本文主要是介绍【C++】左值与右值,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
1. 左值与右值
到了代码的下一行,是否能通过单一变量访问到值。若访问不到,就是右值;否则就是左值。字面量一定是右值。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;#define func(x) __func(x, "func(" #x ")")void __func(int &x, const char *str) {cout << str << " is left value" << endl;return ;
}void __func(int &&x, const char *str) {cout << str << " is right value" << endl;return ;
}//之所以+重载不返回引用,而+=重载返回引用
//就是因为两个操作的结果值的类型不同
class A {
public ://因为+表达式的结果是右值A operator+(int x) {}// += 表达式的结果是左值A &operator+=(int x) {}
};int main() {func(1234);int x = 1234, y = 456;//到了下一行依然能通过x访问到x的值func(x);//x+y的结果是个临时匿名变量,所以到下一行的时候无法访问到该结果值,所以x+y返回值的类型是右值func(x + y);//x++值是x+1之前的值,到下一行无法通过x访问到x+1之前的值func(x++);//x+1以后的值,可以通过x访问到该值,所以++x的值是左值func(++x);//到了代码下一行无法通过单一变量访问到x+123的结果func(x + 123); //右值//到了代码下一行可以通过x访问到 x *= 2的结果func(x *= 2); //左func(y += 3); //左func(y * 3); //右return 0;
}
运行结果:

2. 左值引用和右值引用
右值引用是绑定到右值上的引用,右值引用的定义形式是 int &&;左值引用的定义形式是int &。
正确传递左值和右值的关系:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;#define func(x) __func(x, "func(" #x ")")
#define func2(x) __func2(x, "func2(" #x ")")void __func2(int &x, const char *str) {cout << str << " is left value" << endl;return ;
}void __func2(int &&x, const char *str) {cout << str << " is right value" << endl;return ;
}void __func(int &x, const char *str) {cout << str << " is left value" << endl;func2(x);return ;
}
//int &&x是右值引用
void __func(int &&x, const char *str) {cout << str << " is right value" << endl;//func2(x); //x表现出的是左值特性//func2(move(x));//强制变成右值特性func2(forward<int &&>(x));//以右值引用的形式向下传递,x会保持右值引用的特性,可以理解为强制转换,但是比强制转换更强大,可以转换为某种类型的引用return ;
}//之所以+重载不返回引用,而+=重载返回引用
//就是因为两个操作的结果值的类型不同
class A {
public ://因为+表达式的结果是右值A operator+(int x) {}// += 表达式的结果是左值A &operator+=(int x) {}
};int main() {func(1234);int x = 1234, y = 456;//到了下一行依然能通过x访问到x的值func(x);//x+y的结果是个临时匿名变量,所以到下一行的时候无法访问到该结果值,所以x+y返回值的类型是右值func(x + y);//x++值是x+1之前的值,到下一行无法通过x访问到x+1之前的值func(x++);//x+1以后的值,可以通过x访问到该值,所以++x的值是左值func(++x);//到了代码下一行无法通过单一变量访问到x+123的结果func(x + 123); //右值//到了代码下一行可以通过x访问到 x *= 2的结果func(x *= 2); //左func(y += 3); //左func(y * 3); //右return 0;
}
运行结果:
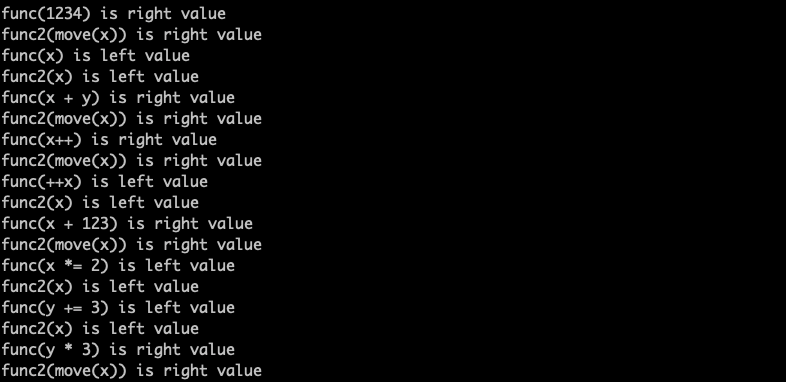
move 和 forward 函数为什么重要呢?本质原因是C++有重载,保证用正确的类型向下传递,保证可以调用到正确的函数重载形式。
forward 叫做 完美转发,比强制转换更厉害的是可以转换为某种类型的引用。
3. 引用绑定的顺序
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;void func1(int &x) {cout << __PRETTY_FUNCTION__ << "called" << endl;
}void func1(const int &x) {cout << __PRETTY_FUNCTION__ << "called" << endl;
}void func1(int &&x) {cout << __PRETTY_FUNCTION__ << "called" << endl;
}void func1(const int &&x) {cout << __PRETTY_FUNCTION__ << "called" << endl;
}int main() {int n;const int y = 123;func1(n); //func1(int &);func1(y); //func1(const int &)func1(123 + 456); //func1(int &&)return 0;
}
运行结果:

const 类型的左值引用可以绑定所有数据类型:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;/*void func1(int &x) {cout << __PRETTY_FUNCTION__ << "called" << endl;
}*/void func1(const int &x) {cout << __PRETTY_FUNCTION__ << "called" << endl;
}/*void func1(int &&x) {cout << __PRETTY_FUNCTION__ << "called" << endl;
}void func1(const int &&x) {cout << __PRETTY_FUNCTION__ << "called" << endl;
}*/int main() {int n;const int y = 123;func1(n); //func1(int &);func1(y); //func1(const int &)func1(123 + 456); //func1(int &&)return 0;
}
运行结果:

不能绑定到func(int &)是因为在func1(int &)中是可能修改该值的,常量值是不能绑定到int &的,但是func1(const int &)是不能修改的参数的,所以绑定到func1(const int &)是为了包含所有情况。绑定顺序就是优先绑定和自己类型匹配的引用,否则绑定到const类型的左值引用。
4. 移动构造
/*************************************************************************> File Name: move_ctor.cpp> Author: Maureen > Mail: Maureen@qq.com > Created Time: 二 1/11 16:17:49 2022************************************************************************/#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//实现自己的vector
namespace maureen {
class vector {
public :vector(int n = 10) : __size(n), data(new int[n]) {cout << "default constructor" << endl;}vector(const vector &v) : __size(v.size()), data(new int[__size]) {cout << "deep copy constructor" << endl;for (int i = 0; i < size(); i++) ++data[i] = v[i];return ;}//合并两个动态数组vector operator+(const vector &v) {vector ret(v.size() + this->size());vector &now = *this;for (int i = 0; i < size(); i++) {ret[i] = now[i];}for (int i = size(); i< ret.size(); i++) {ret[i] = v[i - size()];}return ret;}int &operator[](int ind) const {return this->data[ind];}int size() const { return __size; }
private :int __size;int *data;
};
}//end of maureenostream &operator<<(ostream &out, const maureen::vector &v) {for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++) {out << v[i] << " ";}return out;
}int main() {maureen::vector v1, v2;for (int i = 0; i < v1.size(); i++) v1[i] = rand() % 100;for (int i = 0; i < v2.size(); i++) v2[i] = rand() % 100;maureen::vector v3(v1 + v2);cout << v1 << endl;cout << v2 << endl;cout << v3 << endl;return 0;
}
有返回值优化的运行结果:

没有返回值优化的运行结果:
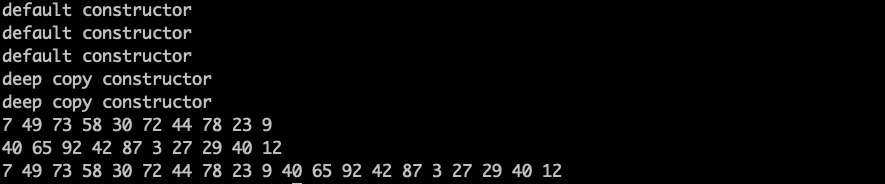
maureen::vector v3(v1 + v2); 中的 v1+v2 会产生一个临时变量,但是却对这个临时变量做了拷贝,这没有必要,何不直接将临时变量的值拿过来。
所以就产生了一类特殊的构造函数: 移动构造
拷贝构造传入的是左值引用,所以在拷贝构造中,必须得做深拷贝;构造函数可以传左值引用,也可以传右值引用。
一旦调用了右值引用对象,说明传入的值是临时值,要不然不会绑定到右值引用上。这种情况下,就直接抢。这就是移动构造:
vector(vector &&v) : __size(v.size()), data(v.data) {v.data = nullptr; //因为有时候可能是在显式调用移动构造v.__size = 0;
}
移动构造就是传入右值引用的构造。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//实现自己的vector
namespace maureen {
class vector {
public :vector(int n = 10) : __size(n), data(new int[n]) {cout << "default constructor" << endl;}vector(const vector &v) : __size(v.size()), data(new int[__size]) { //拷贝构造cout << "deep copy constructor" << endl;for (int i = 0; i < size(); i++) ++data[i] = v[i];return ;}vector(vector &&v) : __size(v.size()), data(v.data) { //移动构造cout << "move copy constructor" << endl;v.data = nullptr;v.__size = 0;}vector operator+(const vector &v) { //合并两个动态数组vector ret(v.size() + this->size());vector &now = *this;for (int i = 0; i < size(); i++) {ret[i] = now[i];}for (int i = size(); i< ret.size(); i++) {ret[i] = v[i - size()];}return ret;}int &operator[](int ind) const {return this->data[ind];}int size() const { return __size; }~vector() {if (data) delete[] data;data = nullptr;__size = 0;}
private :int __size;int *data;
};
}//end of maureenostream &operator<<(ostream &out, const maureen::vector &v) {for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++) {out << v[i] << " ";}return out;
}int main() {maureen::vector v1, v2;for (int i = 0; i < v1.size(); i++) v1[i] = rand() % 100;for (int i = 0; i < v2.size(); i++) v2[i] = rand() % 100;maureen::vector v3(v1 + v2);cout << v1 << endl;cout << v2 << endl;cout << v3 << endl;return 0;
}
去掉返回值优化后的结果:
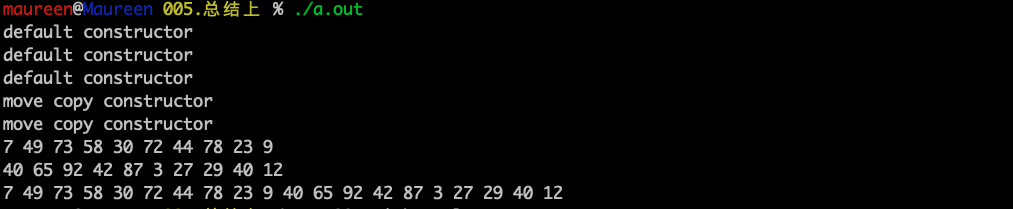
移动构造只是改变了指针的指向,而拷贝构造需要先创建一片存储区再将数据拷贝过来。
发现当前值是临时值的时候,就将它的资源抢过来。
C++因为引入左值引用和右值引用,重回巅峰。因为在有移动构造之前,STL效率不高,因为只要产生拷贝就是深拷贝,如 string,vector。
当拷贝构造是深拷贝时,就一定要配一个移动构造。
显式调用移动构造函数:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//实现自己的vector
namespace maureen {
class vector {
public :vector(int n = 10) : __size(n), data(new int[n]) {cout << "default constructor" << endl;}vector(const vector &v) : __size(v.size()), data(new int[__size]) {cout << "deep copy constructor" << endl;for (int i = 0; i < size(); i++) ++data[i] = v[i];return ;}vector(vector &&v) : __size(v.size()), data(v.data) {cout << "move copy constructor" << endl;v.data = nullptr;v.__size = 0;}vector operator+(const vector &v) { //合并两个动态数组vector ret(v.size() + this->size());vector &now = *this;for (int i = 0; i < size(); i++) {ret[i] = now[i];}for (int i = size(); i< ret.size(); i++) {ret[i] = v[i - size()];}return ret;}int &operator[](int ind) const {return this->data[ind];}int size() const { return __size; }~vector() {if (data) delete[] data;data = nullptr;__size = 0;}
private :int __size;int *data;
};
}//end of maureenostream &operator<<(ostream &out, const maureen::vector &v) {for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++) {out << v[i] << " ";}return out;
}
int main() {maureen::vector v1, v2;for (int i = 0; i < v1.size(); i++) v1[i] = rand() % 100;for (int i = 0; i < v2.size(); i++) v2[i] = rand() % 100;maureen::vector v3(v1 + v2);cout << v1 << endl;cout << v2 << endl;cout << v3 << endl;maureen::vector v4(move(v1));//显式调用移动构造cout << v1 << endl;cout << v4 << endl;return 0;
}
去掉返回值优化的运行结果:

这篇关于【C++】左值与右值的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!








