本文主要是介绍GreenDao 3.0 简介、使用及踩坑,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
一、GreenDao 简介
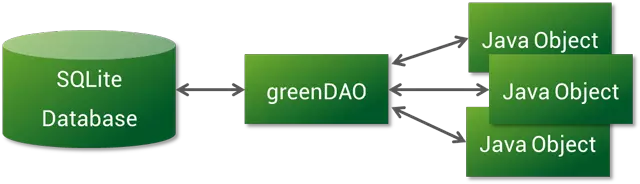
GreenDAO 是一款开源的面向 Android 的轻便、快捷的 ORM 框架,将 Java 对象映射到 SQLite 数据库中,我们操作数据库的时候,不再需要编写复杂的 SQL语句, 在性能方面,greenDAO 针对 Android 进行了高度优化,最小的内存开销 、依赖体积小 同时还是支持 数据库加密。
greenDAO 官网地址:greenrobot.org/greendao/
greenDAO GitHub 源码地址:greenrobot/greenDAO
二、GreenDao 特征
- 1、支持 protocol buffer(protobuf) 协议
GreenDao 支持 protocol buffer(protobuf) 协议数据的直接存储,如果你通过 protobuf 协议与服务器交互,将不需要任何的映射 - 2、代码生成
greenDAO 会根据配置信息自动生成核心管理类以及 DAO 对象 - 3、性能
所有 ORM 数据库的,greenDAO 是最快的,greenDAO 不作性能方面任何妥协
三、核心类介绍
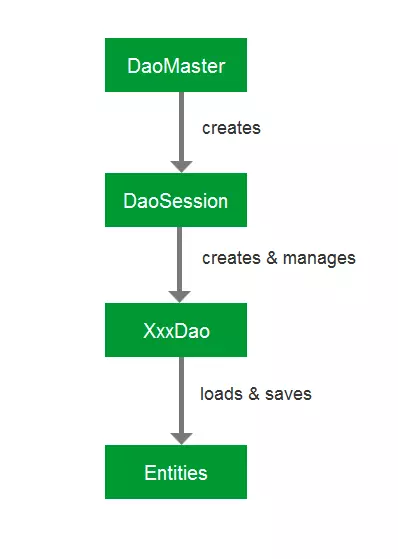
1、DaoMaster:
使用 greenDAO 的入口点。DaoMaster 负责管理数据库对象(SQLiteDatabase)和 DAO 类(对象),我们可以通过它内部类 OpenHelper 和 DevOpenHelper SQLiteOpenHelper 创建不同模式的 SQLite 数据库。
2、DaoSession :
管理指定模式下的所有 DAO 对象,DaoSession 提供了一些通用的持久性方法比如插入、负载、更新和删除实体。
3、XxxDAO :
对于每个实体类, greenDAO 都会生成一个与之对应 DAO 对象,如:User 实体,则会生成一个 UserDao 类
4、Entities:
可持久化对象。通常,实体对象代表一个数据库行,使用标准 Java 属性(如一个 POJO 或 JavaBean )
四、集成 GreenDao
a、设置仓库与插件(Project: build.gradle)
buildscript {repositories {jcenter()mavenCentral() // add repository}dependencies {classpath 'com.android.tools.build:gradle:3.1.3'classpath 'org.greenrobot:greendao-gradle-plugin:3.2.2' // add plugin}
}
b、配置依赖 ( Module:app build.gradle )
apply plugin: 'com.android.application'
apply plugin: 'org.greenrobot.greendao' // apply plugindependencies {compile 'org.greenrobot:greendao:3.2.2' // add library// This is only needed if you want to use encrypted databasescompile 'net.zetetic:android-database-sqlcipher:3.5.6' //加密库依赖(可选项)
}
c、配置数据库相关信息 ( Module:app build.gradle )
greendao {schemaVersion 1 // 数据库版本号daoPackage 'com.example.zhangruirui.greendao' // 设置 DaoMaster、DaoSession、Dao 包名targetGenDir 'src/main/java' // 设置 DaoMaster、DaoSession、Dao 目录
}
d、基本使用步骤
// 生成数据库文件,名为 students-db
DaoMaster.DevOpenHelper helper = new DaoMaster.DevOpenHelper(this, "students-db", null);
SQLiteDatabase db = helper.getWritableDatabase();
// 建立特定模式下的所有的 DAO 对象和数据 db 对象的映射
DaoMaster master = new DaoMaster(db);
// 管理特定模式下的所有 DAO 对象,并提供一些通用的 CRUD 持久化方法
DaoSession session = master.newSession();
// 得到指定的 StudentDao 对象
StudentDao dao = session.getStudentDao();
dao.insert(student);
//...
五、实战
1、我们写一个简单的实体类(User),测试一下
package com.example.zhangruirui;import org.greenrobot.greendao.annotation.Entity;
import org.greenrobot.greendao.annotation.Generated;
import org.greenrobot.greendao.annotation.Id;@Entity
public class User {@Idprivate long id;private String name;private int age;@Generated(hash = 446251977)public User(long id, String name, int age) {this.id = id;this.name = name;this.age = age;}@Generated(hash = 586692638)public User() {}public long getId() {return id;}public void setId(long id) {this.id = id;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}
}
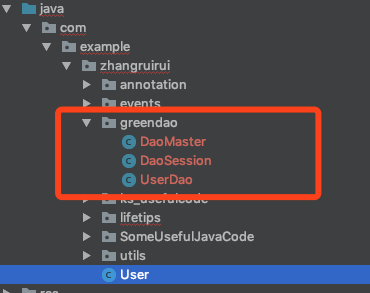
2、点击 Make Project(或者 Make Moudle ‘App’) 编译一下工程 。如果配置正确,会在配置的包目录下自动会生成 DaoMaster,DaoSession 和 UserDao 类 。
3、然后我们定义 OpenHelper 类:UserDBOpenHelper
package com.example.zhangruirui.greendao;import android.content.Context;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;import com.example.zhangruirui.DaoMaster;public class UserDBOpenHelper extends DaoMaster.DevOpenHelper {public UserDBOpenHelper(Context context, String name) {super(context, name);}public UserDBOpenHelper(Context context, String name, SQLiteDatabase.CursorFactory factory) {super(context, name, factory);}@Overridepublic void onDowngrade(SQLiteDatabase db, int oldVersion, int newVersion) {DaoMaster.dropAllTables(wrap(db), true);}
}
4、然后,类似 SQLite ,我们需要定义 DBManager:UserManager 创建单例实例,来供外部操作数据库
package com.example.zhangruirui.greendao;import android.content.Context;
import android.support.annotation.WorkerThread;import com.google.gson.Gson;import java.io.Serializable;
import java.lang.reflect.Type;public class UserManager {private volatile static UserManager mInstance = null;private Context mContext;private UserStorage mUserStorage = new UserStorage(mContext);private UserManager() {}public static UserManager getInstance() {if (mInstance == null) {synchronized (UserManager.class) {if (mInstance == null) {mInstance = new UserManager();}}}return mInstance;}public <T> T getUserAge(String key, Type typeOfT) {try {String json = mUserStorage.getUserAge(key);Gson gson = new Gson();CacheEntry entry = gson.fromJson(json, CacheEntry.class);return gson.fromJson(entry.mJson, typeOfT);} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}return null;}@WorkerThreadpublic void setUserAge(String key, Object entity, Type type) {setUserInner(key, entity, type);}@WorkerThreadprivate void setUserInner(String key, Object entity, Type type) {Gson gson = new Gson();String json = gson.toJson(entity, type);CacheEntry entry = new CacheEntry(json);json = gson.toJson(entry, CacheEntry.class);if (entity == null) {mUserStorage.removeUser(key);} else {mUserStorage.addUser(key, json);}}static class CacheEntry implements Serializable {final String mJson;CacheEntry(String json) {mJson = json;}}
}5、获取 UserDao 对数据库表进行 CRUD 操作即可:UserStorage
package com.example.zhangruirui.greendao;import android.content.Context;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
import android.support.annotation.WorkerThread;import com.example.zhangruirui.User;import org.greenrobot.greendao.query.DeleteQuery;
import org.greenrobot.greendao.query.QueryBuilder;public class UserStorage {private SQLiteDatabase mDatabase;private UserDao mUserDao; // 获取 dao 对象private final static String DB_NAME = "user_name_age.db"; // 定义数据库名// 获取核心类的实例UserStorage(Context context) {DaoMaster.OpenHelper helper = new UserDBOpenHelper(context, DB_NAME, null);try {mDatabase = helper.getWritableDatabase();DaoMaster daoMaster = new DaoMaster(mDatabase);DaoSession daoSession = daoMaster.newSession();mUserDao = daoSession.getUserDao();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}public User getUserByName(String name) {if (!isDataBaseValid()) {return null;}return mUserDao.queryBuilder().where(UserDao.Properties.Name.eq(name)).unique();}/*** 根据用户的名字删除对应的记录*/public void removeUser(String name) {if (!isDataBaseValid()) {return;}try {QueryBuilder<User> qb = mUserDao.queryBuilder();DeleteQuery<User> bd = qb.where(UserDao.Properties.Name.eq(name)).buildDelete();bd.executeDeleteWithoutDetachingEntities();} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}/*** 新增记录,如果存在则更新,不存在直接插入*/@WorkerThreadpublic synchronized void addUser(String name, String json) {if (!isDataBaseValid()) {return;}try {User user = new User();user.setName(name);user.setAge(json);/*** 解决 Exception:* Cannot update entity without key - was it inserted before?*/User oldUser = getUserByName(name);if (oldUser != null) {user.setId(oldUser.getId());}// mUserDao.save(user);if (getUserByName(name) == null) {mUserDao.insert(user);} else {mUserDao.update(user);}} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}/*** 删除所有数据*/@WorkerThreadpublic synchronized void deleteAll() {mUserDao.deleteAll();}private boolean isDataBaseValid() {return mUserDao != null;}public String getUserAge(String key) {return mUserDao.queryBuilder().where(UserDao.Properties.Name.eq(key)).list().get(0).getAge();}
}六、注解
@Entity
表明这个实体类会在数据库中生成一个与之相对应的表
@Entity(// If you have more than one schema, you can tell greenDAO// to which schema an entity belongs (pick any string as a name).schema = "myschema",// Flag to make an entity "active": Active entities have update,// delete, and refresh methods.active = true,// Specifies the name of the table in the database.// By default, the name is based on the entities class name.nameInDb = "AWESOME_USERS",// Define indexes spanning multiple columns here.indexes = {@Index(value = "name DESC", unique = true)},// Flag if the DAO should create the database table (default is true).// Set this to false, if you have multiple entities mapping to one table,// or the table creation is done outside of greenDAO.createInDb = false,// Whether an all properties constructor should be generated.// A no-args constructor is always required.generateConstructors = true,// Whether getters and setters for properties should be generated if missing.generateGettersSetters = true
)
public class User {...
}
@Id(autoincrement = true)
对应数据表中的 Id 字段,主键,必须为 Long 型
如果需要使用主键自增,此时 id 类型为 Long(注意是大写的)
/*** Marks field is the primary key of the entity's table*/
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE)
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
public @interface Id {/*** Specifies that id should be auto-incremented (works only for Long/long fields)* Autoincrement on SQLite introduces additional resources usage and usually can be avoided* @see <a href="https://www.sqlite.org/autoinc.html">SQLite documentation</a>*/boolean autoincrement() default false;
}
@Transient
添加此标记后不会生成数据库表的列,仅仅作为一个普通的 java 类字段,用来临时存储数据的,不会被持久化
@Unique
表名该属性在数据库中只能有唯一值
@Index(unique = true)
七、重要的 api 方法
注意:这些 api 方法中,提到的 key,都是指的主键 Long id
1、查询
http://greenrobot.org/greendao/documentation/queries/
https://juejin.im/post/5abf6ef9f265da2396128456
QueryBuilder.java
2、插入
/*** Insert an entity into the table associated with a concrete DAO.** @return row ID of newly inserted entity*/public long insert(T entity) {return executeInsert(entity, statements.getInsertStatement(), true);}
3、更新
public void update(T entity) {assertSinglePk();DatabaseStatement stmt = statements.getUpdateStatement();if (db.isDbLockedByCurrentThread()) {synchronized (stmt) {if (isStandardSQLite) {updateInsideSynchronized(entity, (SQLiteStatement) stmt.getRawStatement(), true);} else {updateInsideSynchronized(entity, stmt, true);}}} else {// Do TX to acquire a connection before locking the stmt to avoid deadlocksdb.beginTransaction();try {synchronized (stmt) {updateInsideSynchronized(entity, stmt, true);}db.setTransactionSuccessful();} finally {db.endTransaction();}}}
4、插入or更新
public long insertOrReplace(T entity) {return executeInsert(entity, statements.getInsertOrReplaceStatement(), true);}private long executeInsert(T entity, DatabaseStatement stmt, boolean setKeyAndAttach) {long rowId;if (db.isDbLockedByCurrentThread()) {rowId = insertInsideTx(entity, stmt);} else {// Do TX to acquire a connection before locking the stmt to avoid deadlocksdb.beginTransaction();try {rowId = insertInsideTx(entity, stmt);db.setTransactionSuccessful();} finally {db.endTransaction();}}if (setKeyAndAttach) {updateKeyAfterInsertAndAttach(entity, rowId, true);}return rowId;}
save() 方法:
通过 key 属性判断是否存在,如果存在就更新数据,如果 key 为 null 就插入。这里的 key 是什么东东?这就是我今天被坑的地方,这个 key 就是 Long id 这个字段,也就是表中的主键!!!
/*** "Saves" an entity to the database: depending on the existence of the key property, it will be inserted* (key is null) or updated (key is not null).* <p>* This is similar to {@link #insertOrReplace(Object)}, but may be more efficient, because if a key is present,* it does not have to query if that key already exists.*/public void save(T entity) {if (hasKey(entity)) {update(entity);} else {insert(entity);}}
5、删除
/** Deletes the given entity from the database. Currently, only single value PK entities are supported. */public void delete(T entity) {assertSinglePk();K key = getKeyVerified(entity);deleteByKey(key);}
八、入坑系列
1、https://www.jianshu.com/p/7bb9693ea380
2、https://blog.csdn.net/anyanyan07/article/details/73410053
3、打包混淆问题(打包后的 APK,使用不了): 打包后使用不了,debug 能使用,很明显,混淆的问题。报错如下:
https://blog.csdn.net/ddxxii/article/details/54866871
Caused by: org.greenrobot.greendao.DaoException: Could not init DAOConfig
解决办法:
针对 GreenDao 3.0 ,使用时,发布包需要设置混淆
#greendao
-keep class org.greenrobot.greendao.**{*;}
-keep public interface org.greenrobot.greendao.**
-keepclassmembers class * extends org.greenrobot.greendao.AbstractDao {
public static java.lang.String TABLENAME;
}
-keep class **$Properties#optional
-keep class net.sqlcipher.database.**{*;}
-keep public interface net.sqlcipher.database.**
-dontwarn net.sqlcipher.database.**
-dontwarn org.greenrobot.greendao.**
------致所有正在努力奋斗的程序猿们!加油!!
有码走遍天下 无码寸步难行
1024 - 梦想,永不止步!
爱编程 不爱Bug
爱加班 不爱黑眼圈
固执 但不偏执
疯狂 但不疯癫
生活里的菜鸟
工作中的大神
身怀宝藏,一心憧憬星辰大海
追求极致,目标始于高山之巅
一群怀揣好奇,梦想改变世界的孩子
一群追日逐浪,正在改变世界的极客
你们用最美的语言,诠释着科技的力量
你们用极速的创新,引领着时代的变迁
——乐于分享,共同进步,欢迎补充
——Treat Warnings As Errors
——Any comments greatly appreciated
——Talking is cheap, show me the code
——GitHub:https://github.com/selfconzrr
这篇关于GreenDao 3.0 简介、使用及踩坑的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




