SpringBoot的@Enable*注解的使用介绍
@EnableAsync或@EnableConfigurationProperties背后的运行原理,是使用了@Import注解。
@Import({User.class,Role.class,MyConfiguration.class}),@Import里面可以存放数组类型的。
@Import用来导入一个或多个类(bean被spring容器托管)、或者配置类(配置类里面的Bean都会被spring容器托管)。
@Enable*其实就是使用了@Import,@Import其实就是导入了配置类。
1、以如何将配置文件里面的配置注入到bean中。之前贴过了,这里再贴一下,权当自己熟悉了。
1 package com.bie.enable; 2 3 import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties; 4 import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; 5 6 /** 7 * 8 * @Description TODO 9 * @author biehl 10 * @Date 2018年12月31日 下午1:13:07 11 * 12 */ 13 @Component 14 @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "tomcat") 15 public class TomcatProperties { 16 17 private String hosts; 18 private String ports; 19 public String getHosts() { 20 return hosts; 21 } 22 public void setHosts(String hosts) { 23 this.hosts = hosts; 24 } 25 public String getPorts() { 26 return ports; 27 } 28 public void setPorts(String ports) { 29 this.ports = ports; 30 } 31 @Override 32 public String toString() { 33 return "TomcatProperties [hosts=" + hosts + ", ports=" + ports + "]"; 34 } 35 36 37 }
然后在配置文件里面进行配置:
tomcat.hosts=192.168.11.12 tomcat.ports=8090
然后写一个主运行类来进行运行:
可以看到正常运行了。运行效果就不粘贴了。
package com.bie.enable;import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;/*** * @Description TODO* @author biehl* @Date 2018年12月31日 下午1:15:27**/ @SpringBootApplication public class TomcatApplication {public static void main(String[] args) {ConfigurableApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(TomcatApplication.class, args);System.out.println("------------------------------------------------------------");System.out.println(context.getEnvironment().getProperty("tomcat.hosts"));//从容器中获取到对象tomcat.hostsSystem.out.println(context.getEnvironment().getProperty("tomcat.ports"));//从容器中获取到对象tomcat.portsSystem.out.println("------------------------------------------------------------");context.close();} }
2、ctrl键和鼠标左键点开@SpringBootApplication注解,其实可以发现,注解里面主要使用了如此注解@EnableAutoConfiguration和@ComponentScan来实现的功能的。
注意1:@SpringBootConfiguration注解和Spring的@Configuration注解的作用是一样的。
注意2:@EnableConfigurationProperties注解是替代@EnableAutoConfiguration,发挥作用的是@EnableConfigurationProperties注解。

然后呢,你会发现,使用这两个注解和使用@SpringBootApplication注解的作用是一样的。
package com.bie.enable;import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;/*** * @Description TODO* @author biehl* @Date 2018年12月31日 下午1:15:27**/ //@SpringBootApplication @EnableAutoConfiguration @ComponentScan public class TomcatApplication {public static void main(String[] args) {ConfigurableApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(TomcatApplication.class, args);System.out.println("------------------------------------------------------------");System.out.println(context.getEnvironment().getProperty("tomcat.hosts"));System.out.println(context.getEnvironment().getProperty("tomcat.ports"));System.out.println("------------------------------------------------------------");context.close();} }
运行效果如下所示:
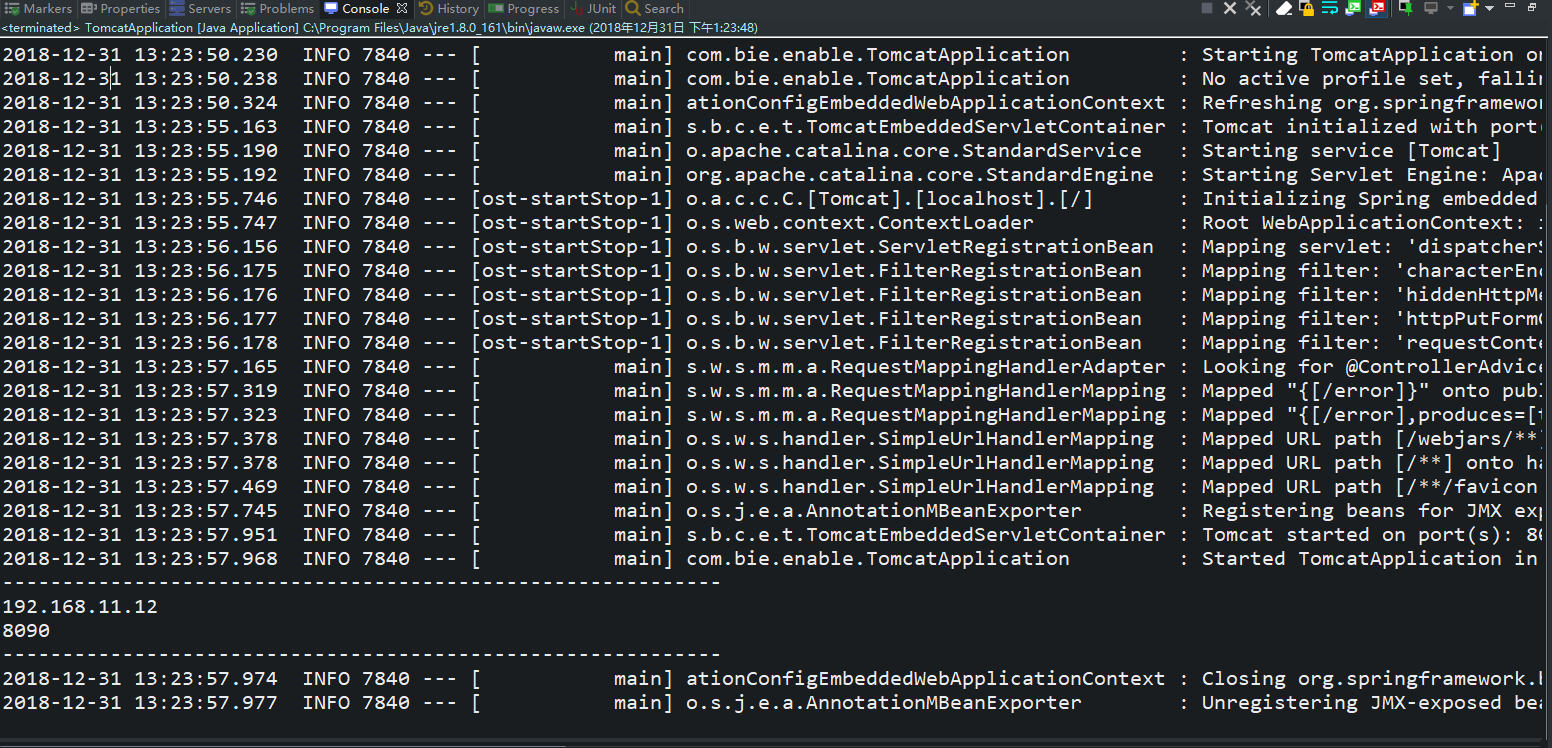
上面说了发挥作用的@EnableConfigurationProperties,然而我测试的时候发现如下所示:
1 . ____ _ __ _ _ 2 /\\ / ___'_ __ _ _(_)_ __ __ _ \ \ \ \ 3 ( ( )\___ | '_ | '_| | '_ \/ _` | \ \ \ \ 4 \\/ ___)| |_)| | | | | || (_| | ) ) ) ) 5 ' |____| .__|_| |_|_| |_\__, | / / / / 6 =========|_|==============|___/=/_/_/_/ 7 :: Spring Boot :: (v1.5.10.RELEASE) 8 9 2018-12-31 13:27:18.515 INFO 2176 --- [ main] com.bie.enable.TomcatApplication : Starting TomcatApplication on DESKTOP-T450s with PID 2176 (E:\eclipeswork\guoban\spring-boot-hello\target\classes started by Aiyufei in E:\eclipeswork\guoban\spring-boot-hello) 10 2018-12-31 13:27:18.521 INFO 2176 --- [ main] com.bie.enable.TomcatApplication : No active profile set, falling back to default profiles: default 11 2018-12-31 13:27:18.600 INFO 2176 --- [ main] ationConfigEmbeddedWebApplicationContext : Refreshing org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.AnnotationConfigEmbeddedWebApplicationContext@101df177: startup date [Mon Dec 31 13:27:18 CST 2018]; root of context hierarchy 12 2018-12-31 13:27:18.932 WARN 2176 --- [ main] ationConfigEmbeddedWebApplicationContext : Exception encountered during context initialization - cancelling refresh attempt: org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextException: Unable to start embedded container; nested exception is org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextException: Unable to start EmbeddedWebApplicationContext due to missing EmbeddedServletContainerFactory bean. 13 2018-12-31 13:27:19.423 ERROR 2176 --- [ main] o.s.boot.SpringApplication : Application startup failed 14 15 org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextException: Unable to start embedded container; nested exception is org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextException: Unable to start EmbeddedWebApplicationContext due to missing EmbeddedServletContainerFactory bean. 16 at org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.EmbeddedWebApplicationContext.onRefresh(EmbeddedWebApplicationContext.java:137) ~[spring-boot-1.5.10.RELEASE.jar:1.5.10.RELEASE] 17 at org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.refresh(AbstractApplicationContext.java:537) ~[spring-context-4.3.14.RELEASE.jar:4.3.14.RELEASE] 18 at org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.EmbeddedWebApplicationContext.refresh(EmbeddedWebApplicationContext.java:122) ~[spring-boot-1.5.10.RELEASE.jar:1.5.10.RELEASE] 19 at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.refresh(SpringApplication.java:693) [spring-boot-1.5.10.RELEASE.jar:1.5.10.RELEASE] 20 at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.refreshContext(SpringApplication.java:360) [spring-boot-1.5.10.RELEASE.jar:1.5.10.RELEASE] 21 at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.run(SpringApplication.java:303) [spring-boot-1.5.10.RELEASE.jar:1.5.10.RELEASE] 22 at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.run(SpringApplication.java:1118) [spring-boot-1.5.10.RELEASE.jar:1.5.10.RELEASE] 23 at org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication.run(SpringApplication.java:1107) [spring-boot-1.5.10.RELEASE.jar:1.5.10.RELEASE] 24 at com.bie.enable.TomcatApplication.main(TomcatApplication.java:21) [classes/:na] 25 Caused by: org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextException: Unable to start EmbeddedWebApplicationContext due to missing EmbeddedServletContainerFactory bean. 26 at org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.EmbeddedWebApplicationContext.getEmbeddedServletContainerFactory(EmbeddedWebApplicationContext.java:189) ~[spring-boot-1.5.10.RELEASE.jar:1.5.10.RELEASE] 27 at org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.EmbeddedWebApplicationContext.createEmbeddedServletContainer(EmbeddedWebApplicationContext.java:162) ~[spring-boot-1.5.10.RELEASE.jar:1.5.10.RELEASE] 28 at org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.EmbeddedWebApplicationContext.onRefresh(EmbeddedWebApplicationContext.java:134) ~[spring-boot-1.5.10.RELEASE.jar:1.5.10.RELEASE] 29 ... 8 common frames omitted
然而就百度呗,发现并没有很清晰说这个问题怎么解决的。
在https://stackoverflow.com/questions/37114076/exception-in-thread-main-org-springframework-context-applicationcontextexcepti发现了一段话,还挺有意思的。如是说,丢失注解,其实是依赖不对的问题,哈哈哈,然后看看自己的依赖。发现了问题所在。

我一开始是使用的<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>,这种web的依赖,修改为了<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>普通项目的依赖,这样使用@EnableConfigurationProperties注解是替代@EnableAutoConfiguration运行就没有问题了。
@EnableConfigurationProperties注解是用来启用一个特性的,这个特性就是,可以把配置文件注入到bean里面去。一般是要和@ConfigurationProperties一起使用。
2、SpringBoot中如何启用一个异步,看看SpringBoot如何对异步进行支持的。
1 package com.bie.enable; 2 3 import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; 4 5 import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async; 6 import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; 7 8 /** 9 * 10 * @Description TODO 11 * @author biehl 12 * @Date 2018年12月31日 下午2:08:52 13 * 1、实现Runnable接口的类要实现run的方法 14 */ 15 @Component //添加到容器中 16 public class SyncRunnable implements Runnable { 17 18 //@Async注解实现,异步执行 19 @Async 20 public void run() { 21 try { 22 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { 23 System.out.println("-------------------" + i); 24 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1); 25 } 26 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 27 e.printStackTrace(); 28 } 29 30 } 31 32 }
然后写主运行类,如下所示:
1 package com.bie.enable; 2 3 import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; 4 import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; 5 import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext; 6 import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync; 7 8 /** 9 * 10 * @Description TODO 11 * @author biehl 12 * @Date 2018年12月31日 下午2:11:52 13 * 14 */ 15 @SpringBootApplication 16 @EnableAsync //启用异步注解 17 public class SyncApplication { 18 19 public static void main(String[] args) { 20 ConfigurableApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(SyncApplication.class, args); 21 SyncRunnable bean = context.getBean(SyncRunnable.class); 22 System.out.println(bean); 23 bean.run(); 24 System.out.println("-----------end-----------"); 25 26 //关闭 27 context.close(); 28 } 29 }
如果使用上面的会报错,如下所示:
1 . ____ _ __ _ _ 2 /\\ / ___'_ __ _ _(_)_ __ __ _ \ \ \ \ 3 ( ( )\___ | '_ | '_| | '_ \/ _` | \ \ \ \ 4 \\/ ___)| |_)| | | | | || (_| | ) ) ) ) 5 ' |____| .__|_| |_|_| |_\__, | / / / / 6 =========|_|==============|___/=/_/_/_/ 7 :: Spring Boot :: (v1.5.10.RELEASE) 8 9 2018-12-31 14:45:34.676 INFO 7500 --- [ main] com.bie.enable.SyncApplication : Starting SyncApplication on DESKTOP-T450s with PID 7500 (E:\eclipeswork\guoban\spring-boot-hello\target\classes started by Aiyufei in E:\eclipeswork\guoban\spring-boot-hello) 10 2018-12-31 14:45:34.682 INFO 7500 --- [ main] com.bie.enable.SyncApplication : No active profile set, falling back to default profiles: default 11 2018-12-31 14:45:34.991 INFO 7500 --- [ main] s.c.a.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext : Refreshing org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext@103f852: startup date [Mon Dec 31 14:45:34 CST 2018]; root of context hierarchy 12 2018-12-31 14:45:38.523 INFO 7500 --- [ main] o.s.j.e.a.AnnotationMBeanExporter : Registering beans for JMX exposure on startup 13 2018-12-31 14:45:38.623 INFO 7500 --- [ main] com.bie.enable.SyncApplication : Started SyncApplication in 5.1 seconds (JVM running for 5.898) 14 Exception in thread "main" org.springframework.beans.factory.NoSuchBeanDefinitionException: No qualifying bean of type 'com.bie.enable.SyncRunnable' available 15 at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory.getBean(DefaultListableBeanFactory.java:353) 16 at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory.getBean(DefaultListableBeanFactory.java:340) 17 at org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.getBean(AbstractApplicationContext.java:1092) 18 at com.bie.enable.SyncApplication.main(SyncApplication.java:21) 19 2018-12-31 14:45:38.663 INFO 7500 --- [ Thread-2] s.c.a.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext : Closing org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext@103f852: startup date [Mon Dec 31 14:45:34 CST 2018]; root of context hierarchy 20 2018-12-31 14:45:38.670 INFO 7500 --- [ Thread-2] o.s.j.e.a.AnnotationMBeanExporter : Unregistering JMX-exposed beans on shutdown
百度了一下,参考链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/javJoker/p/7281688.html
修改为了如下所示,参考链接的问题,确实也问住我了,需要深思一下吧。
@EnableAsync //启用异步注解,一般是和@Async一起使用。来实现异步的功能。
1 package com.bie.enable; 2 3 import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; 4 import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; 5 import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext; 6 import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync; 7 8 /** 9 * 10 * @Description TODO 11 * @author biehl 12 * @Date 2018年12月31日 下午2:11:52 13 * 14 */ 15 @SpringBootApplication 16 @EnableAsync //启用异步注解 17 public class SyncApplication { 18 19 public static void main(String[] args) { 20 ConfigurableApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(SyncApplication.class, args); 21 Runnable bean = context.getBean(Runnable.class); 22 System.out.println(bean); 23 bean.run(); 24 System.out.println("-----------end-----------"); 25 26 //关闭 27 context.close(); 28 } 29 }
运行结果如下所示:
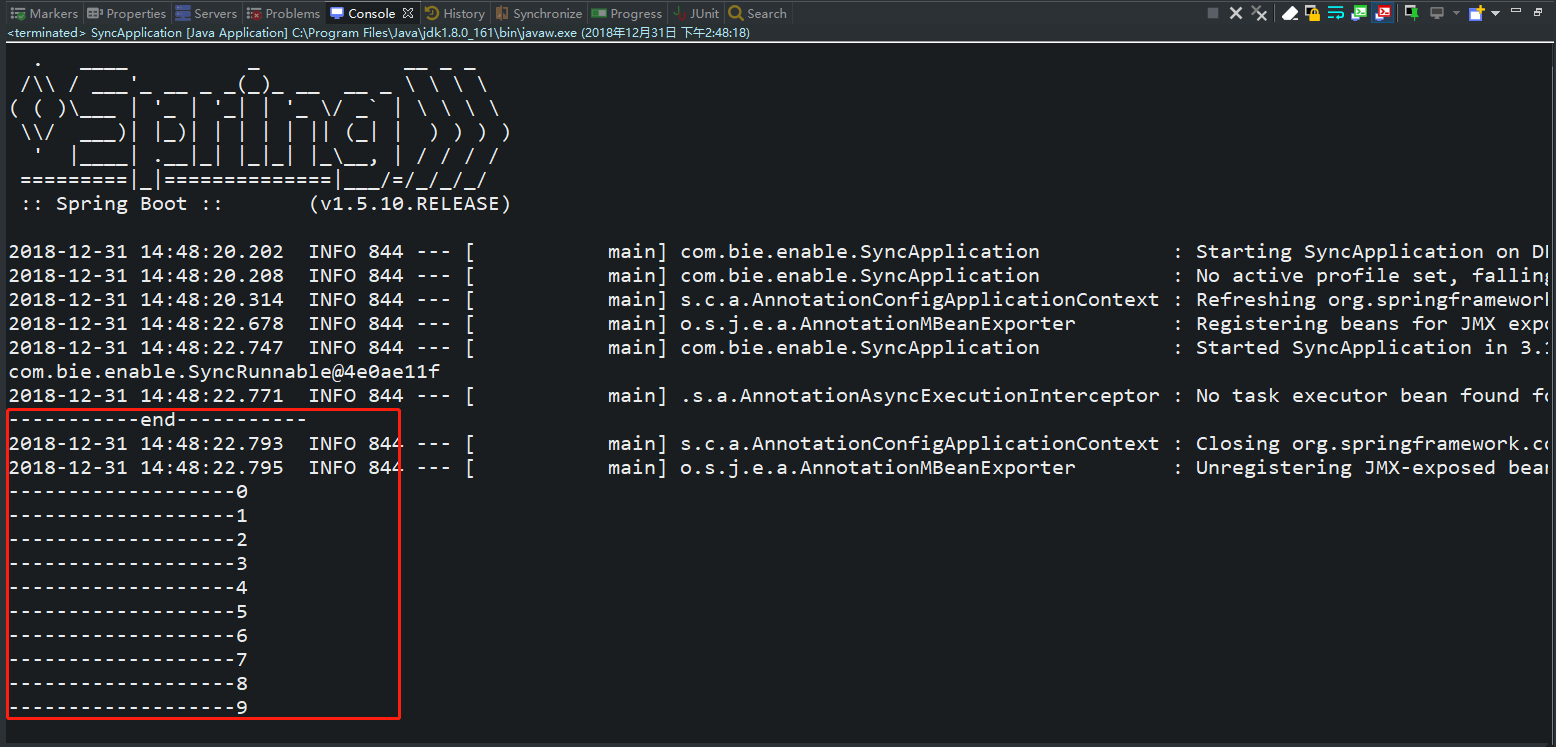
待续......





