本文主要是介绍c++中 unordered_map 与 unordered_set 用法指南,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
unordered_map 与 unordered_set 区别与联系
unordered_map和unordered_set都是 C++ 标准模板库(STL)中的容器,它们使用哈希表作为底层数据结构,提供了快速的查找、插入和删除操作。下面是它们之间的联系与区别:联系
- 底层实现:两者都基于哈希表实现,利用了哈希函数来分布元素。
- 性能特点:它们都提供平均时间复杂度为 O(1) 的查找、插入和删除操作。
- 冲突解决:两者都使用某种形式的链表或红黑树来解决哈希冲突。
- 非线性容器:它们都是非线性容器,不保证元素的顺序。
区别
存储内容:
unordered_map存储键值对,即每个元素包含一个键(key)和一个值(value),键是唯一的。unordered_set只存储唯一的值,不包含键。用途:
unordered_map适用于需要通过键来访问或存储数据的场景,类似于关联数组或字典。unordered_set适用于需要存储唯一元素集合的场景,类似于集合。操作:
unordered_map支持通过键来访问、插入、删除和查找值。unordered_set支持插入、删除和查找元素。内存使用:
unordered_map由于需要存储键和值,通常比unordered_set使用更多的内存。迭代器:
unordered_map的迭代器可以解引用为一个pair,其中包含键和值。unordered_set的迭代器只能解引用为一个值。示例:
元素查找:
unordered_map的find方法返回一个迭代器,指向键值对,可以访问键和值。unordered_set的find方法返回一个迭代器,指向集合中的元素。使用场景
- 当你需要一个键来快速访问数据时,使用
unordered_map。- 当你只需要存储一组不包含重复元素的数据时,使用
unordered_set。总的来说,
unordered_map和unordered_set在实现上有很多相似之处,但它们服务于不同的数据存储需求。选择使用哪一个取决于你的具体应用场景和需求。
unordered_map
unordered_map 是 C++ 中的一个关联容器,它存储了键值对,并且提供了快速的数据访问能力。
- 基本使用:
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>int main() {std::unordered_map<int, std::string> umap;umap[1] = "one";umap[2] = "two";umap[3] = "three";// 打印所有键值对for (const auto& pair : umap) {std::cout << pair.first << ": " << pair.second << std::endl;}
}
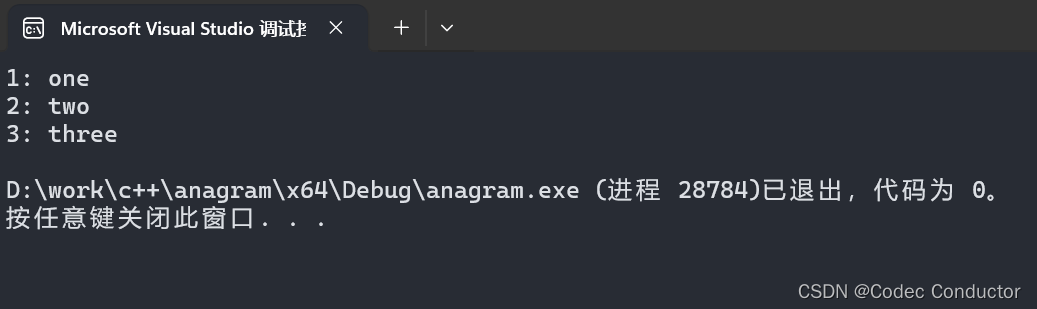
- 输出结果:
1: one
2: two
3: three
- 初始化列表:
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>int main() {std::unordered_map<int, std::string> umap = {{1, "one"},{2, "two"},{3, "three"}};// 打印所有键值对for (const auto& pair : umap) {std::cout << pair.first << ": " << pair.second << std::endl;}
}
- 输出结果:
1: one
2: two
3: three
- 访问元素:
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>int main() {std::unordered_map<int, std::string> umap = {{1, "one"},{2, "two"}};// 访问元素std::cout << "Value for key 1: " << umap[1] << std::endl;// 访问不存在的键将自动插入该键,并为其分配一个默认值std::cout << "Value for key 3: " << umap[3] << std::endl; // 默认值,例如空字符串
}
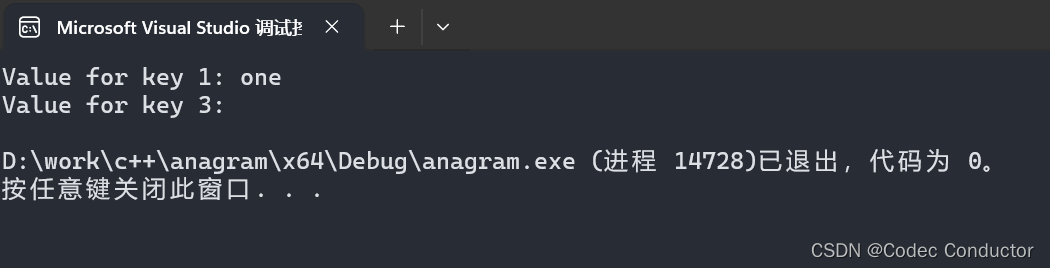
- 输出结果:
Value for key 1: one
Value for key 3:
- 检查键是否存在:
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>int main() {std::unordered_map<int, std::string> umap = {{1, "one"},{2, "two"}};int key = 1;if (umap.find(key) != umap.end()) {std::cout << "Key " << key << " exists." << std::endl;}else {std::cout << "Key " << key << " does not exist." << std::endl;}
}
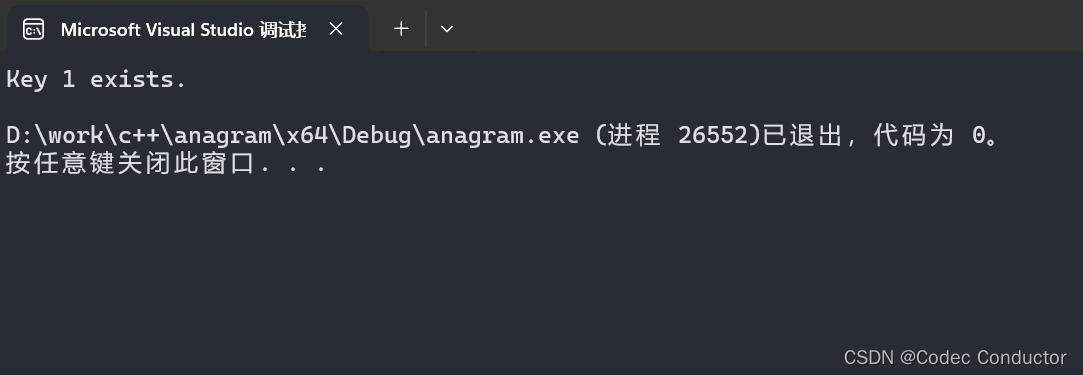
- 输出结果:
Key 1 exists.
- 删除元素:
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>int main() {std::unordered_map<int, std::string> umap = {{1, "one"},{2, "two"}};int keyToRemove = 1;auto it = umap.find(keyToRemove);if (it != umap.end()) {umap.erase(it);}// 打印删除元素后的映射for (const auto& pair : umap) {std::cout << pair.first << ": " << pair.second << std::endl;}
}
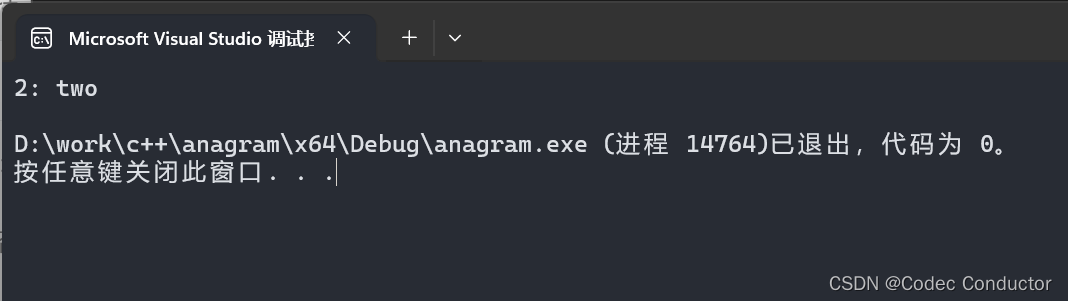
- 输出结果:
2: two
- 使用 emplace 插入元素:
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>int main() {std::unordered_map<int, std::string> umap;// 使用 emplace 插入元素auto result = umap.emplace(1, "one");if (result.second) {std::cout << "Insert successful." << std::endl;}// 尝试再次插入相同的键result = umap.emplace(1, "uno");if (!result.second) {std::cout << "Insert failed, key already exists." << std::endl;}// 打印映射for (const auto& pair : umap) {std::cout << pair.first << ": " << pair.second << std::endl;}
}
- 输出结果:
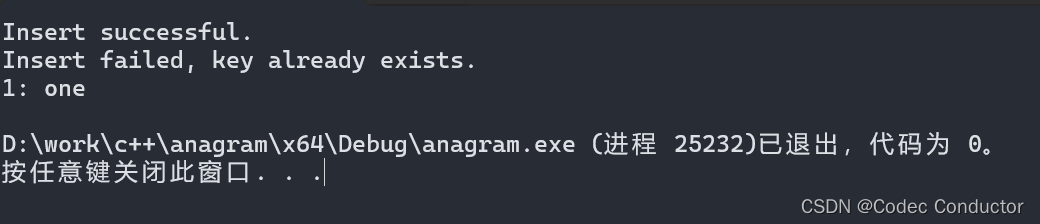
Insert successful.
Insert failed, key already exists.
1: one
- 遍历 unordered_map:
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>int main() {std::unordered_map<int, std::string> umap = {{1, "one"},{2, "two"},{3, "three"}};// 使用范围 for 循环遍历for (const auto& pair : umap) {std::cout << pair.first << ": " << pair.second << std::endl;}// 使用迭代器遍历for (auto it = umap.begin(); it != umap.end(); ++it) {std::cout << it->first << ": " << it->second << std::endl;}
}
- 输出结果:
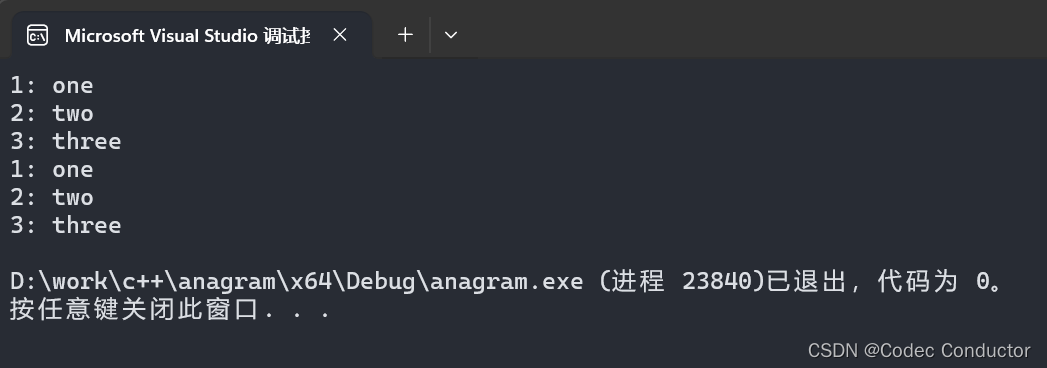
1: one
2: two
3: three
1: one
2: two
3: three
- 使用 unordered_map 的 size 和 empty:
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>int main() {std::unordered_map<int, std::string> umap = {{1, "one"},{2, "two"}};std::cout << "Size of umap: " << umap.size() << std::endl;std::cout << "Is umap empty? " << (umap.empty() ? "Yes" : "No") << std::endl;
}
- 输出结果:
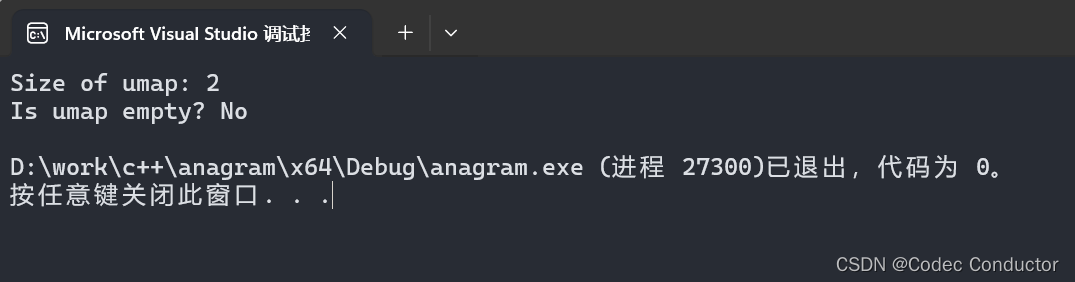
Size of umap: 2
Is umap empty? No
unordered_set
- 基本使用:
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_set>int main() {std::unordered_set<int> uset;uset.insert(10);uset.insert(20);uset.insert(30);std::cout << "Size of uset: " << uset.size() << std::endl;
}
- 输出结果:
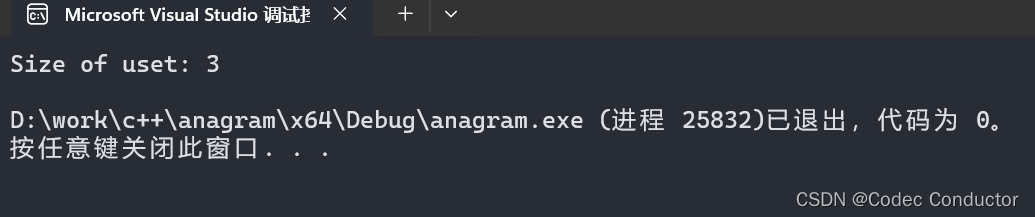
Size of uset: 3
- 初始化列表:
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_set>int main() {std::unordered_set<int> uset = { 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 };for (int num : uset) {std::cout << num << " ";}std::cout << std::endl;
}
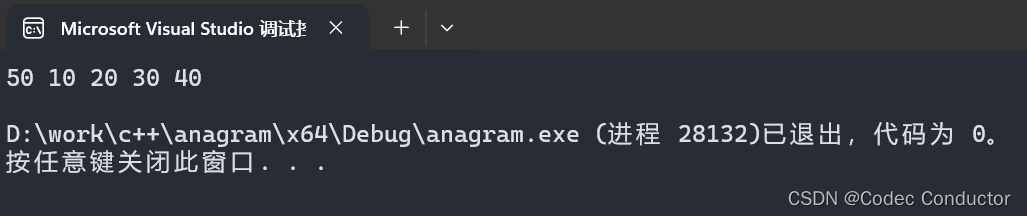
- 输出结果:
50 10 20 30 40
- 检查元素是否存在:
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_set>int main() {std::unordered_set<int> uset = { 1, 2, 3 };int key = 2;if (uset.find(key) != uset.end()) {std::cout << "Element " << key << " exists in uset." << std::endl;}else {std::cout << "Element " << key << " does not exist in uset." << std::endl;}
}
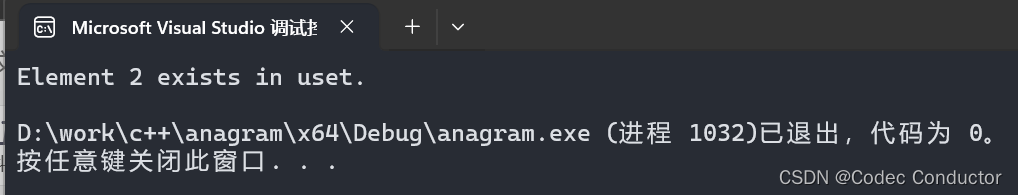
- 输出结果:
Element 2 exists in uset.
- 删除元素:
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_set>int main() {std::unordered_set<int> uset = { 1, 2, 3 };int keyToRemove = 2;if (uset.erase(keyToRemove)) {std::cout << "Element removed from uset." << std::endl;}else {std::cout << "Element not found in uset." << std::endl;}for (int num : uset) {std::cout << num << " ";}std::cout << std::endl;
}
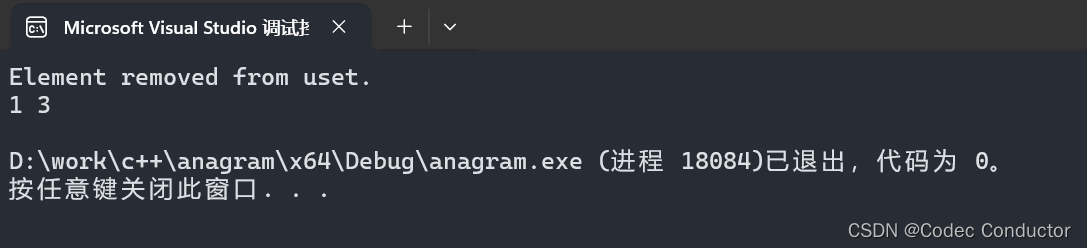
- 输出结果:
Element removed from uset.
1 3
- 使用 emplace 插入元素:
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_set>int main() {std::unordered_set<int> uset;// 使用 emplace 插入元素auto result = uset.emplace(10);if (result.second) {std::cout << "Insert successful." << std::endl;}// 尝试再次插入相同的元素result = uset.emplace(10);if (!result.second) {std::cout << "Insert failed, element already exists." << std::endl;}
}
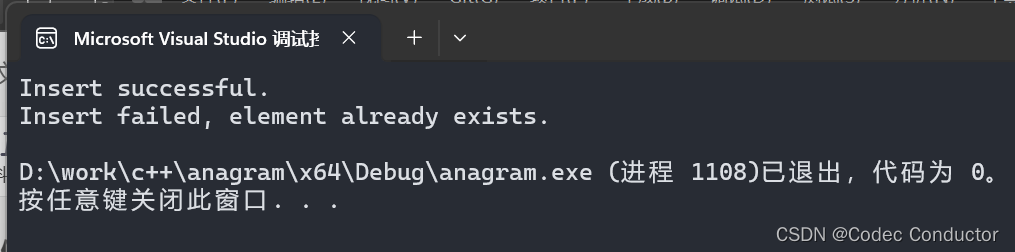
- 输出结果:
Insert successful.
Insert failed, element already exists.
- 遍历 unordered_set:
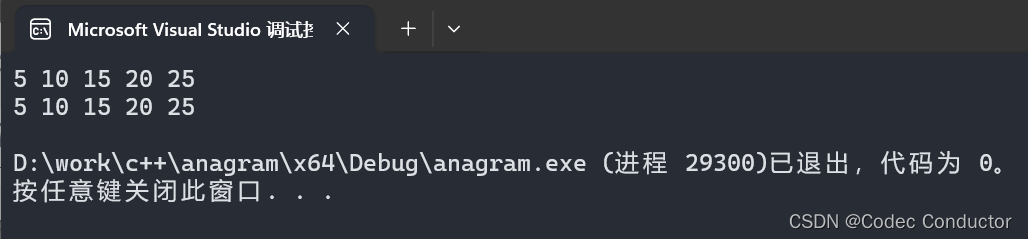
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_set>int main() {std::unordered_set<int> uset = { 5, 10, 15, 20, 25 };// 使用范围 for 循环遍历for (int num : uset) {std::cout << num << " ";}std::cout << std::endl;// 使用迭代器遍历for (auto it = uset.begin(); it != uset.end(); ++it) {std::cout << *it << " ";}std::cout << std::endl;
}
- 输出结果:
5 10 15 20 25
5 10 15 20 25
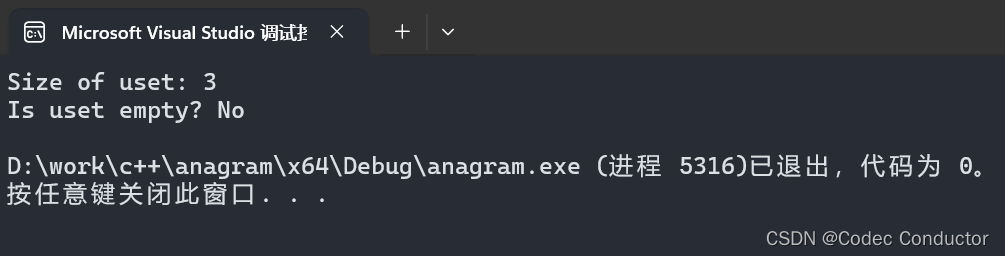
- 使用 unordered_set 的 size 和 empty:
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_set>int main() {std::unordered_set<int> uset = { 1, 2, 3 };std::cout << "Size of uset: " << uset.size() << std::endl;std::cout << "Is uset empty? " << (uset.empty() ? "Yes" : "No") << std::endl;
}
- 输出结果:
Size of uset: 3
Is uset empty? No
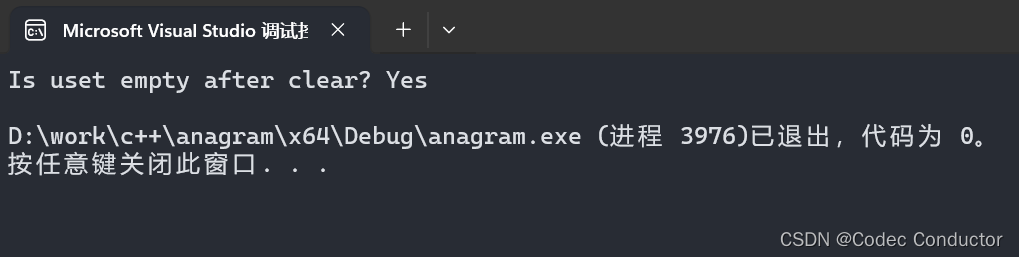
- 清空 unordered_set:
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_set>int main() {std::unordered_set<int> uset = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };uset.clear(); // 清空 usetstd::cout << "Is uset empty after clear? " << (uset.empty() ? "Yes" : "No") << std::endl;
}
- 输出结果:
Is uset empty after clear? Yes
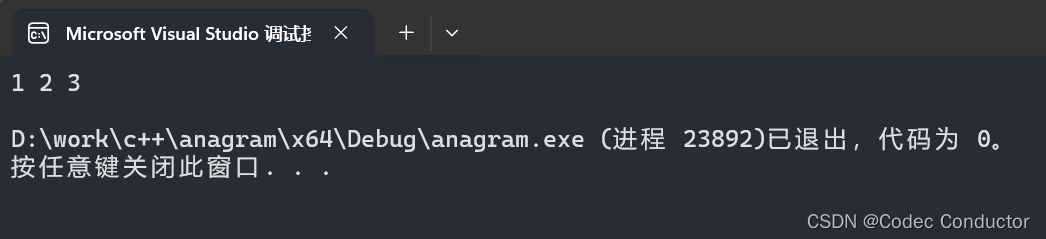
- 自定义哈希函数:
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_set>// 自定义哈希函数
struct custom_hash {std::size_t operator()(int x) const {return std::hash<int>()(x);}
};int main() {std::unordered_set<int, custom_hash> uset = { 1, 2, 3 };for (int num : uset) {std::cout << num << " ";}std::cout << std::endl;
}
- 输出结果:
1 2 3
这篇关于c++中 unordered_map 与 unordered_set 用法指南的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!