本文主要是介绍西南交通大学【操作系统实验2】,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
实验目的
- 本实验要求学生了解什么是信号,掌握软中断的基本原理;掌握中断信号的使用、进程的创建以及系统计时器的使用。
- 通过对本实验的学习,学生能够学会进程的创建方法,更能加深对Linux中的信号机制的认识,并会使用软中断信号来实现进程间的通信。
实验内容
学生根据test2.c理解以下内容:
- 1.父进程接受到软中断信号(SIGQUIT)后,向其子进程分别发送整数值为 16的软中断信号,子进程获得对应软中断信号后,终止运行。
- 2.父进程调用wait()函数等待子进程终止,然后自我终止。
- 3.由父进程创建一个子进程,通过终端输入Crtl+\组合键向父进程发
- 送SIGQUIT软中断信号发送给父进程。
编程实现以下内容:
- 1.由一个父进程创建两个子进程,之后通过终端输入Crtl+\组合键向父进
- 程发送软中断信号,终止两个子进程以及父进程。
- 2.由一个父进程创建一个子进程,之后该子进程再创建一个孙进程,通过终端输入Crtl+\组合键向父进程发送软中断信号,依次终止孙进程、子进程、父进程。
实验环境
Ubuntu 12.04 LTS
Device name: oslinux-virtual-machine
Memory: 1001.2MiB
Processor: 13th Gen Intel Core i5-13500HX
Graphics: Unknown
OS type: 32-bit
Disk: 20.3GB
实验步骤
实验 1:编译并运行程序test2.c,当按下Crtl+\组合键时,打印出子进程结束的信息,最后打印出父进程结束的信息。
- 1.创建一个子进程;
- 2.子进程分别等待信号16,如果收到信号则显示结束信息,并发出结束信号;
- 3.父进程等待SIGQUIT信号,如果收到信号则向子进程发送信号16,接着 等子进程结束,如果都结束了则显示结束信息,并退出进程。
实验2:编写两种三个进程通信情况。
- 1.由一个父进程创建两个子进程,之后通过终端输入Crtl+\组合键向父进 程发送软中断信号,终止两 个子进程以及父进程。
- 2.由一个父进程创建一个子进程,之后该子进程再创建一个孙进程,通过 终端输入Crtl+\组合键向父进程发送软中断信号,依次终止孙进程、子 进程、父进程。
- 3.实验报告附程序源码及对重要代码语句的解释和程序运行结果。
实验结果
结果展示
test2运行结果

进程14571由父进程14570创建,输入Crtl+\后,子进程14571被父进程终止,随后父进程终止。
实验2第一种情况运行结果

子进程14763和14764由父进程14762创建,输入Crtl+\后,子进程分别被父进程终止,随后父进程终止。
实验2第二种情况运行结果
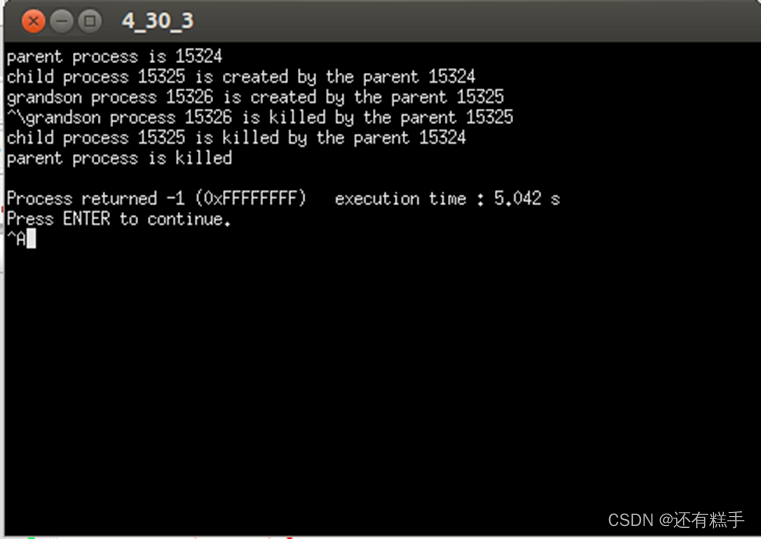
子进程15325由父进程创建,孙进程15326由子进程15325创建,输入Crtl+\后,孙进程被子进程终止,子进程被父进程终止,随后父进程终止。
核心代码
实验2第一种情况源码
#include<cstdio>#include<cstdlib>#include<csignal>#include<unistd.h>#include <sys/wait.h>#include "iostream"using namespace std;void waiting();void stop();int wait_mark;int main(){pid_t p1, p2;p1 = fork();if (p1 != 0) { // if p1 is parent processlockf(1, 1, 0);cout << "Parent Process " << getpid() << endl;lockf(1, 0, 0);wait_mark = 1;::signal(SIGQUIT, reinterpret_cast<__sighandler_t>(stop));p2 = fork();if (p2 == 0) { // if p2 is child processlockf(1, 1, 0);cout << "Child Process " << getpid() << " created by " << getppid() << endl;lockf(1, 0, 0);::signal(SIGQUIT, SIG_IGN);wait_mark = 1;::signal(16, reinterpret_cast<__sighandler_t>(stop));waiting();lockf(1, 1 , 0);cout << "Child Process " << getpid() << " is killed by parent " << getppid() << endl;lockf(1, 0, 0);::exit(0);}waiting();kill(p1, 16); // send signal 16 to end the process p1wait(NULL);kill(p2, 16); // send signal 16 to end the process p2wait(NULL);lockf(1, 1, 0);cout << "parent process if killed" << endl;lockf(1, 0, 0);::exit(0);} else if (p1 == 0) { // if p1 is child processlockf(1, 1, 0);cout << "Child Process " << getpid() << " created by " << getppid() << endl;lockf(1, 0, 0);::signal(SIGQUIT, SIG_IGN);wait_mark = 1;::signal(16, reinterpret_cast<__sighandler_t>(stop));waiting();lockf(1, 1 , 0);cout << "Child Process " << getpid() << " is killed by parent " << getppid() << endl;lockf(1, 0, 0);::exit(0);}return 0;}void waiting( ){while (wait_mark != 0);}void stop(){wait_mark=0;}实验2第二种情况源码
#include<stdio.h>#include<stdlib.h>#include<signal.h>#include<unistd.h>#include <sys/wait.h>void waiting();void stop();int wait_mark;int main() {int p1, p2;while ((p1 = fork()) == -1);if (p1 > 0) //if p1 is parent process{lockf(1, 1, 0);printf("parent process is %d \n", getpid());lockf(1, 0, 0);wait_mark = 1;signal(SIGQUIT, stop);waiting();kill(p1, 16); //send signal 16 to end the process p1wait(0); //waiting for the ending of p1lockf(1, 1, 0);printf("parent process is killed!\n");lockf(1, 0, 0);exit(0); //quit from the parent process} else //if p1 is child process{while ((p2 = fork()) == -1);if (p2 > 0) //if p2 is parent process{lockf(1, 1, 0);printf("child process %d is created by the parent %d \n", getpid(), getppid());lockf(1, 0, 0);signal(SIGQUIT, SIG_IGN);wait_mark = 1;signal(16, stop);waiting();kill(p2, 16); //send signal 16 to end the process p2wait(0); //waiting for the ending of p2lockf(1, 1, 0);printf("child process %d is killed by parent %d \n", getpid(), getppid());lockf(1, 0, 0);exit(0); // p1 quit} else //if p2 is child process{lockf(1, 1, 0);printf("grandson process %d is created by the parent %d \n", getpid(), getppid());lockf(1, 0, 0);signal(SIGQUIT, SIG_IGN);wait_mark = 1;signal(16, stop);waiting();lockf(1, 1, 0);printf("grandson process %d is killed by parent %d \n", getpid(), getppid());lockf(1, 0, 0);exit(0); // p2 quit}}return 0;}void waiting() {while (wait_mark != 0);}void stop() {wait_mark = 0;}这篇关于西南交通大学【操作系统实验2】的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!









