本文主要是介绍R可视化:ggpubr包学习,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
欢迎大家关注全网生信学习者系列:
-
WX公zhong号:生信学习者
-
Xiao hong书:生信学习者
-
知hu:生信学习者
-
CDSN:生信学习者2
介绍
ggpubr是我经常会用到的R包,它傻瓜式的画图方式对很多初次接触R绘图的人来讲是很友好的。该包有个stat_compare_means函数可以做组间假设检验分析。
安装R包
install.packages("ggpubr")
devtools::devtools::install_github("kassambara/ggpubr")
library(ggpubr)
plotdata <- data.frame(sex = factor(rep(c("F", "M"), each=200)),weight = c(rnorm(200, 55), rnorm(200, 58)))
密度图density
ggdensity(plotdata, x = "weight",add = "mean", rug = TRUE, # x轴显示分布密度color = "sex", fill = "sex",palette = c("#00AFBB", "#E7B800"))

柱状图histogram
gghistogram(plotdata, x = "weight",bins = 30,add = "mean", rug = TRUE,color = "sex", fill = "sex",palette = c("#00AFBB", "#E7B800"))

箱线图boxplot
df <- ToothGrowth
head(df)
my_comparisons <- list( c("0.5", "1"), c("1", "2"), c("0.5", "2") )
ggboxplot(df, x = "dose", y = "len",color = "dose", palette =c("#00AFBB", "#E7B800", "#FC4E07"),add = "jitter", shape = "dose")+stat_compare_means(comparisons = my_comparisons)+ # Add pairwise comparisons p-valuestat_compare_means(label.y = 50)

小提琴图violin
ggviolin(df, x = "dose", y = "len", fill = "dose",palette = c("#00AFBB", "#E7B800", "#FC4E07"),add = "boxplot", add.params = list(fill = "white"))+stat_compare_means(comparisons = my_comparisons, label = "p.signif")+ # Add significance levelsstat_compare_means(label.y = 50)

点图dotplot
ggdotplot(ToothGrowth, x = "dose", y = "len",color = "dose", palette = "jco", binwidth = 1)

有序条形图 ordered bar plots
data("mtcars")
dfm <- mtcars
dfm$cyl <- as.factor(dfm$cyl)
dfm$name <- rownames(dfm)
head(dfm[, c("name", "wt", "mpg", "cyl")])
ggbarplot(dfm, x = "name", y = "mpg",fill = "cyl", # change fill color by cylcolor = "white", # Set bar border colors to whitepalette = "jco", # jco journal color palett. see ?ggparsort.val = "asc", # Sort the value in dscending ordersort.by.groups = TRUE, # Sort inside each groupx.text.angle = 90) # Rotate vertically x axis texts

偏差图Deviation graphs
dfm$mpg_z <- (dfm$mpg -mean(dfm$mpg))/sd(dfm$mpg)
dfm$mpg_grp <- factor(ifelse(dfm$mpg_z < 0, "low", "high"), levels = c("low", "high"))
# Inspect the data
head(dfm[, c("name", "wt", "mpg", "mpg_z", "mpg_grp", "cyl")])
ggbarplot(dfm, x = "name", y = "mpg_z",fill = "mpg_grp", # change fill color by mpg_levelcolor = "white", # Set bar border colors to whitepalette = "jco", # jco journal color palett. see ?ggparsort.val = "asc", # Sort the value in ascending ordersort.by.groups = FALSE, # Don't sort inside each groupx.text.angle = 90, # Rotate vertically x axis textsylab = "MPG z-score",rotate = FALSE,xlab = FALSE,legend.title = "MPG Group")

棒棒糖图 lollipop chart
ggdotchart(dfm, x = "name", y = "mpg",color = "cyl", # Color by groupspalette = c("#00AFBB", "#E7B800", "#FC4E07"), # Custom color palettesorting = "descending", # Sort value in descending orderadd = "segments", # Add segments from y = 0 to dotsrotate = TRUE, # Rotate verticallygroup = "cyl", # Order by groupsdot.size = 6, # Large dot sizelabel = round(dfm$mpg), # Add mpg values as dot labelsfont.label = list(color = "white", size = 9, vjust = 0.5), # Adjust label parametersggtheme = theme_pubr()) # ggplot2 theme

偏差图Deviation graph
ggdotchart(dfm, x = "name", y = "mpg_z",color = "cyl", # Color by groupspalette = c("#00AFBB", "#E7B800", "#FC4E07"), # Custom color palettesorting = "descending", # Sort value in descending orderadd = "segments", # Add segments from y = 0 to dotsadd.params = list(color = "lightgray", size = 2), # Change segment color and sizegroup = "cyl", # Order by groupsdot.size = 6, # Large dot sizelabel = round(dfm$mpg_z,1), # Add mpg values as dot labelsfont.label = list(color = "white", size = 9, vjust = 0.5), # Adjust label parametersggtheme = theme_pubr())+ # ggplot2 themegeom_hline(yintercept = 0, linetype = 2, color = "lightgray")

散点图scatterplot
df <- datasets::iris head(df) ggscatter(df, x = 'Sepal.Width', y = 'Sepal.Length', palette = 'jco', shape = 'Species', add = 'reg.line',color = 'Species', conf.int = TRUE)

-
添加回归线的系数
ggscatter(df, x = 'Sepal.Width', y = 'Sepal.Length', palette = 'jco', shape = 'Species', add = 'reg.line',color = 'Species', conf.int = TRUE)+stat_cor(aes(color=Species),method = "pearson", label.x = 3)

-
添加聚类椭圆 concentration ellipses
data("mtcars")
dfm <- mtcars
dfm$cyl <- as.factor(dfm$cyl)
dfm$name <- rownames(dfm)
p1 <- ggscatter(dfm, x = "wt", y = "mpg",color = "cyl", palette = "jco",shape = "cyl",ellipse = TRUE)
p2 <- ggscatter(dfm, x = "wt", y = "mpg",color = "cyl", palette = "jco",shape = "cyl",ellipse = TRUE,ellipse.type = "convex")
cowplot::plot_grid(p1, p2, align = "hv", nrow = 1)

-
添加mean和stars
ggscatter(dfm, x = "wt", y = "mpg",color = "cyl", palette = "jco",shape = "cyl",ellipse = TRUE, mean.point = TRUE,star.plot = TRUE)

-
显示点标签
dfm$name <- rownames(dfm)
p3 <- ggscatter(dfm, x = "wt", y = "mpg",color = "cyl", palette = "jco",label = "name",repel = TRUE)
p4 <- ggscatter(dfm, x = "wt", y = "mpg",color = "cyl", palette = "jco",label = "name",repel = TRUE,label.select = c("Toyota Corolla", "Merc 280", "Duster 360"))
cowplot::plot_grid(p3, p4, align = "hv", nrow = 1)

气泡图bubble plot
ggscatter(dfm, x = "wt", y = "mpg",color = "cyl",palette = "jco",size = "qsec", alpha = 0.5)+scale_size(range = c(0.5, 15)) # Adjust the range of points size

连线图 lineplot
p1 <- ggbarplot(ToothGrowth, x = "dose", y = "len", add = "mean_se",color = "supp", palette = "jco", position = position_dodge(0.8))+stat_compare_means(aes(group = supp), label = "p.signif", label.y = 29) p2 <- ggline(ToothGrowth, x = "dose", y = "len", add = "mean_se",color = "supp", palette = "jco")+stat_compare_means(aes(group = supp), label = "p.signif", label.y = c(16, 25, 29)) cowplot::plot_grid(p1, p2, ncol = 2, align = "hv")

添加边沿图 marginal plots
library(ggExtra) p <- ggscatter(iris, x = "Sepal.Length", y = "Sepal.Width",color = "Species", palette = "jco",size = 3, alpha = 0.6) ggMarginal(p, type = "boxplot")

-
第二种添加方式: 分别画出三个图,然后进行组合
sp <- ggscatter(iris, x = "Sepal.Length", y = "Sepal.Width",color = "Species", palette = "jco",size = 3, alpha = 0.6, ggtheme = theme_bw())
xplot <- ggboxplot(iris, x = "Species", y = "Sepal.Length", color = "Species", fill = "Species", palette = "jco",alpha = 0.5, ggtheme = theme_bw())+ rotate()
yplot <- ggboxplot(iris, x = "Species", y = "Sepal.Width",color = "Species", fill = "Species", palette = "jco",alpha = 0.5, ggtheme = theme_bw())
sp <- sp + rremove("legend")
yplot <- yplot + clean_theme() + rremove("legend")
xplot <- xplot + clean_theme() + rremove("legend")
cowplot::plot_grid(xplot, NULL, sp, yplot, ncol = 2, align = "hv", rel_widths = c(2, 1), rel_heights = c(1, 2))

-
上图主图和边沿图之间的space太大,第三种方法能克服这个缺点
library(cowplot)
# Main plot
pmain <- ggplot(iris, aes(x = Sepal.Length, y = Sepal.Width, color = Species))+geom_point()+ggpubr::color_palette("jco")
# Marginal densities along x axis
xdens <- axis_canvas(pmain, axis = "x")+geom_density(data = iris, aes(x = Sepal.Length, fill = Species),alpha = 0.7, size = 0.2)+ggpubr::fill_palette("jco")
# Marginal densities along y axis
# Need to set coord_flip = TRUE, if you plan to use coord_flip()
ydens <- axis_canvas(pmain, axis = "y", coord_flip = TRUE)+geom_boxplot(data = iris, aes(x = Sepal.Width, fill = Species),alpha = 0.7, size = 0.2)+coord_flip()+ggpubr::fill_palette("jco")
p1 <- insert_xaxis_grob(pmain, xdens, grid::unit(.2, "null"), position = "top")
p2 <- insert_yaxis_grob(p1, ydens, grid::unit(.2, "null"), position = "right")
ggdraw(p2)

-
第四种方法,通过grob设置
# Scatter plot colored by groups ("Species")
#::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::
sp <- ggscatter(iris, x = "Sepal.Length", y = "Sepal.Width",color = "Species", palette = "jco",size = 3, alpha = 0.6)
# Create box plots of x/y variables
#::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::
# Box plot of the x variable
xbp <- ggboxplot(iris$Sepal.Length, width = 0.3, fill = "lightgray") +rotate() +theme_transparent()
# Box plot of the y variable
ybp <- ggboxplot(iris$Sepal.Width, width = 0.3, fill = "lightgray") +theme_transparent()
# Create the external graphical objects
# called a "grop" in Grid terminology
xbp_grob <- ggplotGrob(xbp)
ybp_grob <- ggplotGrob(ybp)
# Place box plots inside the scatter plot
#::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::
xmin <- min(iris$Sepal.Length); xmax <- max(iris$Sepal.Length)
ymin <- min(iris$Sepal.Width); ymax <- max(iris$Sepal.Width)
yoffset <- (1/15)*ymax; xoffset <- (1/15)*xmax
# Insert xbp_grob inside the scatter plot
sp + annotation_custom(grob = xbp_grob, xmin = xmin, xmax = xmax, ymin = ymin-yoffset, ymax = ymin+yoffset) +# Insert ybp_grob inside the scatter plotannotation_custom(grob = ybp_grob,xmin = xmin-xoffset, xmax = xmin+xoffset, ymin = ymin, ymax = ymax)

二维密度图 2d density
sp <- ggscatter(iris, x = "Sepal.Length", y = "Sepal.Width",color = "lightgray")
p1 <- sp + geom_density_2d()
# Gradient color
p2 <- sp + stat_density_2d(aes(fill = ..level..), geom = "polygon")
# Change gradient color: custom
p3 <- sp + stat_density_2d(aes(fill = ..level..), geom = "polygon")+gradient_fill(c("white", "steelblue"))
# Change the gradient color: RColorBrewer palette
p4 <- sp + stat_density_2d(aes(fill = ..level..), geom = "polygon") +gradient_fill("YlOrRd")
cowplot::plot_grid(p1, p2, p3, p4, ncol = 2, align = "hv")

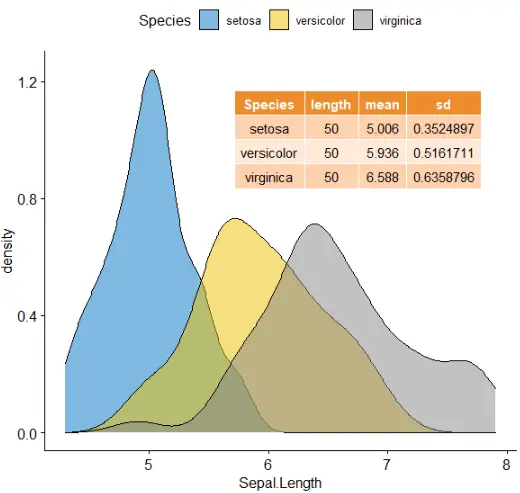
混合图
混合表、字体和图
# Density plot of "Sepal.Length"
#::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::
density.p <- ggdensity(iris, x = "Sepal.Length", fill = "Species", palette = "jco")
# Draw the summary table of Sepal.Length
#::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::
# Compute descriptive statistics by groups
stable <- desc_statby(iris, measure.var = "Sepal.Length",grps = "Species")
stable <- stable[, c("Species", "length", "mean", "sd")]
# Summary table plot, medium orange theme
stable.p <- ggtexttable(stable, rows = NULL, theme = ttheme("mOrange"))
# Draw text
#::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::::
text <- paste("iris data set gives the measurements in cm","of the variables sepal length and width","and petal length and width, respectively,","for 50 flowers from each of 3 species of iris.","The species are Iris setosa, versicolor, and virginica.", sep = " ")
text.p <- ggparagraph(text = text, face = "italic", size = 11, color = "black")
# Arrange the plots on the same page
ggarrange(density.p, stable.p, text.p, ncol = 1, nrow = 3,heights = c(1, 0.5, 0.3))

-
注释table在图上
density.p <- ggdensity(iris, x = "Sepal.Length", fill = "Species", palette = "jco")
stable <- desc_statby(iris, measure.var = "Sepal.Length",grps = "Species")
stable <- stable[, c("Species", "length", "mean", "sd")]
stable.p <- ggtexttable(stable, rows = NULL, theme = ttheme("mOrange"))
density.p + annotation_custom(ggplotGrob(stable.p),xmin = 5.5, ymin = 0.7,xmax = 8)
systemic information
sessionInfo()
R version 3.6.1 (2019-07-05) Platform: x86_64-w64-mingw32/x64 (64-bit) Running under: Windows 10 x64 (build 19042) Matrix products: default locale: [1] LC_COLLATE=Chinese (Simplified)_China.936 LC_CTYPE=Chinese (Simplified)_China.936 [3] LC_MONETARY=Chinese (Simplified)_China.936 LC_NUMERIC=C [5] LC_TIME=Chinese (Simplified)_China.936 attached base packages: [1] stats graphics grDevices utils datasets methods base other attached packages: [1] ggpubr_0.4.0 ggplot2_3.3.2 loaded via a namespace (and not attached):[1] zip_2.0.4 Rcpp_1.0.3 cellranger_1.1.0 pillar_1.4.6 compiler_3.6.1 forcats_0.5.0 [7] tools_3.6.1 digest_0.6.27 lifecycle_0.2.0 tibble_3.0.4 gtable_0.3.0 pkgconfig_2.0.3 [13] rlang_0.4.8 openxlsx_4.2.3 ggsci_2.9 rstudioapi_0.10 curl_4.3 haven_2.3.1 [19] rio_0.5.16 withr_2.1.2 dplyr_1.0.2 generics_0.0.2 vctrs_0.3.4 hms_0.5.3 [25] grid_3.6.1 tidyselect_1.1.0 glue_1.4.2 data.table_1.13.2 R6_2.4.1 rstatix_0.6.0 [31] readxl_1.3.1 foreign_0.8-73 carData_3.0-4 farver_2.0.3 tidyr_1.0.0 purrr_0.3.3 [37] car_3.0-10 magrittr_1.5 scales_1.1.0 backports_1.1.10 ellipsis_0.3.1 abind_1.4-5 [43] colorspace_1.4-1 ggsignif_0.6.0 labeling_0.4.2 stringi_1.4.3 munsell_0.5.0 broom_0.7.2 [49] crayon_1.3.4
这篇关于R可视化:ggpubr包学习的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





