本文主要是介绍Sping源码(八)—Spring事件驱动,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
观察者模式
在介绍Spring的事件驱动之前,先简单的介绍一下设计模式中的观察者模式。
在一个简单的观察者模式只需要观察者和被观察者两个元素。简单举个栗子:
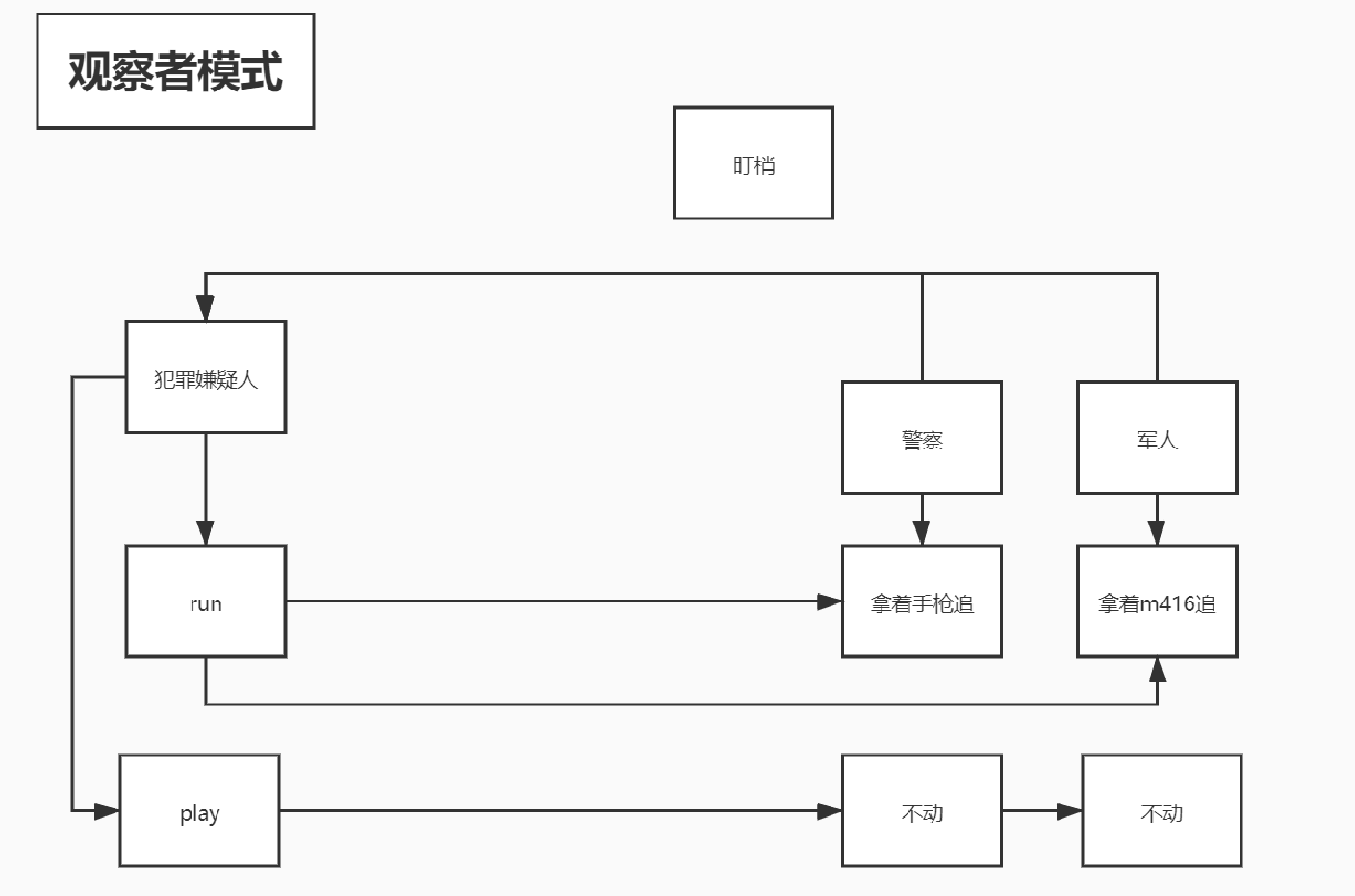
以警察盯梢犯罪嫌疑人的栗子来说:
其中犯罪嫌疑人为被观察者元素而 警察和军人为观察者元素,被观察者的状态发生了改变(run),观察者收到通知并进行相应改变(追捕)。
代码
被观察者
图示中标记可以看出,可能会有多个观察者进行观察,所以会有add、remove方法,如果被观察者状态进行改变,则调用notifyObservers()方法通知所有的观察者。
public interface Observable {//收集对应的观察者到集合中void addObserver(Observer observer);//从集合中移除对应的观察者void removeObserver(Observer observer);//通知所有观察者void notifyObservers(String str);
}
被观察者实现类
public class BadMan implements Observable {List<Observer> observerList = new ArrayList<>();@Overridepublic void addObserver(Observer observer) {this.observerList.add(observer);}@Overridepublic void removeObserver(Observer observer) {this.observerList.remove(observer);}@Overridepublic void notifyObservers(String str) {System.out.println(str);for (Observer observer : observerList) {observer.apprehend();}}public void run(String str) {notifyObservers(str);}public void play(String str){System.out.println(str);}
}
观察者
public interface Observer {//抓捕方法void apprehend();
}
观察者实现类
当接到被观察者通知,做出相应的逻辑。
public class GoodMan1 implements Observer{@Overridepublic void apprehend() {System.out.println("goodman1 ---------抓捕小偷");}
}public class GoodMan2 implements Observer{@Overridepublic void apprehend() {System.out.println("goodman2------------逮捕小偷");}
}
测试
public static void main(String[] args) {GoodMan1 gm1 = new GoodMan1();GoodMan2 gm2 = new GoodMan2();BadMan bm = new BadMan();bm.addObserver(gm1);bm.addObserver(gm2);bm.run("小偷逃跑,开始追踪");bm.play("小偷在玩----不用理会");}
Spring事件驱动
Spring的事件驱动其实和上面介绍的观察者模式差不多,不过进行了更细致的划分,也更加的解耦,我们来看看Spring的事件驱动。
图解
看源码之前先来看看Spring事件驱动和传统观察者模式的区别。
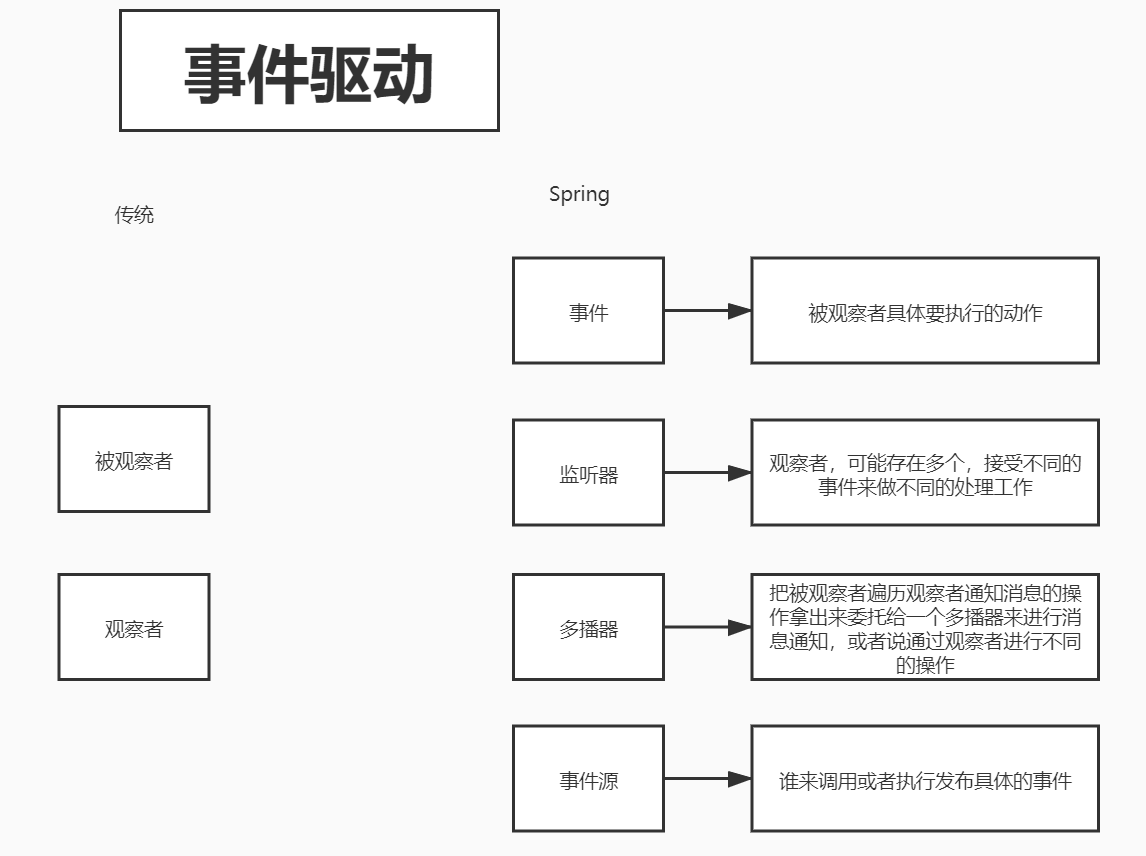
逻辑顺序
将Spring事件驱动的每个组件串联起来执行的顺序就是。

源码
依然是refresh()源码主流程,此时来到了initApplicationEventMulticaster()方法。
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {// Prepare this context for refreshing.prepareRefresh();// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);try {// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);// Initialize message source for this context.// 为上下文初始化message源,即不同语言的消息体,国际化处理,在springmvc的时候通过国际化的代码重点讲initMessageSource();// Initialize event multicaster for this context.// 初始化事件监听多路广播器initApplicationEventMulticaster();// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.onRefresh();// Check for listener beans and register them.//向广播器中注册listenerregisterListeners();// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);// Last step: publish corresponding event.finishRefresh();}}}
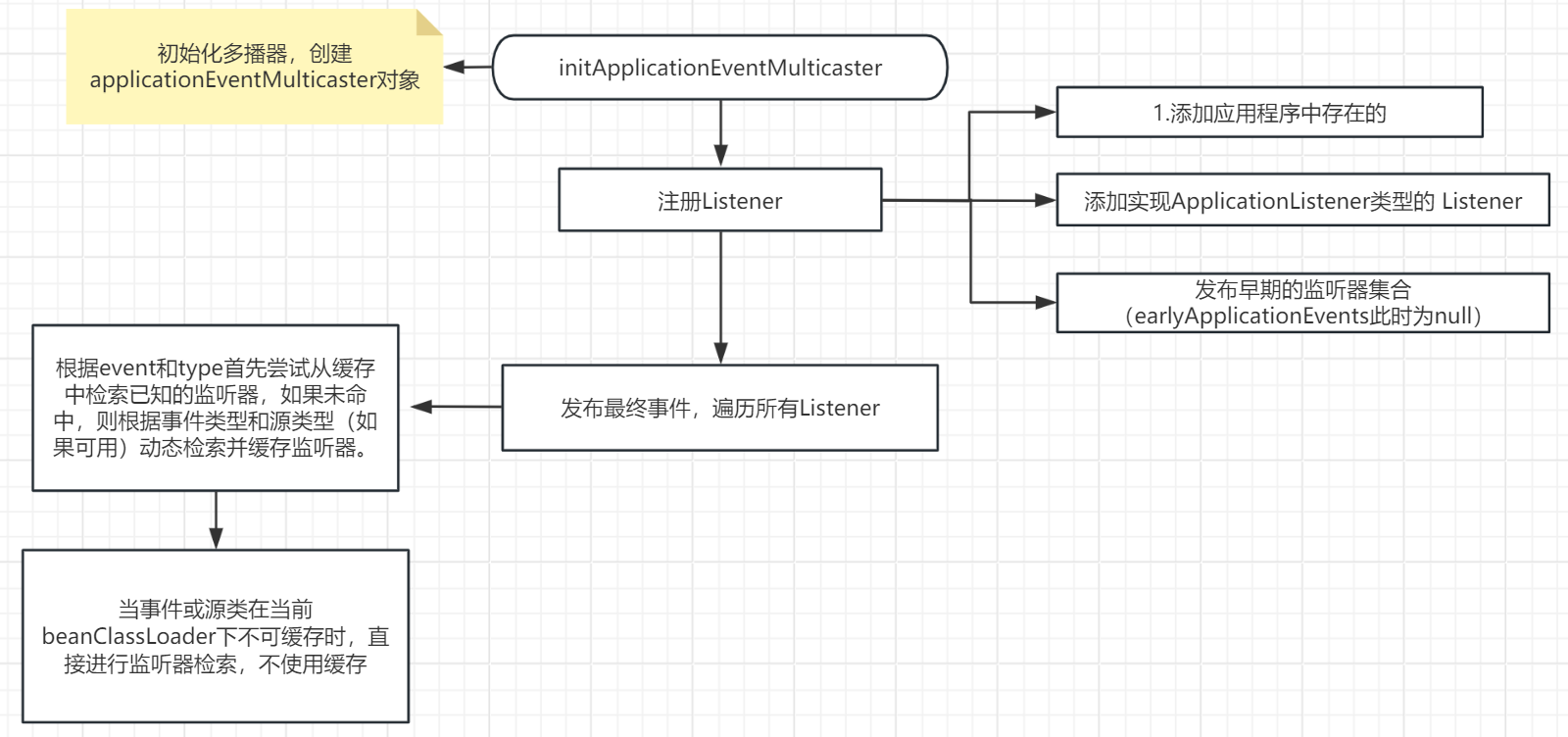
initApplicationEventMulticaster
初始化多播器,如果BeanFactory不包含,则创建一个SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster多播器。
protected void initApplicationEventMulticaster() {//获取beanFactory对象ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();// 如果包含applicationEventMulticaster,则赋值给applicationEventMulticaster变量if (beanFactory.containsLocalBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME)) {this.applicationEventMulticaster =beanFactory.getBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, ApplicationEventMulticaster.class);}else {//创建默认的SimpleApplicationEventMulticasterthis.applicationEventMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster(beanFactory);//注册到beanFactory中beanFactory.registerSingleton(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, this.applicationEventMulticaster);}}
registerListeners
向多播器中注册Listener。应用程序中自带的Lintener -> 实现了ApplicationListener的Listener -> 发布earlyApplicationEvents 事件。
此时的earlyApplicationEvents = null,所以不会进行事件处理。
protected void registerListeners() {// Register statically specified listeners first.//获取应用程序中存在的监听器集合,并添加到多播器中for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners()) {getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListener(listener);}// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans// uninitialized to let post-processors apply to them!//获取实现了ApplicationListener类型的监听器,并注册到多播器中String[] listenerBeanNames = getBeanNamesForType(ApplicationListener.class, true, false);for (String listenerBeanName : listenerBeanNames) {getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListenerBean(listenerBeanName);}// Publish early application events now that we finally have a multicaster...// 此处先发布早期的监听器集合Set<ApplicationEvent> earlyEventsToProcess = this.earlyApplicationEvents;this.earlyApplicationEvents = null;if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(earlyEventsToProcess)) {for (ApplicationEvent earlyEvent : earlyEventsToProcess) {getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(earlyEvent);}}}
finishRefresh
将监听器添加到多播器后,跳过中间方法,我们直接来看事件的发布publishEvent()。
protected void finishRefresh() {// Clear context-level resource caches (such as ASM metadata from scanning).clearResourceCaches();// Initialize lifecycle processor for this context.initLifecycleProcessor();// Propagate refresh to lifecycle processor first.getLifecycleProcessor().onRefresh();// Publish the final event.publishEvent(new ContextRefreshedEvent(this));// Participate in LiveBeansView MBean, if active.LiveBeansView.registerApplicationContext(this);}
事件发布
根据publishEvent方法的调用,event参数为 new ContextRefreshedEvent(),根据上面图示,此时事件源为我当前AbstractApplicationContext类进行的事件发布
protected void publishEvent(Object event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) {Assert.notNull(event, "Event must not be null");// Decorate event as an ApplicationEvent if necessary// 如果事件不是ApplicationEvent,则创建一个PayloadApplicationEventApplicationEvent applicationEvent;if (event instanceof ApplicationEvent) {applicationEvent = (ApplicationEvent) event;}else {applicationEvent = new PayloadApplicationEvent<>(this, event);//如果event = nullif (eventType == null) {// 将applicationEvent转换为PayloadApplicationEvent对象象,引用其ResolvableType对象eventType = ((PayloadApplicationEvent<?>) applicationEvent).getResolvableType();}}// Multicast right now if possible - or lazily once the multicaster is initialized// 如果可能的话,现在就进行组播——或者在组播初始化后延迟// earlyApplicationEvents:在多播程序设置之前发布的ApplicationEvent// 如果earlyApplicationEvents不为 null,这种情况只在上下文的多播器还没有初始化的情况下才会成立,会将applicationEvent// 添加到earlyApplicationEvents保存起来,待多博器初始化后才继续进行多播到适当的监听器if (this.earlyApplicationEvents != null) {this.earlyApplicationEvents.add(applicationEvent);}else {getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(applicationEvent, eventType);}// Publish event via parent context as well...// 如果父上下文不为空,则通过父上下文发布事件if (this.parent != null) {if (this.parent instanceof AbstractApplicationContext) {((AbstractApplicationContext) this.parent).publishEvent(event, eventType);}else {this.parent.publishEvent(event);}}}
public void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) {// 如果eventType不为null就引用eventType;否则将event转换为ResolvableType对象再引用ResolvableType type = (eventType != null ? eventType : resolveDefaultEventType(event));//获取当前多播器的任务线程池Executor executor = getTaskExecutor();//根据给定事件和类型匹配的应用监听器集合// 遍历所有监听器for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners(event, type)) {if (executor != null) {//使用executor回调listener的onApplicationEvent方法,传入eventexecutor.execute(() -> invokeListener(listener, event));}else {//回调listener的onApplicationEvent方法,传入eventinvokeListener(listener, event);}}}
流程图
SpringBoot
事件驱动在Spring中没有明显的处理过程,我们结合SpringBoot来一起验证一下。从SpringBoot的启动run()方法开始。
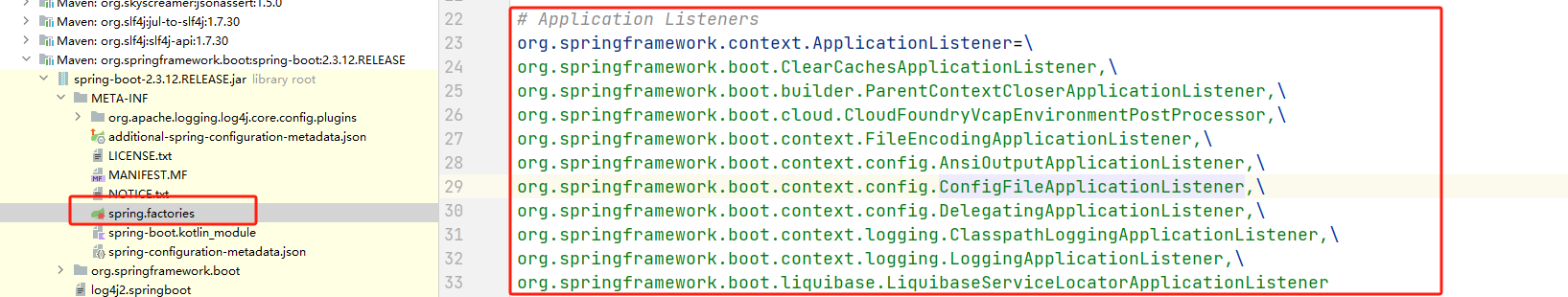
spring.factories
首先我们可以看到配置文件中准备的一些Listener
run
我们的run()方法中,首先通过SpringApplicationRunListeners对Spring自带的Listener进行事件的发布处理。
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();stopWatch.start();ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;configureHeadlessProperty();SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);listeners.starting();try {// 省略部分代码....refreshContext(context);// 省略部分代码....}return context;}
创建SpringApplicationRunListener对象并获取自带Listener集合。
//获取SpringApplicationRunListeners对象
private SpringApplicationRunListeners getRunListeners(String[] args) {Class<?>[] types = new Class<?>[] { SpringApplication.class, String[].class };//创建SpringApplicationRunListeners对象并返回return new SpringApplicationRunListeners(logger,getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringApplicationRunListener.class, types, this, args));}private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type, Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object... args) {ClassLoader classLoader = getClassLoader();// Use names and ensure unique to protect against duplicates//loadFactoryNames会加载spring.factories文件,并转换成key , value的Map放入缓存中//如上图所示,根据key 来获取 ListenerSet<String> names = new LinkedHashSet<>(SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader));List<T> instances = createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes, classLoader, args, names);AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances);return instances;}
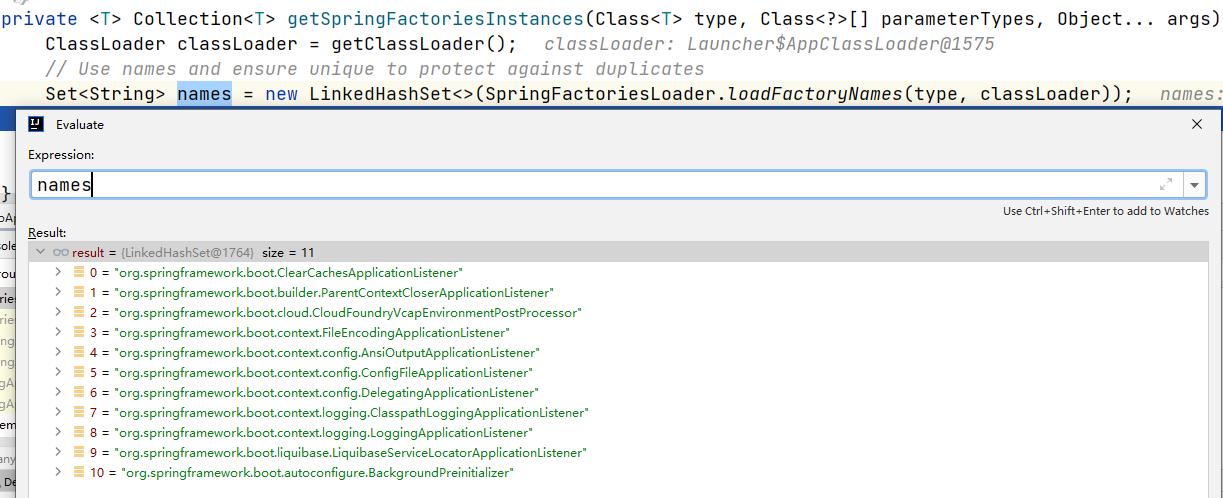
事件发布
listeners.starting() 底层会通过 initialMulticaster 循环遍历对满足条件的Listener 进行事件发布通知,底层同样执行listener.onApplicationEvent方法。
public void starting() {this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(new ApplicationStartingEvent(this.application, this.args));}public void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) {ResolvableType type = (eventType != null ? eventType : resolveDefaultEventType(event));Executor executor = getTaskExecutor();for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners(event, type)) {if (executor != null) {executor.execute(() -> invokeListener(listener, event));}else {invokeListener(listener, event);}}}
initialMulticaster的加载
多播器可能有多个,其中initialMulticaster是一个有别于上文提到的applicationEventMulticaster。但作用都是相同的,遍历Listener过滤出符合条件的监听器进行事件处理。
初始化
initialMulticaster变量是随着EventPublishingRunListener类的加载而进行的初始化,而EventPublishingRunListener的创建也是根据spring.factories的加载而生成的。
public EventPublishingRunListener(SpringApplication application, String[] args) {this.application = application;this.args = args;this.initialMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster();for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : application.getListeners()) {this.initialMulticaster.addApplicationListener(listener);}}
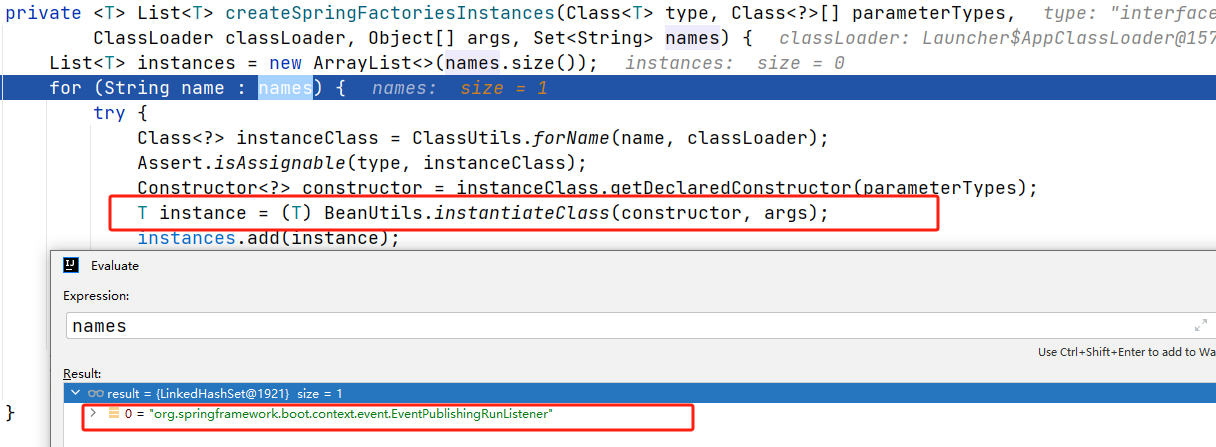
private <T> List<T> createSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type, Class<?>[] parameterTypes,ClassLoader classLoader, Object[] args, Set<String> names) {List<T> instances = new ArrayList<>(names.size());for (String name : names) {try {Class<?> instanceClass = ClassUtils.forName(name, classLoader);Assert.isAssignable(type, instanceClass);Constructor<?> constructor = instanceClass.getDeclaredConstructor(parameterTypes);T instance = (T) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(constructor, args);instances.add(instance);}catch (Throwable ex) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot instantiate " + type + " : " + name, ex);}}return instances;}
同一个监听器的不同事件处理
上面有提到监听器会根据不同的事件作出不同的处理。以ConfigFileApplicationListener 为例,onApplicationEvent方法中会根据event的类型不同,而有不同的实现逻辑。
public class ConfigFileApplicationListener implements EnvironmentPostProcessor, SmartApplicationListener, Ordered {@Overridepublic void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {if (event instanceof ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent) {onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent((ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent) event);}if (event instanceof ApplicationPreparedEvent) {onApplicationPreparedEvent(event);}}
}
这篇关于Sping源码(八)—Spring事件驱动的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






