本文主要是介绍Java Sort 方法的使用(包含Arrays.sort(),Collections.sort()以及Comparable,Comparator的使用 ),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
目录
Comparable && Comparator的使用:
Comparable:
Comparator:
Arrays.sort()的使用:
升序排序:
降序排序:
自定义排序方法:
在日常的刷题或开发中,很多时候我们需要对数据进行排序,以达到我们的预期效果的作用。那么这些排序方法具体怎么实现和使用呢?本文就来好好缕一缕,总结一下这些方法:
Comparable && Comparator的使用:
Comparable:
当我们对类中的对象进行比较时,要保证对象时可比较的,这时我们就需要用到Comparable 或 Comparator接口,然后重写里面的compareTo()方法。假设我们有一个学生类,默认需要按照学生的年龄age排序,具体实现如下:
class Student implements Comparable<Student>{private int id;private int age;private String name;public Student(int id, int age, String name) {this.id = id;this.age = age;this.name = name;}@Overridepublic int compareTo(Student o) {//降序//return o.age - this.age;//升序return this.age - o.age;}public int getId() {return id;}public void setId(int id) {this.id = id;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Student{" +"id=" + id +", age=" + age +", name='" + name + '\'' +'}';}}这里说一下 public int compareTo(Student o) 方法,它返回三种 int 类型的值: 负整数,零 ,正整数:
| 返回值 | 含义 |
| 正整数 | 当前对象的值 > 比较对象的值,升序排序 |
| 零 | 当前对象的值 = 比较对象的值,不变 |
| 负整数 | 当前对象的值 < 比较对象的值,降序排序 |
测试:
public class SortTest {public static void main(String[] args) {List<Student> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add(new Student(103,25,"关羽"));list.add(new Student(104,21,"张飞"));list.add(new Student(108,18,"刘备"));list.add(new Student(101,32,"袁绍"));list.add(new Student(109,36,"赵云"));list.add(new Student(103,16,"曹操"));System.out.println("排序前:");for(Student student : list){System.out.println(student.toString());}System.out.println("默认排序后:");Collections.sort(list);for(Student student : list){System.out.println(student.toString());}}
}
运行结果:
排序前:
Student{id=103, age=25, name='关羽'}
Student{id=104, age=21, name='张飞'}
Student{id=108, age=18, name='刘备'}
Student{id=101, age=32, name='袁绍'}
Student{id=109, age=36, name='赵云'}
Student{id=103, age=16, name='曹操'}
默认排序后:
Student{id=103, age=16, name='曹操'}
Student{id=108, age=18, name='刘备'}
Student{id=104, age=21, name='张飞'}
Student{id=103, age=25, name='关羽'}
Student{id=101, age=32, name='袁绍'}
Student{id=109, age=36, name='赵云'}Comparator:
Comparable的两种使用方法:
Collections.sort(list,Comparator<T>);list.sort(Comparator<T>);
这个时候需求又来了,默认是用 age 排序,但是有的时候需要用 id 来排序怎么办? 这个时候比较器 :Comparator 就排上用场了:
//自定义排序:使用匿名内部类,实现Comparator接口,重写compare方法Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<Student>() {@Overridepublic int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {return o1.getId() - o2.getId();}});//自定义排序2list.sort(new Comparator<Student>() {@Overridepublic int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {return o1.getId() - o2.getId();}});compare(Student o1, Student o2) 方法的返回值跟 Comparable<> 接口的 compareTo(Student o) 方法返回值意思相同
运行结果:
自定义ID排序后:
Student{id=101, age=32, name='袁绍'}
Student{id=103, age=16, name='曹操'}
Student{id=103, age=25, name='关羽'}
Student{id=104, age=21, name='张飞'}
Student{id=108, age=18, name='刘备'}
Student{id=109, age=36, name='赵云'}源码:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;class Student implements Comparable<Student>{private int id;private int age;private String name;public Student(int id, int age, String name) {this.id = id;this.age = age;this.name = name;}@Overridepublic int compareTo(Student o) {//降序//return o.age - this.age;//升序return this.age - o.age;}public int getId() {return id;}public void setId(int id) {this.id = id;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Student{" +"id=" + id +", age=" + age +", name='" + name + '\'' +'}';}}public class SortTest {public static void main(String[] args) {List<Student> list = new ArrayList<>();list.add(new Student(103,25,"关羽"));list.add(new Student(104,21,"张飞"));list.add(new Student(108,18,"刘备"));list.add(new Student(101,32,"袁绍"));list.add(new Student(109,36,"赵云"));list.add(new Student(103,16,"曹操"));System.out.println("排序前:");for(Student student : list){System.out.println(student.toString());}System.out.println("默认排序后:");Collections.sort(list);for(Student student : list){System.out.println(student.toString());}//自定义排序:使用匿名内部类,实现Comparator接口,重写compare方法Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<Student>() {@Overridepublic int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {return o1.getId() - o2.getId();}});System.out.println("自定义ID排序后:");for(Student student : list){System.out.println(student.toString());}//自定义排序2list.sort(new Comparator<Student>() {@Overridepublic int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {return o1.getId() - o2.getId();}});}
}
Arrays.sort()的使用:
升序排序:
1.正常排序一个数组:Arrays.sort(int [] a);
我们看一下源码:
public static void sort(int[] a) {DualPivotQuicksort.sort(a, 0, a.length - 1, null, 0, 0);}本质上还是用到了快排,同时默认时从小到大进行排序的,具体实现:
public static void main(String[] args) {//1.Arrays.sort(int[] a) 默认从小到达排序int[] a = new int[]{10,2,7,8,9,15,7};System.out.println("默认时从小到大排序:");Arrays.sort(a);for(int x : a) System.out.print(x + " ");}运行结果:
默认时从小到大排序:
2 7 7 8 9 10 15 2.在一定区间内排序数组:Arrays.sort(int[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex)
->规则为从fromIndex<= a数组 <toIndex,左闭右开
public static void main(String[] args) {//2.Arrays.sort(int[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex)//规则为从fromIndex<= a数组 <toIndexint[] a = new int[]{2,5,4,1,19,3,2};Arrays.sort(a,1,4);for(int x : a) System.out.print(x + " ");}降序排序:
实现方法:Collections.reverseOrder()
public static <T> void sort(T[] a,int fromIndex, int toIndex, Comparator<? super T> c)要实现降序排序,得通过包装类型的数组来实现,基本数据类型数组是不行的:

正确用法:
//2.java自带的Collections.reverseOrder() 降序排序数组System.out.println("java自带的Collections.reverseOrder():");Integer[] integers = new Integer[]{10, 293, 35, 24, 64, 56};Arrays.sort(integers, Collections.reverseOrder());for (Integer integer : integers) System.out.print(integer + " ");运行结果:
java自带的Collections.reverseOrder():
293 64 56 35 24 10 自定义排序方法:
自定义排序方法,需要实现java.util.Comparetor 接口中的compare方法
//3.自定义排序方法,实现java.util.Comparetor 接口中的compare方法Integer[] integers2 = new Integer[]{10, 293, 35, 24, 64, 56};Arrays.sort(integers2, new Comparator<Integer>() {@Overridepublic int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {return o2.compareTo(o1);}});System.out.println("自定义排序方法:");for (int x : integers2) System.out.print(x + " ");运行结果:
自定义排序方法:
293 64 56 35 24 10 同时,我们可以用lambda表达是简化书写:
//4.lambda表达式简化书写Integer[] integers3 = new Integer[]{10, 293, 35, 24, 64, 56};Arrays.sort(integers3, (o1, o2) -> {return o2 - o1;});System.out.println("lambda表达式简化书写:");for (int x : integers3) System.out.print(x + " ");运行结果:
lambda表达式简化书写:
293 64 56 35 24 10 源码:
import java.util.*;
public class sortTest {public static void main1(String[] args) {//1.Arrays.sort(int[] a) 默认从小到达排序int[] a = new int[]{10,2,7,8,9,15,7};System.out.println("默认时从小到大排序:");Arrays.sort(a);for(int x : a) System.out.print(x + " ");}public static void main2(String[] args) {//2.Arrays.sort(int[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex)//规则为从fromIndex<= a数组 <toIndexint[] a = new int[]{2,5,4,1,19,3,2};Arrays.sort(a,1,4);for(int x : a) System.out.print(x + " ");}public static void main3(String[] args) {/* //1.实现降序排序,基本的数据类型数组是不行的int[] a = new int[]{10,293,35,24,64,56};Arrays.sort(a,Collections.reverseOrder());for(int x : a) System.out.println(x + " ");*///2.java自带的Collections.reverseOrder() 降序排序数组System.out.println("java自带的Collections.reverseOrder():");Integer[] integers = new Integer[]{10, 293, 35, 24, 64, 56};Arrays.sort(integers, Collections.reverseOrder());for (Integer integer : integers) System.out.print(integer + " ");System.out.println();System.out.println("===================================");//3.自定义排序方法,实现java.util.Comparetor 接口中的compare方法Integer[] integers2 = new Integer[]{10, 293, 35, 24, 64, 56};Arrays.sort(integers2, new Comparator<Integer>() {@Overridepublic int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {return o2.compareTo(o1);}});System.out.println("自定义排序方法:");for (int x : integers2) System.out.print(x + " ");System.out.println();System.out.println("===================================");//4.lambda表达式简化书写Integer[] integers3 = new Integer[]{10, 293, 35, 24, 64, 56};Arrays.sort(integers3, (o1, o2) -> {return o2 - o1;});System.out.println("lambda表达式简化书写:");for (int x : integers3) System.out.print(x + " ");}
}
补充,二维数组的排序:通过实现Comparator接口来自定义排序二维数组,以下面为例:
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Comparator;class Cmp implements Comparator<int[]>{@Overridepublic int compare(int[] o1, int[] o2) {return o1[0] - o2[0];}
}
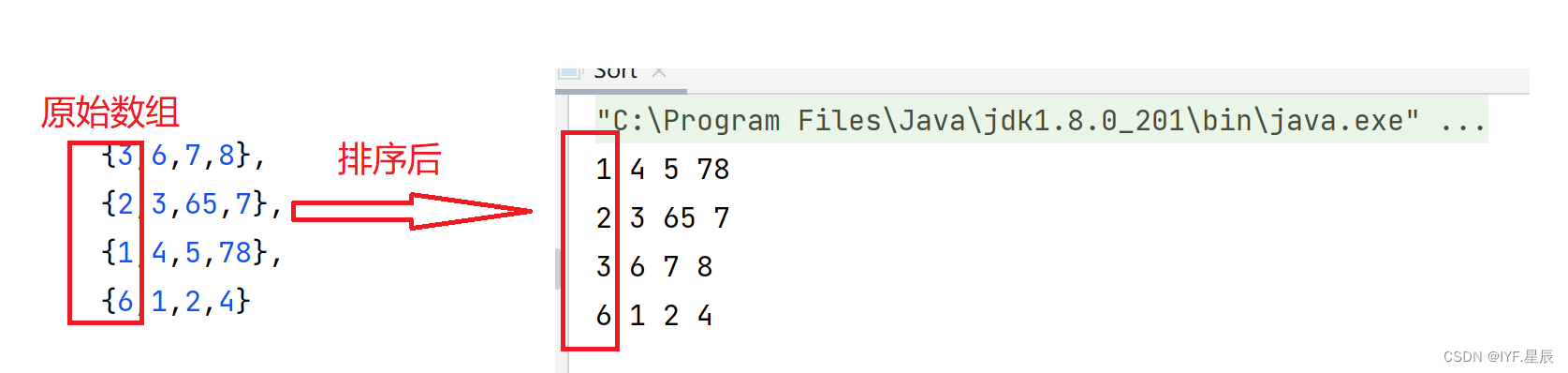
public class Sort {public static void main123(String[] args) {int[][] res = new int[][]{{3,6,7,8},{2,3,65,7},{1,4,5,78},{6,1,2,4}};//自定义排序二维数组,这里是按照每行第一个数字进行排序Arrays.sort(res,new Cmp());for(int i = 0;i < res.length;i++){for(int j = 0;j < res[0].length;j++){System.out.print(res[i][j] + " ");}System.out.println();}}
}运行结果:
好啦~本文到这里也是接近尾声了,希望有帮助到你,整理不易,希望多多三联支持呀~
结语: 写博客不仅仅是为了分享学习经历,同时这也有利于我巩固知识点,总结该知识点,由于作者水平有限,对文章有任何问题的还请指出,接受大家的批评,让我改进。同时也希望读者们不吝啬你们的点赞+收藏+关注,你们的鼓励是我创作的最大动力!

这篇关于Java Sort 方法的使用(包含Arrays.sort(),Collections.sort()以及Comparable,Comparator的使用 )的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






