本文主要是介绍Python进阶-部署Flask项目(以TensorFlow图像识别项目WSGI方式启动为例),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
本文详细介绍了如何通过WSGI方式部署一个基于TensorFlow图像识别的Flask项目。首先简要介绍了Flask框架的基本概念及其特点,其次详细阐述了Flask项目的部署流程,涵盖了服务器环境配置、Flask应用的创建与测试、WSGI服务器的安装与配置等内容。本文旨在帮助读者掌握Flask项目的部署方法,解决在部署过程中可能遇到的问题,确保项目能够稳定高效地运行。
一、Flask简介
Flask是一个轻量级的Web应用框架,由Python语言编写。它是基于Werkzeug WSGI工具包和Jinja2模板引擎的,并且采用BSD许可证。Flask的设计哲学是“微核”,也就是说其核心保持简洁,功能通过扩展实现。这使得Flask非常灵活,能够满足从小型单一页面应用到大型复杂项目的不同需求。
Flask的主要特点包括:
- 轻量级和灵活:Flask仅提供核心功能,开发者可以根据需要引入各种扩展。
- 易于学习和使用:Flask的API设计非常简洁明了,即使是初学者也能快速上手。
- 强大的扩展能力:Flask的生态系统中有许多可用的扩展,可以轻松添加数据库、表单验证、用户认证等功能。
- 社区支持:Flask拥有活跃的社区,大量的教程和文档可以帮助开发者解决问题。
二、Flask项目部署流程
1. 准备工作
在开始部署Flask项目之前,需要完成以下准备工作:
① 服务器安装Anaconda
Anaconda是一个用于科学计算的Python发行版,支持多种数据科学包的快速安装。它还包含了Conda,这是一种包管理器和环境管理器,能够轻松创建和管理不同的Python环境。
首先,下载并安装Anaconda。可以从Anaconda官网下载适用于Windows的安装包。安装过程非常简单,按照提示进行即可。
② Anaconda创建Python环境
安装完成后,使用Conda创建一个新的Python环境。这可以帮助你隔离项目的依赖,确保环境的一致性。打开终端(或命令提示符),输入以下命令创建一个名为opencv的环境,并指定Python版本:
conda create -n opencv python=3.8
创建完成后,激活这个环境:
conda activate opencv
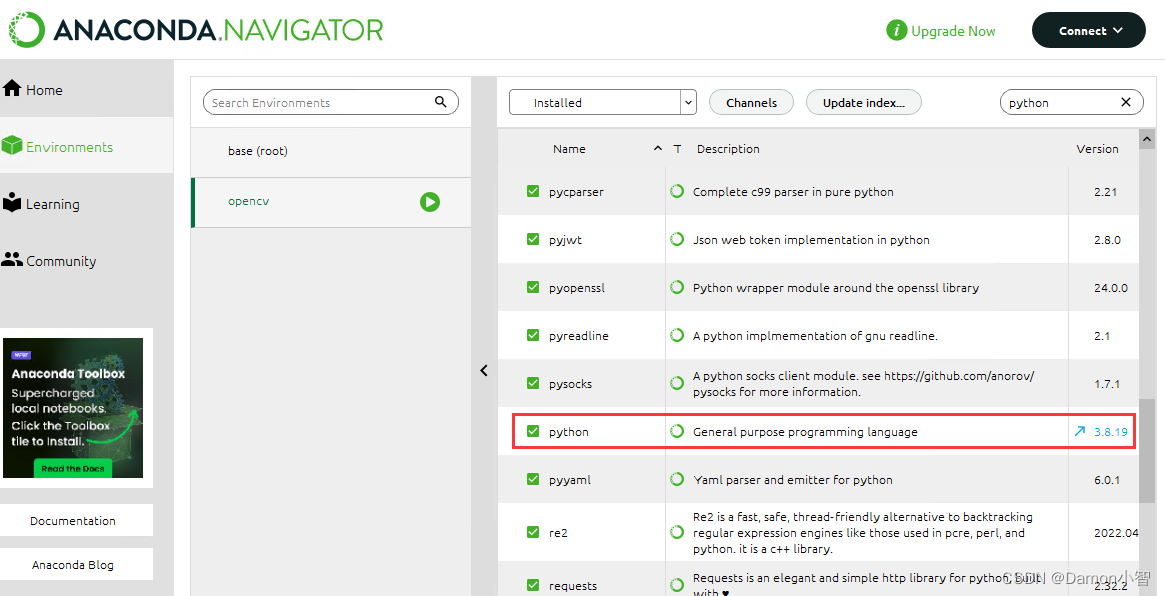
③ Anaconda环境安装相关包
在激活的环境中,安装Flask、Flask-CORS、TensorFlow、scikit-learn和OpenCV等必要的包:
conda install flask flask-cors tensorflow scikit-learn opencv
这些包包含了构建和运行Flask应用及其依赖的所有工具。
2. 创建Flask应用
在本地编写并测试Flask应用代码。以下是一个简单的Flask应用示例,它使用TensorFlow的MobileNetV2模型进行图像分类和相似度计算:
from flask import Flask, request, jsonify
from flask_cors import CORS
import numpy as np
import cv2
from tensorflow.keras.applications.mobilenet_v2 import MobileNetV2, preprocess_input, decode_predictions
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing import image
from sklearn.metrics.pairwise import cosine_similarityapp = Flask(__name__)
CORS(app)# 加载预训练的MobileNetV2模型
model = MobileNetV2(weights='imagenet', include_top=True)def classify_image(img):img = cv2.resize(img, (224, 224)) # MobileNetV2的输入尺寸为224x224x = image.img_to_array(img)x = np.expand_dims(x, axis=0)x = preprocess_input(x)preds = model.predict(x)return decode_predictions(preds, top=1)[0][0][1], model.predict(x) # 返回类别名称和特征向量def calculate_similarity(feature1, feature2):return cosine_similarity(feature1, feature2)[0][0]@app.route('/compare', methods=['POST'])
def compare_images():file1 = request.files['image1']file2 = request.files['image2']npimg1 = np.frombuffer(file1.read(), np.uint8)npimg2 = np.frombuffer(file2.read(), np.uint8)img1 = cv2.imdecode(npimg1, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)img2 = cv2.imdecode(npimg2, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)# 分类和特征提取class1, feature1 = classify_image(img1)class2, feature2 = classify_image(img2)if class1 != class2:similarity = 0.0risk_level = "低"intervention = "否"else:similarity = calculate_similarity(feature1, feature2)risk_level = "高" if similarity > 0.8 else "中" if similarity > 0.5 else "低"intervention = "是" if similarity > 0.8 else "否"return jsonify({'similarity': f'{similarity * 100:.2f}%','risk_level': risk_level,'intervention': intervention,'class1': class1,'class2': class2})if __name__ == '__main__':app.run(debug=True)
在确保代码在本地运行正常。
3、本地运行Flask服务器
在本地Anaconda中启动opencv环境的终端,运行以下命令启动Flask服务器:
python app.py
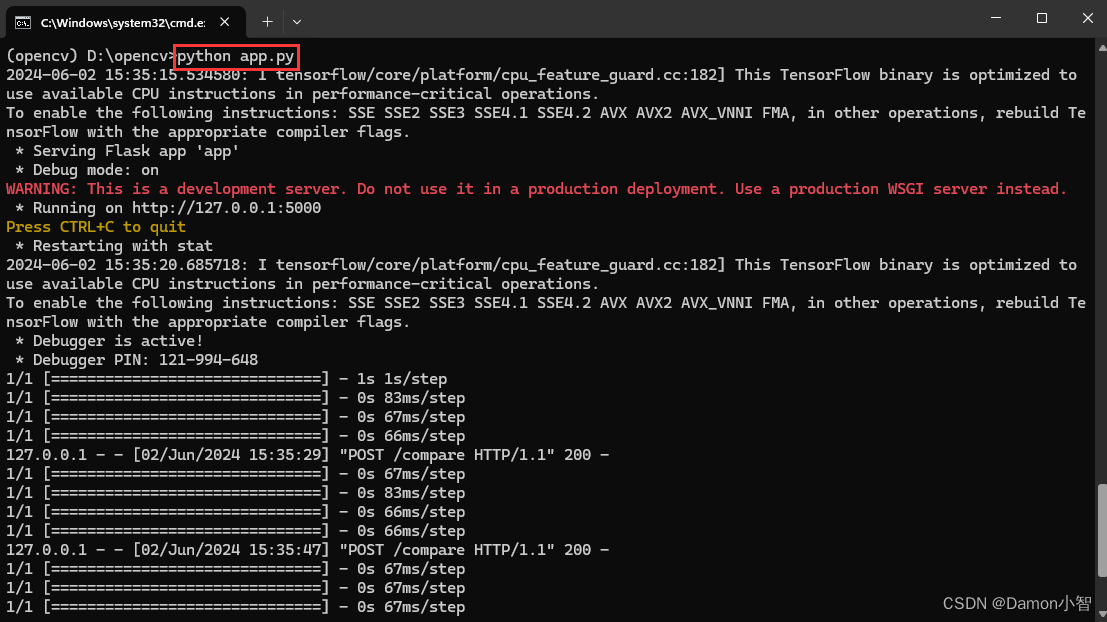
服务器启动后,将会监听在本地的5000端口。
① 页面前端代码实现
创建一个HTML文件(test.html),实现图片上传和结果展示功能,全部代码如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-CN">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><title>图片对比</title><style>body {font-family: Arial, sans-serif;display: flex;flex-direction: column;align-items: center;margin: 0;padding: 20px;}.container {display: flex;justify-content: space-between;width: 80%;margin-bottom: 20px;}.image-box {width: 45%;border: 2px dashed #ccc;padding: 10px;text-align: center;position: relative;}.image-box img {max-width: 100%;max-height: 200px;display: none;}.image-box input {display: none;}.upload-btn {cursor: pointer;color: #007BFF;text-decoration: underline;}.loading-bar {width: 80%;height: 20px;background-color: #f3f3f3;border: 1px solid #ccc;margin-top: 10px;display: none;position: relative;}.loading-bar div {width: 0;height: 100%;background-color: #4caf50;position: absolute;animation: loading 5s linear forwards;}@keyframes loading {to {width: 100%;}}.result {display: none;margin-top: 20px;}</style>
</head>
<body><h1>图片对比</h1><div class="container"><div class="image-box" id="box1"><label for="upload1" class="upload-btn">上传图片</label><input type="file" id="upload1" accept="image/*"><img id="image1" alt="左边文本抓取图片"></div><div class="image-box" id="box2"><label for="upload2" class="upload-btn">上传图片</label><input type="file" id="upload2" accept="image/*"><img id="image2" alt="右边文本数据库图片"></div></div><button id="compare-btn">人工智能对比</button><div class="loading-bar" id="loading-bar"><div></div></div><div class="result" id="result"><p>相似百分比: <span id="similarity">0%</span></p><p>相似度: <span id="risk-level">低</span></p><p>相同个体推测: <span id="intervention">否</span></p><p>图1种类: <span id="class1">-</span></p><p>图2种类: <span id="class2">-</span></p></div><script>document.getElementById('upload1').addEventListener('change', function(event) {loadImage(event.target.files[0], 'image1', 'box1');});document.getElementById('upload2').addEventListener('change', function(event) {loadImage(event.target.files[0], 'image2', 'box2');});function loadImage(file, imgId, boxId) {const reader = new FileReader();reader.onload = function(e) {const img = document.getElementById(imgId);img.src = e.target.result;img.style.display = 'block';document.querySelector(`#${boxId} .upload-btn`).style.display = 'none';}reader.readAsDataURL(file);}document.getElementById('compare-btn').addEventListener('click', function() {const loadingBar = document.getElementById('loading-bar');const result = document.getElementById('result');const image1 = document.getElementById('upload1').files[0];const image2 = document.getElementById('upload2').files[0];if (!image1 || !image2) {alert('请上传两张图片进行对比');return;}const formData = new FormData();formData.append('image1', image1);formData.append('image2', image2);loadingBar.style.display = 'block';result.style.display = 'none';fetch('http://localhost:5000/compare', {method: 'POST',body: formData}).then(response => response.json()).then(data => {loadingBar.style.display = 'none';result.style.display = 'block';document.getElementById('similarity').innerText = data.similarity;document.getElementById('risk-level').innerText = data.risk_level;document.getElementById('intervention').innerText = data.intervention;document.getElementById('class1').innerText = data.class1;document.getElementById('class2').innerText = data.class2;}).catch(error => {loadingBar.style.display = 'none';alert('对比过程中发生错误,请重试');console.error('Error:', error);});});</script>
</body>
</html>
② 运行网页
双击运行,刚刚创建的test.html文件,效果如图:
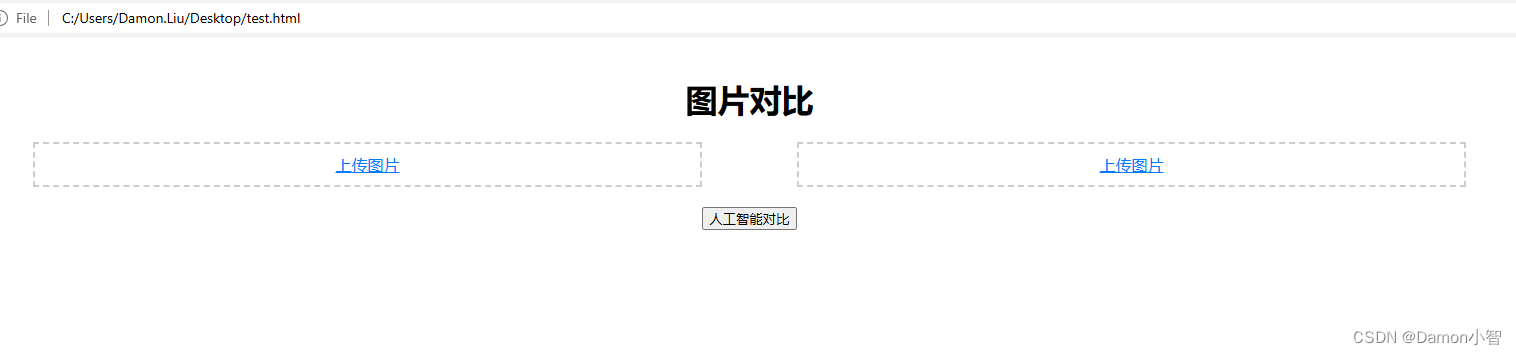
上传左右图片,比较两只相同品种的狗的相似度:

可以看到系统识别出了两只狗的种类相同,相似比也高达75.2%,但因为没有达到我们设置的80%的阈值,所以判断非同一个体。当然,这里的80%非常牵强,实际操作中难免误差较大。由于本文算法使用的是MobileNetV2预训练模型,并没有根据实际应用场景大量训练和调参,所以如果投入应用,仍需重新训练并根据实际效果定义阈值。
确认本地运行正常,接下来就可以进行部署了。
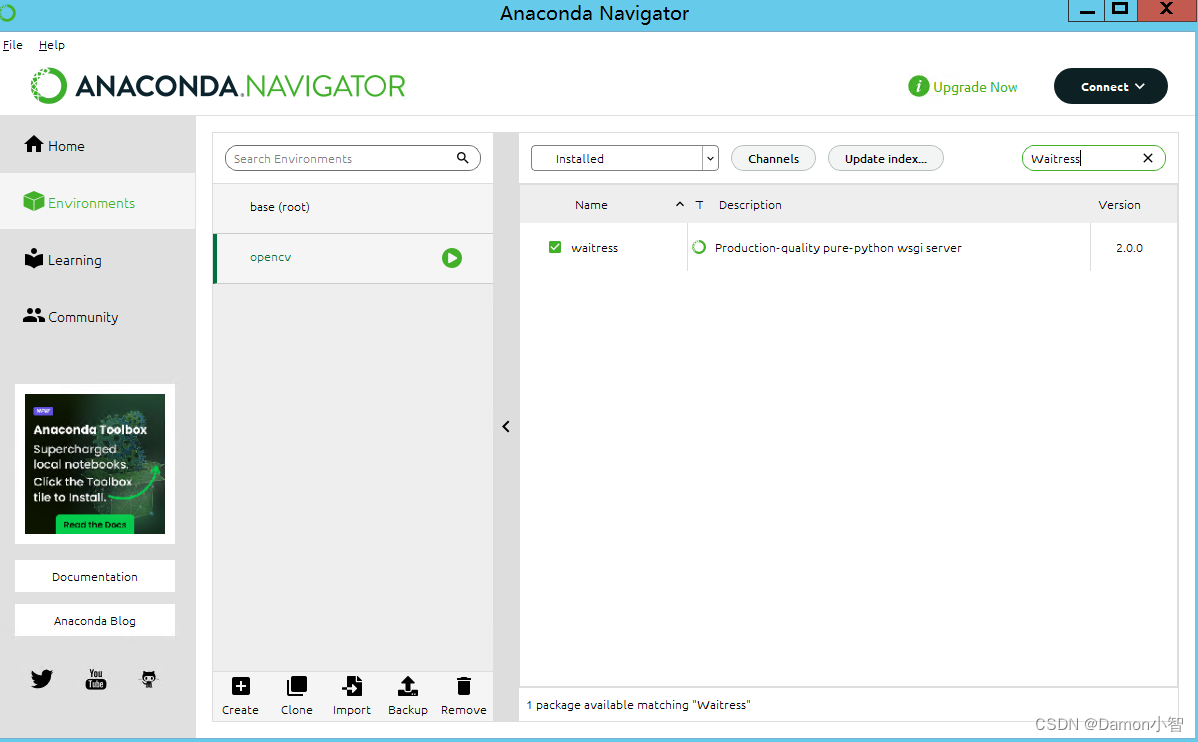
4. 安装Waitress服务器
Waitress是一个Python WSGI服务器,适用于在生产环境中部署Flask应用。它简单易用,适合部署中小型应用。使用pip安装Waitress:
pip install waitress
5. 修改代码以使用Waitress
将Flask应用代码保存为 compare.py,并确保在本地测试通过。然后创建一个批处理文件 start.cmd,内容如下:
@echo off
python -m waitress --listen=*:8000 compare:app
pause
确保 compare.py 文件中的Flask应用对象名为 app,例如:
from flask import Flask, request, jsonify
from flask_cors import CORS
import numpy as np
import cv2
from tensorflow.keras.applications.mobilenet_v2 import MobileNetV2, preprocess_input, decode_predictions
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing import image
from sklearn.metrics.pairwise import cosine_similarityapp = Flask(__name__)
CORS(app)# 加载预训练的MobileNetV2模型
model = MobileNetV2(weights='imagenet', include_top=True)def classify_image(img):img = cv2.resize(img, (224, 224)) # MobileNetV2的输入尺寸为224x224x = image.img_to_array(img)x = np.expand_dims(x, axis=0)x = preprocess_input(x)preds = model.predict(x)return decode_predictions(preds, top=1)[0][0][1], model.predict(x) # 返回类别名称和特征向量def calculate_similarity(feature1, feature2):return cosine_similarity(feature1, feature2)[0][0]@app.route('/compare', methods=['POST'])
def compare_images():file1 = request.files['image1']file2 = request.files['image2']npimg1 = np.frombuffer(file1.read(), np.uint8)npimg2 = np.frombuffer(file2.read(), np.uint8)img1 = cv2.imdecode(npimg1, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)img2 = cv2.imdecode(npimg2, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)# 分类和特征提取class1, feature1 = classify_image(img1)class2, feature2 = classify_image(img2)if class1 != class2:similarity = 0.0risk_level = "低"intervention = "否"else:similarity = calculate_similarity(feature1, feature2)risk_level = "高" if similarity > 0.8 else "中" if similarity > 0.5 else "低"intervention = "是" if similarity > 0.8 else "否"return jsonify({'similarity': f'{similarity * 100:.2f}%','risk_level': risk_level,'intervention': intervention,'class1': class1,'class2': class2})6. 运行启动
配置WSGI启动:
python -m waitress --listen=*:5000 compare:app
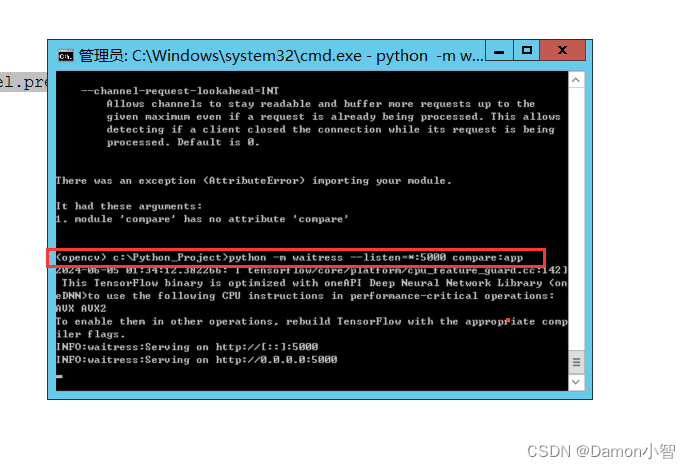
你可以通过访问 http://localhost:5000 来测试你的应用。
然后给5000端口配置安全组/防火墙,实现通过公网访问。
三、Flask项目部署总结
本文详细介绍了如何通过WSGI方式部署一个基于TensorFlow图像识别的Flask项目。从安装和配置Anaconda环境,到编写和测试Flask应用,再到安装和配置WSGI服务器,我们覆盖了部署过程中的每一个步骤。这些步骤帮助确保你的Flask应用能够稳定高效地运行,并且在生产环境中易于维护和扩展。
通过遵循这些步骤,你可以确保你的Flask应用在各种环境中都能够正常运行,避免了在部署过程中可能遇到的许多常见问题。同时,这种方式也为你提供了一种标准化的部署流程,使得以后部署新的Flask项目变得更加简单和高效。希望本文对你的Flask开发和部署之旅有所帮助。
这篇关于Python进阶-部署Flask项目(以TensorFlow图像识别项目WSGI方式启动为例)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




