的时候,就传进去。
function f(){
return this.a;
}
var g=f.bind({a:"test"});
console.log(g()); //test 绑定一次,多次调用,仍然实现这样一个绑定,比apply和call更高效
var o={a:37,f:f,g:g}; // f属性赋值为直接的f方法,g赋值为刚才绑定之后的方法
console.log(o.f(),o.g()); //37 "test" o.f()通过对象的属性的方式调用的,返回37。比较特殊的一点,使用bind方法绑定了之后,即使把新绑定之后的方法作为对象的属性去调用,仍然会按照之前的绑定去走,所以仍然返回test应用【bind的经典例子】
this.x=9; //相当于window.x=9
var module={
x:81,
getX:function(){return this.x;}
};
module.getX(); // 81 作为对象方法调用
var getX=module.getX(); // 把对象的方法赋值给一个变量
getX(); // 9 this指向window,调用的是window的x
var boundGetx=getX.bind(module);
boundGetx(); // 81 通过bind修改运行时的this
本人是以网络视频与网络文章的方式自学的,并按自己理解的方式总结了学习笔记。有不正确之处请各位高手多多指点,一起学习进步。【VX:czlingyun 暗号:CSDN】
这篇关于最详细的JS学习笔记(连载)第二章、函数(this)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




