本文主要是介绍2017ACM EC Final 补题题解,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
M World Cup
傻逼签到不多说
代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=100005;
const int base=131;
typedef long long ll;
#define pi acos(-1)
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define mod 998244353
const int inf=1<<30;
ll p[10];ll slove(int id)
{if(id >= 1 && id < 49)return p[1];if(id >= 49 && id < 57)return p[2];if(id >=57 && id < 61)return p[3]; if(id >=61 && id < 63)return p[4];return p[5];
}
int main()
{int t,n;cin>>t;for(int j = 1; j <= t ;j++){for(int i = 1; i <= 5; i++)scanf("%lld",&p[i]);scanf("%d",&n);int id;ll ans = 0;for(int i =1;i <= n;i++){scanf("%d",&id);ans += slove(id);}ans *= 10000;printf("Case #%d: %lld\n",j,ans);}return 0;
}
A Chat Group
数学题
看一下n的数据范围,显然直接暴力不可能,看一下k的数据1e5,可以想到往k上面转化。
经典二项式的性质Cn0+Cn1+Cn2+……cnn=2^n,直接把加法转化为减法。注意由于算组合数有分母,需要用到逆元。
然后取余这个东西真的恶心,建议有结果的地方就取余,少了一个取余被卡了一小时还换了一种写法。
代码一(提前处理阶乘和全排列)
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=100005;
const int base=131;
typedef long long ll;
#define pi acos(-1)
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define mod 1000000007
const int inf=1<<30;
ll A[maxn];
ll J[maxn];
ll ksm(ll a,ll b,ll m)
{ll ans = 1;while(b){if(b & 1) ans = (ans*a) % m ;a = (a * a) % m;b >>= 1;}return ans;
}void amn(ll m,ll n){A[0] = 1;for(ll i = 1,j = m;i<= n;i++){A[i] = A[i-1] * j;A[i] %= mod;j--; }
}void jiechen(ll k)
{J[0] = 1;for(int i = 1 ; i <= k;i++ ){J[i] = (J[i-1] * i) % mod;}
}ll cmn(ll m ,ll n)
{return (A[n] * ksm(J[n],mod-2,mod)) %mod;
}int main()
{int t,n,k;cin>>t;jiechen(100000);for(int i = 1; i <= t; i++){cin>>n>>k;if( k > n){printf("Case #%d: 0\n",i);continue;}ll ans = ksm(2,n,mod);ll jishu = 0;amn(n,k);for(ll j = k-1 ; j >= 0; j--){jishu += cmn(n,j);jishu %= mod;}ans = (ans - jishu + mod) % mod;printf("Case #%d: %lld\n",i,ans);}return 0;
}
代码二 递推处理
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=100005;
const int base=131;
typedef long long ll;
#define pi acos(-1)
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define mod 1000000007
const int inf=1<<30;
ll A[maxn];
ll J[maxn];
ll ksm(ll a,ll b,ll m)
{ll ans = 1;while(b){if(b & 1) ans = (ans*a) % m ;a = (a * a) % m;b >>= 1;}return ans;
}int main()
{int t,n,k;cin>>t;for(int i = 1; i <= t; i++){cin>>n>>k;if( k > n){printf("Case #%d: 0\n",i);continue;}ll ans = ksm(2,n,mod);ll jishu = 1;ll tmp = 1;for(ll j = 1,kk = n ; j <= k-1; j++){tmp = ((tmp * kk) % mod * ksm(j,mod-2,mod)) %mod;kk--;jishu += tmp;jishu %= mod;}ans = (ans - jishu + mod) % mod;printf("Case #%d: %lld\n",i,ans);}return 0;
}
KDowngrade
阅读理解题
可能是我英语不好吧,反正看了题解才知道题意。虽然它叫降级但是题意好像和降级并没有什么关系。
拿样例举例此时位于A-B(3-2),这一天羊神缺席,B舍弃,A转化为经验值3点,从零开始升级就是2-1,继续第二天,1舍弃,2转化为经验值2点,从零开始升级就是1-2。
题意知道了就是纯模拟了。
代码:(二分查找)
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=100005;
const int base=131;
typedef long long ll;
#define pi acos(-1)
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define mod 1000000007
const int inf=1<<30;
ll l[maxn];
ll up[maxn];ll find(ll x)
{ll l = 1;ll r = x;while(l <= r){ll m = (l + r) / 2;if(up[m] < x && up[m+1] >= x)return m;else if(x <= up[m])r = m-1;elsel = m+1;}return 0;
}int main()
{int t,a,b,n;cin>>t;for(int c = 1; c <= t ; c++ ){memset(up,0,sizeof(up));cin>>a>>b>>n;for(int i = 1; i <= a; i++){scanf("%lld",&l[i]);up[i] = up[i-1] + l[i];}ll x,y,lx;x = a;y = b;while(n--){if(x == lx)break;lx = x;x = find(x) + 1;y = lx - up[x-1];}printf("Case #%d: %lld-%lld\n",c,x,y); }return 0;
}
普通:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=100005;
const int base=131;
typedef long long ll;
#define pi acos(-1)
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define mod 1000000007
const int inf=1<<30;
ll l[maxn];int main()
{int t,a,b,n;cin>>t;for(int c = 1; c <= t ; c++ ){cin>>a>>b>>n;for(int i = 1; i <= a; i++)scanf("%lld",&l[i]);ll x,y,lx;x = a;y = b;while(n--){if(x == lx)break;lx = x;y = x;x = 1;for(int i = 1; i <= x;i++){if(y > l[i]){y -= l[i];x++;}elsebreak;}if(x == 1 && y == 1)break;}printf("Case #%d: %lld-%lld\n",c,x,y); }return 0;
}
CTraffic Light
又是一个阅读理解,最糟糕的情况下最短时间就是等最长的红灯,其他都是绿灯。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=100005;
const int base=131;
typedef long long ll;
#define pi acos(-1)
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define mod 1000000007
const int inf=1<<30;
ll s[maxn];
ll a[maxn],b[maxn];int main()
{int t,n;cin>>t;for(int c =1 ;c <= t ;c++){cin>>n;double ans = 0.0;for(int i = 1;i <= n+1; i++){scanf("%lld",&s[i]);ans += s[i];}for(int i = 1;i <= n; i++ )scanf("%lld %lld",&a[i],&b[i]);sort(b+1, b+1+n);ans += b[n];printf("Case #%d: %.8lf\n",c,ans); }return 0;
}
B. Scapegoat
题意:每个人都对应一个麻烦,n个人可以对应同一个麻烦,找最小方差。
思路:一个贪心的思维,平均值一定,那么先把所有的麻烦分出去,这时候有一个方差,然后加人,每个麻烦下面都可以加,然后计算方差的变化,每次往下降最多的那个麻烦下加人。
平均数不会变,每个麻烦分的人加一个人后的方差改变为:
c n t ∗ ( n u m / c n t − a v g ) 2 − ( c n t + 1 ) ∗ ( n u m / ( c n t + 1 ) − a v g ) 2 cnt * (num / cnt - avg)^2 - (cnt + 1) * (num / (cnt + 1) - avg)^2 cnt∗(num/cnt−avg)2−(cnt+1)∗(num/(cnt+1)−avg)2
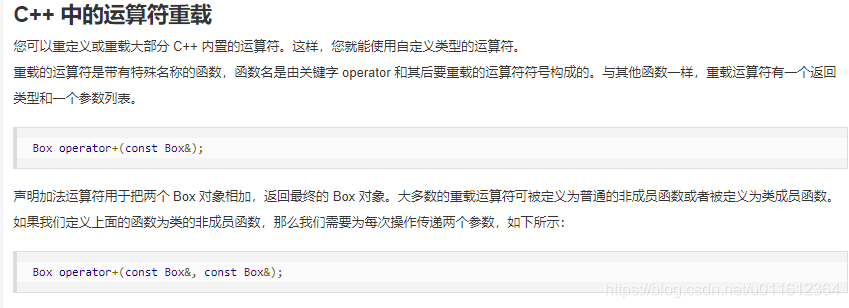
不会写重载比较操作符函数,见下图
代码
- #include<bits/stdc++.h>#include<iostream>#include <stdio.h> using namespace std; const int maxn=200005; const int base=131; typedef long long ll;#define pi acos(-1)#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f#define mod 998244353 const int inf=1<<30; double a[maxn]; double avg,sum;struct node {double num,cnt;double val;bool operator < (const node& b) const {return val < b.val;} };double cal(node x) {return x.cnt * (x.num / x.cnt - avg) * (x.num / x.cnt - avg) - (x.cnt + 1) * (x.num / (x.cnt + 1) - avg) * (x.num / (x.cnt + 1) -avg);//增加一个后方差的减小量 }int main() {int t,n,m;cin>>t;for (int c = 1; c <= t; c++){double ans = 0.0;sum = 0.0;cin>>n>>m;for(int i = 1 ;i <= n; i++){scanf("%lf",&a[i]);sum += a[i];}avg = sum / m;priority_queue<node> q;for(int i = 1 ;i <= n; i++){node now;now.num = a[i];now.cnt = 1;now.val = cal(now);q.push(now);} for(int i = 1 ;i <= m - n; i++){node now = q.top();q.pop();now.cnt++;now.val = cal(now);q.push(now);}while(!q.empty()){node now = q.top();q.pop();ans += now.cnt * (now.num / now.cnt - avg) * (now.num / now.cnt - avg);}//cout<<ans<<endl;printf("Case #%d: %.12lf\n",c,ans/m);}return 0; }以上是铜牌题
J. Straight Master
题意:给出一副扑克牌每张牌的张数,问能否以3张或5张顺子的形式将扑克牌打出去。
知识点:
思路:差分,然后看差分数组 b b b最后能否变为全为0的差分数组。
差分后对 [ l , r ] [l,r] [l,r]操作,就相当于减小差分数组中 b [ l ] b[l] b[l],增加 b [ r + 1 ] b[r+1] b[r+1]。
从差分组数组第一项开始,对于大于0的项 i i i,找到最接近的小于0的项 j j j,如果 i i i和 j j j距离大于3就对这个范围操作,把此时的 b [ i ] b[i] b[i]变成 m i n ( 0 , b [ i ] + b [ j ] ) min(0,b[i] + b[j]) min(0,b[i]+b[j]),之所以这里不管距离大于5的限制,是因为完全可以通过多次连续合法的操作,完成距离大于5的操作。
可以预处理每一次的差分组数组值小于0的项的位置,节约时间。
最后如果全都变为0,就是yes,反之为no
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=200005;
const int base=131;
typedef long long ll;
#define pi acos(-1)
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define mod 998244353
const int inf=1<<30;
int a[maxn];
int b[maxn];
vector<int> pos;
int main()
{//freopen("data.in","r",stdin);//freopen("1.out","w",stdout);int t,n,m;cin>>t;for(int c = 1 ; c <= t;c++ ){pos.clear();cin>>n;for(int i = 1 ; i <= n;i++){scanf("%d",&a[i]);b[i] = a[i] - a[i-1];if(b[i] < 0)pos.push_back(i);}b[n+1] = 0 - a[n];if(b[n+1] < 0)pos.push_back(n+1);int j = 0;int f = 1;for(int i = 1;i <= n+1;){if(b[i] > 0){if((pos[j] - i) >= 3 ){if(b[i] + b[pos[j]] > 0){b[i] = b[i] + b[pos[j]];b[pos[j]] = 0;j++;continue;}else{b[pos[j]] = b[i] + b[pos[j]];b[i] = 0;if(b[pos[j]] == 0)j++;}}else{f = 0;break;}}if(j >= pos.size() && b[i] != 0){f = 0;break;}i++;}if(f)printf("Case #%d: Yes\n",c);elseprintf("Case #%d: No\n",c);}return 0;
}
这篇关于2017ACM EC Final 补题题解的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!







